Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tutorial 6
Uploaded by
Aiman FadzilCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial 6
Uploaded by
Aiman FadzilCopyright:
Available Formats
REACTION ENGINEERING 1 CHE502
TUTORIAL - Topic 6: Multiple Reactions
1. Determine the instantaneous selectivity, SD/U, for the liquid phase reactions:
Sketch the selectivity as a function of the concentration of A. Is there an optimum and if so what
is it?
2. Reactant A decomposes by three simultaneous reactions to form three products, one that is
desired B and two that are undesired X and Y.
A→X -r1A=rX=k1=0.0003 mol/dm3.s
A→B -r2A=rB=k2CA=(0.0017 s-1)CA
A→Y -r3A=rY=k3CA2=(0.01 dm3/mol.s)CA2
(i)Determine the rate selectivity parameter, SD/U , volume of reactor, VCSTR and conversion; if the
reaction carried out to maximize selectivity of desired product for an entering concentration of A
is 0.4M and a volumetric flow rate of 2.0 dm3/s in CSTR.
(ii)Calculate the final conversion
(iii)Calculate the exit concentration of X, B and Y.
3. For the following reactions, suggest your reactor system and condition to maximize the
selectivity of your desired product.
(a) A+B→D -rA1=10exp(-8,000 K/T)CACB
A+B→U -rA2=100exp(-1,000 K/T)CA½CB3/2
(b) A+B→D -rA1=100exp(-1,000 K/T)CACB
A+B→U -rA2=106exp(-8,000 K/T) CACB
4. Problem 6-6 pg 363 (Fogler 4th Edition)
5. The oxidation of propanol to form an aldehyde, B is carried out in CSTR, on a catalyst of 4 wt %
Cu-2 wt % Cr on Al2O3. Unfortunately, the aldehyde, B is also oxidized on this catalyst to form
carbon dioxide. Derive the concentration, CB of the aldehyde, B as a function of space time.
CH3CH2CH2OH→B→CO2
6. Problem 6-14 pg 368 (Fogler 4th Edition)
You might also like
- Tutorial Problems (Set 5)Document2 pagesTutorial Problems (Set 5)Manishaa Varatha RajuNo ratings yet
- Tut1 2016 QDocument5 pagesTut1 2016 QAbhishek SardaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4Document2 pagesAssignment 4Ram Lakhan MeenaNo ratings yet
- 3 - Prob PFR 11-12 23-35 English-1Document4 pages3 - Prob PFR 11-12 23-35 English-1Biniyam haileNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Rev1 Multiple ReactionDocument37 pagesChapter 6 Rev1 Multiple ReactionHakashiMirudoNo ratings yet
- Tutorial For Chapter 1Document3 pagesTutorial For Chapter 1Thurgah VshinyNo ratings yet
- CHEM311 182 Major2 SolvedDocument10 pagesCHEM311 182 Major2 SolvedhussainNo ratings yet
- Question Bank of Engineering ChemistryDocument2 pagesQuestion Bank of Engineering ChemistryColab practiceNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction EngineeringDocument30 pagesChemical Reaction EngineeringsureshNo ratings yet
- Sample Exams Problems CHE 402Document3 pagesSample Exams Problems CHE 402Ricardo VelozNo ratings yet
- 344W13FinalExam Solution PDFDocument22 pages344W13FinalExam Solution PDFTysir SarhanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5drtuhDocument2 pagesTutorial 5drtuhFikrie MuhdNo ratings yet
- Bgas Question Paper (Part-2)Document243 pagesBgas Question Paper (Part-2)phani prabhakarNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Flak Combustion MethodDocument2 pagesOxygen Flak Combustion MethodSandip Firke100% (2)
- Assignment 1 CHE594 April 2013Document1 pageAssignment 1 CHE594 April 2013riniz92No ratings yet
- Calculations - Exercise 1 - Question Paper - 1Document1 pageCalculations - Exercise 1 - Question Paper - 1kellary liawNo ratings yet
- BGas Excercise Page 2Document1 pageBGas Excercise Page 2Bayu FalenNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document1 pageAssignment 3Kai Faha LukumNo ratings yet
- B-GAS-GRADE - 2-Theory GoodDocument34 pagesB-GAS-GRADE - 2-Theory GoodCERTS100% (1)
- Coverage Spreading Rate and Paint Consumption Calculations 01nov2022Document4 pagesCoverage Spreading Rate and Paint Consumption Calculations 01nov2022Tirumala PrasadNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document2 pagesTutorial 2EreenNo ratings yet
- Protect Your Investment with Proper Refractory InspectionDocument33 pagesProtect Your Investment with Proper Refractory InspectionDenzil D'SouzaNo ratings yet
- PHD Thesis Samira Telschow.Document180 pagesPHD Thesis Samira Telschow.Jackson VuNo ratings yet
- CRE PYQ (1988-2020) : BY Shailendra Sir (SKS50)Document60 pagesCRE PYQ (1988-2020) : BY Shailendra Sir (SKS50)Romil GandhiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction Engineering Mole Balances: ContentDocument29 pagesChemical Reaction Engineering Mole Balances: ContentMhmad E. HerzallahNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 CHE502/594 Reaction Engineering 1 Due Date: Monday (14 OF MAY 2018)Document1 pageAssignment 1 CHE502/594 Reaction Engineering 1 Due Date: Monday (14 OF MAY 2018)nazirulNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4Document1 pageTutorial 4Aisyah ShaariNo ratings yet
- Tute 1 PDFDocument1 pageTute 1 PDFRBNo ratings yet
- For Student Test1 Version 3 SKKK1113 1112-1 PDFDocument3 pagesFor Student Test1 Version 3 SKKK1113 1112-1 PDFDon Jer Bear FirdausNo ratings yet
- Gazi University Chemical Reaction Engineering ProblemsDocument4 pagesGazi University Chemical Reaction Engineering ProblemsJerson Mendoza CNo ratings yet
- CHE 140A Problem Set No. 2: Fogler, 1-15 (A-C), P. 33Document5 pagesCHE 140A Problem Set No. 2: Fogler, 1-15 (A-C), P. 33No NamaaNo ratings yet
- Reaction Kinetics Sample ProblemsDocument1 pageReaction Kinetics Sample ProblemsBenedict MarzanNo ratings yet
- CRE1 Fogler 1 Mole Balances Reactors 2016Document56 pagesCRE1 Fogler 1 Mole Balances Reactors 2016Rathish RagooNo ratings yet
- Test2 SolutionDocument10 pagesTest2 SolutionHua KhienNo ratings yet
- NACE CIP Part II - (5) Corrosion - (Qs - As)Document6 pagesNACE CIP Part II - (5) Corrosion - (Qs - As)MIREYA RUBI SARAO ORUETANo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 - Questions PDFDocument2 pagesTutorial 2 - Questions PDFRaymond KakalaNo ratings yet
- MM435 - CDP-4 - Nernst Equation+Ref ElectrodesDocument23 pagesMM435 - CDP-4 - Nernst Equation+Ref ElectrodesAbdul Ahad ShamsNo ratings yet
- Previous Question Papers of Metallurgy and Material SciencesDocument10 pagesPrevious Question Papers of Metallurgy and Material SciencesRajeev SaiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4Document3 pagesTutorial 4EreenNo ratings yet
- Corrosion MechanismsDocument64 pagesCorrosion MechanismsRahul PandeyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Introduction of CREDocument6 pagesLecture 1 - Introduction of CRENizam JumadiNo ratings yet
- Reaction Engineering EP 319/EP 327: Chapter 4 (Part Ii) Multiple ReactionsDocument25 pagesReaction Engineering EP 319/EP 327: Chapter 4 (Part Ii) Multiple ReactionsWoMeiYouNo ratings yet
- 6.multiple ReactionsDocument22 pages6.multiple ReactionsFarah Talib Al-sudaniNo ratings yet
