0% found this document useful (0 votes)
275 views25 pagesAdvanced RC Retaining Wall Design
The document discusses different types of retaining walls, including:
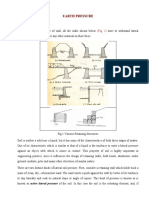
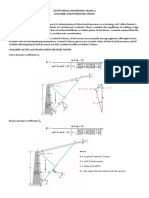
1) Gravity retaining walls rely on their own weight for stability, while cantilever retaining walls derive stability from backfill soil above the heel.
2) MSE walls use soil reinforcement elements to derive stability from stresses at the soil-reinforcement interface.
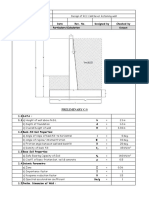
3) The document provides an example design for a cantilever retaining wall, checking for overturning stability, bearing capacity, and shear strength. Flexural reinforcement is designed at the heel section.
Uploaded by
Megh Raj KCCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
275 views25 pagesAdvanced RC Retaining Wall Design
The document discusses different types of retaining walls, including:
1) Gravity retaining walls rely on their own weight for stability, while cantilever retaining walls derive stability from backfill soil above the heel.
2) MSE walls use soil reinforcement elements to derive stability from stresses at the soil-reinforcement interface.
3) The document provides an example design for a cantilever retaining wall, checking for overturning stability, bearing capacity, and shear strength. Flexural reinforcement is designed at the heel section.
Uploaded by
Megh Raj KCCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd