Professional Documents
Culture Documents
III. Ratioed Logic Circuit
Uploaded by
aishwarya waghOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
III. Ratioed Logic Circuit
Uploaded by
aishwarya waghCopyright:
Available Formats
III.
Ratioed Logic Circuit
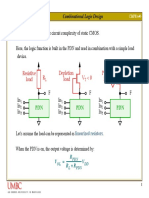
Ratioed MOS circuits have been known for many years, and were used widely in the past despite
their high power dissipation because they are fast static circuits[3]. Ratioed circuits use weak
pull-up devices and stronger pull-down devices. They reduce the input capacitance and hence
improve logical effort by eliminating large PMOS transistors loading the inputs. Fig.4 shows the
schematic circuit diagram of 4-input NAND gate using pseudo-NMOS logic gates, which are the
most common form of CMOS ratioed logic. The pull-down network is like that of a static
gate,but the pull-up network has been replaced with a single pMOS transistor that is grounded so
it is always ON[1]. The main advantage of 4 -input pseudo NMOS logic gate is that there is 1-
pMOS and 4-NMOS transistors is used, so the number of components has reduced and area also
reduced. It also reduces the complexities of the circuit. Because of less hardware used so the
capacitance become reduced.
You might also like
- 1.1 Logic Family: CMOS Differential Logic Family For Low Power ApplicationDocument27 pages1.1 Logic Family: CMOS Differential Logic Family For Low Power ApplicationnishiyavijayanNo ratings yet
- CMOS (Disambiguation) : For Other Uses, SeeDocument6 pagesCMOS (Disambiguation) : For Other Uses, SeeManas NagNo ratings yet
- VLSI Design (Online Lectures) Assignment-1Document3 pagesVLSI Design (Online Lectures) Assignment-1TarushiNo ratings yet
- Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor (CMOS) (PronouncedDocument7 pagesComplementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor (CMOS) (PronouncedArchana SadanandanNo ratings yet
- 3.8-ns Cmos 16 16-b Multiplier Using Complementary Pass-Transistor LogicDocument8 pages3.8-ns Cmos 16 16-b Multiplier Using Complementary Pass-Transistor LogicNarendra AchariNo ratings yet
- Imp For IntDocument3 pagesImp For IntsaticitechNo ratings yet
- Analysis of CMOS 45nm Transmission Gate Based Pulsed Latch AbstractDocument12 pagesAnalysis of CMOS 45nm Transmission Gate Based Pulsed Latch AbstractbaluNo ratings yet
- Ec3352 Vlsi and Chip DesignDocument15 pagesEc3352 Vlsi and Chip DesignParanthaman GNo ratings yet
- Mtech HandoutsDocument4 pagesMtech HandoutsJyothi PoornaNo ratings yet
- Memory Related To VLSIDocument63 pagesMemory Related To VLSIIndrajeet GautamNo ratings yet
- Double Pass Transistor Logic For High PeDocument5 pagesDouble Pass Transistor Logic For High PeVLSISD36 Edwin DominicNo ratings yet
- Advantages of CmosDocument4 pagesAdvantages of CmosvinaycmosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Analog Integrated Circuit Design by John ChomaDocument92 pagesChapter 4 - Analog Integrated Circuit Design by John ChomaAriana Ribeiro LameirinhasNo ratings yet
- Advanced Project Patan SirDocument12 pagesAdvanced Project Patan SirRajeevReddyNareddulaNo ratings yet
- Vlsi My PrepDocument3 pagesVlsi My PrepHemanth BattinaNo ratings yet
- Frequently Asked VLSI Interview Questions and AnswersDocument6 pagesFrequently Asked VLSI Interview Questions and AnswersbhargatejaNo ratings yet
- For Other Uses, See .: CMOS (Disambiguation)Document11 pagesFor Other Uses, See .: CMOS (Disambiguation)Smitha KollerahithluNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document30 pagesChapter 3tejomurtNo ratings yet
- Difference Between CMOS and NMOS TechnologyDocument5 pagesDifference Between CMOS and NMOS TechnologyShavel Kumar100% (1)
