Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Trig Cheat Sheet: Definition of The Trig Functions
Uploaded by
amitkharb111195Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Trig Cheat Sheet: Definition of The Trig Functions
Uploaded by
amitkharb111195Copyright:
Available Formats
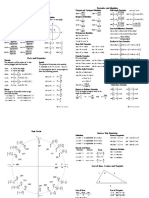
Trig Cheat Sheet
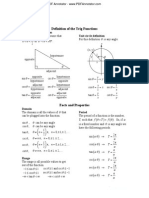
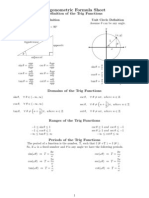
Definition of the Trig Functions
Right triangle definition
For this definition we assume that Unit circle definition
p For this definition q is any angle.
0 < q < or 0 < q < 90 .
2 y
( x, y )
hypotenuse 1
y q
opposite x
x
q
adjacent
opposite hypotenuse y 1
sin q = csc q = sin q = =y csc q =
hypotenuse opposite 1 y
adjacent hypotenuse x 1
cos q = sec q = cos q = = x sec q =
hypotenuse adjacent 1 x
opposite adjacent y x
tan q = cot q = tan q = cot q =
adjacent opposite x y
Facts and Properties
Domain
The domain is all the values of q that Period
can be plugged into the function. The period of a function is the number,
T, such that f (q + T ) = f (q ) . So, if w
sin q , q can be any angle is a fixed number and q is any angle we
cos q , q can be any angle have the following periods.
1
tan q , q n + p , n = 0, 1, 2,K
2 2p
sin ( wq ) T=
csc q , q n p , n = 0, 1, 2,K w
1 2p
sec q , q n + p , n = 0, 1, 2,K cos (wq ) T =
2 w
cot q , q n p , n = 0, 1, 2,K p
tan (wq ) T =
w
Range 2p
csc (wq ) T =
The range is all possible values to get w
out of the function. 2p
-1 sin q 1 csc q 1 and csc q -1 sec (wq ) T =
w
-1 cos q 1 sec q 1 and sec q -1 p
- < tan q < - < cot q < cot (wq ) T =
w
2005 Paul Dawkins
Formulas and Identities
Tangent and Cotangent Identities Half Angle Formulas (alternate form)
sin q cos q q 1 - cos q 1
tan q = cot q = sin = sin 2 q = (1 - cos ( 2q ) )
cos q sin q 2 2 2
Reciprocal Identities
q 1 + cos q 1
csc q =
1
sin q =
1 cos
2
=
2
cos 2 q =
2
(1 + cos ( 2q ) )
sin q csc q
1 1 q 1 - cos q 1 - cos ( 2q )
sec q = cos q = tan = tan 2 q =
cos q sec q 2 1 + cos q 1 + cos ( 2q )
1 1 Sum and Difference Formulas
cot q = tan q =
tan q cot q sin (a b ) = sin a cos b cos a sin b
Pythagorean Identities cos (a b ) = cos a cos b m sin a sin b
sin 2 q + cos 2 q = 1
tan a tan b
tan 2 q + 1 = sec 2 q tan (a b ) =
1 m tan a tan b
1 + cot 2 q = csc 2 q Product to Sum Formulas
1
Even/Odd Formulas sin a sin b = cos (a - b ) - cos (a + b )
sin ( -q ) = - sin q csc ( -q ) = - csc q 2
1
cos ( -q ) = cos q sec ( -q ) = sec q cos a cos b = cos (a - b ) + cos (a + b )
2
tan ( -q ) = - tan q cot ( -q ) = - cot q 1
sin a cos b = sin (a + b ) + sin (a - b )
Periodic Formulas 2
If n is an integer. 1
cos a sin b = sin (a + b ) - sin (a - b )
sin (q + 2p n ) = sin q csc (q + 2p n ) = csc q 2
Sum to Product Formulas
cos (q + 2p n ) = cos q sec (q + 2p n ) = sec q
a + b a - b
tan (q + p n ) = tan q cot (q + p n ) = cot q sin a + sin b = 2sin cos
2 2
Double Angle Formulas
a + b a - b
sin a - sin b = 2 cos sin
sin ( 2q ) = 2sin q cos q 2 2
cos ( 2q ) = cos 2 q - sin 2 q cos a + cos b = 2 cos
a + b a - b
cos
= 2 cos 2 q - 1 2 2
a + b a - b
= 1 - 2sin 2 q cos a - cos b = -2sin sin
2 2
2 tan q
tan ( 2q ) = Cofunction Formulas
1 - tan 2 q
p p
Degrees to Radians Formulas sin - q = cos q cos - q = sin q
