Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Elizabethan England, c1568-1603
Uploaded by
dladsn1Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Elizabethan England, c1568-1603
Uploaded by
dladsn1Copyright:
Available Formats
Elizabethan England, c1568-1603
6
1
11
1555
1558: Elizabeth crowned
1559: Religious settlement
1562: Elizabeth nearly dies of smallpox
2. Life in Elizabethan times
1565
7
2
12
3. Troubles at home and abroad
1568: Mary, Queen of Scots exiled to England
1. Elizabeth’s court and Parliament
1569: The Northern Rebellion
1570: Papal Bull
1. Elizabeth’s court and Parliament
1571: Ridolfi Plot
1572: Actors in England have to be licensed
1575
1576: Peter Wentworth arrested
8
3
13
1580: Drake completes circumnavigation
1581: Elizabeth knights Sir Francis Drake
1583: Throckmorton Plot
1584: Raleigh given royal permission to explore
2. Life in Elizabethan times
1585: Colony established at Roanoke
1585
9
4
1586: Babington Plot
14 1587: Mary, Queen of Scots executed
1588: Spanish Armada
1590s: Series of bad harvests
1592: Raleigh dismissed from court
1593: Catholics not to travel further than 5 miles
1595
10
15
1600: East India Company established
1599: Opening of The Globe theatre
1601: Essex’s rebellion
1601: Poor Law introduced
3. Troubles at home and abroad
1603: Elizabeth dies
1605
1. Elizabeth’s court and Parliament 2. Life in Elizabethan times 3. Troubles at home and abroad
Hardwick Hall How to structure your answer: ‘The main change that Elizabethan manor houses
demonstrated was stated factor’. How far does a study of
Hardwick Hall support this statement? Explain your answer. You
Paragraph 1: should refer to Hardwick Hall and your contextual knowledge.
Stated factor
Factors: (The main change that Elizabeth manor houses
Paragraph 2: Paragraph 3: demonstrated was…)
Elizabethan England, c1568-1603
Other factor 1 Other factor 2 the greater prosperity of their owners
the gentry class was becoming wealthy
Paragraph 4: the country was at peace
Judgement new renaissance architecture
new technological developments
1. Elizabeth’s court and Parliament
Elizabeth becomes the Queen Elizabeth’s royal court Privy Council The marriage question Earl of Essex’s rebellion (1601)
Elizabeth’s legitimacy (right to rule) The royal court was a collection of Elizabeth’s group of her 19 must 1562: Elizabeth nearly dies of smallpox; Robert Devereux, Dudley’s step-son,
questioned due to her mother’s (Anne people, not a place. trusted advisers Parliament concerned about the lack of became close to Elizabeth and was sent
Boleyn) marriage to Henry VIII She was surrounded by 500 courtiers, Made up members of the nobility and an heir to Ireland to defeat a rebellion (failed)
Also faced the challenge of being a who all competed for power/influence the gentry Suitor 1: Robert Dudley; possibly Essex banned from court and had his
female ruler Elizabeth used patronage to encourage William Cecil; Elizabeth’s chief minister murdered his wife sweet wine monopoly removed
Arrested for treason twice before loyalty; giving courtiers land/titles in Robert Dudley (Earl of Leicester); Suitor 2: King Philip of Spain; a Catholic Essex mounted a poorly led rebellion to
becoming Queen return for their support Elizabeth’s favourite and keen Puritan and had been married to Mary take Elizabeth prisoner
Her early troubled life prepared her The royal court was the source of the Sir Francis Walsingham; Elizabeth’s spy Suitor 3: Francis, Duke of Anjou and 1601: Arrested; executed for treason
well for her reign. major trends/fashions in England. master and keen Puritan. Alencon; Elizabeth was too old for him. Elizabeth’s authority still strong in 1601.
