Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pid Controller
Uploaded by
Madiha ZaimuriCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pid Controller
Uploaded by
Madiha ZaimuriCopyright:
Available Formats
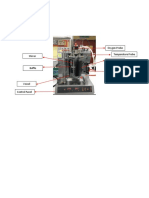
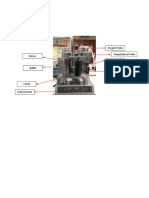
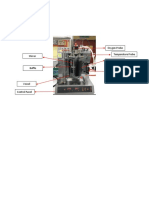
The basic idea behind a PID controller is to read a sensor, then compute the desired
actuator output by calculating proportional, integral, and derivative responses and summing
those three components to compute the output. Initially, PID controller’s parameters are
set as P = 0.02, I = 0.01, D = 0. Then, the value of proportional (P) is increased to 0.05, while
the values of Integral (I) and Derivative (D) are remain constant. Lastly, the value of
proportional (P) is further increase to 0.08 while the values of Integral (I) and Derivative (D)
remains constant. The system is run every each after the changes of value of the
proportional (P) and the oscillation trend is shown in the graph. For the first one, value
proportional (P) of 0.02 is observed to be with the highest oscillation. Then, the changes of
value proportional (P) to 0.05 is shown to be the second highest with oscillation. The value
of proportional (P) of 0.08 is observed to have the lowest oscillation in the graph. This can
be conclude that the increase in the value of proportional (P) will decrease the oscillation
trend of the system, thus decrease the speed of the overall control system response.
You might also like
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Flow Over WeirsDocument9 pagesFlow Over WeirsFaiq AqillahNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mixing LabDocument3 pagesFluid Mixing LabMadiha ZaimuriNo ratings yet
- Flow Meter Lab ReportDocument28 pagesFlow Meter Lab ReportMadiha Zaimuri50% (2)
- Gantt Chart For StudentDocument1 pageGantt Chart For StudentMadiha ZaimuriNo ratings yet
- Drying Procedures and Methodology for Potato SamplesDocument2 pagesDrying Procedures and Methodology for Potato SamplesMadiha ZaimuriNo ratings yet
- 221 04 PDFDocument18 pages221 04 PDFEr Mayur PatilNo ratings yet
- 1.3.1) Concept of ScreeningDocument2 pages1.3.1) Concept of ScreeningMadiha ZaimuriNo ratings yet
- APPARATUSDocument1 pageAPPARATUSMadiha ZaimuriNo ratings yet
- CHE241 - Lab Report Solteq Flow Over Wei PDFDocument22 pagesCHE241 - Lab Report Solteq Flow Over Wei PDFHaziq HaikalNo ratings yet
- Gas Solubility in Aqueous SolutionDocument93 pagesGas Solubility in Aqueous SolutionArgie Adduru73% (11)
- CBE658: Food Irradiation Safety and AwarenessDocument3 pagesCBE658: Food Irradiation Safety and AwarenessMadiha ZaimuriNo ratings yet
- Exp3 IntroductionDocument6 pagesExp3 IntroductionMadiha ZaimuriNo ratings yet
- GAPS Plant LayoutDocument11 pagesGAPS Plant Layoutvb_pol@yahooNo ratings yet
- ApparatusDocument1 pageApparatusMadiha ZaimuriNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 - Theory of FailureDocument38 pagesCHAPTER 4 - Theory of FailureMadiha ZaimuriNo ratings yet
- GAPS Plant LayoutDocument11 pagesGAPS Plant Layoutvb_pol@yahooNo ratings yet
- FATIN - Benzene and BiosurfactantsDocument3 pagesFATIN - Benzene and BiosurfactantsMadiha ZaimuriNo ratings yet
- Aluminium MaterialDocument3 pagesAluminium MaterialMadiha ZaimuriNo ratings yet
- Tuto 6 Q2&Q3Document3 pagesTuto 6 Q2&Q3Madiha ZaimuriNo ratings yet
- Aluminium MaterialDocument3 pagesAluminium MaterialMadiha ZaimuriNo ratings yet
- GAPS Plant LayoutDocument11 pagesGAPS Plant Layoutvb_pol@yahooNo ratings yet
- The Equations of Change For Energy BlnceDocument11 pagesThe Equations of Change For Energy BlnceSaiful BahriNo ratings yet
