Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Oil and Gas Industry Overview
Oil and Gas Industry Overview
Uploaded by
Mary GuzmanOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Oil and Gas Industry Overview
Oil and Gas Industry Overview
Uploaded by
Mary GuzmanCopyright:
Available Formats
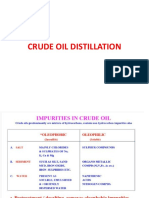
THE THREE STAGES OF OIL REFINING
MAIN IDEAS
1. molecules are separated through atmospheric distillation (i.e. at normal atmospheric
pressure), according to their molecular weight.
2. During the process topping (refining), the oil is heated at the bottom of a 60-meter
distillation column at a temperature of 350 to 400C, causing it to vaporize.
3. The liquids, which are become increasingly light the higher they are found in the column,
are collected on trays located at different heights of the column.
4. The conversion process, which is carried out at 500C, is also known as catalytic cracking
because it uses a substance called a catalyst to speed up the chemical reaction.
5. The more complex the operation, the more it costs and the more energy it uses.
6. Treating involves removing or significantly reducing molecules that are corrosive or cause
air pollution, especially sulfur.
7. For diesel, desulfurization, or sulfur removal, is performed at 370C, at a pressure of 60
bar.
8. Automotive fuels must also be treated to increase their octane rating, which is a measure
of a fuel's resistance to detonation, based on a scale of 0 to 100.
9. The process used to produce high-octane products is called catalytic reforming.
10. Other chemical reactions, such as alkylation, also improve the octane rating.
You might also like
- Emulsions and Oil Treating Equipment: Selection, Sizing and TroubleshootingFrom EverandEmulsions and Oil Treating Equipment: Selection, Sizing and TroubleshootingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Crude Oil ProcessingDocument19 pagesCrude Oil ProcessingYinka OlatunjiNo ratings yet
- Vacuum DistillationDocument6 pagesVacuum DistillationnuclearengineerNo ratings yet
- Catalytic CrackingDocument17 pagesCatalytic Crackingtariq fareedNo ratings yet
- Fractional DistillationDocument2 pagesFractional DistillationSaeed AbdNo ratings yet
- Petroleum Refining L 4Document18 pagesPetroleum Refining L 4Karrar Alka'byNo ratings yet
- A Turbine Flow Meter Is A Widely Used Tool For Measuring The Rate of Flow of A Given FluidakamDocument10 pagesA Turbine Flow Meter Is A Widely Used Tool For Measuring The Rate of Flow of A Given FluidakamIbrahimNo ratings yet
- Crude Oil and Product Properties 2nd Lecture 2nd Stage 2021 2022Document20 pagesCrude Oil and Product Properties 2nd Lecture 2nd Stage 2021 2022Montazer WorkNo ratings yet
- Steps in RefiningDocument2 pagesSteps in RefiningmehranNo ratings yet
- Purifier Maintenance 1Document54 pagesPurifier Maintenance 1Noel Nico FernandoNo ratings yet
- Refinery 3Document53 pagesRefinery 3Patel AshokNo ratings yet
- CHE 586 Lecture 2Document18 pagesCHE 586 Lecture 2Charles ObiefunaNo ratings yet
- Fossil FuelDocument7 pagesFossil FuelJerome BalatbatNo ratings yet
- How Oil Refining WorksDocument6 pagesHow Oil Refining WorksAnonymous NyvKBWNo ratings yet
- Crude Oil PlantDocument10 pagesCrude Oil PlantEkbal 6MNo ratings yet
- Cracking of Heavy OilDocument4 pagesCracking of Heavy OilPritamNo ratings yet
- Kolom Distilasi Tinjauan UmumDocument22 pagesKolom Distilasi Tinjauan Umummaulia farahNo ratings yet
- Catalytic Cracking: University of Zakho Faculty of Engineering Petroleum Eng. DepDocument9 pagesCatalytic Cracking: University of Zakho Faculty of Engineering Petroleum Eng. DepSaMiHRNo ratings yet
- Petroleum Technology-Part Iii: The Process & Technology of CrackingDocument23 pagesPetroleum Technology-Part Iii: The Process & Technology of CrackingSrikrishnan KrishNo ratings yet
- Crude Oil RefiniringDocument96 pagesCrude Oil RefiniringNamwangala Rashid Natindu100% (1)
- Fractional DestilationDocument6 pagesFractional DestilationCarlos Luis Esquerdo MarcanoNo ratings yet
- Teaching 922 18783 1613332733 1Document39 pagesTeaching 922 18783 1613332733 1Stark JohnNo ratings yet
- Vacuum DistillationDocument6 pagesVacuum DistillationKhaqan AminNo ratings yet
- Assignment NO 3:: Question 1: Define Cracking. Classify Cracking OperationsDocument6 pagesAssignment NO 3:: Question 1: Define Cracking. Classify Cracking OperationsMilan MoradiyaNo ratings yet
- Cracking 151114162534 Lva1 App6891Document33 pagesCracking 151114162534 Lva1 App6891Truth SeekerNo ratings yet
- Solvent Extraction and DewaxingDocument21 pagesSolvent Extraction and DewaxingAnwesh SatapathyNo ratings yet
- Fractional DistillationDocument5 pagesFractional Distillationwayen8100% (1)
- Haldia Institute of Technology: Name: Bipasha Barai Class Roll No: 17/CHE/054 University Roll No: 10300617054Document9 pagesHaldia Institute of Technology: Name: Bipasha Barai Class Roll No: 17/CHE/054 University Roll No: 10300617054Roshan Kumar LohaniNo ratings yet
- Sami Matar Ph.d. Lewis F. Hatch Ph.d. Chemistry of Petrochemical Processes 2001 Gulf Professional Publishing 62 68Document7 pagesSami Matar Ph.d. Lewis F. Hatch Ph.d. Chemistry of Petrochemical Processes 2001 Gulf Professional Publishing 62 68Gómez Aguilar Angelica BelenNo ratings yet
- History: Government Polytechnic Jalna Atmospheric DistillationDocument11 pagesHistory: Government Polytechnic Jalna Atmospheric DistillationMs. YMPNo ratings yet
- Thermal Recovery MethodDocument25 pagesThermal Recovery Methodmahmud masudNo ratings yet
- Application of Lubricant OilDocument2 pagesApplication of Lubricant OilM Asrar SidonNo ratings yet
- Petroleum ProcessingDocument22 pagesPetroleum ProcessingMark Anthony FauneNo ratings yet
- Bitumen ManufactureDocument46 pagesBitumen Manufacturegeorgiadisg100% (2)
- Cracking DefinitionDocument4 pagesCracking Definitionasim zeeshanNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Geology and Petroleum Engineering 2Document11 pagesFaculty of Geology and Petroleum Engineering 2Алишер ДжумагуловNo ratings yet
- Controls and InstrumentationDocument4 pagesControls and InstrumentationEr WinNo ratings yet
- Atmospheric Crude FractionatorDocument3 pagesAtmospheric Crude Fractionatornedian_2006No ratings yet
- Petrochemicals Process FlowchartDocument2 pagesPetrochemicals Process FlowchartShivkumar DalalNo ratings yet
- Fraction DistillationDocument4 pagesFraction DistillationBella JosephNo ratings yet
- Crude Oil DistillationDocument109 pagesCrude Oil Distillationshreshth chawlaNo ratings yet
- Al Ain UniversityDocument6 pagesAl Ain UniversityHassan AlaliNo ratings yet
- Guide To Refinery ProcessDocument131 pagesGuide To Refinery Processvazzoleralex6884100% (2)
- Distillation ColumnsDocument6 pagesDistillation ColumnsAbed Med MedNo ratings yet
- Dewaxing of Distilate Oil Fraction (400 - 500 ºC) Using UreaDocument15 pagesDewaxing of Distilate Oil Fraction (400 - 500 ºC) Using UreaNima FakherNo ratings yet
- Distillation Characteristics of Petroleum DieselDocument30 pagesDistillation Characteristics of Petroleum DieselT Richie100% (2)
- Group 5 CrackingDocument31 pagesGroup 5 CrackingCharles ObiefunaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Petroleum Technology - 3Document21 pagesIntroduction To Petroleum Technology - 3Anish VazeNo ratings yet
- Petroleum IndustryDocument49 pagesPetroleum IndustryQueenie BalisongNo ratings yet
- Liquid FuelsDocument21 pagesLiquid FuelsvaibhavNo ratings yet
- CrackingDocument32 pagesCrackingMuhammad HAmAd QureshiNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Distillation of Crude Oil 25Document19 pagesPreliminary Distillation of Crude Oil 25ravi2007No ratings yet
- Fluid Catalytic Craking Unit (Fccu)Document6 pagesFluid Catalytic Craking Unit (Fccu)Nitin VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Literature Review of FYPDocument7 pagesLiterature Review of FYPRiethanelia UsunNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2023-24 BCHE314L TH VL2023240501233 2024-02-19 Reference-Material-IDocument75 pagesWINSEM2023-24 BCHE314L TH VL2023240501233 2024-02-19 Reference-Material-IamitheserathinasamyNo ratings yet
- Catalytic Cracking3Document12 pagesCatalytic Cracking3Abdurabu AL-MontaserNo ratings yet
- Hydrocracking. Hydrocracking Is A Hydrogen-Consuming Reaction That Leads To Higher GasDocument4 pagesHydrocracking. Hydrocracking Is A Hydrogen-Consuming Reaction That Leads To Higher GasJefferson EndaraNo ratings yet
- Chemistry and Technology of PetroleumDocument83 pagesChemistry and Technology of PetroleumManish TiwariNo ratings yet
- EorDocument13 pagesEorAnuragNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Diesel and Petrol EnginesFrom EverandComparison of Diesel and Petrol EnginesRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)