2. Life in Elizabethan times
Rise of the gentry Elizabethan theatre Poverty Sir Francis Drake Sir Walter Raleigh
Pre-Elizabeth, nobility had been the Actors had to be licensed from 1572 Growing poverty levels in Elizabeth’s Privateers and sailors challenged 1584: Raleigh given royal permission to
most powerful people in England onwards reign; population growth, bad harvests, Spanish dominance in the Americas explore and colonise American land
Members of the gentry went from local First theatre, The Theatre, built in 1576 enclosures and closure of monasteries 1560s: John Hawkins captured and Raleigh claimed an area in America and
landowners to national influence The Globe opens in 1599 Elizabethans categorised the poor into traded African slaves in the Americas named it Virginia after Elizabeth
The gentry became richer during Theatre popular due to both rich and the deserving poor (need help) and the 1580: Sir Francis Drake became first 1585: Raleigh establishes colony at
Elizabeth’s reign (trade/exploration and poor being able to attend undeserving poor (no help needed) English to circumnavigate the globe Roanoke (does not last)
the rising population) Strong opposition to theatre from the Workhouses set up to provide support 1581: Drake knighted by Elizabeth 1592: Raleigh banned from court for
Gentry keen to demonstrate their new London Authorities and the puritans 1601: Poor Law introduced; turning Frequent attacks and raids on Spanish secretly marrying one of Elizabeth’s
wealth; Bess of Hardwick for example. Actors performed for Elizabeth at court. point in attitudes/help for the poor. ships; Cadiz in 1587. ladies-in-waiting.
3. Troubles at home and abroad
Religious settlement Puritanism Catholic threat Mary, Queen of Scots Spanish Armada
Elizabeth inherited a country divided Extremely strict Protestants 1568: seminary set up in Netherlands 1568: Elizabeth’s Catholic cousin and 1588: Armada launched by Philip in
and scarred by religious tension Wanted rid of all Catholic features; to train priests who would come to heir to the throne, exiled to England response to Mary’s execution
1559: Elizabeth embraced features of opposed religious settlement England to convert Protestants 1569: Northern Rebellion; northern Spanish forces sailed to Calais to collect
both Protestantism and Catholicism Dudley and Walsingham were puritans 1570: Pope Pius V issued the Papal Bull Earls try to put Mary on the throne. Dutch soldiers; attacked by Drake who
Elizabeth made herself head of the Edmund Grindal, Archbishop of that excommunicated Elizabeth; he did 1571: Ridolfi Plot; as above used fireships to split up the armada
Church in English; all church services Canterbury, sacked by Elizabeth for this encourage rebellions in England 1583: Throckmorton Plot; as above Battle of Gravelines; 5 ships destroyed
and texts had to be in English encouraging prophesyings Jesuit missionary priests arrived in 1580 1586: Babington Plot; as above, but The wind blew the Spanish around
Catholic practices banned in public Replaced by John Whitgift; cracked 1581: Recusancy fines increased Walsingham proves Mary’s involvement England; shipwrecks and starvation
Allowed private Catholic worship. down on Puritanism. 1585: All Catholic priests exiled. 1587: Mary executed. Spanish ships and leadership inferior.
