Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DOCTOR'S ORDERS AND RATIONALE
Uploaded by
Stephen S. Padayhag0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
266 views3 pagesMedications: Hydralazine 5mg IV bolus Lowers blood pressure and allows blood to flow more easily now then refer to NOD then q6h PRN for DBP >= 110 mm Hg MgSO4 administered intravenously is indicated to control life-threatening convulsions in the treatment of severe toxemias (preeclampsia) in pregnancy.
Original Description:
Original Title
Doctor's Order
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMedications: Hydralazine 5mg IV bolus Lowers blood pressure and allows blood to flow more easily now then refer to NOD then q6h PRN for DBP >= 110 mm Hg MgSO4 administered intravenously is indicated to control life-threatening convulsions in the treatment of severe toxemias (preeclampsia) in pregnancy.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
266 views3 pagesDOCTOR'S ORDERS AND RATIONALE
Uploaded by
Stephen S. PadayhagMedications: Hydralazine 5mg IV bolus Lowers blood pressure and allows blood to flow more easily now then refer to NOD then q6h PRN for DBP >= 110 mm Hg MgSO4 administered intravenously is indicated to control life-threatening convulsions in the treatment of severe toxemias (preeclampsia) in pregnancy.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
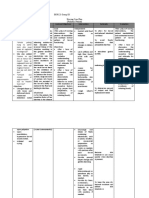
DOCTOR’S ORDER WITH RATIONALE
DATE ORDER RATIONALE
8-9-10 Diet: NPO temporary Maintaining NPO status aids
Monday except medication in resting the GI tract from
11:50pm paralysis caused by
anesthesia.
Laboratory: Complete blood count is the
CBC, UA, Creatinine, NA, determination of the quantity of
K, BT, BS, HSAG, ECG, each type of each blood cell in
Chest X-ray, Uric Acid. a given specimen blood. Urine
analysis is helpful in the
detection of renal or metabolic
disorders and in detecting
disorders in other parts of the
body such as metabolic or
endocrinic abnormalities in
which the kidneys function
normally. Measuring serum
creatinine is used to indicate
renal function. Other laboratory
results are also significant in
determining the possible cause
of disease.
Medications:
Hydralazine 5mg IV bolus Lowers blood pressure and
now then repeat BP after allows blood to flow more easily
30 minutes and refer to through the veins and arteries.
NOD then q6h PRN for
DBP ≥ 110 mm Hg
MgSO₄ a LD: 4mg IVTT MgSO₄ administered
very slowly then maintain intravenously is indicated to
5gms deep IM alternate control life-threatening
buttocks q6 x 4 doses convulsions in the treatment of
severe toxemias (pre-
eclampsia) in pregnancy.
Alternate administration in
buttocks will promote proper
absorption of medication.
Monitor Vital Sign SBP, Monitoring at a regular
FHT q15minutes interval, the changes in
condition and note progress
can be evaluated through vital
signs and BP
O₂ inhalation at 5L/min Short-term supplementary
via nasal cannula oxygen may increase oxidative
stress and inflammation within
the airways.
8-10-10 DAT This particular diet is only
Tuesday given when client is either fully
(8am) awake or can now tolerate any
food she desires that is
nutritious, if this will not lead to
any complications and if the
client needs further monitoring
for lab test.
Vital Signs q15mins then Monitoring at a regular
for q4h if stable interval, the changes in
condition and note progress
can be evaluated through vital
signs and BP
Infuse oxytocin 10’0’ IVF To stimulate breasts to
regulated @30 gtts/min produce breastmilk and
promote pair bonding between
the baby and the mother.
Medication:
Cefalexin 500mg TID PO To stop or slow the growth of
bacterial cells that can cause
genitourinary tract infections.
Mefenamic acid 500 mg To reduce postpartum pain
TID PO and pain in episiotomy wound
Perineal Care To provide comfort, prevent
skin irritation and break down,
decrease the potential for body
odor and control spread of
infection.
Breast Feeding per To gain more antibodies and
demand nutrition for the baby and to
have better bonding for mother
and infant.
Please refer if profuse To take prompt actions in
bleeding preventing excessive blood
loss.
Input and Output q 8 Continued monitoring is
necessary, to provide means
for evaluating improvement or
deterioration in the clients
status
8-10-10 Transfer to OB1 OB1 is a pathological ward
Tuesday and is transferred for
(1:15pm) observation
IVF D5NSS; run 500 cc To restore lost fluid from
as fast drip then regulated profuse bleeding
@ 30 gtts/min
Continue medications To achieve full treatment
Monitor BP q4h Vital signs monitoring has
lessen because of BP within
normal limts (120/70mmHg)
Encourage breast To gain more antibodies and
feeding nutrition for the baby and to
have better bonding for mother
and infant.
