Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCP: Patient With Peptic Ulcer Disease
Uploaded by
ICa MarlinaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NCP: Patient With Peptic Ulcer Disease
Uploaded by
ICa MarlinaCopyright:
Available Formats
Page 1 of 3
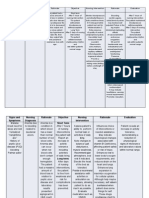
NCP: Patient with Peptic Ulcer Disease
Acute pain related to increased gastric secretion, decreased mucosal protection, and ingestion of gastric irritants as evidenced by
Nursing diagnosis burning cramplike pain in epigastrium and abdomen ; pain onset 1-2 hr after meals with gastric ulcer ; pain onset 2-4 hr after meals
(midmorning, mid efternoon) and middle night with duodenal ulcer
Patient goal Reports pain controlled without the use of analgesics
Intervention (NIC) Outcome (NOC)
Pain Management Outcomes (NOC)
Perform a comprehensive assessment of pain to include Pain Control
location, characteristics, onset/duration, frequency, quality, Describes causal factors.............
intensity or severity of pain, and precipitating factors to Uses Preventive measures.....
determine appropriate intervention Uses nonanalgesic relief measures......
Provide the person optimal pain relief with prescribed Uses analgesics appropriately....
analgesics to provide comfort Reports chane in pain symptoms or sites to health care professional.......
Select and implement a variety of measures (e.g Reports pain controlled.......
pharmacologic, nonpharmacologic, interpersonal) to Measurement Scale
facilitate pain relief 1= never demonstrated
Teach the use of nonpharmacologic techniques (e.g 2= rarely demonstrated
relaxation, guided imagery, music therapy, distraction, 3= sometimes demonstrated
acupressure, massage) before, after, and if possible, during 4= often demonstrated
painful activities ; before pain occurs of increases ; and 5= consistently demonstrated
along with other pain relief measures because relaxation
results in decreased acid production and reduction in pain
Institute and modify pain control measures of the basis of the
patient’s response so that management can be individualized
NCP: Peptic Ulcer
Page 2 of 3
Ineffective self- health management related to lack of knowledge of long term management of peptic ulcer disease and
Nursing diagnosis consequences of not following treatmen plan ; unwillingness to modify lifestyle as evidence of exacerbation of symptoms
Patient goal 1. Verbalizes understanding of the therapeutik regimen, including knowledge of disease , rationale for treatment plan, and
benefits for disease management
2. Verbalize as commitment to self-care and management of the disease
Intervention (NIC) Outcome (NOC)
Teaching : Disease Process Outcomes (NOC)
Review the patient’s knowledge about condition to Knowledge : Treatment regimen
determine if ineffective management is a knowledge problem Spesific disease process.......
Explain the pathophysiology of the disease and how it relates Rationale for treatment........
to anatomy and physiologi to foster understanding Self-care responsibilities for ongoing treatment.......
Dicuss therapy/treatment options Prescribed medication regimen......
Describe rationale behind management/therapy/treatment Measurement Scale
recommendations to faster understanding of the therapy 1= no knowledge
Discuss lifestyle changes that may be required to prevent 2= limited knowledge
future complications and /or control the disease process 3= moderate knowledge
Explore with patient what she or he has already done to 4= substansial knowledge
manage the symptoms to confirm the patient has the ability 5= Extensive knowledge
to manage the disease
Instruct patient on which signs and symptoms to report to Compliace Behavior
health care provider to ensure early the initiation of Performs treatment regimen as prescribed.....
treatment Modifies treatment regimen as directed by health professional......
