Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Problem 2.17: Solution
Problem 2.17: Solution
Uploaded by
MilOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Problem 2.17: Solution
Problem 2.17: Solution
Uploaded by
MilCopyright:
Available Formats
Problem 2.
17 At an operating frequency of 300 MHz, a lossless 50- air-spaced
transmission line 2.5 m in length is terminated with an impedance ZL = (40 + j20) .
Find the input impedance.
Solution: Given a lossless transmission line, Z0 = 50 , f = 300 MHz, l = 2.5 m,
and ZL = (40 + j20) . Since the line is air filled, up = c and therefore, from
Eq. (2.48),
2 300 106
= = = 2 rad/m.
up 3 108
Since the line is lossless, Eq. (2.79) is valid:
ZL + jZ0 tan l (40 + j20) + j50 tan (2 rad/m 2.5 m)
Zin = Z0 = 50
Z0 + jZL tan l 50 + j(40 + j20) tan (2 rad/m 2.5 m)
= 50 [(40 + j20) + j50 0] 50 + j(40 + j20) 0
= (40 + j20) .
Problem 2.37 On a lossless transmission line terminated in a load ZL = 100 ,
the standing-wave ratio was measured to be 2.5. Use the Smith chart to fin the two
possible values of Z0 .
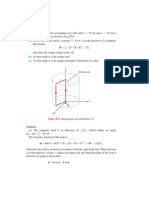
Solution: Refer to Fig. P2.52. S = 2.5 is at point L1 and the constant SWR
circle is shown. zL is real at only two places on the SWR circle, at L1, where
zL = S = 2.5, and L2, where zL = 1/S = 0.4. so Z01 = ZL /zL1 = 100 /2.5 = 40
and Z02 = ZL /zL2 = 100 /0.4 = 250 .
0.12 0.13
0.11 0.14
0.38 0.37 0.15
0.1 0.39 0.36
90
0.4 100 80 0.35 0.1
.09 6
1.0
0
0.9
1.2
70 0.3
0.8
0.4
1 110 4
0.1
1.4
8
0.7
0.0 7
2 Yo) 0.3
1.6
0.4 0 jB/ 60 3
12 E (+
0.6
.07 NC 0.1
TA 8
1.8
0 EP 0.2 0.3
3 SC
0.4 SU 2
2.0
0 VE 50
0.5
13 TI
CI
06
0.
PA
19
0.
CA
44
0.
31
0.
R
,O 0.4
4
0. o)
/Z
0
40
5
14
0.2
0.0
jX
(+
5
0.3
0.4
3.0
EN
0.6
N
PO
4
0.2
OM
0.3
0.0
0.2
0
1
30
0.4
15
EC
0.8
9
>
4.0
NC
R
TA
TO
1.0
AC
0.22
ERA
0.47
0.28
5.0
E
1.0
R
GEN
0.2
IVE
160
20
UCT
8
0.
ARD
IND
0.23
TOW
0.48
0.27
0.6
ANG
GTHS
10
LE OF
170
0.1
0.4
0.0 > WAVELEN
0.24
0.49
0.26
REFLECTION
20
0.2
50
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1.0
1.2
1.4
1.6
1.8
2.0
3.0
4.0
5.0
10
20
50
L2 L1
0.25
0.25
180
< 0.0
RESISTANCE COMPONENT (R/Zo), OR CONDUCTANCE COMPONENT (G/Yo)
50 COEFFICIENT IN
0.2
RD LOAD
20
0.24
0.49
0.26
0
0.4
DEGR
-17
0.1
TOWA
10
EES
0.23
0.6
THS
0.48
0.27
Yo)
G
/
N
8
0.
j
E
(-
-160
VEL
-20
CE
0.2
N
0.22
1.0
A
5.0
TA
0.47
0.28
W
EP
<
1.0
SC
SU
4.0
E
0.8
4
0.2
0
-30
V
.0
-15
TI
6
0.2
0
1
0.4
0.3
C
9
DU
IN
0.6
R
3.0
,O
5
0.2
0.0
o)
5
0.3
Z
0.4
-4
X/
4
-1
4
0. (-j
T 0.4
EN
06
0.
19
N
0.
PO
44
0.
31
M
0.
O -5
EC 30
0.5
-1 0
2.0
NC 7 0.1
TA 0.0 8
AC 0.3
1.8
RE 3 0.2
IVE 0.4 2
0.6
IT 0 -60
AC -12 0.08
0.1
1.6
CAP 7
0.3
0.7
.4 2 3
1.4
0 0.1
9 -70
-110
0.8
0.0 6
1.2
0.9
1.0
1 0.3
0.1 0.4 -100 -80 0.15 4
-90
0.11 0.14 0.35
0.4 0.12 0.13
0.39 0.36
0.38 0.37
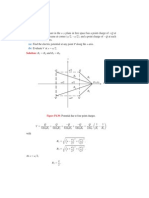
Figure P2.37: Solution of Problem 2.37.
Problem 2.38 A lossless 50- transmission line is terminated in a load with
ZL = (50 + j25) . Use the Smith chart to fin the following:
(a) The reflectio coefficien .
(b) The standing-wave ratio.
(c) The input impedance at 0.35 from the load.
(d) The input admittance at 0.35 from the load.
(e) The shortest line length for which the input impedance is purely resistive.
(f) The position of the firs voltage maximum from the load.
0.12 0.13
0.11 0.14
0.38 0.37 0.15
0.1 0.39 0.36
90
0.4 100 80 0.35 0.1
r
9
0.0 6
1.0
0.9
1.2
70 0.3
0.8
0.41 110 4
0.1
1.4
8
0.7
0.0 7
) 0.3
2 /Yo
1.6
0.4 0 60 3
12 (+jB
0.6
CE 0.1
0.0
7 AN 8
1.8
PT 0.2
.43 SCE 0.3
2
0 SU
2.0
0 VE 50
0.5
13 TI
CI
06
0.
PA
0.106
19
0.
CA
44
0.
31
0.
R
,O 0.4
4
0. o)
/Z
0
40
5
14
0.2
0.0
jX
(+
5
0.3
0.4
3.0
EN
0.6
N
PO
4
0.2
OM
0.3
0.0
0.2
0
1
30
0.4
15
EC
0.8
9
>
4.0
NC
R
TA
TO
1.0
AC
0.22
ERA
0.47
0.28
5.0
E
1.0
R
GEN
0.2
IVE
160
20
UCT
8
0.
ARD
IND
0.23
TOW
0.48
0.27
0.6
ANG
Z-LOAD
GTHS
10
LE OF
170
0.1
0.4
0.0 > WAVELEN
0.24
0.49
0.26
REFLECTION
20
0.2
50
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1.0
1.2
1.4
1.6
1.8
2.0
3.0
4.0
5.0
10
20
50
SWR
0.25
0.25
180
< 0.0
COEFFICIENT IN
Z-IN 50
RESISTANCE COMPONENT (R/Zo), OR CONDUCTANCE COMPONENT (G/Yo)
0.2
RD LOAD
20
0.24
0.49
0.26
0
0.4
DEGR
-17
0.1
TOWA
10
EES
0.23
0.6
THS
0.48
0.27
Yo)
G
/
N
8
0.
j
E
(-
-160
VEL
-20
CE
0.2
N
0.22
1.0
A
5.0
TA
0.47
0.28
W
EP
<
1.0
SC
SU
4.0
E
0.8
4
0.2
0
-30
V
.0
-15
TI
6
0.2
0
1
0.4
0.3
C
9
DU
IN
0.6
R
3.0
,O
5
0.2
0.0
o)
5
0.3
Z
0.4
-4
X/
4
-1
0
4
0. (-j
T 0.4
EN
06
0.
19
N
0.
PO
44
0.
31
M
0.
O -5
EC 30
0.5
-1 0
2.0
NC 7 0.1
TA 0.0 8
AC 0.3
1.8
RE 3 0.2
VE 0.4 2
0.350
0.6
C ITI 0 -60 0.1
A -12 0.08
1.6
CAP 7
0.3
0.7
2
0.4 3
1.4
9 -70 0.1
-110
0.8
0.0 6
1.2
0.9
1.0
1 0.3
0.1 0.4 -100 -80 0.15 4
-90
0.11 0.14 0.35
0.4 0.12 0.13
0.39 0.36
0.38 0.37
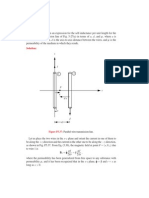
Figure P2.53: Solution of Problem 2.53.
