Professional Documents
Culture Documents
portableEKG Weitere Informationen PDF
Uploaded by
girishOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
portableEKG Weitere Informationen PDF
Uploaded by
girishCopyright:
Available Formats
DailyCare BioMedical Inc.
INTRODUCTORY GUIDE TO IDENTIFYING
ECG IRREGULARITIES
NOTICE: This is an introductory guide for a user to understand basic ECG
tracings and parameters. The guide will allow user to identify some of the
differences between regular and irregular ECG tracings based on Lead I alone.
WARNINGS: Please note that this guide does not cover all irregular electrical
activities and rhythms of the heart. This guide contains simulated and real
examples of ECG tracings. This guide is for reference ONLY. If you find your
ECG tracing different from a normal sinus rhythm, or if the tracing resembles
any of the irregular ECG tracings, please consult a physician for advices.
Proprietary information of DailyCare BioMedical Inc. No reproduction is allowed.
DailyCare BioMedical Inc.
CONTENTS
CARDIO SYSTEM ...............................................................1
1.1 BASIC FUNCTION OF THE HEART:..................................1
1.2 CONDUCTION SYSTEM OF THE HEART:..........................2
1.3 ABOUT ARRHYTHMIA:...................................................3
1.4 EXAMPLE OF 12-LEAD ECG:........................................3
BASIS OF THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM (ECG) .............4
2.1 UNDERSTANDING ECG PARAMETERS: ..........................4
2.2 ECG WAVES AND PARAMETERS ....................................5
ECG TRACING ....................................................................7
3.1 NORMAL SINUS RHYTHM ..............................................7
3.2 SINUS BRADYCARDIA ...................................................7
3.3 SINUS TACHYCARDIA ...................................................7
3.4 SUPRAVENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA (SVT)....................8
3.5 ATRIAL FIBRILLATION, COARSE .....................................8
3.6 ATRIAL FIBRILLATION, FINE ...........................................9
3.7 ATRIAL FLUTTER ..........................................................9
3.8 VENTRICULAR RHYTHM ..............................................10
3.9 VENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA ......................................10
3.10 VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION .......................................11
3.11 SINUS ARRHYTHMIA ...................................................11
3.12 MISSED BEAT.............................................................12
3.13 PAROXYSMAL ATRIAL TACHYCARDIA (PAT) ..................13
3.14 NODAL RHYTHM ........................................................13
3.15 LEFT VENTRICULAR HYPERTROPHY ............................14
3.16 FIRST DEGREE A-V HEART BLOCK: ............................14
Proprietary information of DailyCare BioMedical Inc. No reproduction is allowed.
DailyCare BioMedical Inc.
3.17 SECOND DEGREE A-V HEART BLOCK: ........................15
3.18 THIRD DEGREE A-V BLOCK:.......................................15
3.19 RIGHT BUNDLE BRANCH BLOCK (RBBB) ....................16
3.20 LEFT BUNDLE BRANCH BLOCK (LBBB).......................16
3.21 PREMATURE ATRIAL CONTRACTION (PAC) ..................17
3.22 PREMATURE NODAL CONTRACTION (PNC) .................17
3.23 PREMATURE VENTRICULAR CONTRACTION (PVC).......18
3.24 BIGEMINY ..................................................................19
3.25 TRIGEMINY ................................................................19
3.26 TWO PVCS TOGETHER COUPLET ............................20
OTHER EXAMPLES..........................................................21
4.1 IRREGULAR ECG.......................................................21
4.2 REVERSE SIGNALS ....................................................21
4.3 PACEMAKER MONITING...............................................22
4.4 SMALL SIGNALS .........................................................23
4.5 NOISE SIGNALS .........................................................24
GLOSSARY: ......................................................................25
APPENDIX.........................................................................27
12-LEAD ECG ANALOGY BY RMH2.0..................................27
LEAD I .......................................................................27
LEAD II ......................................................................28
LEAD III .....................................................................29
LEAD AVR ...................................................................30
LEAD AVL ...................................................................31
LEAD AVF ...................................................................32
V1-V6.........................................................................33
Proprietary information of DailyCare BioMedical Inc. No reproduction is allowed.
DailyCare BioMedical Inc.
