0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views2 pagesUnderstanding UTI and Renal Issues
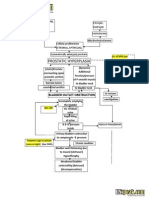
This document summarizes the pathophysiology of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). It outlines that the genitourinary system, particularly the prostate gland, can be affected by age, sex hormones, and other factors which cause the prostate to compress the urethra. This obstruction of the urethra results in an overdistended bladder, urinary retention, and dilated kidneys. The clinical manifestations include symptoms like oliguria, dribbling urine, nocturia, and difficulty voiding. Laboratory and radiological findings can help diagnose BPH.
Uploaded by
Vanah DomingoCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views2 pagesUnderstanding UTI and Renal Issues
This document summarizes the pathophysiology of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). It outlines that the genitourinary system, particularly the prostate gland, can be affected by age, sex hormones, and other factors which cause the prostate to compress the urethra. This obstruction of the urethra results in an overdistended bladder, urinary retention, and dilated kidneys. The clinical manifestations include symptoms like oliguria, dribbling urine, nocturia, and difficulty voiding. Laboratory and radiological findings can help diagnose BPH.
Uploaded by
Vanah DomingoCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd