0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views2 pagesLangmuir and Freundlich Isotherm Analysis
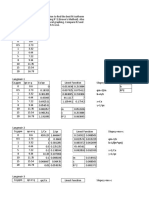
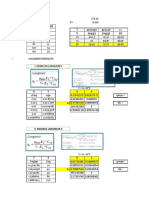
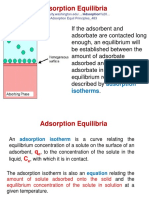
The document contains data for Ci (initial concentration) and Ce (equilibrium concentration) values. It then plots the Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm models from the data. For the Langmuir model, it calculates the maximum monolayer capacity qm as 39.0625 mg/g and the Langmuir constant KL as 0.21 L/mg. For the Freundlich model, it calculates the Freundlich constant KF as 27.233 and the heterogeneity factor n as 15.822. It determines that the Langmuir model fits the data better based on its regression coefficient being closer to 1.
Uploaded by
Maharghya BiswasCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views2 pagesLangmuir and Freundlich Isotherm Analysis
The document contains data for Ci (initial concentration) and Ce (equilibrium concentration) values. It then plots the Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm models from the data. For the Langmuir model, it calculates the maximum monolayer capacity qm as 39.0625 mg/g and the Langmuir constant KL as 0.21 L/mg. For the Freundlich model, it calculates the Freundlich constant KF as 27.233 and the heterogeneity factor n as 15.822. It determines that the Langmuir model fits the data better based on its regression coefficient being closer to 1.
Uploaded by
Maharghya BiswasCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd