Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Rolling Sphere
Uploaded by
RaghuRamCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Rolling Sphere
Uploaded by
RaghuRamCopyright:
Available Formats
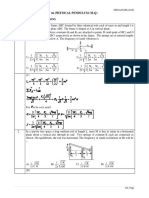
a
Total energy of rolling object is the sum of translational and
rotational kinetic energy.
KE KEtrans KErot
1 1
mv 2 I 2
2 2
Here, m is mass of object and its linear velocity is v and
angular velocity of rolling object.
The expression for moment of inertia of the object is,
I mK 2
Here, K is the radiu of gyration.
KE mv 2 mK 2 2
1 1
2 2
Relation between linear and angular velocity is,
v
v r
r
2
v
KE mv 2 mK 2
1 1
2 2 r
1 K2
mv 2 1 2
2 r
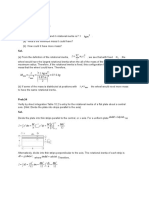
The expression for work done on rolling object along inclined plane is,
W mg sin L
From work-energy conservation principle,
W KE
1 K2
mg sin L mv 2 1 2 here h L sin
2 r
2 gh
v ........ 1
K2
1
r2
You might also like
- Tables of Coefficients for the Analysis of Triple Angular Correlations of Gamma-Rays from Aligned NucleiFrom EverandTables of Coefficients for the Analysis of Triple Angular Correlations of Gamma-Rays from Aligned NucleiNo ratings yet
- Physics Math NoteDocument16 pagesPhysics Math Notefaridaakter583No ratings yet
- An Introduction to Field Quantization: International Series of Monographs in Natural PhilosophyFrom EverandAn Introduction to Field Quantization: International Series of Monographs in Natural PhilosophyNo ratings yet
- Sambhav Test Answer Key 25.07.2023Document12 pagesSambhav Test Answer Key 25.07.2023Shreya VarmaNo ratings yet
- Work Energy Power All DerivationsDocument6 pagesWork Energy Power All DerivationsNaman Singh BishtNo ratings yet
- PHM031 - Modern Mechanics - Lecture 10Document20 pagesPHM031 - Modern Mechanics - Lecture 10Mohammed ZaitounNo ratings yet
- Jee 1 PCM Test Paper Ms 16-02-2024Document10 pagesJee 1 PCM Test Paper Ms 16-02-2024k6tt2ntxjdNo ratings yet
- Reflection & Transmission em Waves: Vincensius Gunawan, PHDDocument24 pagesReflection & Transmission em Waves: Vincensius Gunawan, PHDTango SariNo ratings yet
- Rotational Motion - Miscellaneous SolutionsDocument16 pagesRotational Motion - Miscellaneous SolutionsJee AspirantNo ratings yet
- PHY11 Lesson 4 Rotational MotionDocument45 pagesPHY11 Lesson 4 Rotational MotionMaMtNo ratings yet
- The Chaotic Motion of A Double PendulumDocument24 pagesThe Chaotic Motion of A Double PendulumjuanNo ratings yet
- Hints and Solutions - XI Test Paper JEE (Main) Dt. 02.02.2023 - SET-BDocument9 pagesHints and Solutions - XI Test Paper JEE (Main) Dt. 02.02.2023 - SET-Bujjwal guptaNo ratings yet
- Complete Solution of Half Course Test 2 Class XiiDocument3 pagesComplete Solution of Half Course Test 2 Class XiiAvik DasNo ratings yet
- Rigid RotorDocument38 pagesRigid RotorSergeyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Machinery Dynamics Part 3Document5 pagesIntroduction To Machinery Dynamics Part 3Fatima NusserNo ratings yet
- Radius of Gyration #17Document2 pagesRadius of Gyration #17haroon100% (1)
- Aits 2021 PT I Jeem Sol PDFDocument17 pagesAits 2021 PT I Jeem Sol PDFmehul pant100% (1)
- Chapter One PhysicsDocument31 pagesChapter One PhysicsNardos AlemayewNo ratings yet
- 16 Bohr ModelDocument23 pages16 Bohr ModelengshimaaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 03 RCDocument12 pagesAssignment 03 RCHidden TalentNo ratings yet
- PH141 Recommended Problems Chapt.10 EvenDocument3 pagesPH141 Recommended Problems Chapt.10 Evennomio12No ratings yet
- Physics - Shift 1 - 24 2 2021Document22 pagesPhysics - Shift 1 - 24 2 2021totalrcksNo ratings yet
- 11.1 Calculation of Loads On Spur, Helical, and Double-Helical GearsDocument7 pages11.1 Calculation of Loads On Spur, Helical, and Double-Helical GearsJoseph SmithNo ratings yet
- V MGR K K Is The TorsionalDocument1 pageV MGR K K Is The TorsionalA MusicloverNo ratings yet
- Frame BucklingDocument11 pagesFrame BucklingJuan DiegoNo ratings yet
- Rigid RotorDocument38 pagesRigid RotorRaniaNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Information For A Given Mechanism Example 1.: A A A BDocument2 pagesKinetic Information For A Given Mechanism Example 1.: A A A BRAGHAV MOARNo ratings yet
- NEET UG Physics Rational Motion MCQsDocument40 pagesNEET UG Physics Rational Motion MCQssouravthakur17aNo ratings yet
- Momentum Applications in Open Channel Flow: Thanks To Prof. Sjwright, Um, For AnimationsDocument24 pagesMomentum Applications in Open Channel Flow: Thanks To Prof. Sjwright, Um, For AnimationsLTE002No ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 Solutions - Energy MethodsDocument5 pagesTutorial 2 Solutions - Energy MethodsHuzaifa KhalidiNo ratings yet