Cardio System
1.1 Basic Function of the Heart:
The heart has 4 chambers that act together to pump blood throughout the body. The 2
smaller upper chambers are called atria, and the larger lower chambers are called
ventricles. The right atrium receives oxygen-depleted blood coming back from the
body via 2 large veins: the superior vena cava and inferior vena cava. The right
atrium pumps this blood into the right ventricle, which then pumps the blood into the
lungs, which is oxygenated. The blood then comes back into the left atrium, which is
then pumped into the left ventricle. The left ventricle then pumps the blood back to
the circulatory system via the aorta, the largest artery in the body. The pressure that
the left ventricle exerts to keep the blood moving throughout the whole body is the
blood pressure.
Proprietary information of DailyCare BioMedical Inc. No reproduction is allowed. 1
DailyCare BioMedical Inc.
1.2 Conduction System of the Heart:
The chambers of the heart pump with the automatic discharge of electricity from the
sinoatrial (SA) node, a group of specialized cells located in the right atrium, also
known as the hearts natural pacemaker. On average, there are 60 to 100 times
discharges per minute. When the SA node discharges, both atria contract, and the
electrical impulse is relayed to the atrioventricular (AV) node, located between the 2
ventricles. The electrical wave is then transmitted from the AV node to the lower
chambers of the heart, or ventricles, via the bundle branches. The ventricles will
contract and pump blood to the whole body. The normal delay between the atrium
and ventricle contractions is 0.12 to 0.20 seconds. By studying the electrical activity
that results when heart muscle cells contract, we gain insight to the health and
workings of the heart. These electrical activities can be detected, recordered and
studied with an electrocardiograph, for example ReadMyHeart.
Proprietary information of DailyCare BioMedical Inc. No reproduction is allowed. 2
DailyCare BioMedical Inc.
1.3 About Arrhythmia:
Arrhythmia is an abnormal or irregular hear rhythm resulting from any changes,
deviation or malfunction in the conduction system of the heart. Early diagnosis of an
arrhythmia is very important. This is because the longer an arrhythmia lasts without
any detection or treatment, the greater the chances of permanent damage and
additional heart dysfunction.
1.4 Example of 12-Lead ECG:
(Arrhythmia)
Proprietary information of DailyCare BioMedical Inc. No reproduction is allowed. 3
DailyCare BioMedical Inc.
Basis of the Electrocardiogram (ECG)
2.1 Understanding ECG Parameters:
A normal ECG Waveform (Lead I)
Reading the graph
The Y-axis represents voltage in mV. The bar indicated below represents 1
millivolt (mV). This denotes the electrical strength of the signal. Therefore, each
big square represent 0.5 mV and each small square represent 0.1mV. The X-axis
represents time in seconds. Each big square represent 0.2 seconds. Therefore,
each small square represents 0.04 seconds.
bar
1 mV
0.2 seconds
Proprietary information of DailyCare BioMedical Inc. No reproduction is allowed. 4
DailyCare BioMedical Inc.
2.2 ECG waves and parameters
The following is a summary of the ECG wave morphologies and parameters
that users can use as a guide to understand more about their ECG recordings.
P wave: The P wave results from atria contraction. P wave is generally
about 1 box wide or 1 box tall. P wave that exceeds these might indicate
atria hypertrophy, i.e., enlargement.
PR Interval: The PR interval is measured from the start of the P wave to
the start of Q wave. It represents the duration of atria depolarization.
Regular duration is from 0.12 to 0.20 seconds, about 3 to 5 box wide. If the
PR interval is greater than 0.20 seconds, then an AV block might be present.
QRS Complex: The QRS complex is measured from the start of Q wave
to the end of S wave. It represents the duration of ventricle
depolarization. Regular duration is from 0.08 0.12 seconds, about 2 to
3 box wide. If duration is longer, it might indicate presence of bundle
branch blocks.
QT/QTc: The Q T/QTc is measured from the start of the Q wave to the end
of T wave. QT interval represents the duration of activation and recovery
of the ventricular muscle. This duration varies inversely with the heart rate.
The regular QTc is approximately 0.41 seconds or an accurate measurement,
it is corrected with the heart rate with the following formula to get QTc:
QTc = QT + 1.75 (HR 60)
ST Segment: The ST segment is measured from end of S wave, J point, to
the start of T wave. This segment is important in identifying pathology such
as myocardial infarctions (elevations) and ischemia (depressions).
Proprietary information of DailyCare BioMedical Inc. No reproduction is allowed. 5
DailyCare BioMedical Inc.
