Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Interior of The Earth
Interior of The Earth
Uploaded by
juhair al habib0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesmenjelaskan tentang bentuk-bentuk bumi
Original Title
Interior of the Earth
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentmenjelaskan tentang bentuk-bentuk bumi
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesInterior of The Earth
Interior of The Earth
Uploaded by
juhair al habibmenjelaskan tentang bentuk-bentuk bumi
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Read the article identify the noun phrases, subject, verb, adverb, and translate in Bahasa Indonesia !
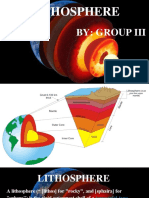
Interior of the Earth
The earth consists of four concentric shells, which are separated by three discontinuities. At
these boundaries, earthquake waves changes in speed and direction. These four shells of the earth are
called the crust, the mantle, the outer core, and the inner core. They differ in state or condition, in
composition, in density, and in elasticity. The degree of elasticity is factor that determines the speed of
earthquake.
The crust extends down to the Mohorovieie (M-) discontinuity (or Moho) and includes the
continents (which consist mostly of granite) and the ocean basins which consist mostly of basalt. Only
the outer part of crust is visible; deeper rocks may become exposed by uplift, erosion, or may be
brought to the surface by volcanism
The continent and ocean basins are more or less in balance with another. This tendency toward
equilibrium is termed isostasy. The continents stand higher than the ocean basins because they are
lighter. Both the heavy and the light columns of rock, however, are in balance at an unknown depth
called the level of compensation.
Below the crust is the mantle. It consists of two or three zones of rock that are under
considerable pressure, which keeps the rock from the melting at the high temperature that exists there.
The bottom of the mantle is marked by the Wiechert-Gutenberg discontinuity, 1,800 mile down.
The outer core is 1,360 mile thick. In spite of increased pressure at this depth, the temperature is
high enough to keep this zone in a molten state. The composition is believed to be largely iron, perhaps
like that of iron-nickel meteorites.
The inner core extends 790 miles to the center of the earth, where its specific gravity may be
more than 17. The enormous pressure (perhaps 3 million times that at the surface) keeps this zone solid
in spite of the high temperature.
Zoning of the earth is one of the major that must be accounted for by any acceptable hypothesis
of the origin of the earth (see Chap. 1).
Question of comprehension
1. How many concentric shell does the earth consist of ?
2. Name the concentric shells of the earth !
3. Where does Moho Discontinuety lay down ?
4. What does the crust consist of ?
5. When does deeper rock become exposed on the surface ?
6. The outer core zone is in solid state. True or false?
7. How is the condition of the mantle ?
8. How is the pressure in the zone of inner core ?
9. Is the inner core in solid or molted state ?
10. Draw deiagram describing the interior of the earth.
Answer these questions!
1. The rocky part of the earth is the ( a. core b. lithosphere c.
isostasy )
2. The molten zone within the earth is the ( a. mantle b. ocean c.
outer core )
3. The zone between the crust and the core is the……………
4. A discontinuity is ( a. the boundary between zones of the earth’s interior
b. an anomaly in isostatic balance c. the margin of the continents )
5. Deep rocks of the earth’s crust may come to the surface: true or false?
6. The continents and ocean basins are in balance because of ( a. anomalies
b. volcanism c. isostasy )
7. The earth’s crust is thickest ( a. in the center of the pacific ocean
b. beneath mountain ranges c. in river deltas )
8. The Moho is the boundary ( a. between the outer and inner core
b. between the mantle and core c. between the crust and mantle)
9. The crust of the earth is composed of ( a. granite and basalt b.
hydrosphere and atmosphere c. peridotite and pallasite )