You might also like
- Factsheet Tudordynasty PDFDocument1 pageFactsheet Tudordynasty PDFveronicaNo ratings yet
- Major Elizabethan Authors and Their WorksDocument1 pageMajor Elizabethan Authors and Their WorksAkad NikaNo ratings yet
- Tudor Stuart DynastyDocument8 pagesTudor Stuart DynastyAlessandra ViscaNo ratings yet
- WL Hu 1682679641 The Elizabethan Age 1558 1603 Timeline - Ver - 3Document3 pagesWL Hu 1682679641 The Elizabethan Age 1558 1603 Timeline - Ver - 3Hafiz ShemeerNo ratings yet
- McPherson Full TextDocument852 pagesMcPherson Full TextMohamed HusseinNo ratings yet
- The Dutch RevoltDocument1 pageThe Dutch RevoltChristine AghaNo ratings yet
- British Rule-FlowchartDocument1 pageBritish Rule-Flowchartଖପର ପଦା ଜନତାNo ratings yet
- American Historical TimelineDocument7 pagesAmerican Historical TimelineYuh972No ratings yet
- 1509-1745 TimelineDocument2 pages1509-1745 Timelineapi-376873271No ratings yet
- Elizabethan Authors & Major WorksDocument2 pagesElizabethan Authors & Major WorksAkad NikaNo ratings yet
- Elizabethan Periods: John Lily (1554-1906)Document2 pagesElizabethan Periods: John Lily (1554-1906)Akad NikaNo ratings yet
- Lec 4Document73 pagesLec 4api-420810768No ratings yet
- Life Experience of Francis BaconDocument13 pagesLife Experience of Francis BaconZXF ZXFNo ratings yet
- Cutthroat Year Amuse-Bouche Amuse-Douche Amuse-GueuleDocument33 pagesCutthroat Year Amuse-Bouche Amuse-Douche Amuse-Gueulemanuel.grisaceoNo ratings yet
- Lista Exhaustiva: Louis PhilippeDocument1 pageLista Exhaustiva: Louis PhilippelepetitebeureNo ratings yet
- Wuolah Free CULTURA T4Document17 pagesWuolah Free CULTURA T4Thalia SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Villagra Camila .Timeline From James I To Charles IDocument11 pagesVillagra Camila .Timeline From James I To Charles ICamilaNo ratings yet
- JSBL MapDocument2 pagesJSBL Mapapi-334280935No ratings yet
- Mapa Kompozitora PDFDocument1 pageMapa Kompozitora PDFkucicaucvecuNo ratings yet
- American Colonies ChartDocument3 pagesAmerican Colonies Chartrosie100% (2)
- UNIT 5 SummaryDocument8 pagesUNIT 5 SummarypistolillaNo ratings yet
- Weekly Timesheet for Advent Electric IncDocument1 pageWeekly Timesheet for Advent Electric IncJeremy ProffittNo ratings yet
- ARC 110x: The Meaning of Rome Timeline of Events - The 1500sDocument3 pagesARC 110x: The Meaning of Rome Timeline of Events - The 1500sarabianddrumsNo ratings yet
- House of Hesse Family Tree: Kaarle IDocument1 pageHouse of Hesse Family Tree: Kaarle IZiggy MordovicioNo ratings yet
- Family Tree of British MonarchsDocument4 pagesFamily Tree of British Monarchsvictoria.melliadoNo ratings yet
- Book1Document20 pagesBook1Valerixal PlayzzNo ratings yet
- Unit 2. British History TimelineDocument2 pagesUnit 2. British History Timeline21Nguyễn Đặng Hoàng My12A6NTTNo ratings yet
- Falmouth Coaster TimetableDocument2 pagesFalmouth Coaster TimetableJoshua RaynerNo ratings yet
- 04 StuartsDocument14 pages04 StuartsDanae Fernanda Cerda RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Share Prices8 PDFDocument1 pageShare Prices8 PDFKyler GreenwayNo ratings yet
- American History TimelineDocument2 pagesAmerican History TimelineDiego Acevedo100% (1)
- List of Prime Ministers of The United Kingdom - WDocument2 pagesList of Prime Ministers of The United Kingdom - WcomputerqwertyNo ratings yet
- Elizabeth I Life and ReignDocument21 pagesElizabeth I Life and ReignAurelian PetreaNo ratings yet