ECG Parameters:
Parameters Reference Range
Average Heart Rate (HR) 60 < HR <100 bpm
ST Segment (ST) -2 < ST < +2 mm
QRS Interval (QRS) 0.08 < QRS < 0.12 sec
PR interval 0.12 ~ 0.20 sec
QT/QTc 0.32 ~ 0.44 sec /0 .41 ~ 0.44 sec
Note: The information above is for reference ONLY. If the measured parameters fall
within the reference range and the user still feel any discomfort, please consult your
physician. Data generated by RMH can be provided to the physicians for reference
and further analysis.
Cautions:
The followings are some simulations and examples of Lead I ECG
tracings.
Please NOTE that these simulations and examples of ECG
irregularities are from Lead I only.
Professionals need to perform a standard 12 lead ECG and/or other
tests before diagnosing your exact heart conditions.
Warnings:
This guide is for you to understand some of the many ECG
irregularities through Lead I ONLY. You should NOT self-diagnosis
and self-medicate based on this guide or Lead I ECG alone.
Proprietary information of DailyCare BioMedical Inc. No reproduction is allowed. 6
DailyCare BioMedical Inc.
ECG Tracing
3.1 Normal Sinus Rhythm
Descriptions: All complexes normal and frequency is between 60 to 100
beats per minute.
3.2 Sinus Bradycardia
Descriptions: A sinus rhythm of less than 60 beats per minute.
3.3 Sinus Tachycardia
Descriptions: The sinus node sends out electrical signals faster than usual,
speeding up the rate. A sinus rhythm of more than 100 beats per minute.
Proprietary information of DailyCare BioMedical Inc. No reproduction is allowed. 7
DailyCare BioMedical Inc.
3.4 Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT)
Descriptions: Usually caused by reentry currents within the atria or
between ventricles and atria producing higher heart rates of 140~250. (Sinus
rhythm at 160 BPM.)
3.5 Atrial Fibrillation, Coarse
Descriptions: Rapid irregular atrial signal with no real P-waves. Irregular
ventricular rate.
Proprietary information of DailyCare BioMedical Inc. No reproduction is allowed. 8
DailyCare BioMedical Inc.
3.6 Atrial Fibrillation, Fine
Descriptions: Rapid irregular atrial signal with no real P-waves. Irregular
ventricular rate.
3.7 Atrial Flutter
Descriptions: Large regular P-waves (sinus rate of 250~350BPM).
Ventricular response varies.
Proprietary information of DailyCare BioMedical Inc. No reproduction is allowed. 9
DailyCare BioMedical Inc.
3.8 Ventricular Rhythm
Descriptions: (Extremely Serious-near death conditions) Similar to left
focus PVCs at 120 BPM
3.9 Ventricular Tachycardia
Descriptions: (Extremely Serious-near death conditions) Similar to left
focus PVCs at 180BPM
Proprietary information of DailyCare BioMedical Inc. No reproduction is allowed. 10
DailyCare BioMedical Inc.
3.10 Ventricular Fibrillation
Descriptions: (Extremely Serious-near death conditions) Irregular
ventricular waveform
3.11 Sinus Arrhythmia
Descriptions: Normal beats, but triggered at an irregular interval from 60 to
100 BPM, causing varying R-R interval.
Proprietary information of DailyCare BioMedical Inc. No reproduction is allowed. 11
DailyCare BioMedical Inc.
3.12 Missed beat
A. Missed beat at 80 BPM
Descriptions: Missed beat at 80 BPM. Normal sinus rhythm, but every 10th
beat is missing
B. Missed beat at 120 BPM
Descriptions: Missed beat at 120 BPM. Normal sinus rhythm, but every
10th beat is missing
Proprietary information of DailyCare BioMedical Inc. No reproduction is allowed. 12
DailyCare BioMedical Inc.
3.13 Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia (PAT)
Descriptions: A repeated periods of very fast heartbeat which begin and
ends suddenly. 160 BPM for 5 seconds alternating with normal sinus rhythm
at 80 BPM.
3.14 Nodal Rhythm
Descriptions: Normal sinus rhythm except P-wave originates in the AV
node instead of SA node. Shortened PR internal of 0.09 seconds.
Proprietary information of DailyCare BioMedical Inc. No reproduction is allowed. 13
DailyCare BioMedical Inc.
