Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bajaj Auto LTD Business Strategy Case Study
Bajaj Auto LTD Business Strategy Case Study
Uploaded by
Amol Nagap0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views5 pagesmms
Original Title
36421489 Bajaj Auto Ltd Business Strategy Case Study Ppt
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentmms
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views5 pagesBajaj Auto LTD Business Strategy Case Study
Bajaj Auto LTD Business Strategy Case Study
Uploaded by
Amol Nagapmms
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
Bajaj Auto Ltd: Overtaken in the
Indian Scooter Market
"Group F":-
Manish Kumar (09BS0002819)
Taslim Qureshi (09BS0002530)
Umang Jalan (09BS0002611)
Varun Saxena (09BS0002653)
Vibhuti Bhardwaj (09BS0002667)
Vinay Verma (09BS0002703)
Yashaskar Paliwal (09BS0002776)
Overview
Founded in 1926 by JamnaLal Baiai.
His son, Kamalnayan Baiai, then 27, took over the reins oI
business in 1942.
The present Chairman oI the group, Rahul Baiai, took charge oI
the business in 1965. Under his leadership, the turnover oI the
Baiai Auto the Ilagship company has gone up Irom Rs.72
million to Rs.100.76 billion (USD 2.3 billion).
The company was incorporated on April 30, 2007 as a wholly
owned subsidiary oI erstwhile Baiai Auto Ltd (the holding
company) with the name Baiai Investment & Holding Ltd. The
company received the certiIicate oI commencement oI business
on May 7, 2007.
Baiai Auto Ltd.(BAL)
Baiai is India's second largest motorcycle maker,
smaller than Honda Motorcycle Scooter India, but
larger than TVS Motor Co. Ltd.
Baiai Auto, is ranked as the world`s Iourth largest
two- and three- wheeler manuIacturer.
The company is well known Ior their R&D, product
development, process engineering and low-cost
manuIacturing skills.
INTRODUCTION
In the mid -1940s,BAL started as an important oI two and
three-wheelers .in the early 1960s,BAL ,in collaboration with
piaggo ,started manuIacturing vespa brand scooters at its
plant near Pune , Maharashtra.
In 1970s,BAL started manuIacturing scooters under the Baiai
brand.
Bal`s Iirst scooter model under the Baiai brand was
introduced in 1972.(Chetak)
In the late 1990`s the Indian two wheeler market witnessed a
shiIt in consumer preIerences.
In 2005-06 scooter sales in the Indian market were around 1
million units annually and consisted predominantly oI
gearless scooters. In early 2006 BAL announced that it would
launch two new models oI gearless scooters in 2006-07.
CSR
Baiai Auto is committed to nation-building and
contributing to the upliIt and development oI the
weaker sections oI society. This is a legacy oI the
Iounders, Jamanalalii, Kamalnayanii and Ramkrishna
Baiai.
Jankidevi Baiai Gram Vikas Sanstha (JBGVS)
Samai Seva Kendra.
Kamalnayan Baiai Hospital
BACKGROUND NOTE:
1926- Baiai Auto was Iound by JamnaLal Baiai.
1956- Company secured a license Irom the GOI.
1960- Company went public & collaboration with
Piaggio.
1961- Started the production oI scooters.
1962- Started the production oI three wheelers.
1971- Started selling scooters under the Baiai brand
1972- BAL Introduced the Baiai Chetak scooters.
1975- BAL entered into a ioint venture with western
Maharashtra Development corporation.
Cont.
BACKGROUND 4nt...
1986:- BAL entered into a technical partnership with
Kawasaki Heavy Industries & launched the
Kawasaki Baiai.
1990:- The Baiai 'Sunny was introduced.
1997:- BAL launched the 'Bajaj Boxer.
1998:- BAL introduce the 'Bajaj Caliber.
1999:- The company launched the 'Bravo, a geared scooter.
2000:- Bal launched the 'Saffire, a gearless scooter.
2001:- It introduced the 'Pulsar.
2004:- Bal created a new Logo.
2005:- The 'SaIIire was relaunched as the Wave.
2006:- Bal launched the 'Platina.
2006:- Indian two wheeler industry was the second largest in
the world.
BAL & the Indian Two-Wheeler
Market.
1950s -1980s: "License Rai .
Domestic market protected-Govt.restriction.
1950s-Automobile Products oI India(API).
Other players:
EnIield(Bullet),Escorts(Raidoot),Jawa(Yezdi).