To provide comfort, prevent
Self perineal care skin irritation and break down,
decrease the potential for body
odor and control spread of
infection.
To drain distended urine from
Please attach catheter bladder or provide a line to
collect urine for laboratory
purposes.
Give paracetamol 500 To lessen high body
grms of 4 hrs PRN for fever temperature to normal limits
Give furosemide 40 mg Furosemide is indicated to
IVTT now (STAT) remove excess water and slat
from the body (edema) and
treat hypertension.
You might also like
- Doctor's OrdersDocument6 pagesDoctor's OrdersKryza Dale Bunado BaticanNo ratings yet
- Choledolithiasis Cs 103 1Document34 pagesCholedolithiasis Cs 103 1Merlene Sarmiento SalungaNo ratings yet
- NCP of Difficulty of BreathingDocument2 pagesNCP of Difficulty of BreathingMan GatuankoNo ratings yet
- GORDON'S FUNCTIONAL HEALTH PATTERNSDocument3 pagesGORDON'S FUNCTIONAL HEALTH PATTERNSGen RodriguezNo ratings yet
- ASSESSMENTDocument2 pagesASSESSMENTColeen PequitNo ratings yet
- Dr. H. Achmad Fuadi, SPB-KBD, MkesDocument47 pagesDr. H. Achmad Fuadi, SPB-KBD, MkesytreiiaaNo ratings yet
- Physical Evaluation Checklist For NurseDocument3 pagesPhysical Evaluation Checklist For NurseGiridhar RagavasimhanNo ratings yet
- Description:: Materials/ Equipment NeededDocument6 pagesDescription:: Materials/ Equipment NeededMarc Renz R. ChanNo ratings yet
- Total Abdominal Hysterectomy Bilateral Salpingo Oophorectomy (Tahbso) Nursing Responsibilities Rationale Pre-OperativeDocument4 pagesTotal Abdominal Hysterectomy Bilateral Salpingo Oophorectomy (Tahbso) Nursing Responsibilities Rationale Pre-OperativeMiar QuestNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument40 pagesDrug StudyLyka Milo AvilaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Mechanis M OF ActionDocument9 pagesDrug Study: Mechanis M OF ActionLovely San SebastianNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Domperidone CompressDocument1 pageDrug Study Domperidone CompressAngelica TolledoNo ratings yet
- Diet: Bath: ActivityDocument2 pagesDiet: Bath: ActivityKristian Karl Bautista Kiw-isNo ratings yet
- Managing Post-TURP Care for Prostate IssuesDocument13 pagesManaging Post-TURP Care for Prostate IssuesTepperoni0% (1)
- Acute Tonsillopharyngitis Case AnalysisDocument12 pagesAcute Tonsillopharyngitis Case AnalysisLemuel GuevarraNo ratings yet
- Midpoint Reflection Journal ImmersionDocument3 pagesMidpoint Reflection Journal Immersionapi-433144546No ratings yet
- NCM 114 - NCPDocument3 pagesNCM 114 - NCPReysiela Mae ValinoNo ratings yet
- Managing Labor Pain in PregnancyDocument2 pagesManaging Labor Pain in PregnancyJACOB AQUINTEYNo ratings yet
- Javier, Jomar A. BSN121 Group 83 Nursing Care Plan (Pediatric Patient)Document7 pagesJavier, Jomar A. BSN121 Group 83 Nursing Care Plan (Pediatric Patient)Julie AnnNo ratings yet
- MannitolDocument3 pagesMannitolAlexandra AntondyNo ratings yet
- Case Study - Dengue Fever V - S UtiDocument12 pagesCase Study - Dengue Fever V - S UtiHarlene Joyce ReyNo ratings yet
- NCP PTBDocument9 pagesNCP PTBecbarticanNo ratings yet
- CAP Pneumonia CaseDocument46 pagesCAP Pneumonia CaseMatty FelNo ratings yet
- Physical AssessmentDocument4 pagesPhysical AssessmentAj Ann VillapazNo ratings yet
- Post C-Section Delivery Care PlanDocument5 pagesPost C-Section Delivery Care Planᒙᕧᖇᕦᙏᖻ ᗴᔛᓦᗩᖆᗩNo ratings yet
- Declaration of Helsinki: History & Summary: LessonDocument3 pagesDeclaration of Helsinki: History & Summary: LessonMelodia Turqueza GandezaNo ratings yet
- Week 3. COURSE TASK - Acute PancreatitisDocument3 pagesWeek 3. COURSE TASK - Acute PancreatitisqwertNo ratings yet
- Discharge Discharge Summary AlzheimerDocument10 pagesDischarge Discharge Summary Alzheimermp1757No ratings yet
- Physical Assessment AGE With Diarrhea FINALDocument5 pagesPhysical Assessment AGE With Diarrhea FINALMiggy MiggyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management of Common IV DrugsDocument6 pagesNursing Management of Common IV DrugsStephanie Dellera AgdanNo ratings yet