3.15 Left Ventricular Hypertrophy
Descriptions: Tall R wave caused by possible thickening of heart muscle
wall.
3.16 First Degree A-V Heart Block:
Descriptions: P wave always precedes the QRS complex, but PR interval is
prolonged over 0.2 second, or 5 small squares. Missed beats are from
occasional signals not reaching the ventricles.
Proprietary information of DailyCare BioMedical Inc. No reproduction is allowed. 14
DailyCare BioMedical Inc.
3.17 Second Degree A-V Heart Block:
Descriptions: PR interval progressively lengthens and leading finally to the
dropout of QRS complex, also known as Wenkebach Phenomenon.
3.18 Third Degree A-V Block:
Descriptions: Complete lack of synchronism between the P wave and QRS
complex. No signals reaching ventricles.
Proprietary information of DailyCare BioMedical Inc. No reproduction is allowed. 15
DailyCare BioMedical Inc.
3.19 Right Bundle Branch Block (RBBB)
Descriptions: Wide QRS, usually more than 120ms or 3 small squares, and
wide S wave, caused by partial or complete blockage of signal along the
right branch below the bundle of HIS.
3.20 Left Bundle Branch Block (LBBB)
Descriptions: Wide QRS, and wide S wave, caused by partial or complete
blockage of signal along the right branch below the bundle of HIS.
Proprietary information of DailyCare BioMedical Inc. No reproduction is allowed. 16
DailyCare BioMedical Inc.
3.21 Premature Atrial Contraction (PAC)
Descriptions: A beat occurs early in the atria causing the heart to beat
before the next regular beat.
3.22 Premature Nodal Contraction (PNC)
Descriptions: A beat occurs early in the AV node causing the heart to beat
before the next beat. (Nodal rhythm a cardiac rhythm paced by the AV
node short PR interval)
Proprietary information of DailyCare BioMedical Inc. No reproduction is allowed. 17
DailyCare BioMedical Inc.
3.23 Premature Ventricular Contraction (PVC)
Descriptions: Ventricles contract before signals reached AV node. Time
interval between normal R peaks is a multiple of R-R intervals.
Proprietary information of DailyCare BioMedical Inc. No reproduction is allowed. 18
DailyCare BioMedical Inc.
3.24 Bigeminy
Descriptions: Each normal beat (normal R-R) is followed by a premature
contraction (PVC).
3.25 Trigeminy
Descriptions: Every second beat is followed by a premature contraction
(two normal QRS complexes followed by a PVC).
Proprietary information of DailyCare BioMedical Inc. No reproduction is allowed. 19
DailyCare BioMedical Inc.
3.26 Two PVCs together Couplet
Descriptions: Two PVCs together. Also called a couplet.
Proprietary information of DailyCare BioMedical Inc. No reproduction is allowed. 20
DailyCare BioMedical Inc.
OTHER EXAMPLES
4.1 Irregular ECG
Descriptions: Arrhythmia, ST depression, reverse T wave
Descriptions: ST depression, reverse T wave
4.2 Reverse Signals
Descriptions: Reverse positioning of heart, all signals reversed
Proprietary information of DailyCare BioMedical Inc. No reproduction is allowed. 21
DailyCare BioMedical Inc.
4.3 Pacemaker moniting
Descriptions: ECG tracing of users with pacemakers.
Proprietary information of DailyCare BioMedical Inc. No reproduction is allowed. 22
DailyCare BioMedical Inc.
4.4 Small Signals
Descriptions: Small signals from Lead I (Suggestion: Use Lead II)
Descriptions: Lead II for the above ECG (Right arm and Left leg)
+
Lead II
Proprietary information of DailyCare BioMedical Inc. No reproduction is allowed. 23
DailyCare BioMedical Inc.
4.5 Noise Signals
Descriptions: The Noise is the interference with the recording of these
signals due to poor contact between the thumbs and the electrodes,
excessive movement of the body, and other the environment, etc. Please
follow standard operating procedure and measure again.
Dry thumbs, Unclean thumbs, Unclean electrodes
Unstable environments
Small movement during measurement, (talking & breathing)
Dry thumbs, Unclean thumbs, Unclean electrodes
Unstable environment
Proprietary information of DailyCare BioMedical Inc. No reproduction is allowed. 24
DailyCare BioMedical Inc.
GLOSSARY:
Aorta The main trunk of the systemic arteries, carrying blood from
the left side of the heart to the arteries of all limbs and organs
except the lungs.