1960s:Govt.relaxation to domestic companies.
1970s: BAL manuIacture scooters under the "Baiai
Brand.
Scooter were more preIerred to motorcycles.2-
wheelers demand increased due to ineIIicient
transport system, the Chetak & the Super launched.
Contd..
It act as Sellers Market like other consumer goods &
customers had to wait Ior many years Ior
delivery.(10-12 yrs Ior Baiai Chetak).
It plays a maior role in dowry in India.
1970s-1980s-Govt. introduced MRTP Act & FERA.
Indian manuIacturing motorcycles were not Iuel
eIIicient, results low sell.
GoI changed several policies in 1970s & early 1980s
to give impetus to auto industry.
Focus on :modernization. technologv upgradations.&
healthv competitions in domestic market.
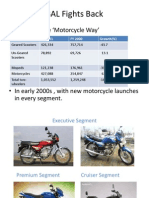
Motorcycle segment
Joint Venture: Foreign players had only option)
Many players like Honda,Suzuki,Yamaha had ioint ventures
with Indian companies.
The Ioreign players came with latest technology, eIIicient
production system etc that enhance the quality oI the motorcycle
in India .
Soon new models come with new style, advanced technology &
Iuel eIIicient.
Scooter segment
LML entered into ioint venture with Piaggio in 1982 , to
produce 'espa. sold well in 1980s-1990s after Chetak.
1984:The Kinetic tied up with Honda ,introduced new models ,
new Ieatures like selI start & automatic gear transmissions.
1980-1990s :BAL dominate by Chetak & Super model with their
values Ior money appeal durability, versatility, low
maintenance,avaliablity oI spare parts ,etc.Hamara Baiai ' add
campaign.
The Turning P4int:
In 1991 & 1992 overall sales oI two wheelers declined by
15 & 8 respectively because oI a recession in the Indian
two wheeler market
The scooter segment was the largest sub-segment in the two
wheeler market with 42 share (in terms oI unit sales)
Iollowed by motorcycles (37) & mopeds (21)
However, in 1990, the pattern oI demand changed &
motorcycles became the Iastest growing segment
Motorcycles were preIerred to scooters in the rural areas
because oI poor road conditions
Demographic changes Increasing proportion oI younger
people in the overall population
4nt...
Lower interest rates on vehicle loans made motorcycles more
aIIordable
Sales oI motorcycles surpassed that oI scooters Ior the Iirst
time in 1999 (with Hero Honda SPLENDOR)
In 1999-2000 scooter sales Iell by around 75,000 units, while
motorcycle sales increased by more than 400,000 units
BAL had volumes Ialling 40 year-on-year as scooters were
80 oI their total business
In 2000 Bharat Stage II, a new set oI emission norms, came
into eIIect. It was Ior petrol two-stroke engines & it gave a
blow to BAL, which primarily sold two-wheelers with two-
stroke engines
ategory FY 2001 FY 2000 Growth (%)
eared Sc44ters 426,334 757,714 -43.7
Un eared
Sc44ters
78,892 69,726 13.1
M45eds 121,238 176,961 -31.5
M4t4rcycles 427,088 254,847 67.6
T4tal tw4-
wheelers
1,053,552 1,259,248 -16.3
BAL FTS BAK
Failed t4 antici5ate c4nsumer res54nse.
P44r research.
BAL increased its 5r4ducti4n 41 m4t4rcycles by 67.6% in
2001 even as the 5r4ducti4n 41 sc44ters 1ell by44%
By 2001, the c4m5any was manu1acturing as many
m4t4rcycles as geared sc44ters.
BAJAJ HAS REORD FY 2010,
TARGETS 4 MILLION VEHILES
IN FY 2011
ParticuIars ApriI ~ March
2010
ApriI ~ March
2009
Growth %
MOTORYLES 2,506,749 1,907,853 31
TOTAL 2
WHEELERS
2,511,600 1,919,625 31
hange P4rt14li4
New Iaunch gave
wider range
Refresh image.
Pulsar
28%
Disc4ver
48%
3w
16%
Others
8%
Oct 2010 saIes Data For Domestic Market
Rebranding 41 amara Bajaj
The
Flying
Brand Positioning
Statement
.-.~.- ~-
Trying t4 resurrect Sc44ter
sales
Trying to Resurrect Scooter Sales
Price diIIerential between scooter and motorcycles had
narrowed.
