0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views22 pagesSOP For Administration IV Injection
SOP for Administration IV Injection
Uploaded by
LimYiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views22 pagesSOP For Administration IV Injection
SOP for Administration IV Injection
Uploaded by
LimYiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Definition: Defines intravenous bolus medication and its therapeutic objectives.
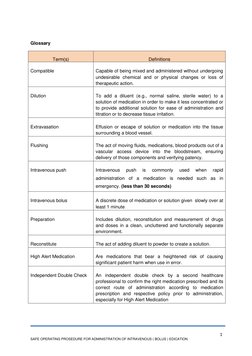
- Glossary: Provides definitions for key terms related to intravenous medication administration and safety protocols.
- Introduction: Explains the significance of administering IV bolus medications, focusing on teaching and safety.
- Objectives: Outlines the key goals for improving the administration of intravenous medications.
- Special Instruction: Gives specific instructions for administering IV medications using dedicated tools.
- Policy: Details the policies guiding the certification and administration of IV bolus medications.
- Classes/Categories of High Alert Medications: Lists medications classified as high alert with associated administration guidelines.
- Different Size of Cannula: Describes various cannula sizes and their clinical applications in IV therapy.
- Preparation of Injection Trolley: Lists the necessary items and setup for preparing an injection trolley.
- Responsibility Pre During and Post Administration: Details responsibilities and actions to be taken by medical staff before, during, and after IV administration.
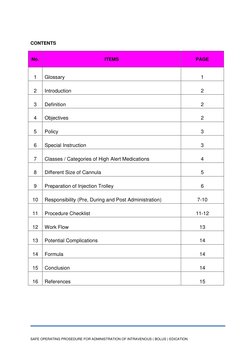
- Procedure Checklist: Provides a step-by-step checklist for verifying and executing IV procedures.
- Work Flow: Illustrates the workflow process for administering IV medications through a flowchart.
- Formula: Discusses formulation calculations for preparing and administering IV doses.
- References: Cites references and resources used for preparing the IV administration guidelines.