Arrhythmia Irregularity in the force or rhythm of the heart beat.
Atrioventricular (AV) A small mass of specialized cardiac muscle fibers, located in
node the wall of the right atrium of the heart, that receives
heartbeat impulses from the sinoatrial node and directs them
to the walls of the ventricles.
Bundle of His A slender bundle of modified cardiac muscle that passes
from the atrioventricular node in the right atrium to the right
and left ventricles by way of the septum and that maintains
the normal sequence of the heartbeat by conducting the wave
of excitation from the right atrium to the ventricles called
also atrioventricular bundle, His bundle.
Electrocardiogram The curve traced by an electrocardiograph.
Electrocardiograph An instrument used in the detection of heart abnormalities
that. It measures electrical potentials on the body surface
and generates a record of the electrical currents associated
with heart muscle activity.
Heart Rate (HR) The number of heartbeat per unit time, usually in minutes.
Hypertrophy A non-tumorous enlargement of an organ or a tissue as a
result of an increase in the size rather than number of
constituent cells.
Inferior vena cava Large vein formed by the union of the two common iliac
veins that receives blood from the lower limbs and the pelvic
and abdominal viscera and empties into the right atrium of
the heart.
Left Atrium Top left chamber of the heart.
Left Ventricle Bottom left chamber of the heart.
mm One mm is one small square on the electrocardiograph.
Myocardial Infarction Formation of an area of tissue that undergo necrosis as a
result of obstruction of local blood supply, as by a thrombus
or embolus.
P wave Atrial Depolarization (contraction). Regular duration is
0.06 - 0.11 second.
Proprietary information of DailyCare BioMedical Inc. No reproduction is allowed. 25
DailyCare BioMedical Inc.
Parameters A distinguishing characteristic or feature.
PR Interval Atrial and AV node depolarization. Regular duration is
0.12 - 0.20 seconds.
QRS Complex Ventricular depolarization. Regular duration is no longer
than 0.1 second.
QT Interval Ventricular refractory time. Duration varies according to
rate, age and sex.
Right Atrium Top right chamber of the heart.
Right Ventricle Bottom right chamber of the heart.
Right/Left Bundle Either of the parts of the bundle of His passing respectively
Branch to the right and left ventricles.
Sinoatrial (SA) node A small mass of specialized cardiac muscle fibers located in
the posterior wall of the right atrium of the heart that acts as
a pacemaker by generating at regular intervals the electric
impulses of the heartbeat.
ST segment ST segment represents the period from the end of ventricular
depolarization to the beginning of ventricular repolarization.
Superior vena cava A large vein formed by the union of the two brachiocephalic
veins and the azygos vein that receives blood from the head,
neck, upper limbs, and chest, and empties into the right
atrium of the heart.
T wave Ventricular Repolarization. Usually 0.5mV or less in Lead
I, II and III.
References:
1. American Heart Association www.americanheart.org
2. eMedicine www.emedicine.com
3. ECG Library www.ecglibrary.com
4. Guidant Inc. www.guidant.com
5. Heart Center Online www.heartcenteronline.com
6. National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute www.nhlbi.nih.gov
Contact:
DailyCare BioMedical Inc,
8F, 25-3, Ji-Lin Rd, Chungli, 320, Taiwan, R.O.C.
Website: www.dcbiomed.com
Tel: +886-3-262-1688 Fax:+886-3-261-7688
Proprietary information of DailyCare BioMedical Inc. No reproduction is allowed. 26
DailyCare BioMedical Inc.
Appendix
12-lead ECG analogy by RMH2.0
Lead I
Traditional 3-electrode ECG RMH 2.0
Proprietary information of DailyCare BioMedical Inc. No reproduction is allowed. 27
DailyCare BioMedical Inc.
Lead II
Traditional 3-electrode ECG RMH 2.0
Proprietary information of DailyCare BioMedical Inc. No reproduction is allowed. 28
DailyCare BioMedical Inc.
Lead III
Traditional 3-electrode ECG RMH 2.0
Proprietary information of DailyCare BioMedical Inc. No reproduction is allowed. 29
DailyCare BioMedical Inc.
Lead aVR
Traditional 3-electrode ECG RMH 2.0
Proprietary information of DailyCare BioMedical Inc. No reproduction is allowed. 30
DailyCare BioMedical Inc.