- Impact of Hybrid Pass-Transistor Logic (HPTL) On Power, Delay and Area in VLSI DesignDocument6 pagesImpact of Hybrid Pass-Transistor Logic (HPTL) On Power, Delay and Area in VLSI DesignIJMERNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Write Power Consumption For Single Gate and Dual Gate MOS Based SRAMDocument6 pagesAnalysis of Write Power Consumption For Single Gate and Dual Gate MOS Based SRAMresearchinventyNo ratings yet
- Technical Details: Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor (CMOS)Document4 pagesTechnical Details: Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor (CMOS)Testing toolsNo ratings yet
- Course Coordinator Module CoordinatorDocument166 pagesCourse Coordinator Module CoordinatorBituNo ratings yet
- Testing Paper CorrectedDocument9 pagesTesting Paper CorrectedSakthiPriyaNo ratings yet
- A Low-Power 8-Read 4-Write Register File DesignDocument4 pagesA Low-Power 8-Read 4-Write Register File DesignEdmund LeongNo ratings yet
- Low Power Design and Simulation of 7T SRAM Cell Using Various Circuit TechniquesDocument6 pagesLow Power Design and Simulation of 7T SRAM Cell Using Various Circuit TechniquesseventhsensegroupNo ratings yet
- CHPTR 5 Designing Cmos Circuits For Low PowerDocument27 pagesCHPTR 5 Designing Cmos Circuits For Low Powerharikirthika100% (1)
- Leakage Current Reduction 6TDocument3 pagesLeakage Current Reduction 6Tshoaib nadeemNo ratings yet
- Bicmos TechnologyDocument37 pagesBicmos TechnologyPriya SinghNo ratings yet
- A New Loadless 4-Transistor SRAM Cell With A 0.18 M CMOS TechnologyDocument4 pagesA New Loadless 4-Transistor SRAM Cell With A 0.18 M CMOS TechnologyLanku J GowdaNo ratings yet
- Sram Memory Cell: By:-Udit Shah & Rajdeep KandiyalDocument13 pagesSram Memory Cell: By:-Udit Shah & Rajdeep KandiyalSrasVelNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Conventional CMOS and FinFET Based 6-TDocument7 pagesAnalysis of Conventional CMOS and FinFET Based 6-Tswetha sillveriNo ratings yet
- Technical Details: Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor (CMOS) (Document9 pagesTechnical Details: Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor (CMOS) (RailyNo ratings yet
- Static Cmos DesignDocument7 pagesStatic Cmos Designtechspaceofatul100% (3)
- Vlsi Technologies On Various AnglesDocument12 pagesVlsi Technologies On Various AnglesJasmin K SamNo ratings yet
- Wiki Loves Love: Documenting Festivals and Celebrations of Love On Commons. Help Wikimedia and Win Prizes by Sending PhotosDocument10 pagesWiki Loves Love: Documenting Festivals and Celebrations of Love On Commons. Help Wikimedia and Win Prizes by Sending PhotosraoNo ratings yet
- Code SnippetDocument2 pagesCode Snippetvjvi2002No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 PDFDocument10 pagesChapter 1 PDFAmanuel TesemaNo ratings yet
- Design and VLSI Implementation of 8 MB Low Power SRAM in 90nmDocument10 pagesDesign and VLSI Implementation of 8 MB Low Power SRAM in 90nmcnnprem_eeeNo ratings yet
- For Other Uses, See .: CMOS (Disambiguation)Document10 pagesFor Other Uses, See .: CMOS (Disambiguation)Ashutosh DabasNo ratings yet
- Experiment-08: AIM: Study and Understand A Research Paper. Title of The PaperDocument2 pagesExperiment-08: AIM: Study and Understand A Research Paper. Title of The PaperSamiksha GautamNo ratings yet
- 3 Transceiver DesignDocument6 pages3 Transceiver DesignUtsav PopliNo ratings yet
- New Design Methodologies For High-Speed Mixed-Mode Cmos Full Adder CircuitsDocument21 pagesNew Design Methodologies For High-Speed Mixed-Mode Cmos Full Adder CircuitsAnonymous e4UpOQEPNo ratings yet
- CMOS Interview QuestionsDocument3 pagesCMOS Interview QuestionsAjay G BellamNo ratings yet