Solution: Refer to Fig. P2.53. The normalized impedance
(50 + j25)
zL = = 1 + j0.5
50
is at point Z-LOAD.
(a) = 0.24e j76.0 The angle of the reflectio coefficien is read of that scale at
the point r .
(b) At the point SW R: S = 1.64.
(c) Zin is 0.350 from the load, which is at 0.144 on the wavelengths to generator
scale. So point Z-IN is at 0.144 + 0.350 = 0.494 on the WTG scale. At point
Z-IN:
Zin = zin Z0 = (0.61 j0.022) 50 = (30.5 j1.09) .
(d) At the point on the SWR circle opposite Z-IN,
yin (1.64 + j0.06)
Yin = = = (32.7 + j1.17) mS.
Z0 50
(e) Traveling from the point Z-LOAD in the direction of the generator (clockwise),
the SWR circle crosses the xL = 0 line firs at the point SWR. To travel from
Z-LOAD to SWR one must travel 0.250 0.144 = 0.106 . (Readings are on the
wavelengths to generator scale.) So the shortest line length would be 0.106 .
(f) The voltage max occurs at point SWR. From the previous part, this occurs at
z = 0.106 .
You might also like
- DrillsDocument93 pagesDrillsjulioNo ratings yet
- Hayt Cap 8 SolutionDocument26 pagesHayt Cap 8 SolutionVitor Campos100% (4)
- Problem 4.21: Y-Direction and Infinitely Long in The X-Direction. If The Strip Is in Air and Has ADocument2 pagesProblem 4.21: Y-Direction and Infinitely Long in The X-Direction. If The Strip Is in Air and Has AEric KialNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Selected SolutionsDocument41 pagesChapter 10 Selected SolutionsFaizan Bhatti50% (2)
- METU EE 303 YR 200 9 Some Transmission Line Problems With SolutionsDocument7 pagesMETU EE 303 YR 200 9 Some Transmission Line Problems With SolutionsAliBaranIşıkNo ratings yet
- Instructor Solutions Manual For Engineering Electromagnetics (Chapter 7)Document23 pagesInstructor Solutions Manual For Engineering Electromagnetics (Chapter 7)Ryan Howard0% (1)
- Problem 4.17: SolutionDocument1 pageProblem 4.17: SolutionEric KialNo ratings yet
- Spring 2014 HW 4 SolnsDocument24 pagesSpring 2014 HW 4 SolnsZahraa TajAlssir AbouSwarNo ratings yet
- ECE3442F05HW3Document12 pagesECE3442F05HW3JacobNo ratings yet
- Chap13 PDFDocument36 pagesChap13 PDFAngelica Ramos100% (1)
- HW2 SolutionDocument15 pagesHW2 SolutionEugene KrabsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document34 pagesChapter 11blooms93No ratings yet
- Homework 4 SolutionDocument3 pagesHomework 4 SolutionMUJAHIDNo ratings yet
- Gejala GelombangDocument6 pagesGejala GelombangVincent VetterNo ratings yet
- Cap. 32 PDFDocument75 pagesCap. 32 PDFwallaNo ratings yet
- ECE 107, Quiz 1 (Jan 30, 2012) : NameDocument3 pagesECE 107, Quiz 1 (Jan 30, 2012) : Namecourse her o daNo ratings yet
- RCC Beam3Document18 pagesRCC Beam3Sudip Kumar SwainNo ratings yet
- Practice Midterm1Document30 pagesPractice Midterm1thisguypoorNo ratings yet
- TLDocument16 pagesTLMannanHarshaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 06Document13 pagesChapter 06Johnny Lee Worthy IIINo ratings yet
- Transmission Lines CH 2Document12 pagesTransmission Lines CH 2Richard JoserNo ratings yet
- HkgssDocument5 pagesHkgssNguyen TranNo ratings yet
- Teoría ElectromagnéticaDocument34 pagesTeoría ElectromagnéticaAdry CarrilloNo ratings yet
- RCC Design 3/7Document18 pagesRCC Design 3/7Nandan Anil GaikwadNo ratings yet
- SolutionsDocument9 pagesSolutionsdavid_benavidez_3No ratings yet
- 8 02pset9solDocument12 pages8 02pset9solZyra ArcosNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete BeamDocument22 pagesReinforced Concrete Beamkhaas engineers and consultantsNo ratings yet
- Rec3 SolutionsDocument6 pagesRec3 SolutionsOscar Martinez0% (1)
- 2 34Document2 pages2 34Eric KialNo ratings yet