Lead aVL
Traditional 3-electrode ECG RMH 2.0
Proprietary information of DailyCare BioMedical Inc. No reproduction is allowed. 31
DailyCare BioMedical Inc.
Lead aVF
Traditional 3-electrode ECG RMH 2.0
Proprietary information of DailyCare BioMedical Inc. No reproduction is allowed. 32
DailyCare BioMedical Inc.
V1-V6
v1 v2
v4 v6
+ +
v3 v5 v1 v2 + + + +
v3 v4 v5 v6
v6
v5
v4
v3
v1 v2
Traditional 3-electrode ECG RMH 2.0
V1
V2
V3
Proprietary information of DailyCare BioMedical Inc. No reproduction is allowed. 33
DailyCare BioMedical Inc.
V4
V5
v6
Proprietary information of DailyCare BioMedical Inc. No reproduction is allowed. 34
You might also like
- ECG/EKG Interpretation: An Easy Approach to Read a 12-Lead ECG and How to Diagnose and Treat ArrhythmiasFrom EverandECG/EKG Interpretation: An Easy Approach to Read a 12-Lead ECG and How to Diagnose and Treat ArrhythmiasRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Ecg SimulatorDocument47 pagesEcg SimulatorSafwan ShaikhNo ratings yet
- EKG | ECG: An Ultimate Step-By-Step Guide to 12-Lead EKG | ECG Interpretation, Rhythms & Arrhythmias Including Basic Cardiac DysrhythmiasFrom EverandEKG | ECG: An Ultimate Step-By-Step Guide to 12-Lead EKG | ECG Interpretation, Rhythms & Arrhythmias Including Basic Cardiac DysrhythmiasRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (5)
- The 12-Lead Electrocardiogram for Nurses and Allied ProfessionalsFrom EverandThe 12-Lead Electrocardiogram for Nurses and Allied ProfessionalsNo ratings yet
- Understanding The 12 Lead ECGDocument7 pagesUnderstanding The 12 Lead ECGccbrown7No ratings yet
- EKG | ECG Interpretation. Everything You Need to Know about 12-Lead ECG/EKG InterpretationFrom EverandEKG | ECG Interpretation. Everything You Need to Know about 12-Lead ECG/EKG InterpretationRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Major Project Phase 1 Report CloudDocument35 pagesMajor Project Phase 1 Report CloudPraj CNo ratings yet
- Real Time Ecg & Body Temperature Monitoring Device: Mini Project ReportDocument73 pagesReal Time Ecg & Body Temperature Monitoring Device: Mini Project ReportLadvine D'AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Basics of Ecg InterpretationDocument76 pagesBasics of Ecg InterpretationDennis MiritiNo ratings yet
- What Is A Defibrillator?Document8 pagesWhat Is A Defibrillator?Rajib RajuNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiography II StudentDocument20 pagesElectrocardiography II StudentArmando Valdez ZamoranoNo ratings yet
- Rohini 13809826106Document7 pagesRohini 13809826106shivalishivali590No ratings yet
- ECGfinalDocument10 pagesECGfinalSarah FerguzonNo ratings yet
- EKG/ECG Interpretation Made Easy: A Practical Approach to Passing the ECG/EKG Portion of NCLEXFrom EverandEKG/ECG Interpretation Made Easy: A Practical Approach to Passing the ECG/EKG Portion of NCLEXRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Experiment No.: 06: Title: Study and Simulation of ECG RecorderDocument7 pagesExperiment No.: 06: Title: Study and Simulation of ECG RecorderVISHWESH KULKARNINo ratings yet
- Pacemaker InformatiiDocument4 pagesPacemaker InformatiiAndreea MitranNo ratings yet
- Modern Electronic InstrumentsDocument7 pagesModern Electronic InstrumentsuatilakarathnaNo ratings yet
- Ecg en LabviewDocument61 pagesEcg en LabviewHarold David Gil MuñozNo ratings yet
- البحث الاول طبيةDocument7 pagesالبحث الاول طبيةمحمد خالدNo ratings yet
- BME 6480: Biomedical Instrumentation Jason Kabzinski, Alex Lau, Mounica Naraharisetti, Jody PaulanDocument22 pagesBME 6480: Biomedical Instrumentation Jason Kabzinski, Alex Lau, Mounica Naraharisetti, Jody PaulanMona NaiduNo ratings yet