10. Our knowledge of the earth’s interior has been gained mostly by ( a. drilling oil wells b.
studying seismic waves c. observing volcanoes )
You might also like
- RESEARCH MWTHODS M.ADocument11 pagesRESEARCH MWTHODS M.ADacosta FlectureNo ratings yet
- Murphy Autostart 700 PDFDocument2 pagesMurphy Autostart 700 PDFBEN100% (1)
- Read The Article Identify The Noun Phrases, Subject, Verb, Adverb, and Translate in Bahasa Indonesia !Document3 pagesRead The Article Identify The Noun Phrases, Subject, Verb, Adverb, and Translate in Bahasa Indonesia !Luth Alfaridzi SammanaNo ratings yet
- Interior of The EarthDocument11 pagesInterior of The Earthhanes laurensNo ratings yet
- Intensive Reading: Translate The Paragraph and IdentifyDocument11 pagesIntensive Reading: Translate The Paragraph and IdentifyTools SharerNo ratings yet
- Interior of The Earth-2Document11 pagesInterior of The Earth-2Students RIAND FAIZ MUJADDIDNo ratings yet
- Interior of The EarthDocument2 pagesInterior of The EarthWaskitaMurtyNo ratings yet
- Geomophology PDFDocument20 pagesGeomophology PDFJoel T MbulanjeNo ratings yet
- 2 Ocean Basins and Plate Tectonics AMS 2018Document10 pages2 Ocean Basins and Plate Tectonics AMS 2018Brandon PraterNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE M1 Week1Document8 pagesSCIENCE M1 Week1Vyrox MPNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 - Disaster ManagementDocument153 pagesUnit 5 - Disaster ManagementRathnavel PonnuswamiNo ratings yet
- I. Plate TectonicsDocument16 pagesI. Plate TectonicsChristian GanganNo ratings yet
- Science 6 Lesson 1 The Composition and Structure of The EarthDocument10 pagesScience 6 Lesson 1 The Composition and Structure of The EarthMary Jane WatsonNo ratings yet
- The Earth's LithosphereDocument29 pagesThe Earth's LithosphereKRISTINE UMBAONo ratings yet
- Session 9Document9 pagesSession 9Abdelrahman HishamNo ratings yet
- Earth Science AssignmentDocument7 pagesEarth Science AssignmentOFFICE OF THE CLERK OF COURT ILOILO CITYNo ratings yet
- Geology For Engineers (Sci 3) : Earth Structure and Composition BSCE 2B and 2C Engr. Jovin ManarinDocument26 pagesGeology For Engineers (Sci 3) : Earth Structure and Composition BSCE 2B and 2C Engr. Jovin ManarinJovin ManarinNo ratings yet
- Petro Unit 2Document24 pagesPetro Unit 2ethanNo ratings yet
- Q1 M1 PPT Layers of The EarthDocument97 pagesQ1 M1 PPT Layers of The EarthMarilyn LaquindanumNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science SHS Unit 5 Compositional Layers of EarthDocument64 pagesEarth and Life Science SHS Unit 5 Compositional Layers of EarthSherna BaitingNo ratings yet
- Earth Crust WSDocument2 pagesEarth Crust WSMarc Lawrence FallegaNo ratings yet
- Environmental LithosphereDocument44 pagesEnvironmental LithosphereRichard II RemisNo ratings yet
- Structure of The Earth - MNADocument46 pagesStructure of The Earth - MNAHatim AhmadNo ratings yet
- General Science NotesDocument15 pagesGeneral Science Notesomgpop100% (2)
- Earth'S Layers Layers Based On Chemical Composition Mantle: Seismic TomographyDocument2 pagesEarth'S Layers Layers Based On Chemical Composition Mantle: Seismic TomographyDudrey Anne SalcedaNo ratings yet
- Geo-205 - Sec-01 - Assignment-01 - Name - Maisha - ID - 1531348630Document16 pagesGeo-205 - Sec-01 - Assignment-01 - Name - Maisha - ID - 1531348630Maisha Zenan Hossain 1531348630No ratings yet
- Geomorphology CH 2Document16 pagesGeomorphology CH 2Tezera Mark TmhNo ratings yet
- Enviro Geo Notes 3 CompressedDocument26 pagesEnviro Geo Notes 3 CompressedAlaiza mae BongcayNo ratings yet
- Page 148-161 and Page 172-180Document25 pagesPage 148-161 and Page 172-18005 陳宗榮 RYAN GERALD CHUANo ratings yet