In 2001, BAL lowered the prices oI Chetak and Super by Rs.
5000 to Rs. 8000 and removed some accessories like spare
wheel, luggage box, etc., Irom the base models.
In the late 1990s while geared scooter sales were Ialling, the
gearless scooter segments had been growing at 25 per
annum.
Main purchaser oI gearless scooters were teenagers, women,
and older people.
In 1999-2000, BAL had a market share oI 20 in this
segment. In 2000 BAL introduced a new gearless scooter with
a Iour stoke engine 'SaIIire.
In 2002, the Legend NXT 2, a Iour stroke geared scooter that
was claimed to oIIer a motorcycle like mileage oI 60-70kmpl
was launched
To add to BAL`s problems, HMSI`s sold about 10,100 unites
oI the Activa within iust three months oI its launch in 2001.
Kinetic launched the Nova, another gearless scooter in 2002,
which also become quite popular.
In April 2003, TVS launched the Scooty Pep (with a 75cc,
Iour-stroke engine), an upgrade version oI its Scooty, with
better styling, technology, and storage capacity.
In 2004 Chetak was introduced with a new gear system called
wondergear` in which no gear shiIting require.
New ad campaigns were also launched to brush up the
Chetak`s image.
BAL was Iorced to phase out several models including the
Spirit, the Sunny Spice, the Legend and NXT 2, and the
Barvo.The SaIIire, reportedly, suIIered Irom several technical
problems. It was replaced by Wave 2005.
The Fall OF An Icon
In Jan 2006, BAL announced that it had stopped
production oI the Chetak. So that the company could
upgrade its scooter portIolio and regain the title oI
India`s largest scooter manuIacturer.
Chetak had to phase out because BAL had neglected
it in terms oI design, technology, and innovation.
Chetak had remained unchanged Ior more than 30
years. Customer used to call it car on two wheels.
At that time BAL had iust one scooter model, the
Wave. By 2005-2006 HMSI was leader in scooter
segment with 50 market share.
Outl44k:
Late 1990's- 545ularity 41 sc44ters vanish &
m4t4rcycles c4me int4 sight
Reas4n- uncared 14r this segment, mileage
5r4blem and 1ashi4nable techn4l4gy design &
launch 41 new m4t4rcycles m4del
Demand 41 gearless sc44ter was set t4 rise(20%
every year)
Reas4n- Trendy Style, better techn4l4gy &
mileage, targeted t4 w4men and aged 5e45le,
easy t4 1uncti4n
Auto expo 2006 (New Delhi), BAL Launched two
new gearless scooters
ristal DTS-I (100cc); Target- Teenage Girls
Blade DTS-I (150cc); Target- Young Males
4ntinued.
The case traces the company's rise to dominance in
the scooter segment oI the market, and its eventual
Iall, against a backdrop oI changes in customer tastes
and preIerences.
It describes the reasons Ior the shiIt in demand and
discusses the initiatives that the company undertook
to regain lost ground. The case also discusses the
competition in the Indian scooter market, and ends
with a brieI discussion on recent developments in the
two-wheeler market.