- Exam I Sem I 2011 12 Cheng 323Document7 pagesExam I Sem I 2011 12 Cheng 323Faisal MumtazNo ratings yet
- TRK1 2013 Chapt 2Document14 pagesTRK1 2013 Chapt 2Putri JulietaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 DR Azizul PDFDocument4 pagesAssignment 2 DR Azizul PDFjinNo ratings yet
- Ethylene Dichloride (Edc) / Vinyl Chloride Monomer (VCM) : Customer Process BrochureDocument4 pagesEthylene Dichloride (Edc) / Vinyl Chloride Monomer (VCM) : Customer Process Brochurerkapoor584199No ratings yet
- Corrosion Measurement UNIT-5: CHE-545-172 DR Ime B.ObotDocument48 pagesCorrosion Measurement UNIT-5: CHE-545-172 DR Ime B.ObotArielNo ratings yet
- CH 6701 Cre IiDocument230 pagesCH 6701 Cre IiVaibhav Gupta100% (1)
- Questions and AnswersDocument22 pagesQuestions and AnswersjanakNo ratings yet
- Chbi502 Chapter 2Document24 pagesChbi502 Chapter 2Chau MaiNo ratings yet
- Design and Function of Spray GunDocument5 pagesDesign and Function of Spray GunHomayoon GeramifarNo ratings yet
- Conversion & Reactor SizingDocument39 pagesConversion & Reactor SizingReyhan97No ratings yet
- Kinetics and Reactor Design Assignment 1Document2 pagesKinetics and Reactor Design Assignment 1Muhd HafetzNo ratings yet
- Semi-Batch Reactor: Chemical Reaction Engineering (CRE) Is TheDocument28 pagesSemi-Batch Reactor: Chemical Reaction Engineering (CRE) Is TheJohn Patrick DagleNo ratings yet
- Maximizing Product Selectivity in Multiple Parallel ReactionsDocument21 pagesMaximizing Product Selectivity in Multiple Parallel ReactionsMark Antony LevineNo ratings yet
- Reaction Engineering I-Problem Sheet IIDocument7 pagesReaction Engineering I-Problem Sheet IISimay AydoganNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument3 pagesChemical KineticsRSLNo ratings yet
- CHE3044F Reactor Design 1 Tutorial 7 Equilibrium Calculations and Reactor SelectionDocument2 pagesCHE3044F Reactor Design 1 Tutorial 7 Equilibrium Calculations and Reactor SelectionnmhatityeNo ratings yet
- Chp 482- TutorialsDocument4 pagesChp 482- Tutorialsgeofrey oburuNo ratings yet
- SOP Cleaning EggDocument1 pageSOP Cleaning EggAiman FadzilNo ratings yet
- 247 W013Document4 pages247 W013Mark Vincent EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Introduction and FundamentaDocument166 pagesIntroduction and FundamentaAiman FadzilNo ratings yet
- 01 HW P&id 2018 Sep PDFDocument7 pages01 HW P&id 2018 Sep PDFAiman FadzilNo ratings yet
- Water Quality: Definitions, Characteristics and PerspectivesDocument59 pagesWater Quality: Definitions, Characteristics and PerspectivesSiti Mastura Abdul RahmanNo ratings yet
- Solution ThermoDocument31 pagesSolution ThermoEiman UzmiNo ratings yet
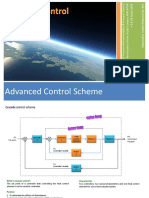
- 06 Cascade Control PDFDocument11 pages06 Cascade Control PDFAiman FadzilNo ratings yet
- Tutorial3 Q2bcDocument1 pageTutorial3 Q2bcAiman FadzilNo ratings yet
- FLUID MIXING APPARATUS FORCE MEASUREMENTDocument2 pagesFLUID MIXING APPARATUS FORCE MEASUREMENTatiqahNo ratings yet
- Ewc661 Proposal Sample (260118)Document6 pagesEwc661 Proposal Sample (260118)Aiman Fadzil100% (2)
- Assignment 1 Heat TransferDocument3 pagesAssignment 1 Heat Transferhafizi naim IsmailNo ratings yet
- Link Springer ComDocument5 pagesLink Springer ComAiman FadzilNo ratings yet
- Film Boiling CondensationDocument5 pagesFilm Boiling CondensationMohamad Fahmi Abd Rased100% (3)