Measurement Scale
Decision Making Support 1= never demonstrated
Determine whether there are differences between the 2= rarely demonstrated
patient’s view of own condition and the view of health care 3= sometimes demonstrated
providers to be able to establish common ground for disease 4= often demonstrated
management 5= consistently demonstrated
Help patient identify the advantages and disadvantages of
each alternative to promote decision making
NCP: Peptic Ulcer
Page 3 of 3
Nausea related to acute exacerbaton of disease process as evidenced by episodes of nausea and/or vomiting (see NCP Nausea and
Nursing diagnosis vomiting )
Collaborative Problems
Potential Complications : hemorrhage secondary to eroded mucosal tissue
Nursing diagnosis
Patient goal hemorrhage secondary to eroded mucosal tissue
Intervention (NIC) Outcome (NOC)
Nursing Interventions and Rationales Nursing Goals
Assess for evidence of hematemesis, bright red or melena stool, Monitor for signs of hemorrhage
abdominal pain or discomfort symptoms of shock (e.g decreased Carry out appropriate medical and nursing interventions if hemorrhage
blood pressure, cool, clammy skin, dyspnea, tachycardia, occurs
decreased urine output) to plan appropriate interventions
If ulcer is actively bleeding, observe NG tube aspirate or emesis
for amount and color to assess degree of bleeding
Take vital sign every 15-30 min to determine patient’s
hemodynamic status and as indicators of shock
Maintain IV infusion line to provide ready access for blood and
fluid replacement
If RBC transfusion is given, observe for transfusion reaction so
appropriate actions can be taken immediately
Monitor hematocrit and hemoglobin every 4-6 hr during active
bleeding as indicators of severity of hemorrhage and need for
fluid and blood replacement (in early phase of bleeding,
hematocrit may be falsely high or low)
Record intake and output to monitor fluid balance
Reassure patient and family to decrease their anxiety
Remain calm and confident in plan of care to foster calm and
confidence in patient and family
Prepare patient for possible endoscopy or surgery
NCP: Peptic Ulcer
You might also like
- NCP Peptic Ulcer DsDocument4 pagesNCP Peptic Ulcer Dsplug0650% (10)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationJhaypee Soriano100% (3)
- NCP Crohn'sDocument2 pagesNCP Crohn'sJanice Marco100% (1)
- ALL PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesALL PathophysiologyDeo Michael Rivera LlamasNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Fluid Volume DeficitDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Fluid Volume DeficitGenEsis CarandangNo ratings yet
- Signs and Symptoms Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Objective Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument5 pagesSigns and Symptoms Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Objective Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationRemuelMagsinoNo ratings yet
- NCP For GERD (Risk For Aspiration)Document2 pagesNCP For GERD (Risk For Aspiration)Ma Kristina Apolonio63% (8)
- HoplessnessDocument16 pagesHoplessnessHamza IshtiaqNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Peptic UlcerDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Peptic UlcerMichael Joaquin0% (2)
- NCP PainDocument2 pagesNCP PainKarizza Reyes Mamaradlo100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of PudDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of PudAngel-Jeh De Guzman100% (1)
- A Grand Case UgibDocument84 pagesA Grand Case UgibAdrianne Kricia100% (2)
- DRUG PantoprazoleDocument1 pageDRUG PantoprazoleEngelbert CruzNo ratings yet
- NCP Imbalanced NutritionDocument3 pagesNCP Imbalanced NutritionAav Canlas100% (1)
- NCP - Drug Study - Peptic UlcerDocument18 pagesNCP - Drug Study - Peptic UlcerEmi EspinoNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluation S: Patient Was SeenDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluation S: Patient Was Seenkaren kate ablesNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation IndependentDocument5 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation IndependentLayne GazeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Peptic Ulcer NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Peptic Ulcer NCPderic85% (46)
- GERDDocument5 pagesGERDSteve Randolph67% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan For Peptic Ulcer NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Peptic Ulcer NCPJose Escobar100% (3)
- Impaired Physical Mobility NCPDocument3 pagesImpaired Physical Mobility NCPYan ReyesNo ratings yet
- Liver Cirrhosis NCPDocument3 pagesLiver Cirrhosis NCPSharmaine MadlaNo ratings yet