- 2011 and 2012 FOOTBALL DIVISIONS: Central RegionDocument4 pages2011 and 2012 FOOTBALL DIVISIONS: Central Regionesherryva67No ratings yet
- War of The Three Kingdoms (1639-51) : TH TH THDocument3 pagesWar of The Three Kingdoms (1639-51) : TH TH THShannonSmithNo ratings yet
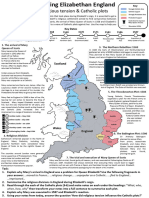
- Eliz England MapDocument2 pagesEliz England MapMorgan DitchburnNo ratings yet
- Seneca - Learn 2x FasterDocument1 pageSeneca - Learn 2x FasterLayla JNo ratings yet
- 17th CenturyDocument1 page17th CenturyNICCOLO' FERRERANo ratings yet
- The Story of England (History Arts Ebook)Document234 pagesThe Story of England (History Arts Ebook)Maria Adam100% (1)
- The Puritan AgeDocument33 pagesThe Puritan AgeNinna NannaNo ratings yet
- Spains Empire and European AbsolutismDocument7 pagesSpains Empire and European AbsolutismGERMAINE JOY TUBIDNo ratings yet
- Major Writers of The Elizabethan PeriodDocument7 pagesMajor Writers of The Elizabethan PeriodArindam SenNo ratings yet
- The Life and Reign of Queen Elizabeth IDocument2 pagesThe Life and Reign of Queen Elizabeth Iyassine madaniNo ratings yet
- Elizabeth 1603Document11 pagesElizabeth 1603belitobelitoNo ratings yet
- Historical Romance Novels - Historical Fiction RomanceDocument2 pagesHistorical Romance Novels - Historical Fiction RomanceJo0% (1)
- He Spanish Armada of ... 1597?: Short FeatureDocument3 pagesHe Spanish Armada of ... 1597?: Short FeaturemendesNo ratings yet
- Polygar War - (1795 - 1805) - 14221858 - 2023 - 12 - 07 - 13 - 13Document2 pagesPolygar War - (1795 - 1805) - 14221858 - 2023 - 12 - 07 - 13 - 13deekshaa685No ratings yet
- II. A Short History of The MonarchyDocument1 pageII. A Short History of The Monarchydi raimondoNo ratings yet
- Lee-Kay-Unwin Family Tree 22 September 2012: Frederick Henry Lee b.1922Document1 pageLee-Kay-Unwin Family Tree 22 September 2012: Frederick Henry Lee b.1922dave leeNo ratings yet
- The Children S Encyclopedia Vol3Document655 pagesThe Children S Encyclopedia Vol3WellingtonNo ratings yet
- List of Dukedoms in The Peerages of Britain and Ireland (Wikipedia)Document18 pagesList of Dukedoms in The Peerages of Britain and Ireland (Wikipedia)Kappa NanpaNo ratings yet
- Elizabethan EraDocument27 pagesElizabethan EraMaria Glaiza BartolomeNo ratings yet
- Timeline of Francis Bacon: 1617-March 7, MadeDocument1 pageTimeline of Francis Bacon: 1617-March 7, MadeJULIUS L. LEVENNo ratings yet
- Jacobean Era: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument4 pagesJacobean Era: Jump To Navigation Jump To Searchcalypso greyNo ratings yet
- Indian History Timeline 1500-1900Document15 pagesIndian History Timeline 1500-1900ayushNo ratings yet
- European Monarchs TimelineDocument5 pagesEuropean Monarchs TimelineJames FodorNo ratings yet
- 22Document1 page22张。。No ratings yet
- ArenbergDocument3 pagesArenbergRomano AccardoNo ratings yet
- Bully Kutta Price and DetailsDocument4 pagesBully Kutta Price and DetailsDr Dogs 4 UNo ratings yet
- Grammar rules and prefixes for nouns, verbs and adjectivesDocument22 pagesGrammar rules and prefixes for nouns, verbs and adjectivesNguyen Kieu GiangNo ratings yet
- MIDTERM QUIZ 2 - Attempt ReviewDocument5 pagesMIDTERM QUIZ 2 - Attempt ReviewAshnesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Concept of Professional Ethics and BioethicsDocument21 pagesConcept of Professional Ethics and BioethicsTina TalmadgeNo ratings yet