- Array SubsystemDocument29 pagesArray SubsystemMukesh MakwanaNo ratings yet
- Design of High Speed Addressable Memory Based On Memory-Resistance Using 45nm CMOS TechnologyDocument11 pagesDesign of High Speed Addressable Memory Based On Memory-Resistance Using 45nm CMOS TechnologyInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Computational Structures For Analog Signal ProcessingDocument456 pagesSynthesis of Computational Structures For Analog Signal ProcessingRocío CardosoNo ratings yet
- Design of ALU Circuits Using Pass Transistor LogicDocument71 pagesDesign of ALU Circuits Using Pass Transistor LogicVivek GuntumuduguNo ratings yet
- Gate-Diffusion Input (GDI) A Power Efficient Method For Digital Combinatorial CircuitsDocument16 pagesGate-Diffusion Input (GDI) A Power Efficient Method For Digital Combinatorial Circuitsmdzakir_hussainNo ratings yet
- Vlsi DesignDocument31 pagesVlsi Designajas777BNo ratings yet
- 0.9V 32Nm Dual-Gate Si Finfet: Low-Power Ptl-Based Multiplexer Design inDocument4 pages0.9V 32Nm Dual-Gate Si Finfet: Low-Power Ptl-Based Multiplexer Design inNamrata SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Vlsi Very Imp QaDocument38 pagesVlsi Very Imp QaAjay Kumar MattupalliNo ratings yet
- CMOS Logic Circuits: DR S. C. WongDocument28 pagesCMOS Logic Circuits: DR S. C. WongMuni Sankar MatamNo ratings yet
- CMOS BasicsDocument41 pagesCMOS BasicsYeshoda MallikarjunaNo ratings yet
- PXC 3873796Document6 pagesPXC 3873796Sai PraveenNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - 1Document65 pagesUnit 4 - 1sparsh kaudinyaNo ratings yet
- Advanced CMOS CircuitsDocument20 pagesAdvanced CMOS CircuitsAnonymous IXvuFdeNo ratings yet
- 2 PLDDocument42 pages2 PLDlalap5727No ratings yet
- Abap MaterialDocument3 pagesAbap Materialaishwarya waghNo ratings yet
- Data-Flow Modeling (A Practical Introduction To HW/SW Codesign, P. Schaumont)Document25 pagesData-Flow Modeling (A Practical Introduction To HW/SW Codesign, P. Schaumont)aishwarya waghNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Three Iot-Based Wireless Sensors For Environmental MonitoringDocument9 pagesAnalysis of Three Iot-Based Wireless Sensors For Environmental Monitoringaishwarya waghNo ratings yet
- Lossless In-Network Processing in Wsns For Domain-Specific Monitoring ApplicationsDocument10 pagesLossless In-Network Processing in Wsns For Domain-Specific Monitoring Applicationsaishwarya waghNo ratings yet
- Imp Questions TestDocument2 pagesImp Questions Testaishwarya waghNo ratings yet
- Secure Data AggregationDocument5 pagesSecure Data Aggregationaishwarya waghNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument1 pageAssignmentaishwarya waghNo ratings yet
- RCDocument175 pagesRCaishwarya waghNo ratings yet
- KeyboardDocument16 pagesKeyboardaishwarya waghNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument13 pagesDocumentaishwarya waghNo ratings yet
- cách kết nối LCD 16x2 với vi điều khiển.Document3 pagescách kết nối LCD 16x2 với vi điều khiển.vansonhuongNo ratings yet
- Ratioed CircuitsDocument5 pagesRatioed Circuitsnrp_rahulNo ratings yet
- Life CycleDocument31 pagesLife Cycleaishwarya waghNo ratings yet
- Embedded Systems Design: A Unified Hardware/Software IntroductionDocument39 pagesEmbedded Systems Design: A Unified Hardware/Software Introductionnandan_asNo ratings yet
- What Is A Pilot SurveyDocument2 pagesWhat Is A Pilot Surveyaishwarya waghNo ratings yet
- FSM 1Document2 pagesFSM 1aishwarya wagh0% (1)
- Vivado Design SuiteDocument1 pageVivado Design Suiteaishwarya waghNo ratings yet
- Arduino DetailsDocument23 pagesArduino Detailsaishwarya wagh100% (2)
- Arduino DetailsDocument23 pagesArduino Detailsaishwarya wagh100% (2)