- ApparatusDocument1 pageApparatusMadiha ZaimuriNo ratings yet
- Titration table for NaOH volume neededDocument1 pageTitration table for NaOH volume neededMadiha ZaimuriNo ratings yet
- The Advantages: Level MeasurementDocument1 pageThe Advantages: Level MeasurementMadiha ZaimuriNo ratings yet
- Table Lab 5 2xxDocument7 pagesTable Lab 5 2xxMadiha ZaimuriNo ratings yet
- Date: . . .Document1 pageDate: . . .Madiha ZaimuriNo ratings yet
- Table Lab 5 2xxDocument7 pagesTable Lab 5 2xxMadiha ZaimuriNo ratings yet
- Exp3 IntroductionDocument6 pagesExp3 IntroductionMadiha ZaimuriNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- "Hybrid" Light Steel Panel and Modular Systems PDFDocument11 pages"Hybrid" Light Steel Panel and Modular Systems PDFTito MuñozNo ratings yet
- Introduction, Concepts, Scope of Community Health NursingDocument32 pagesIntroduction, Concepts, Scope of Community Health Nursingmuthukumar82% (28)
- Republic vs. Roque - JD1ADocument4 pagesRepublic vs. Roque - JD1AQueenie Boado100% (1)
- Anchor ChairDocument3 pagesAnchor ChairrsubramaniNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Rev08242018Document188 pagesStudy Guide Rev08242018chong pak limNo ratings yet
- 78ac PDFDocument7 pages78ac PDFvhgiaoNo ratings yet
- NN43001-712 02.02 SwIOFAULTDocument2,474 pagesNN43001-712 02.02 SwIOFAULTJoeNo ratings yet
- Network Fundamentals - Chapter 4 Exam AnswersDocument4 pagesNetwork Fundamentals - Chapter 4 Exam AnswersBart AbraasNo ratings yet
- DATACOM Multiple Choice Question 6Document1 pageDATACOM Multiple Choice Question 6girijamohapatraNo ratings yet
- Measuring The Sustainability of Urban Water ServicesDocument10 pagesMeasuring The Sustainability of Urban Water ServicesWalter RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Nameet Kumar Jain: Education ProjectsDocument1 pageNameet Kumar Jain: Education ProjectsNameet JainNo ratings yet
- Aoc ts185 LCD MonitorDocument56 pagesAoc ts185 LCD MonitoraldinaenNo ratings yet
- Baranda v. GustiloDocument2 pagesBaranda v. GustiloRiena MaeNo ratings yet
- Excel calendarDocument28 pagesExcel calendarThanh LêNo ratings yet
- Benguet Management v. Keppel BankDocument3 pagesBenguet Management v. Keppel BankChester BryanNo ratings yet
- CSC V CADocument2 pagesCSC V CAAllen GrajoNo ratings yet
- Zodax Collection 2011Document129 pagesZodax Collection 2011njlaporteNo ratings yet
- Petron Corporate PresentationDocument46 pagesPetron Corporate Presentationsivuonline0% (1)
- Forms of Hooke's Law: C C C C CDocument2 pagesForms of Hooke's Law: C C C C Cali dimaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0304885323009770 MainDocument8 pages1 s2.0 S0304885323009770 Mainzmaxprom5No ratings yet
- Ball ValveDocument12 pagesBall ValveIdabaNo ratings yet
- Hello World in FortranDocument43 pagesHello World in Fortranhussein alsaedeNo ratings yet
- Bulk PricesDocument2 pagesBulk PricesMega Byte0% (1)
- Edmonton Report On Flood MitigationDocument6 pagesEdmonton Report On Flood MitigationAnonymous TdomnV9OD4No ratings yet
- Tall VarietiesDocument23 pagesTall VarietiessakthivelNo ratings yet
- Palacio VsDocument2 pagesPalacio VsRaymart SalamidaNo ratings yet
- Smith & Wesson Semi-Automatic Light Rifle HandbookDocument12 pagesSmith & Wesson Semi-Automatic Light Rifle Handbookxamxam0987654321100% (1)
- Dual-band patch antenna for 5G applicationsDocument3 pagesDual-band patch antenna for 5G applicationsHarini VemulaNo ratings yet
- ADF BasicsDocument7 pagesADF BasicsKalieswaranNo ratings yet
- Channelling Done: Channel DetailsDocument2 pagesChannelling Done: Channel DetailsKaushala SamarawickramaNo ratings yet