- COMPETENCY 12 AY 2023 2024 StudentsDocument17 pagesCOMPETENCY 12 AY 2023 2024 StudentschaibalinNo ratings yet
- Layers of The EarthDocument7 pagesLayers of The EarthBiancaAsyifa PritadewiNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics AsssignmentDocument11 pagesPlate Tectonics AsssignmentAdikalie Kholifa KamaraNo ratings yet
- Lithosphere 1Document17 pagesLithosphere 1PainationNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument35 pagesPlate TectonicsSyed sikander ali shah SyedNo ratings yet
- Eq WordDocument8 pagesEq WordMahesh UniyalNo ratings yet
- The Earth (Surface, Structure and Age)Document7 pagesThe Earth (Surface, Structure and Age)Marc MathieuNo ratings yet
- Layers of The Earth Reading Comprehension Worksheet 1Document3 pagesLayers of The Earth Reading Comprehension Worksheet 1caffeinatedjems97No ratings yet
- EARTHDocument5 pagesEARTHOscar MasindeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document10 pagesChapter 2Jashan MatadeenNo ratings yet
- The Earth Can Be Divided Into Four LayersDocument3 pagesThe Earth Can Be Divided Into Four LayersClarin Perez OrdinarioNo ratings yet
- Crust and Plate BoundariesDocument46 pagesCrust and Plate BoundariesQueencess Ara TorresNo ratings yet
- 4 Plate Tectonics KDDocument16 pages4 Plate Tectonics KDStephen Richard Kirkley100% (1)
- Composition of The Earth SummaryDocument3 pagesComposition of The Earth Summaryclarence antalanNo ratings yet
- Morphology of EarthDocument19 pagesMorphology of EarthBalaji VicharapuNo ratings yet
- Morphology of EarthDocument19 pagesMorphology of EarthBalaji VicharapuNo ratings yet
- Geology: Surface and Interior of EarthDocument15 pagesGeology: Surface and Interior of EarthClarice Albo BatangosoNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE Grade10 Quarter1 Module1 Week1 PDFDocument15 pagesSCIENCE Grade10 Quarter1 Module1 Week1 PDF알랙스No ratings yet
- LP-G10 Processes and Types of BoundariesDocument4 pagesLP-G10 Processes and Types of BoundariesJohnie Rey VillaruzNo ratings yet
- LAS Science Grade 10 - Q1 - Week 6Document11 pagesLAS Science Grade 10 - Q1 - Week 6Lowie avisadoNo ratings yet
- Teacher'S Input Teacher'S Input Pupil'S Output Pupil'S Output Pupil'S Output Pupil'S OutputDocument7 pagesTeacher'S Input Teacher'S Input Pupil'S Output Pupil'S Output Pupil'S Output Pupil'S OutputCherrie May Arturo OsmanNo ratings yet
- 1 Plate TectonicsDocument11 pages1 Plate TectonicsAyman M SNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Geo 205 Faculty: SZR Submitted by:MD Shariful Islam ID:1530429030 Section:9 Datej:21 July 2020Document8 pagesAssignment 1 Geo 205 Faculty: SZR Submitted by:MD Shariful Islam ID:1530429030 Section:9 Datej:21 July 2020MSI SajeebNo ratings yet
- Zone Structure of EarthDocument2 pagesZone Structure of EarthMukul PŏįṥonoůşNo ratings yet
- 4 BB 8 e 44 Fdad 5 Fa 7381 e 9Document12 pages4 BB 8 e 44 Fdad 5 Fa 7381 e 9api-612927747No ratings yet
- Unit 2 English Contents. Relief and LandformsDocument11 pagesUnit 2 English Contents. Relief and LandformsJulia Casanova GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Activity 6Document2 pagesActivity 6Aimahr LopezNo ratings yet
- Interior of The EarthDocument7 pagesInterior of The EarthAENA JangraNo ratings yet
- The Earth and Earth SystemsDocument22 pagesThe Earth and Earth SystemsJhuryzae LandacanNo ratings yet
- 2 Interior Structure of EARTHDocument6 pages2 Interior Structure of EARTHSHAGUN YADAVNo ratings yet
- Earths Planetary StructureDocument6 pagesEarths Planetary StructureRODJHEN ANNE P. BARQUILLANo ratings yet
- Science PPTDocument28 pagesScience PPTquencia beth radinNo ratings yet
- Geology of the Great Plains and Mountain West: Investigate How the Earth Was Formed with 15 ProjectsFrom EverandGeology of the Great Plains and Mountain West: Investigate How the Earth Was Formed with 15 ProjectsNo ratings yet