mages 41 Bajaj Bikes:
Thank you
You might also like
- Montgomery Fleet Equipment Inventory FA PART 1 ENDDocument2 pagesMontgomery Fleet Equipment Inventory FA PART 1 ENDSahil Dahiya50% (2)
- Case Study of Bajaj Auto LTDDocument19 pagesCase Study of Bajaj Auto LTDtanmoyIIPM63% (19)
- Bajaj Auto Limited Case StudyDocument6 pagesBajaj Auto Limited Case StudyNitin Mahajan100% (1)
- Oldsmobile W-Powered Muscle Cars: Includes W-30, W-31, W-32, W-33, W-34 and moreFrom EverandOldsmobile W-Powered Muscle Cars: Includes W-30, W-31, W-32, W-33, W-34 and moreNo ratings yet
- Bajaj Auto LTD - Case Analysis PDFDocument39 pagesBajaj Auto LTD - Case Analysis PDFpragadeeshwaranNo ratings yet
- Samyak Agarwal (M-703) - Vaibhav Agarwal (M-704)Document31 pagesSamyak Agarwal (M-703) - Vaibhav Agarwal (M-704)Vaibhav AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Submitted By: Aditya Sikder Nidhi Raj Prerna Malhotra Richa Bigghe Shreyas Shah Ivth Semester MhrodDocument21 pagesSubmitted By: Aditya Sikder Nidhi Raj Prerna Malhotra Richa Bigghe Shreyas Shah Ivth Semester MhrodpmprernaNo ratings yet
- Bajaj Chetak: Group MembersDocument19 pagesBajaj Chetak: Group MembersPranoti Pandey50% (2)
- I Will Make Scooters When Royal Enfield Makes Scooters: Rajiv Bajaj To ShareholdersDocument7 pagesI Will Make Scooters When Royal Enfield Makes Scooters: Rajiv Bajaj To ShareholdersShreya VengurlekarNo ratings yet
- Bajaj Auto LTDDocument44 pagesBajaj Auto LTDVishal BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Bs PresentationDocument53 pagesBs PresentationVikas MishraNo ratings yet
- Product Life Cycle of Bajaj: Y.Srikanth Reddy Mba 1 Year Sec-C Roll NO-1225110358Document19 pagesProduct Life Cycle of Bajaj: Y.Srikanth Reddy Mba 1 Year Sec-C Roll NO-1225110358Yettapu SrikanthNo ratings yet
- Bajaj PulsarDocument15 pagesBajaj PulsarjahasmmNo ratings yet
- Principals of Management-Project: Sunil Jaiswal - 9819212154 Masters in Marketing ManagementDocument65 pagesPrincipals of Management-Project: Sunil Jaiswal - 9819212154 Masters in Marketing ManagementNikhil TiwariNo ratings yet
- Bajaj Pulsar IDocument7 pagesBajaj Pulsar Irdx216No ratings yet
- Principals of Management-Project: Sunil Jaiswal - 9819212154 Masters in Marketing ManagementDocument63 pagesPrincipals of Management-Project: Sunil Jaiswal - 9819212154 Masters in Marketing ManagementPrashin VermaNo ratings yet
- Principals of Management-Project: Sunil Jaiswal - 9819212154 Masters in Marketing ManagementDocument65 pagesPrincipals of Management-Project: Sunil Jaiswal - 9819212154 Masters in Marketing ManagementniravNo ratings yet
- Bajaj RestructuringDocument61 pagesBajaj RestructuringKirtivardhan BhaleraoNo ratings yet
- Presented By:: Vidhi. M. Amrutiya Vaishali Dolly. RanaDocument47 pagesPresented By:: Vidhi. M. Amrutiya Vaishali Dolly. RanaVikramaditya MuralidharanNo ratings yet
- Project On Bajaj Auto LTDDocument65 pagesProject On Bajaj Auto LTDranjeetsoniNo ratings yet
- Principals of Management-Project: Sunil Jaiswal - 9819212154 Masters in Marketing ManagementDocument65 pagesPrincipals of Management-Project: Sunil Jaiswal - 9819212154 Masters in Marketing ManagementDebi Prasan DasNo ratings yet
- Welcome: Presented By: K.R. Sudhakar Jr. MBA (ABM)Document16 pagesWelcome: Presented By: K.R. Sudhakar Jr. MBA (ABM)raviksabmNo ratings yet
- BBA Bajaj Vs Hero Honda Project ReportDocument53 pagesBBA Bajaj Vs Hero Honda Project Reportmahendrakaya33% (3)
- Bajaj Auto LTDDocument11 pagesBajaj Auto LTDraunakNo ratings yet
- Two Wheeler Industry HERO MOTO CORP & BAJAJ AUTO LTD (ROLL NO 39)Document16 pagesTwo Wheeler Industry HERO MOTO CORP & BAJAJ AUTO LTD (ROLL NO 39)sakshiNo ratings yet
- Bajaj Vs Herohonda1Document19 pagesBajaj Vs Herohonda1Pramod PandeyNo ratings yet