- Electrostate - 1 (Theory) PDFDocument27 pagesElectrostate - 1 (Theory) PDFPawan VijayvergiaNo ratings yet
- The Nature of The Dirac Equation: I T C I X M CDocument4 pagesThe Nature of The Dirac Equation: I T C I X M CjsnvrghseNo ratings yet
- Internal Gear Pump DesignDocument14 pagesInternal Gear Pump Designafriyan.inbox capcxNo ratings yet
- Work Energy Rigid Bodies 1Document7 pagesWork Energy Rigid Bodies 1Mark Angelo CarganillaNo ratings yet
- Note These Points - : Even If Not AskedDocument68 pagesNote These Points - : Even If Not Askedvibhakar4uNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument40 pagesPhysicsSanjiv KumarNo ratings yet
- Test For PhysicsDocument1 pageTest For PhysicsRe NacionNo ratings yet
- WORK POWER ENERGY-03-Subjective SolvedDocument11 pagesWORK POWER ENERGY-03-Subjective SolvedRaju SinghNo ratings yet
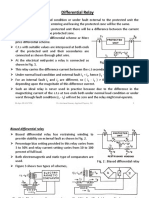
- Differential RelayDocument9 pagesDifferential RelaysourabhNo ratings yet
- Kindin 1Document24 pagesKindin 1bagusNo ratings yet
- IOQP Part I NSEP SolutionDocument10 pagesIOQP Part I NSEP SolutionAditya MondalNo ratings yet
- Gaya Dan Medan ListrikDocument18 pagesGaya Dan Medan ListrikFaiza Nur LailaNo ratings yet
- Quadratic and Inequations 4 SolnsDocument16 pagesQuadratic and Inequations 4 SolnsB GALANo ratings yet
- Problem 13.142: Given: Find: SolutionDocument1 pageProblem 13.142: Given: Find: SolutionLucas Baldo CardosoNo ratings yet
- Work and Potensial Energy PresentasiDocument5 pagesWork and Potensial Energy PresentasiEvaNo ratings yet
- X Raydiffraction Chapter3Document18 pagesX Raydiffraction Chapter3Mohammed HamedNo ratings yet
- Lecture06 FEG Basics & Heat Capacity1Document51 pagesLecture06 FEG Basics & Heat Capacity1lalitbickNo ratings yet
- Iare em PPT Slides and PDFDocument17 pagesIare em PPT Slides and PDFGv IareNo ratings yet
- Problem27 56Document1 pageProblem27 56IENCSNo ratings yet
- MD 2 Page (29-33) Flywheels (Revised Equations)Document17 pagesMD 2 Page (29-33) Flywheels (Revised Equations)Jerome Russel PublìcòNo ratings yet
- JEE Main Atomic Structure Revision Notes - Free PDF DownloadDocument11 pagesJEE Main Atomic Structure Revision Notes - Free PDF DownloadTammudu AbhayNo ratings yet
- HHM - Unit III RVFDocument15 pagesHHM - Unit III RVF032 HarshithNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document33 pagesModule 2Onii ChanNo ratings yet
- Physical Pendulum (MDocument16 pagesPhysical Pendulum (Mthathalakshman121407No ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics - 2022 (Mains)Document21 pagesChemical Kinetics - 2022 (Mains)AmukNo ratings yet
- DerivationRydbergConstant PDFDocument24 pagesDerivationRydbergConstant PDFBakhita MaryamNo ratings yet
- Angle Is The Angle That The String Makes With The Vertical When Released From Rest Will Affect TheDocument8 pagesAngle Is The Angle That The String Makes With The Vertical When Released From Rest Will Affect TheHidayah SakinahNo ratings yet
- 1.02.mathematical Background - AnswersDocument1 page1.02.mathematical Background - AnswersRonald CordovaNo ratings yet
- Vietnam ECat Cinetique Reelle 2Document31 pagesVietnam ECat Cinetique Reelle 2Hoai LinhNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity-09-Subjective and Objective SolutionsDocument26 pagesCurrent Electricity-09-Subjective and Objective SolutionsRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- JS Atomic Lecture5-6Document19 pagesJS Atomic Lecture5-6Sandile SynthaxError MabikaNo ratings yet
- Solutions10 13Document4 pagesSolutions10 13RaghuRamNo ratings yet
- 06 Writing Across The Curriculum v001 (Full)Document34 pages06 Writing Across The Curriculum v001 (Full)RaghuRamNo ratings yet
- Email Quick Start v8.3.0Document6 pagesEmail Quick Start v8.3.0RaghuRamNo ratings yet
- An Approach To An Effective MethodologyDocument0 pagesAn Approach To An Effective MethodologyJason AaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 18Document18 pagesLecture 18RaghuRamNo ratings yet
- Aakash-Iit Physics..Target 1 To 7Document1 pageAakash-Iit Physics..Target 1 To 7RaghuRamNo ratings yet
- Advanced Excel: Teachucomp, IncDocument8 pagesAdvanced Excel: Teachucomp, IncRaghuRamNo ratings yet
- An Approach To An Effective MethodologyDocument0 pagesAn Approach To An Effective MethodologyJason AaNo ratings yet
- QM 18 Questions v3Document3 pagesQM 18 Questions v3RaghuRamNo ratings yet
- Resume SAMPLEDocument5 pagesResume SAMPLERaghuRamNo ratings yet