- Flanged Beams NumericalsDocument18 pagesFlanged Beams NumericalsSonam BajpaiNo ratings yet
- Calcular La Corriente de Cortocircuito 3F (I, I Yi) y FT en F1, F2 y F3Document5 pagesCalcular La Corriente de Cortocircuito 3F (I, I Yi) y FT en F1, F2 y F3luisNo ratings yet
- EET416 Problem Set #3 Solution Transmission Line TheoryDocument9 pagesEET416 Problem Set #3 Solution Transmission Line TheoryAbdallah E. Abdallah100% (2)
- Bode Diagram-2: Dode Diagrams For Complex Poles and ZerosDocument7 pagesBode Diagram-2: Dode Diagrams For Complex Poles and ZerosAdrianNo ratings yet
- Problem29 44Document1 pageProblem29 44IENCSNo ratings yet
- Calcular La Corriente de Cortocircuito 3F (I, I Yi) y FT en F1, F2 y F3Document6 pagesCalcular La Corriente de Cortocircuito 3F (I, I Yi) y FT en F1, F2 y F3FLORES TORREZ VICMARNo ratings yet
- Chp2-Planar Transmission LineswithexamplesDocument56 pagesChp2-Planar Transmission LineswithexamplesdhruvaaaaaNo ratings yet
- HW3 SolutionDocument19 pagesHW3 SolutionNguyen Thanh HungNo ratings yet
- 2.19 (A) (B) (C) (D) : SolutionDocument5 pages2.19 (A) (B) (C) (D) : Solutionpankaj chaurasiaNo ratings yet
- Problem29 29Document1 pageProblem29 29IENCSNo ratings yet
- December - 2017Document2 pagesDecember - 2017Suresh ThalllapelliNo ratings yet
- EM Waves and Guide Structure Chapter 3 & 4 WorksheetDocument5 pagesEM Waves and Guide Structure Chapter 3 & 4 WorksheetAbrham GojjamNo ratings yet
- Design of A Singly Reinforced T-BeamDocument2 pagesDesign of A Singly Reinforced T-BeamVivek Thakur SujanianNo ratings yet
- 5.6 5.10 5.14 5.17 5.22Document10 pages5.6 5.10 5.14 5.17 5.22pitayutNo ratings yet
- Rec10 SolutionsDocument4 pagesRec10 SolutionsvirjogNo ratings yet
- Selected - Ch18 - WavesDocument8 pagesSelected - Ch18 - WavesVincent VetterNo ratings yet
- Final Practice Problems IDocument30 pagesFinal Practice Problems IAlluri Appa RaoNo ratings yet
- Probset 13 SolnDocument9 pagesProbset 13 SolnmrsadeghiNo ratings yet
- YF Ch35 Exmpls New - PDF (35.51 Punto 2)Document5 pagesYF Ch35 Exmpls New - PDF (35.51 Punto 2)Cristian Julián Díaz BohórquezNo ratings yet
- Experiment # 09Document5 pagesExperiment # 09Hafeez AliNo ratings yet
- MWA Question Set 1Document2 pagesMWA Question Set 1Mahesh PatelNo ratings yet
- CES522 A 07 - Topic 4b - 2. Short Column - ExamplesDocument22 pagesCES522 A 07 - Topic 4b - 2. Short Column - ExamplesAizuddinNo ratings yet
- 1051-455-20073 Solution Set #2Document11 pages1051-455-20073 Solution Set #2Muzamil ShahNo ratings yet
- Thermal StrainDocument14 pagesThermal StrainMavrix AgustinNo ratings yet
- Chap 11Document18 pagesChap 11ashinkumarjerNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- Hyrdoacoustic Ocean Exploration: Theories and Experimental ApplicationFrom EverandHyrdoacoustic Ocean Exploration: Theories and Experimental ApplicationNo ratings yet
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyFrom EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyNo ratings yet
- The Plasma Dispersion Function: The Hilbert Transform of the GaussianFrom EverandThe Plasma Dispersion Function: The Hilbert Transform of the GaussianRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Problem 5.37: SolutionDocument2 pagesProblem 5.37: SolutionEric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 5.38: SolutionDocument2 pagesProblem 5.38: SolutionEric Kial0% (1)