- Temporary Pacemakers-SICU's 101 PrimerDocument51 pagesTemporary Pacemakers-SICU's 101 Primerwaqas_xsNo ratings yet
- Mount Zoin Engineering & Technology Cycle Test Ii Medical Electronic-Ec1006Document11 pagesMount Zoin Engineering & Technology Cycle Test Ii Medical Electronic-Ec1006bhagyampNo ratings yet
- 6heart Sound PacemakerDocument28 pages6heart Sound PacemakerJack OneNo ratings yet
- ECG Monitoring in TheatreDocument17 pagesECG Monitoring in TheatrePhani NadellaNo ratings yet
- 12 Lead EKG Interpretation Part 1Document7 pages12 Lead EKG Interpretation Part 1Nuru99100% (1)
- Pacemaker and TypesDocument7 pagesPacemaker and TypesPrathamesh ShindeNo ratings yet
- The Wiring Diagram of The HeartDocument4 pagesThe Wiring Diagram of The Heartgurneet kourNo ratings yet
- Interpreting AV (Heart) Blocks: Breaking Down The Mystery: 2 Contact HoursDocument29 pagesInterpreting AV (Heart) Blocks: Breaking Down The Mystery: 2 Contact HoursAsri RachmawatiNo ratings yet
- A Review On Pacemakers: Device Types, Operating Modes and Pacing Pulses. Problems Related To The Pacing Pulses DetectionDocument12 pagesA Review On Pacemakers: Device Types, Operating Modes and Pacing Pulses. Problems Related To The Pacing Pulses DetectionsdekapureNo ratings yet
- SBM1403 Unit1Document64 pagesSBM1403 Unit1Balasaraswathi SNo ratings yet
- Nageen 4Document6 pagesNageen 4saadshahab622No ratings yet
- 4 2 3 A Ekg Student Response Sheet (Revised 2 23 15)Document8 pages4 2 3 A Ekg Student Response Sheet (Revised 2 23 15)api-281824634100% (1)
- Unit 3 Cardiovascular System and MeasurementsDocument16 pagesUnit 3 Cardiovascular System and MeasurementsChaitanya KiritiNo ratings yet
- Ecg PDFDocument70 pagesEcg PDFlauras3005No ratings yet
- Ecg / EkgDocument10 pagesEcg / EkgSilver Villota Magday Jr.No ratings yet
- Ekg Ecg Interpretation by DR Jason Lowe PDF Bb3 DR NotesDocument79 pagesEkg Ecg Interpretation by DR Jason Lowe PDF Bb3 DR NotesGuru RewriNo ratings yet
- How To Read An Electrocardiogram (ECG) - Part One: Basic Principles of The ECG. The Normal ECGDocument84 pagesHow To Read An Electrocardiogram (ECG) - Part One: Basic Principles of The ECG. The Normal ECGshaine htetNo ratings yet
- Student ProtocolDocument14 pagesStudent ProtocolCristian AmadoNo ratings yet
- Pacemaker Learning Package: Paula Nekic CNE Liverpool Hospital ICU January 2016Document46 pagesPacemaker Learning Package: Paula Nekic CNE Liverpool Hospital ICU January 2016Deepak BhatNo ratings yet
- Design and Development Virtual ECG Machine With Problem Identification Using LabviewDocument4 pagesDesign and Development Virtual ECG Machine With Problem Identification Using LabviewtheijesNo ratings yet
- Implantable PacemakerDocument33 pagesImplantable PacemakerShifa Fauzia AfrianneNo ratings yet
- Principles of Electrocardiography: Indiana University-Purdue UniversityDocument11 pagesPrinciples of Electrocardiography: Indiana University-Purdue UniversityqhqhqNo ratings yet
- C Is A Method To Mechanically Assist or Replace Spontaneous BreathingDocument6 pagesC Is A Method To Mechanically Assist or Replace Spontaneous BreathingsnairbNo ratings yet
- Automatic Detection of Cardiac Arrhythmia Through ECG Signal Analysis: A ReviewDocument12 pagesAutomatic Detection of Cardiac Arrhythmia Through ECG Signal Analysis: A ReviewJose Angel Duarte MartinezNo ratings yet
- Cardiac PacingDocument9 pagesCardiac PacingmatzoneNo ratings yet