- Constitutional Validity of Citizenship Amendment Act 2019Document3 pagesConstitutional Validity of Citizenship Amendment Act 2019Pratibha DixitNo ratings yet
- ARB Inclusion/Exclusion RulesDocument14 pagesARB Inclusion/Exclusion RulesanneNo ratings yet
- Finding the Common Point of Convex SetsDocument18 pagesFinding the Common Point of Convex SetsAditya PillaiNo ratings yet
- Lal Bahadur ShastriDocument17 pagesLal Bahadur Shastribhaskar124970No ratings yet
- SPE67756 - BHI - Innovations in Reservoir NavigationDocument10 pagesSPE67756 - BHI - Innovations in Reservoir NavigationDivine SomiariNo ratings yet
- Day 4Document3 pagesDay 4Elizer Tabil TabugaderNo ratings yet
- Scientific Theological Aspects of GeocentricityDocument222 pagesScientific Theological Aspects of GeocentricityAdi Dumitru100% (1)
- Argumentative Essay - Sample 2 - Students Should Spend Less Time Listening To MusicDocument2 pagesArgumentative Essay - Sample 2 - Students Should Spend Less Time Listening To MusicRidhwan AfiffNo ratings yet
- 10th MICROCURRICULAR - PLANNING PROJECT 1Document7 pages10th MICROCURRICULAR - PLANNING PROJECT 1Vinicio Marcelo ChicaizaNo ratings yet
- Bayan Ko anthem of opposition to Aquino regimeDocument2 pagesBayan Ko anthem of opposition to Aquino regimemicaela vergara67% (3)
- List of 400 English Synonyms & Antonyms - Practice To Beat Competition PDFDocument18 pagesList of 400 English Synonyms & Antonyms - Practice To Beat Competition PDFSaket SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Cylindrical Rectangular Microstrip Antennas Using Slot CouplingDocument6 pagesCylindrical Rectangular Microstrip Antennas Using Slot CouplingSumanta KunduNo ratings yet
- Harivamsa, Constituted Text With Star Passages Plain Text VersionDocument448 pagesHarivamsa, Constituted Text With Star Passages Plain Text VersionZaytsev HvostNo ratings yet
- Mutuum CommodatumDocument12 pagesMutuum CommodatumArceli MarallagNo ratings yet
- Friedan Explores "Problem With No NameDocument13 pagesFriedan Explores "Problem With No NameRoxana Daniela AjderNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan: Video Clip On Paradox of LifeDocument2 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan: Video Clip On Paradox of LifeFLOREVIL BASAYNo ratings yet
- NIH Public Access: Sleep and Women's HealthDocument31 pagesNIH Public Access: Sleep and Women's HealthHusni FaridNo ratings yet
- James Et Al-2017-Earth Surface Processes and LandformsDocument20 pagesJames Et Al-2017-Earth Surface Processes and Landformsqwerrty1029384756No ratings yet
- Harry Potter and The Voices of Our Actions: Prepared by Mr. Benedict B. DiazDocument42 pagesHarry Potter and The Voices of Our Actions: Prepared by Mr. Benedict B. DiazBen0% (1)
- Scanners Accurrcy PDFDocument73 pagesScanners Accurrcy PDFdanielcorrea999No ratings yet
- ĐỀ 15Document7 pagesĐỀ 15DistressNo ratings yet
- Access NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Chapter 14 - UpDocument5 pagesAccess NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Chapter 14 - UpKamjith PadinjareveeduNo ratings yet
- Cs504-Midterm Solved Subjective With Refrences by Moaaz PDFDocument14 pagesCs504-Midterm Solved Subjective With Refrences by Moaaz PDFSijjusha100% (1)
- ElectrodynamicsDocument4 pagesElectrodynamicsHarold Favian Diaz LeonisNo ratings yet
- Turkmen Language Grammar Guide (Peace Corps)Document86 pagesTurkmen Language Grammar Guide (Peace Corps)asunitaursaNo ratings yet