2 2
If x is an angle in degrees and t is an
angle in radians then p p
csc - q = sec q sec - q = csc q
p t px 180t 2 2
= t= and x = p p
180 x 180 p tan - q = cot q cot - q = tan q
2 2
2005 Paul Dawkins
Unit Circle
y
( 0,1)
p 1 3
1 3 2 , 2
- , 2
2 2 p 2 2
2p 90 ,
2 2 3 2 2
- , 3
2 2 120 p
3p 60 3 1
4 2 , 2
3 1 4 45 p
- , 135
2 2 5p
6
6 30
150
( -1,0 ) p 180 0 0 (1,0 )
360 2p x
210
7p 330
11p
6 225
3 1 6 3 1
- ,- 5p 315 ,-
2 2 2 2
4 240 300 7p
2 4p 270
-
2
,- 5p 4 2 2
2 2 3 3p
2
,-
2
3
1 3 2
- ,- 1 3
2 2 ,-
2 2
( 0,-1)
For any ordered pair on the unit circle ( x, y ) : cos q = x and sin q = y
Example
5p 1 5p 3
cos = sin =-
3 2 3 2
2005 Paul Dawkins
Inverse Trig Functions
Definition Inverse Properties
y = sin -1 x is equivalent to x = sin y cos ( cos -1 ( x ) ) = x cos -1 ( cos (q ) ) = q
y = cos -1 x is equivalent to x = cos y sin ( sin -1 ( x ) ) = x sin -1 ( sin (q ) ) = q
y = tan -1 x is equivalent to x = tan y
tan ( tan -1 ( x ) ) = x tan -1 ( tan (q ) ) = q
Domain and Range
Function Domain Range Alternate Notation
p p sin -1 x = arcsin x
y = sin -1 x -1 x 1 - y
2 2 cos -1 x = arccos x
y = cos -1 x -1 x 1 0 y p tan -1 x = arctan x
p p
y = tan -1 x - < x < - < y<
2 2
Law of Sines, Cosines and Tangents
c b a
a g
Law of Sines Law of Tangents
sin a sin b sin g
= = a - b tan 12 (a - b )
=
a b c a + b tan 12 (a + b )
Law of Cosines b - c tan 12 ( b - g )
=
a 2 = b2 + c 2 - 2bc cos a b + c tan 12 ( b + g )
b 2 = a 2 + c 2 - 2ac cos b a - c tan 12 (a - g )
=
c = a + b - 2ab cos g a + c tan 12 (a + g )
2 2 2
Mollweides Formula
a + b cos 12 (a - b )
=
c sin 12 g
2005 Paul Dawkins
You might also like
- Trig Cheat Sheet 1.4Document2 pagesTrig Cheat Sheet 1.4agentc0re0% (1)
- Solution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsFrom EverandSolution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Volumetirc Analysis Lab CsecDocument3 pagesVolumetirc Analysis Lab CsecGabriella SteeleNo ratings yet
- Monitoring and EvalutionDocument40 pagesMonitoring and EvalutionWilmie Joy Dela TorreNo ratings yet
- (Advanced Chemistry) Herbert August Laitinen, Walter E. Harris-Chemical Analysis - An Advanced Text and Reference-McGraw-Hill (1975) PDFDocument627 pages(Advanced Chemistry) Herbert August Laitinen, Walter E. Harris-Chemical Analysis - An Advanced Text and Reference-McGraw-Hill (1975) PDFarefNo ratings yet
- Calculus Cheat Sheet IntegralsDocument1 pageCalculus Cheat Sheet IntegralsLawrence 'Lorenzo' AzureNo ratings yet
- Math 53 SyllabusDocument3 pagesMath 53 SyllabusRoberto SantosNo ratings yet
- Trig Cheat Sheet ReducedDocument2 pagesTrig Cheat Sheet ReducedMritunjay KumarNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Condensed Formula SheetDocument2 pagesTrigonometry Condensed Formula SheetRiza Azari0% (1)
- Trig Cheat Sheet: Formulas and IdentitiesDocument2 pagesTrig Cheat Sheet: Formulas and IdentitiesMuzamilNo ratings yet
- 29 QusDocument16 pages29 QusAsafAhmadNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes On CircleDocument10 pagesRevision Notes On CircleaskiitianNo ratings yet
- Oscillation Solved Examples - AskIITiansDocument5 pagesOscillation Solved Examples - AskIITiansthiripura sundariNo ratings yet
- Trig No Metric FormulasDocument4 pagesTrig No Metric FormulasZee Shan100% (1)