- Wave Equation DerivationDocument1 pageWave Equation DerivationRaghuRamNo ratings yet
- Web Based Training User's Guide: California State University, ChicoDocument25 pagesWeb Based Training User's Guide: California State University, ChicoRaghuRamNo ratings yet
- EE130/230A Discussion 2: Peng ZhengDocument10 pagesEE130/230A Discussion 2: Peng ZhengRaghuRamNo ratings yet
- Cap A 14Document6 pagesCap A 14Brian BlocksNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Dynamics and Analysis of MotionDocument1 pageFundamentals of Dynamics and Analysis of MotionRaghuRamNo ratings yet
- Linear MomentumDocument51 pagesLinear MomentumRaghuRamNo ratings yet
- Sphere EnergyDocument1 pageSphere EnergyRaghuRamNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Fields and Waves - Lorrain and Corson PDFDocument383 pagesElectromagnetic Fields and Waves - Lorrain and Corson PDFAndres Moreno100% (4)
- Viscosity-Reynold Number DerivationDocument1 pageViscosity-Reynold Number DerivationRaghuRamNo ratings yet
- Wave Equation DerivationDocument1 pageWave Equation DerivationRaghuRamNo ratings yet
- Wave Equation DerivationDocument1 pageWave Equation DerivationRaghuRamNo ratings yet
- Binding EnergyDocument1 pageBinding EnergyRaghuRamNo ratings yet
- Viscosity-Reynold Number DerivationDocument1 pageViscosity-Reynold Number DerivationRaghuRamNo ratings yet
- Chapter12 PDFDocument12 pagesChapter12 PDFRaghuRamNo ratings yet
- HW 13 SolDocument14 pagesHW 13 SolJohn BraveauNo ratings yet
- Chapter12 PDFDocument12 pagesChapter12 PDFRaghuRamNo ratings yet
- Scalar Quantity Magnitude: Vectors and ScalarsDocument89 pagesScalar Quantity Magnitude: Vectors and ScalarsK-Cube MorongNo ratings yet
- Scalar Quantity Magnitude: Vectors and ScalarsDocument89 pagesScalar Quantity Magnitude: Vectors and ScalarsK-Cube MorongNo ratings yet
- The Branch of Mechanics That Studies The Motion of A Body Without Caring About What Caused The MotionDocument56 pagesThe Branch of Mechanics That Studies The Motion of A Body Without Caring About What Caused The MotionNasir IqbalNo ratings yet
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldFrom EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (64)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessFrom EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Giza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyFrom EverandGiza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyNo ratings yet
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesFrom EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2193)
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceFrom EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (51)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingFrom EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidFrom EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1396)
- Bedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceFrom EverandBedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterFrom EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (410)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayFrom EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (125)
- The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldFrom EverandThe Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (60)
- Black Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseFrom EverandBlack Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)From EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (157)
- The Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldFrom EverandThe Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (54)
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowFrom EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (49)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeFrom EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeNo ratings yet
- Let There Be Light: Physics, Philosophy & the Dimensional Structure of ConsciousnessFrom EverandLet There Be Light: Physics, Philosophy & the Dimensional Structure of ConsciousnessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (57)
- The Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceFrom EverandThe Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (23)
- A Natural History of Color: The Science Behind What We See and How We See itFrom EverandA Natural History of Color: The Science Behind What We See and How We See itRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (13)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeFrom EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)