- Case Study: Bajaj Auto LimitedDocument30 pagesCase Study: Bajaj Auto Limitedsinghabhi7No ratings yet
- Project Report of Research Methodology OnDocument44 pagesProject Report of Research Methodology OnMohit Sugandh100% (1)
- "Comparative Study Between Bajaj and Hero Honda": Project ReportDocument75 pages"Comparative Study Between Bajaj and Hero Honda": Project Reporttariquewali11No ratings yet
- Project Report of Research Methodology On Comparative Study of Bajaj Vs Hero HondaDocument10 pagesProject Report of Research Methodology On Comparative Study of Bajaj Vs Hero HondariteshmathriyaNo ratings yet
- Business Strategy of Bajaj Auto Limited (For Non Seminar Students)Document3 pagesBusiness Strategy of Bajaj Auto Limited (For Non Seminar Students)Ashvin BalarNo ratings yet
- Details of 2 Wheeler Companies in IndiaDocument32 pagesDetails of 2 Wheeler Companies in Indiaapurva_chunarkarNo ratings yet
- Hero Honda Vs Bajaj Project ReportDocument45 pagesHero Honda Vs Bajaj Project Reportraviniec005100% (3)
- Introduction To TopicDocument4 pagesIntroduction To TopicSharvin GhadigaonkarNo ratings yet
- Two Wheeler Industry in India and Integrated Marketing CommunicationDocument32 pagesTwo Wheeler Industry in India and Integrated Marketing Communicationnmaini1No ratings yet
- Product Life Cycle of Bajaj ChetakDocument19 pagesProduct Life Cycle of Bajaj ChetakChetna Mandhare0% (2)
- Bajaj Chetak: Rural MarketingDocument25 pagesBajaj Chetak: Rural Marketingprashant1723No ratings yet
- Alliance Joint Venture Indian 2 Wheeler and Global 4 WheelerDocument80 pagesAlliance Joint Venture Indian 2 Wheeler and Global 4 WheelerSahil SinglaNo ratings yet
- A Study On Two Wheeler Bike inDocument37 pagesA Study On Two Wheeler Bike inBhavin_Patel_948167% (12)
- Presented by Vimal Mohan P Research Guide DR Anitha SDocument44 pagesPresented by Vimal Mohan P Research Guide DR Anitha Svimalmohanp60% (5)
- Bajaj Chetak Marketing StrategyDocument7 pagesBajaj Chetak Marketing Strategyprashant1723No ratings yet
- Comparative Study OF Bajaj V/S Hero Honda: Project Report of Research Methodology OnDocument60 pagesComparative Study OF Bajaj V/S Hero Honda: Project Report of Research Methodology OnPrakash DubeyNo ratings yet
- Summer Training Report On Hero MotocorpDocument15 pagesSummer Training Report On Hero MotocorpSaurav093No ratings yet
- Hero Honda and Bajaj BikeDocument37 pagesHero Honda and Bajaj BikeAnurag Chhirolya100% (1)
- Bajaj Auto - Strategic ManagementDocument42 pagesBajaj Auto - Strategic ManagementShashank JoganiNo ratings yet
- Two Wheeler Indusarty Analysis Industrial Work OutDocument20 pagesTwo Wheeler Indusarty Analysis Industrial Work OutAzhar k.pNo ratings yet
- Karan 4th ProDocument61 pagesKaran 4th ProAmarbant Singh DNo ratings yet
- Motor BikeDocument22 pagesMotor BikeSofia ShamrinNo ratings yet
- Index: - Profile - Key Person - Bajaj Intro - Company History - Timeline of New ReleasesDocument44 pagesIndex: - Profile - Key Person - Bajaj Intro - Company History - Timeline of New ReleasesSharma KawalNo ratings yet
- 10 - Chapter 3 PDFDocument66 pages10 - Chapter 3 PDFSaranya SandhyaNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study OF Bajaj V/S Hero Honda: Project Report of Research Methodology OnDocument44 pagesComparative Study OF Bajaj V/S Hero Honda: Project Report of Research Methodology OnBhupendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study OF V/S: Project Report of Research Methodology OnDocument47 pagesComparative Study OF V/S: Project Report of Research Methodology OnPari SavlaNo ratings yet
- Project Report of ResearchDocument39 pagesProject Report of ResearchnagararpitNo ratings yet
- Marketing VespaDocument9 pagesMarketing VesparichauNo ratings yet
- Bajaj The Brand and The Way ForwardDocument5 pagesBajaj The Brand and The Way ForwardAdil SiddiqiNo ratings yet