- Lectures On Theoretical Mechanics - 7 (Rotating Coordinate System: Coriolis Force Etc.)Document6 pagesLectures On Theoretical Mechanics - 7 (Rotating Coordinate System: Coriolis Force Etc.)Abhijit Kar Gupta100% (1)
- 1 Class Assignments TrigonometryDocument2 pages1 Class Assignments TrigonometryV.No ratings yet
- Aieee-2012 Study MaterialDocument41 pagesAieee-2012 Study MaterialAbhay GoyalNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - Math.lamar - Edu PDF Trig Cheat Sheet ReducedDocument2 pagesTutorial - Math.lamar - Edu PDF Trig Cheat Sheet ReducedAnonymous vyXcR9No ratings yet
- Trig Cheat Sheet ReducedDocument2 pagesTrig Cheat Sheet ReducedPhirak KhimNo ratings yet
- Trig Cheat Sheet: Definition of The Trig FunctionsDocument4 pagesTrig Cheat Sheet: Definition of The Trig FunctionsMihir SethiNo ratings yet
- Trig Cheat Sheet: Definition of The Trig FunctionsDocument3 pagesTrig Cheat Sheet: Definition of The Trig Functionstripathi_girishNo ratings yet
- EquationsDocument17 pagesEquationshasanmt23100% (1)
- Mathematics???Document6 pagesMathematics???DEFRON GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Mathematics TrigonometryDocument129 pagesMathematics TrigonometryUdayveerSinghNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Formula Sheet: Definition of The Trig FunctionsDocument10 pagesTrigonometric Formula Sheet: Definition of The Trig Functionsmonelmetal100% (1)
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Transformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandTransformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesFrom EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- Introductory Differential Equations: with Boundary Value Problems, Student Solutions Manual (e-only)From EverandIntroductory Differential Equations: with Boundary Value Problems, Student Solutions Manual (e-only)No ratings yet
- Instructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYFrom EverandInstructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYNo ratings yet
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandInverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- AP Calculus Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeFrom EverandAP Calculus Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeNo ratings yet
- Sweet Baby Dresses in Crochet: 4 Dresses in Sizes Newborn to 24 Months, with Matching AccessoriesFrom EverandSweet Baby Dresses in Crochet: 4 Dresses in Sizes Newborn to 24 Months, with Matching AccessoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Applications of Derivatives Errors and Approximation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandApplications of Derivatives Errors and Approximation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsFrom EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsNo ratings yet
- Productivity Now: Social Administration, Training, Economics and Production DivisionFrom EverandProductivity Now: Social Administration, Training, Economics and Production DivisionNo ratings yet
- Data Science Course Brochure - One Year CourseDocument4 pagesData Science Course Brochure - One Year CourseRamesh KummamNo ratings yet
- 5 MCQ LR No AnswerDocument12 pages5 MCQ LR No AnswerĐồng DươngNo ratings yet