- Problem 5.40: 20 A. Determine The Magnetic Flux Through TheDocument1 pageProblem 5.40: 20 A. Determine The Magnetic Flux Through TheEric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 5.2: SolutionDocument1 pageProblem 5.2: SolutionEric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 5.39: SolutionDocument1 pageProblem 5.39: SolutionEric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 5.41: SolutionDocument2 pagesProblem 5.41: SolutionEric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 5.18: X-Direction Lies in The X-Y Plane and Carries A Current I in TheDocument2 pagesProblem 5.18: X-Direction Lies in The X-Y Plane and Carries A Current I in TheEric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 5.4: SolutionDocument1 pageProblem 5.4: SolutionEric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 5.20: 5 A. If A Straight, Long Conductor Carrying A Current I 10 A IsDocument1 pageProblem 5.20: 5 A. If A Straight, Long Conductor Carrying A Current I 10 A IsEric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 5.14: 2 M. If The Two Loops Have 3 M, Determine The Magnetic Field At: 0 1 M 2 MDocument2 pagesProblem 5.14: 2 M. If The Two Loops Have 3 M, Determine The Magnetic Field At: 0 1 M 2 MEric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 5.17: SolutionDocument2 pagesProblem 5.17: SolutionEric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 5.16: SolutionDocument2 pagesProblem 5.16: SolutionEric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 5.8: 3 M and 7 M and Carries A Current I 15 A, Find H at P (2,, 0)Document1 pageProblem 5.8: 3 M and 7 M and Carries A Current I 15 A, Find H at P (2,, 0)Eric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 5.15: SolutionDocument2 pagesProblem 5.15: SolutionEric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 5.10: SolutionDocument2 pagesProblem 5.10: SolutionEric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 5.9: SolutionDocument1 pageProblem 5.9: SolutionEric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 5.13: SolutionDocument1 pageProblem 5.13: SolutionEric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 5.7: SolutionDocument1 pageProblem 5.7: SolutionEric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 5.12Document1 pageProblem 5.12Eric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 5.5: 4 CM, /2, and 1 M Z 1 M. R 0.2 Cos 4 CM) ?Document2 pagesProblem 5.5: 4 CM, /2, and 1 M Z 1 M. R 0.2 Cos 4 CM) ?Eric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 5.3: SolutionDocument1 pageProblem 5.3: SolutionEric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 5.6: 30 CM and W 10 CM Is 10 A, Is in The Presence of A Magnetic 2 × 10 ( X + Y2) (T)Document3 pagesProblem 5.6: 30 CM and W 10 CM Is 10 A, Is in The Presence of A Magnetic 2 × 10 ( X + Y2) (T)Eric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 5.1: × 10 ( x4 z3) T. Given That e 1.6 × 10 9.1 × 10Document1 pageProblem 5.1: × 10 ( x4 z3) T. Given That e 1.6 × 10 9.1 × 10Eric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 4.30Document2 pagesProblem 4.30Eric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 4.23: Repeat Problem 4.22 For D (C/M)Document1 pageProblem 4.23: Repeat Problem 4.22 For D (C/M)Eric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 4.18: 9e, and The Other Located On The Positive X-Axis at 36e. Determine The LocationDocument2 pagesProblem 4.18: 9e, and The Other Located On The Positive X-Axis at 36e. Determine The LocationEric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 4.19: SolutionDocument1 pageProblem 4.19: SolutionEric KialNo ratings yet
- Problem 4.28: If The Charge Density Increases Linearly With Distance From The Origin Such That Atr Variation of DDocument1 pageProblem 4.28: If The Charge Density Increases Linearly With Distance From The Origin Such That Atr Variation of DEric KialNo ratings yet