- Althamas Bba Project - 051613Document59 pagesAlthamas Bba Project - 051613kabilanNo ratings yet
- BAL Fights Back: - Following The Motorcycle Way'Document4 pagesBAL Fights Back: - Following The Motorcycle Way'Manish GadhwalNo ratings yet
- Prateek Research ProjectDocument70 pagesPrateek Research Projectabhi141089No ratings yet
- Bajaj Automobiles Sales Marketing Project (Print Out)Document51 pagesBajaj Automobiles Sales Marketing Project (Print Out)Sushant Bhasin100% (1)
- Chassis: by Naveen KDocument56 pagesChassis: by Naveen KNaveen KandasamyNo ratings yet
- GD8JLKADocument2 pagesGD8JLKAjeane jacques RosoueNo ratings yet
- Merger and AcquisitionDocument7 pagesMerger and AcquisitionjimsrohiniNo ratings yet
- Linde EN Ds 139 l12r l16r 1103 BDocument4 pagesLinde EN Ds 139 l12r l16r 1103 BNadeem AhmedNo ratings yet
- Khos Khas PM ListDocument6 pagesKhos Khas PM ListJamyansuren TseveendorjNo ratings yet
- Technical Poster Pares de Apriete y DemasDocument1 pageTechnical Poster Pares de Apriete y Demasej_aguadoNo ratings yet
- Operation & Maintenance Manual Landpower en PDFDocument228 pagesOperation & Maintenance Manual Landpower en PDFPMV DeptNo ratings yet
- HyundaiDocument24 pagesHyundaiMaiChiVu0% (1)
- G9wvkov4 Volvo AtfDocument6 pagesG9wvkov4 Volvo AtfRikrdoNo ratings yet
- Basic Install Guide - Audi R8 Exhaust SystemDocument23 pagesBasic Install Guide - Audi R8 Exhaust SystemohshafiNo ratings yet
- Bulk Water Truck Operations - GuideDocument84 pagesBulk Water Truck Operations - GuidexpressjobsNo ratings yet
- List of Pre-Owned Vehicles For Sale - 09.09.22Document36 pagesList of Pre-Owned Vehicles For Sale - 09.09.22adFWSVNo ratings yet
- 89212693-Wiring Diagram, FH4 Corrections (ENG)Document4 pages89212693-Wiring Diagram, FH4 Corrections (ENG)EDUARDO BARRIENTOSNo ratings yet
- SD110 - Power DistributionDocument6 pagesSD110 - Power Distributionjanuar1983No ratings yet
- Catalogo Rines AutomovilDocument92 pagesCatalogo Rines AutomovilYimmy MorenoNo ratings yet
- Rough Terrain Crane: Japanese SpecificationsDocument12 pagesRough Terrain Crane: Japanese SpecificationslyguyenquocduyNo ratings yet
- H25TPX-UK-BD Especificaciones Manlfit HaulotteDocument2 pagesH25TPX-UK-BD Especificaciones Manlfit HaulotteLarry AguirreNo ratings yet
- Audi Q7 - 6-Speed Automatic Gearbox 09D - Self-Study Programme 367Document72 pagesAudi Q7 - 6-Speed Automatic Gearbox 09D - Self-Study Programme 367rakamamabeNo ratings yet
- Myvi W sst2022Document1 pageMyvi W sst2022johanbesarNo ratings yet
- CAR DatasetDocument263 pagesCAR DatasetMohammad ShamsherNo ratings yet
- New Dodge Chrysler Jeep Airbag Squib Spiral Cable Clock Spring 56046533ae 3 Plug EbayDocument1 pageNew Dodge Chrysler Jeep Airbag Squib Spiral Cable Clock Spring 56046533ae 3 Plug EbayJohan LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Corvette C5 - 2004 Service Manuals - Drive ShaftsDocument223 pagesCorvette C5 - 2004 Service Manuals - Drive Shaftsken cevaNo ratings yet
- Braking System Suggested For The AtvDocument9 pagesBraking System Suggested For The AtvAkash SaxenaNo ratings yet
- 3-DTC IndexDocument34 pages3-DTC Indexvance grayNo ratings yet
- Experimental Examination of Test Maneuvers That May Induce On-Road, Untripped Light Vehicle RolloverDocument42 pagesExperimental Examination of Test Maneuvers That May Induce On-Road, Untripped Light Vehicle RolloverKuldeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Atek Tractor Price List-2022Document4 pagesAtek Tractor Price List-2022MM SparesNo ratings yet
- Error Code ListDocument3 pagesError Code Listميلاد النعيريNo ratings yet
- руководство ATLAS 350MHDocument10 pagesруководство ATLAS 350MHЛеонид СтепановNo ratings yet
- Rolls Royce / Bentley Service Handbook 1955Document1,283 pagesRolls Royce / Bentley Service Handbook 1955head_masterNo ratings yet