- NCP Gastric CancerDocument7 pagesNCP Gastric CancerAnonymous XvwKtnSrMR100% (4)
- NCP CholelithiasisDocument2 pagesNCP Cholelithiasiskmpg11100% (2)
- Ugib Case StudyDocument36 pagesUgib Case StudyRJ MarquezNo ratings yet
- Daily NCPDocument5 pagesDaily NCPKuennie SabalNo ratings yet
- NCP Stomach CancerDocument2 pagesNCP Stomach CancerJohn Derick BangsoyNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPranee diane0% (1)
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPkristina_zamoraNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Renal Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesIneffective Renal Tissue PerfusionHendra Tanjung100% (4)
- Nursing Care Plan (Peptic Ulcer)Document4 pagesNursing Care Plan (Peptic Ulcer)JennyLapitanNo ratings yet
- NCP-fluid Volume DeficitDocument4 pagesNCP-fluid Volume DeficitChrissa Mae Aranilla MayoNo ratings yet
- NCP T2DMDocument5 pagesNCP T2DMFrancym R. BatengaNo ratings yet
- Pantoprazole DrugDocument1 pagePantoprazole Drugman12No ratings yet
- Risk For FallsDocument1 pageRisk For FallsEugene UCNo ratings yet
- PUD PathophysiologyDocument1 pagePUD PathophysiologyHerbert A Serquina100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Hopelessness NCPDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For Hopelessness NCPderic100% (13)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument11 pagesNursing Care PlanKevin John ReaLubit SaLisi100% (6)
- NCP For COLON Cancer PatientDocument4 pagesNCP For COLON Cancer PatientCarolina Tardecilla100% (1)
- NCP Loss of AppetiteDocument5 pagesNCP Loss of AppetiteStenneli Gumban Trojillo50% (2)
- Cues Nursing DX Objectives Nursing Interventions RationaleDocument5 pagesCues Nursing DX Objectives Nursing Interventions RationaleJamie IcabandiNo ratings yet
- Mod 5 Health TeachingDocument4 pagesMod 5 Health TeachingMabelle SorianoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Tissue InjuryDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Tissue InjuryJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Ugib Case StudyDocument30 pagesUgib Case StudyVenus Glaze Verzola80% (5)
- Hypertonic SolutionsDocument4 pagesHypertonic SolutionsVanessa PaguiriganNo ratings yet
- NCP - Suicidal TendencyDocument2 pagesNCP - Suicidal Tendencyяoxel яayмoи eитяeиa100% (5)
- NCP Chronic ConfusionDocument4 pagesNCP Chronic ConfusionLyka DianaNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument8 pagesNCPJayrald RosalesNo ratings yet
- Disturbed Sleeping Pattern NCPDocument4 pagesDisturbed Sleeping Pattern NCPSamVelascoNo ratings yet
- Gordon's Pattern of Health: He Assumes Total Responsibility For Decision-Making and Self-Care - NotDocument6 pagesGordon's Pattern of Health: He Assumes Total Responsibility For Decision-Making and Self-Care - NotleibogiciousNo ratings yet
- CHOLECYSTECTOMYDocument35 pagesCHOLECYSTECTOMYfaitheee100% (3)
- Care Map UtiDocument1 pageCare Map UtiJonathonNo ratings yet
- 10 NCP FractureDocument4 pages10 NCP FractureICa Marlina0% (1)
- Chapter - 018 Nursing Care PlanDocument8 pagesChapter - 018 Nursing Care PlansiewyonglimNo ratings yet
- Case Stduy Med SurgDocument5 pagesCase Stduy Med SurgKevean Kimi LimNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlansDocument7 pagesNursing Care PlansNicholaiCabadduNo ratings yet
- DX Burns PDFDocument6 pagesDX Burns PDFSherree HayesNo ratings yet
- 12 NCP Spinal Cord InjuryDocument7 pages12 NCP Spinal Cord InjuryDessy Ratna S100% (3)
- Siti Nur Qomariah, S.Kep.,Ns.,M.Kep Prodi Ilmu Keperawatan Fakultas Ilmu Kesehatan Universitas GresikDocument14 pagesSiti Nur Qomariah, S.Kep.,Ns.,M.Kep Prodi Ilmu Keperawatan Fakultas Ilmu Kesehatan Universitas GresikBudi RohmanNo ratings yet
- Medical Management-Nursing Management and NCP For Acute ApendicitisDocument4 pagesMedical Management-Nursing Management and NCP For Acute ApendicitisArki ObusanNo ratings yet
- Review Article: Psychiatric Morbidity and Other Factors Affecting Treatment Adherence in Pulmonary Tuberculosis PatientsDocument38 pagesReview Article: Psychiatric Morbidity and Other Factors Affecting Treatment Adherence in Pulmonary Tuberculosis PatientsICa MarlinaNo ratings yet
- NCP: Patient With A Pressure UlcerDocument2 pagesNCP: Patient With A Pressure UlcerICa Marlina100% (1)
- NCP: Acute Coronary Syndrome: Nursing DiagnosisDocument17 pagesNCP: Acute Coronary Syndrome: Nursing DiagnosisICa MarlinaNo ratings yet
- 18 NCP Ileal ConduitDocument11 pages18 NCP Ileal ConduitICa MarlinaNo ratings yet
- NCP: Patient Receiving Enteral NutritionDocument9 pagesNCP: Patient Receiving Enteral NutritionICa MarlinaNo ratings yet
- 11 NCP Pressure UlcerDocument6 pages11 NCP Pressure UlcerICa MarlinaNo ratings yet
- 10 NCP FractureDocument4 pages10 NCP FractureICa Marlina0% (1)