- Freescale Solutions For Electrocardiograph and Heart Rate Monitor ApplicationsDocument42 pagesFreescale Solutions For Electrocardiograph and Heart Rate Monitor ApplicationsJosé De Jesús Dávila HernándezNo ratings yet
- Heart Electr Act-120830-StudentDocument10 pagesHeart Electr Act-120830-Studentapi-400575655No ratings yet
- Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillators: Pacemakers & DefibrillatorsDocument2 pagesImplantable Cardioverter-Defibrillators: Pacemakers & DefibrillatorsGo StargNo ratings yet
- Design of DC Shock Simulator: 0Xkdppdg $plu 0D Uxi, Bambang Guruh Irianto, Tri Bowo IndratoDocument7 pagesDesign of DC Shock Simulator: 0Xkdppdg $plu 0D Uxi, Bambang Guruh Irianto, Tri Bowo IndratoنزیرNo ratings yet
- Two Phase Heart Disease Diagnosis System Using Deep LearningDocument16 pagesTwo Phase Heart Disease Diagnosis System Using Deep LearninganuragNo ratings yet
- Clinical Relevance of ECGDocument4 pagesClinical Relevance of ECGdrfelixNo ratings yet
- EKG Interpretation Basics Guide: Electrocardiogram Heart Rate Determination, Arrhythmia, Cardiac Dysrhythmia, Heart Block Causes, Symptoms, Identification and Medical Treatment Nursing HandbookFrom EverandEKG Interpretation Basics Guide: Electrocardiogram Heart Rate Determination, Arrhythmia, Cardiac Dysrhythmia, Heart Block Causes, Symptoms, Identification and Medical Treatment Nursing HandbookNo ratings yet
- School of Engineering Department of Biomedical Engineering: EENG424L-Medical Instrumentation I LabDocument8 pagesSchool of Engineering Department of Biomedical Engineering: EENG424L-Medical Instrumentation I LabMahdi BraitehNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Basic of ElectrocardiographyDocument27 pagesUnit 5 Basic of ElectrocardiographyJack TomarNo ratings yet
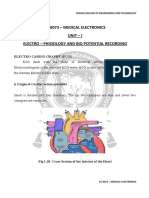
- Ec 8073 - Medical Electronics Unit - I Electro - Phisiology and Bio Potential RecordingDocument9 pagesEc 8073 - Medical Electronics Unit - I Electro - Phisiology and Bio Potential RecordingJackie SparrowNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Output by N.Anisha MPT OrthoDocument53 pagesCardiac Output by N.Anisha MPT OrthoAnisha NallasamyNo ratings yet
- DepartmentDocument75 pagesDepartmentKavi RasuNo ratings yet
- Implantable CardioverterDocument9 pagesImplantable CardioverterInnocent OkidiNo ratings yet
- Copd - 2 Penting 13Document14 pagesCopd - 2 Penting 13Rahmat MuliaNo ratings yet
- Life Threatening Arrhythmia and ManagementDocument40 pagesLife Threatening Arrhythmia and ManagementRuki HartawanNo ratings yet
- 03 Pathophysiology of CommunityDocument3 pages03 Pathophysiology of CommunityVenerandaNo ratings yet
- J Oftalmologi Vol 7 No 1 (Heni Riyanto)Document4 pagesJ Oftalmologi Vol 7 No 1 (Heni Riyanto)Mahanani SubagioNo ratings yet
- Tinea Pedis An UpdateDocument5 pagesTinea Pedis An UpdateRahmat MuliaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 56Document57 pagesChapter 56Rahmat MuliaNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATORY DISORDERS (Abdurahman S)Document19 pagesRESPIRATORY DISORDERS (Abdurahman S)Rahmat MuliaNo ratings yet
- Tinea Pedis An UpdateDocument5 pagesTinea Pedis An UpdateRahmat MuliaNo ratings yet
- Oleh: Dr. Abdurachman Sukadi, Dr.,SpakDocument31 pagesOleh: Dr. Abdurachman Sukadi, Dr.,SpakRahmat MuliaNo ratings yet
- Hidrosefalus Nonkomunikan Pada Perdarahan Intraserebral/IntraventrikularDocument2 pagesHidrosefalus Nonkomunikan Pada Perdarahan Intraserebral/IntraventrikularRahmat MuliaNo ratings yet
- Coveram Symcard DR Yerizal PDFDocument47 pagesCoveram Symcard DR Yerizal PDFRahmat MuliaNo ratings yet