0% found this document useful (0 votes)
96 views20 pagesEE-940 Advanced RF Measurements
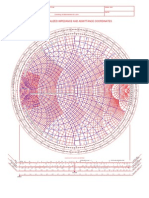
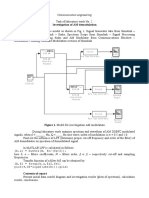
This document provides an overview of topics to be covered in the EE-940 Advanced RF Measurements course offered in Spring 2018. The 3-credit course will be taught by Dr. Nosherwan Shoaib and cover fundamental RF concepts including Fourier series and transforms, mixers, S-parameters, multi-port networks, and antennas. Specific topics that will be discussed include representing periodic signals using Fourier series, the spectrum of trapezoidal waveforms, bandwidth of digital waveforms, using the Fourier transform to represent non-periodic waveforms, and an introduction to mixers, S-parameters, multi-port networks, and antennas.
Uploaded by
chinchouCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
96 views20 pagesEE-940 Advanced RF Measurements
This document provides an overview of topics to be covered in the EE-940 Advanced RF Measurements course offered in Spring 2018. The 3-credit course will be taught by Dr. Nosherwan Shoaib and cover fundamental RF concepts including Fourier series and transforms, mixers, S-parameters, multi-port networks, and antennas. Specific topics that will be discussed include representing periodic signals using Fourier series, the spectrum of trapezoidal waveforms, bandwidth of digital waveforms, using the Fourier transform to represent non-periodic waveforms, and an introduction to mixers, S-parameters, multi-port networks, and antennas.
Uploaded by
chinchouCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 20