0% found this document useful (0 votes)
995 views3 pagesSimple Machine: Wall Mounted Screw Jack
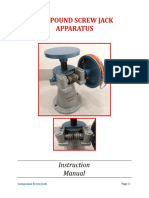
The document describes an experiment to examine a screw jack as a simple machine. It details the apparatus used, which is a wall mounted jack. The procedure involves wrapping the thread around the larger diameter pulley and connecting a hanger to load weights. Effort is measured by adding small weights to the hanger connected to the smaller pulley. Readings are taken for both loading and unloading. The observations and calculations section provides details of the pulleys, threads, and formulas that will be used to determine mechanical advantage and efficiency for both square and vee threads.
Uploaded by
ernest amponsahCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
995 views3 pagesSimple Machine: Wall Mounted Screw Jack
The document describes an experiment to examine a screw jack as a simple machine. It details the apparatus used, which is a wall mounted jack. The procedure involves wrapping the thread around the larger diameter pulley and connecting a hanger to load weights. Effort is measured by adding small weights to the hanger connected to the smaller pulley. Readings are taken for both loading and unloading. The observations and calculations section provides details of the pulleys, threads, and formulas that will be used to determine mechanical advantage and efficiency for both square and vee threads.
Uploaded by
ernest amponsahCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Introduction and Aim
- Procedure
- Observations and Calculations