- PKCS#15Document81 pagesPKCS#15pinkbubbles2013No ratings yet
- BGM User ManualDocument48 pagesBGM User ManualAlgebra92No ratings yet
- NHS Character Form SampleDocument1 pageNHS Character Form Samplepkhanna25No ratings yet
- Grand Case Study V7 Final 030310Document49 pagesGrand Case Study V7 Final 030310Jemimah Ruth Madayag ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Class:12 Physics Assignment 9 Topic: Alternating CurrentDocument3 pagesClass:12 Physics Assignment 9 Topic: Alternating CurrentAkshat RawatNo ratings yet
- Service Quotation For HY40BU & HY20BK - TURBOPOWER 20140703Document2 pagesService Quotation For HY40BU & HY20BK - TURBOPOWER 20140703Tony ChánhNo ratings yet
- Iron Deficiency AnemiaDocument16 pagesIron Deficiency Anemiaكشخه عراقيNo ratings yet
- Ginantara Ecoturism MangroveDocument12 pagesGinantara Ecoturism MangroveC2-89Henricus Rotarius Octavianus TariganNo ratings yet
- Isi Sains Dan IslamDocument15 pagesIsi Sains Dan IslamSILMI QORINALLAH 2021No ratings yet
- Beverage Brochure EnglishDocument16 pagesBeverage Brochure Englishsalicurri0% (1)
- Dream Jumper #1 - Hi Res - 9780545826037 - Interior - Epdf PDFDocument208 pagesDream Jumper #1 - Hi Res - 9780545826037 - Interior - Epdf PDFEsther TaiwoNo ratings yet
- Final Year Project YP - Proposal - Format - BSCSDocument4 pagesFinal Year Project YP - Proposal - Format - BSCSogoo tomNo ratings yet
- LABP0311Document4 pagesLABP0311Mr. JalilNo ratings yet
- Reading Comprehension Workshop 2 Texts For English IDocument2 pagesReading Comprehension Workshop 2 Texts For English IPROFESORAGURTONo ratings yet
- Leeks Cookbook A Root Vegetable Cookbook Filled With Delicious Leeks RecipesDocument147 pagesLeeks Cookbook A Root Vegetable Cookbook Filled With Delicious Leeks RecipesAna PerišićNo ratings yet
- AMDE Brochure-Mine Safety Accountability Integrated SystemDocument1 pageAMDE Brochure-Mine Safety Accountability Integrated SystemHakimNo ratings yet
- History and Working Principle of CNC MachinesDocument308 pagesHistory and Working Principle of CNC MachinesYash IngleNo ratings yet
- Stretching Mesh Reduced FileDocument5 pagesStretching Mesh Reduced FileMerlie Fuentes Fiel ValentinoNo ratings yet
- Interface Between Competition Commission OF India AND Sectoral RegulatorsDocument20 pagesInterface Between Competition Commission OF India AND Sectoral RegulatorspraharshithaNo ratings yet
- Ventil Preventest LTC Int v5Document3 pagesVentil Preventest LTC Int v5Teodoro Escobar Riveros100% (1)
- Project Report On Multi Speciality Hospital (70 Beds)Document5 pagesProject Report On Multi Speciality Hospital (70 Beds)EIRI Board of Consultants and PublishersNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION - To BackpackDocument2 pagesINTRODUCTION - To BackpackMohammad Afnan BugtiNo ratings yet
- Week 1 IntroductionDocument13 pagesWeek 1 Introductionobai AlhwimelNo ratings yet
- High-Strength Steels For Cold-Forming, Thermomechanically-RolledDocument2 pagesHigh-Strength Steels For Cold-Forming, Thermomechanically-RolledTrần Văn ĐươngNo ratings yet
- Well-Developed Oral and Written Communication SkillsDocument3 pagesWell-Developed Oral and Written Communication Skillslyca_limNo ratings yet
- CSS 12 Top TenDocument2 pagesCSS 12 Top Tennesto chetaNo ratings yet
- Retrofitting of Reinforced Concrete BuildingsDocument44 pagesRetrofitting of Reinforced Concrete BuildingsKrupakl Gowda100% (8)
- Verification and Validation in CFD and Heat Transfer: ANSYS Practice and The New ASME StandardDocument22 pagesVerification and Validation in CFD and Heat Transfer: ANSYS Practice and The New ASME StandardMaxim100% (1)