- Nursing care plans for schizophrenia symptoms and interventionsDocument6 pagesNursing care plans for schizophrenia symptoms and interventionsMarius Clifford BilledoNo ratings yet
- KAren LFD ManangoDocument2 pagesKAren LFD ManangoKaren Joyce Costales MagtanongNo ratings yet
- SOAPIE and FDAR DocumentationDocument3 pagesSOAPIE and FDAR DocumentationDanna Kim AuxteroNo ratings yet
- SabutamolDocument1 pageSabutamolKathzkaMaeAgcaoiliNo ratings yet
- Which It Is A Process Whereby Pancreatic Enzymes Destroy Its Own Tissue Leading ToDocument8 pagesWhich It Is A Process Whereby Pancreatic Enzymes Destroy Its Own Tissue Leading ToAriane-Gay Cristobal DuranNo ratings yet
- NCP & Drug Study (Tondo Med)Document5 pagesNCP & Drug Study (Tondo Med)Kevin_Remollo_2431No ratings yet
- Cefuroxime, Celecoxib, ChloridineDocument2 pagesCefuroxime, Celecoxib, ChloridinekrizzywhizzyNo ratings yet
- RRS at RRLDocument19 pagesRRS at RRLNicole MangosanNo ratings yet
- CYSTOCLYSISDocument1 pageCYSTOCLYSISzerpthederpNo ratings yet
- Nursing responsibilities for ampicillinDocument3 pagesNursing responsibilities for ampicillinCharlene Serino JavierNo ratings yet
- Nursing Prognosis Criteria DocumentDocument3 pagesNursing Prognosis Criteria DocumentJaye DangoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Physical AssessmentDocument5 pagesNursing Physical AssessmentApril Louise PaluganNo ratings yet
- Avandia RosiglitazoneDocument1 pageAvandia RosiglitazoneCassieNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindications Side Effects/Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationDocument5 pagesDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindications Side Effects/Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationWyeth Earl Padar EndrianoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyJohn Ronald P. RamosNo ratings yet
- Zocor (Simvastatin)Document3 pagesZocor (Simvastatin)E100% (1)
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument5 pagesIneffective Tissue PerfusionKryza Dale Bunado BaticanNo ratings yet
- Nursing responsibilities for generic medicationsDocument6 pagesNursing responsibilities for generic medicationsAngelito LeritNo ratings yet
- Propranolol 1 PresentationDocument17 pagesPropranolol 1 Presentationapi-284092317100% (1)
- Proper home visit proceduresDocument2 pagesProper home visit procedureslea mae andoloyNo ratings yet
- Dynastat: What Is in This LeafletDocument4 pagesDynastat: What Is in This LeafletBenj GilbuenaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Drug StudyDocument12 pagesNursing Drug StudyJoshkorro Geronimo100% (2)
- Assess The Knowledge and Attitude On Prevention of Dengue Among The Patients AttendantsDocument6 pagesAssess The Knowledge and Attitude On Prevention of Dengue Among The Patients AttendantsIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan EportfolioDocument14 pagesNursing Care Plan Eportfolioapi-279212367No ratings yet
- Pneumonia PathoDocument2 pagesPneumonia PathoDerick Nyl PascualNo ratings yet
- Doctors Progress Note - Module 5Document4 pagesDoctors Progress Note - Module 5adrian nakilaNo ratings yet
- CASE STUDY PPT Group1 - Revised WithoutvideoDocument34 pagesCASE STUDY PPT Group1 - Revised WithoutvideoSamantha BolanteNo ratings yet
- FaciitisDocument17 pagesFaciitisdalaginding clophNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 1Document1 pageNursing Care Plan 1Janhabi BeheraNo ratings yet
- Cholecystitis CSDocument24 pagesCholecystitis CSMASII100% (1)
- Preeclampsia Disease Process and ComplicationsDocument5 pagesPreeclampsia Disease Process and ComplicationsStephen S. PadayhagNo ratings yet
- Anatomy&PhysiologyDocument5 pagesAnatomy&PhysiologyStephen S. PadayhagNo ratings yet
- Anatomy&PhysiologyDocument5 pagesAnatomy&PhysiologyStephen S. PadayhagNo ratings yet
- Anatomy&PhysiologyDocument5 pagesAnatomy&PhysiologyStephen S. PadayhagNo ratings yet
- Anatomy&PhysiologyDocument5 pagesAnatomy&PhysiologyStephen S. PadayhagNo ratings yet
- Causes: Hemorrhoids (Document14 pagesCauses: Hemorrhoids (Stephen S. PadayhagNo ratings yet
