Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Spirometry Intrepretation
Uploaded by
springdingOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Spirometry Intrepretation
Uploaded by
springdingCopyright:
Available Formats
Indications of Pulmonary Function Test
Evaluate respiratory symptoms, signs ,and correlate with abnormal laboratory or radiographic findings
Assist in diagnosing respiratory diseases
Monitor respiratory disease activity and response to therapy
Determine respiratory disease prognosis
Evaluate the pulmonary effects of occupations, environmental and drug exposures
Provide objective assessment of impairment or disability
Evaluate risk prior to lung resection surgery
(Murray and Nadel’s Textbook of Respiratory Medicine Clinical )
Goals of PFT:
To categorize the physiological impairment from lung disease (obstructive vs restrictive)
To quantify the degree of functional impairment
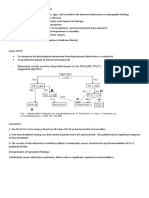
Spirometry results must be interpreted based on the ATS-ERS-TFLFT2
suggested algorithm.
Comments:
1. The FEV1/FVC is low (using a fixed cut-off value of 0.70 as the lower limit of normality).
2. Post bronchodilator testing was done and the patient had a 6% improvement. The patient had no significant response
to bronchodilator.
3. The severity of the obstructive ventilatory defect is moderately severe, based on the post bronchodilator FEV1 %
predicted of 58%.
Interpretation of Spirometry findings:
Moderately severe obstructive ventilatory defect with no significant response to bronchodilator.
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Let The Saints Be JoyfulDocument1 pageLet The Saints Be JoyfulspringdingNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Attia General Surgery Review ManualDocument158 pagesAttia General Surgery Review Manualbphage100% (2)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Must Know Parasitology TermsDocument22 pagesMust Know Parasitology TermsvillajanellaNo ratings yet
- MUST To KNOW in Medical Technology Laws EthicsDocument12 pagesMUST To KNOW in Medical Technology Laws EthicsRona Salando100% (3)
- Anaerobic BacteriaDocument16 pagesAnaerobic BacteriaPriti Go0% (1)
- Anaerobic BacteriaDocument16 pagesAnaerobic BacteriaPriti Go0% (1)
- GlaucomaDocument5 pagesGlaucomaspringdingNo ratings yet
- Femur 151205075833 Lva1 App6891Document14 pagesFemur 151205075833 Lva1 App6891springdingNo ratings yet
- CPM16TH Intrapartum and Immediate Postpartum CareDocument25 pagesCPM16TH Intrapartum and Immediate Postpartum CarespringdingNo ratings yet
- Wound ManagementDocument19 pagesWound ManagementspringdingNo ratings yet
- MJ Legal FundamentalsDocument2 pagesMJ Legal FundamentalsspringdingNo ratings yet
- Airway MGTDocument8 pagesAirway MGTspringdingNo ratings yet
- Pedia Gi NotesDocument34 pagesPedia Gi NotesspringdingNo ratings yet
- Philippine CPG On The Diagnosis and Management of Urinary Tract Infections in Adults-2015 Update - Part 2 PDFDocument140 pagesPhilippine CPG On The Diagnosis and Management of Urinary Tract Infections in Adults-2015 Update - Part 2 PDFspringdingNo ratings yet
- Spirometry IntrepretationDocument1 pageSpirometry IntrepretationspringdingNo ratings yet
- Airway MGTDocument8 pagesAirway MGTspringdingNo ratings yet
- Intracranial and Spinal Tumors 10 ItemsDocument2 pagesIntracranial and Spinal Tumors 10 ItemsspringdingNo ratings yet
- Digging Up The Bones - MicrobiologyDocument31 pagesDigging Up The Bones - MicrobiologyMossa Di Base100% (1)
- Intracranial and Spinal Tumors 10 ItemsDocument2 pagesIntracranial and Spinal Tumors 10 ItemsspringdingNo ratings yet
- What Is Secondhand SmokeDocument3 pagesWhat Is Secondhand SmokespringdingNo ratings yet
- Zako HematologyDocument35 pagesZako Hematologydoctormehmeteren8292No ratings yet
- RNA VirusesDocument11 pagesRNA VirusesKate Alyssa CatonNo ratings yet
- Indirect Inguinal Hernias Are The Most Common Groin Hernias in Men and WomenDocument2 pagesIndirect Inguinal Hernias Are The Most Common Groin Hernias in Men and WomenspringdingNo ratings yet
- FIGOCEDocument11 pagesFIGOCEAldwin TanuwijayaNo ratings yet
- Glycogen Metabolism Index CardDocument3 pagesGlycogen Metabolism Index CardspringdingNo ratings yet
- ShapesDocument10 pagesShapesRosalind GohNo ratings yet
- Neeraj's Notes Plan A Trip: USMLE CS: Step-1: Arrange The DocumentsDocument0 pagesNeeraj's Notes Plan A Trip: USMLE CS: Step-1: Arrange The DocumentsvarrakeshNo ratings yet
- 07 - Memorial AcclamationDocument1 page07 - Memorial AcclamationspringdingNo ratings yet
- Cancer in The Philippines Vol. IV Part 1 PDFDocument78 pagesCancer in The Philippines Vol. IV Part 1 PDFspringdingNo ratings yet