- Patient With Neutropenia Risk For Infection Related To Inadequate Secondary Defenses (Leukopenia, Neutropenia), Altered Response To MicrobialDocument2 pagesPatient With Neutropenia Risk For Infection Related To Inadequate Secondary Defenses (Leukopenia, Neutropenia), Altered Response To MicrobialICa MarlinaNo ratings yet
- NCP: Patient With Headache: Nursing DiagnosisDocument3 pagesNCP: Patient With Headache: Nursing DiagnosisICa MarlinaNo ratings yet
- 12 NCP Spinal Cord InjuryDocument21 pages12 NCP Spinal Cord InjuryICa MarlinaNo ratings yet
- DLR - Tips and Tricks PDFDocument9 pagesDLR - Tips and Tricks PDFSelda CoktasarNo ratings yet
- ACL Rehab Protocol 2019Document8 pagesACL Rehab Protocol 2019Sam100% (1)
- Speck - X-Ray Contrast Media - Overview, Use and Pharmaceutical AspectsDocument134 pagesSpeck - X-Ray Contrast Media - Overview, Use and Pharmaceutical AspectsSimona Mariana DutuNo ratings yet
- #NephJC CTscan TranscriptDocument22 pages#NephJC CTscan TranscriptSatrio Budi WicaksonoNo ratings yet
- Report CapsicumDocument105 pagesReport CapsicumRina WijayantiNo ratings yet
- Lab 7 - DNA Fingerprinting and Gel ElectrophoresisDocument22 pagesLab 7 - DNA Fingerprinting and Gel ElectrophoresisAmy HollingsworthNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Tumor Biology On Cancer Treatment and Multidisciplinary Strategies - M. Molls, Et Al., (Springer, 2009) WWDocument363 pagesThe Impact of Tumor Biology On Cancer Treatment and Multidisciplinary Strategies - M. Molls, Et Al., (Springer, 2009) WWiuliNo ratings yet
- Renal Cell Carcinoma - Nursing Considerations With The Use of Targeted TherapyDocument50 pagesRenal Cell Carcinoma - Nursing Considerations With The Use of Targeted TherapyMarivic DianoNo ratings yet
- Assessment Standard 4 Traits Employability Skills TESTDocument5 pagesAssessment Standard 4 Traits Employability Skills TESTnurse1990No ratings yet
- Surving Sepsis Campaign ResultDocument8 pagesSurving Sepsis Campaign Resultmaria arenas de itaNo ratings yet
- Case Study - Women EntrepreneursDocument14 pagesCase Study - Women EntrepreneursAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics Chart 1Document7 pagesAntibiotics Chart 1Vee MendNo ratings yet
- CostIt-example (Primary Health Care Facility)Document69 pagesCostIt-example (Primary Health Care Facility)Parimalakrishnan100% (1)
- We Want The Airwaves - Star Amerasu PT 1Document9 pagesWe Want The Airwaves - Star Amerasu PT 1Nia KingNo ratings yet
- Harvard Mens Health Watch January 2021 Harvard HealthDocument8 pagesHarvard Mens Health Watch January 2021 Harvard HealthJefferson Medinaceli MalayaoNo ratings yet
- End-Of-Life Care in The Icu: Supporting Nurses To Provide High-Quality CareDocument5 pagesEnd-Of-Life Care in The Icu: Supporting Nurses To Provide High-Quality CareSERGIO ANDRES CESPEDES GUERRERONo ratings yet
- Drug-Study MethyldopaDocument4 pagesDrug-Study MethyldopamayangernszNo ratings yet
- Changes in The Body: What Is Puberty?Document4 pagesChanges in The Body: What Is Puberty?Mitch MarananNo ratings yet
- (Essentials in Ophthalmology) Ahmad A. Aref, Rohit Varma (Eds.) - Advanced Glaucoma Surgery-Springer International Publishing (2015)Document140 pages(Essentials in Ophthalmology) Ahmad A. Aref, Rohit Varma (Eds.) - Advanced Glaucoma Surgery-Springer International Publishing (2015)Inna Bujor100% (1)
- Significance of The Structure of Human SkeletonDocument5 pagesSignificance of The Structure of Human SkeletonTodirenche LarisaNo ratings yet
- Answers and Rationale Medical Surgical Nursing Practice Test Part 3Document4 pagesAnswers and Rationale Medical Surgical Nursing Practice Test Part 3Anna Marie AmpoNo ratings yet
- Final Letter To NLM Re - IJOEH Nov 2017Document35 pagesFinal Letter To NLM Re - IJOEH Nov 2017Celeste MonfortonNo ratings yet
- Ophtalmology Record Acute Glaucoma: Examiner: DR. Dr. Gilbert W. Simanjuntak, SP.M (K)Document6 pagesOphtalmology Record Acute Glaucoma: Examiner: DR. Dr. Gilbert W. Simanjuntak, SP.M (K)Rashellya RasyidaNo ratings yet
- نسخة نسخة الاشعةDocument10 pagesنسخة نسخة الاشعةDina MohamedNo ratings yet
- Immuno Cheat Sheet 1Document2 pagesImmuno Cheat Sheet 1yolo51No ratings yet
- Cardiac Troponin IDocument1 pageCardiac Troponin IPABRIK SEPULUHNo ratings yet
- Problems and Remedies For MarsDocument4 pagesProblems and Remedies For MarsSunil RupaniNo ratings yet
- DkaDocument32 pagesDkanatheNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Stress On Academic Success in College StudentsDocument4 pagesThe Impact of Stress On Academic Success in College StudentsSha RonNo ratings yet
- Arixtra: (Fondaparinux Sodium) InjectionDocument26 pagesArixtra: (Fondaparinux Sodium) InjectionTri Purma SariNo ratings yet