- The Horwitz Ratio (HorRat) A Useful Index of Method Performance With Respect PrecisionDocument15 pagesThe Horwitz Ratio (HorRat) A Useful Index of Method Performance With Respect PrecisionLuis LuisinNo ratings yet
- Unlock The AWL Sublist 1Document75 pagesUnlock The AWL Sublist 1Шунаси ХалиловNo ratings yet
- Slide - MATEMATIKA EKONOMI 2023Document16 pagesSlide - MATEMATIKA EKONOMI 2023uunarjunNo ratings yet
- Function of Complex Variable: Z X + IyDocument10 pagesFunction of Complex Variable: Z X + IyPratik GuptaNo ratings yet
- REVIEW TEST Unfamiliar Functions Calculus Mar 2014 PDFDocument3 pagesREVIEW TEST Unfamiliar Functions Calculus Mar 2014 PDFNick MNo ratings yet
- GRR 751 Learner Centered Activity 5Document2 pagesGRR 751 Learner Centered Activity 5ian92193No ratings yet
- Math HLSL Calculator Instructions PDFDocument75 pagesMath HLSL Calculator Instructions PDFapdpjpNo ratings yet
- Deflection of BeamDocument18 pagesDeflection of BeamTare Er KshitijNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solution For CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 14 StatisticsDocument23 pagesNCERT Solution For CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 14 StatisticsJitesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Linear RegressionDocument44 pagesLinear RegressionPratik TagwaleNo ratings yet
- ECTS-Bogen - Mec. Engineer. Mngm.Document2 pagesECTS-Bogen - Mec. Engineer. Mngm.Gajanan JadhavNo ratings yet
- Matlab: Symbolic Math Toolbox, Control System Toolbox: Dr. Luis SánchezDocument35 pagesMatlab: Symbolic Math Toolbox, Control System Toolbox: Dr. Luis SánchezmiscaelNo ratings yet
- Multiple integral: r sinθdr d θd ∅ ρ r sinθd ∅ ρ ρ a sinθ dθd ∅ ρ a ρ aDocument3 pagesMultiple integral: r sinθdr d θd ∅ ρ r sinθd ∅ ρ ρ a sinθ dθd ∅ ρ a ρ aMitra geaNo ratings yet
- Solutions Manual Probability Statistics and Random Processes For PDFDocument11 pagesSolutions Manual Probability Statistics and Random Processes For PDFbrainnytanNo ratings yet
- MA 105 TutorialsDocument29 pagesMA 105 TutorialsABHIJEET SHARMANo ratings yet
- Population Pharmacokinetics II: Estimation MethodsDocument9 pagesPopulation Pharmacokinetics II: Estimation MethodsrajeshNo ratings yet
- ATH Roficiency Xams: (C A, T, P - , C)Document2 pagesATH Roficiency Xams: (C A, T, P - , C)CadornaNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iii - Complex Integration: F (Z) DZ 0Document20 pagesUnit-Iii - Complex Integration: F (Z) DZ 0Curious ManNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1-Rolle's Theorem and Lagrange's Mean Value TheoremDocument17 pagesLecture 1-Rolle's Theorem and Lagrange's Mean Value TheoremDuffer BoysNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter Exam in Math 8Document2 pages3rd Quarter Exam in Math 8Danilo Cumpio93% (14)
- Identifikasi Dan Kuantifikasi Kimia Pertemuan 4Document38 pagesIdentifikasi Dan Kuantifikasi Kimia Pertemuan 4Sona ErlanggaNo ratings yet
- Fourier Series1 PDFDocument35 pagesFourier Series1 PDFAbdulaziz hazemNo ratings yet
- Powell Modern Approach To Teaching Optimization Submitted November 9 2023Document93 pagesPowell Modern Approach To Teaching Optimization Submitted November 9 2023M sNo ratings yet