- Cannabis Use and Disorder - Epidemiology, Comorbidity, Health Consequences, and Medico-Legal Status - UpToDateDocument34 pagesCannabis Use and Disorder - Epidemiology, Comorbidity, Health Consequences, and Medico-Legal Status - UpToDateAnonymous kvI7zBNNo ratings yet
- Dystocia - Case ReportDocument51 pagesDystocia - Case ReportPaijo SusenoNo ratings yet
- Radiology Report-R5016547Document4 pagesRadiology Report-R5016547Rajeev SNo ratings yet
- Antibióticos para La Neumonía Asociada Al Ventilador.Document96 pagesAntibióticos para La Neumonía Asociada Al Ventilador.Julio GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Sleep: Michael Schupp MD FRCA Christopher D Hanning MD FRCADocument6 pagesPhysiology of Sleep: Michael Schupp MD FRCA Christopher D Hanning MD FRCArichie_ciandraNo ratings yet
- F7.6 Seafarers Medical Examination-CertificateDocument7 pagesF7.6 Seafarers Medical Examination-CertificateHerbert Maganga100% (1)
- Ranula: A Review of LiteratureDocument6 pagesRanula: A Review of LiteratureNicco MarantsonNo ratings yet
- Medicinal Properties of GarlicDocument7 pagesMedicinal Properties of GarlicFawzia Haznah Nurul Imani0% (1)
- 3rd Periodical Grade 10Document3 pages3rd Periodical Grade 10diomedescolar.13No ratings yet
- Sermon On Spirituality & Mental Illness by Rev Laura MancusoDocument12 pagesSermon On Spirituality & Mental Illness by Rev Laura MancusoRev. Laura L. MancusoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Herbs That Clear HeatDocument159 pagesChapter 2 Herbs That Clear HeatCarleta Stan100% (1)
- Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2Document31 pagesSevere Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2Ian VillacrusisNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Community Health Nursing ExposureDocument33 pagesIntroduction To Community Health Nursing ExposureRay LaderaNo ratings yet
- Blastomycosis: Narendra Shanmugam Group 22Document17 pagesBlastomycosis: Narendra Shanmugam Group 22Naren ShanNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmic Drops 101Document9 pagesOphthalmic Drops 101David NgNo ratings yet
- Baterial & Fungal Corneal UlcersDocument28 pagesBaterial & Fungal Corneal UlcersVasishta NadellaNo ratings yet
- Borderline Personality Disorder, Bipolar Disorder, Depression, Attention ... Narcissistic Personality Disorder, Diferential Diagnostic, KernbergDocument23 pagesBorderline Personality Disorder, Bipolar Disorder, Depression, Attention ... Narcissistic Personality Disorder, Diferential Diagnostic, KernbergjuaromerNo ratings yet
- SEMINAR-Clinical Microbiology: Topic-Human Immuno-Deficiency Virus (HIV)Document54 pagesSEMINAR-Clinical Microbiology: Topic-Human Immuno-Deficiency Virus (HIV)sushant_dharNo ratings yet
- Faecal AnalysisDocument83 pagesFaecal AnalysisJoseph SabidoNo ratings yet
- Biochem SGD 3Document4 pagesBiochem SGD 3Hemanth KokaNo ratings yet
- Comparison and Summary of Types of ArthritisDocument2 pagesComparison and Summary of Types of ArthritisShaz Chindhy50% (2)
- Interstitial Cystitis (Painful Bladder Syndrome) - Causes & TreatmentDocument12 pagesInterstitial Cystitis (Painful Bladder Syndrome) - Causes & TreatmentJimmy GillNo ratings yet
- Science Learning Sheet 1 RESPIRATORY SYSTEMDocument3 pagesScience Learning Sheet 1 RESPIRATORY SYSTEMexelainedivineNo ratings yet
- 03 Biosecurity Jit PPT FinalDocument20 pages03 Biosecurity Jit PPT FinalReza WratsongkoNo ratings yet
- Cement CSRDocument35 pagesCement CSRKasak Gupta100% (1)
- 15 Immunogenetics-89402Document34 pages15 Immunogenetics-89402SunuNo ratings yet
- Pteridophytes MorphologyDocument79 pagesPteridophytes MorphologyBoopathiAyyanarMNo ratings yet
- Transfusion-Related Acute Lung Injury: HistoryDocument20 pagesTransfusion-Related Acute Lung Injury: HistoryBladimir CentenoNo ratings yet
- Colposcopic Findings Prepubertal Assessed For Sexual Abuse: Genital GirlsDocument5 pagesColposcopic Findings Prepubertal Assessed For Sexual Abuse: Genital GirlsSusi PuspitaNo ratings yet
- New Drugs 2014-2018Document31 pagesNew Drugs 2014-2018Prem Goel0% (1)