Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Admin 601-01 Midterm 2018筆記
Uploaded by
Jen ChangCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Admin 601-01 Midterm 2018筆記
Uploaded by
Jen ChangCopyright:
Available Formats
BI-BS-BM Together we use the concept of statistics, methods of managing supply chain, and information technologies to collect and
analyze data to
help make better business decisions.
PPAR-Plan to apply a tool for the business question. 2. Perform statistical analysis 3. Analyze and evaluate results. 4. Reflect results to gain insights
5. Then, we go back to the first step to plan the next step. Each time we repeat this process, we gain a little more insight, and we repeat it until we
have sufficient results to tell a story.
We take random samples, so they have equal chances of being selected, and we can better estimate their corresponding population parameters.
The central limit theorem is the distribution of sample means approaches a normal pattern as the sample size gets larger
“All models are wrong, some models are useful” Every model is wrong because it’s a simplification of reality. Sometimes, there’s not enough
details to make conclusion, but sometimes they are useful because they help us explain or predict the various components.
Big Data Companies collect personal info, demographic info, and shopping habits from us, through our purchases, internet, mailbox, etc., and build
a big data warehouse. After that, their business analytics analyze the data and predict what we desire to accomplish efficient marketing.
Napoleon he puts many info in one single map, and the map is clear and easy to understand. The map successfully depicted the battle with the
number of soldiers, longitude, latitude, time schedule, temperature, advance and retreat routs, etc. in a 2D graph.
Data dashboards provide at-a-glance views of key performance indicators of an objective or business. It provides visual answers. It must be easy to
read, colored, with numbers and graphics. The data must perform in a right tool to have the data dashboards meaningful.
Nominal: items that are differentiated by a simple naming system. You may have numbers assigned to them, but they are categorical and can’t do
arithmetic with them. Ordinal: the position or the scale of items. It is often defined by assigning numbers to them to show their relative position,
but they are categorical and can’t do arithmetic with them. Continuous: a measurement, a scale which numbers can be compared as multiples of
one another. They measure quantities and can be measured.
Correlation is not Causation.
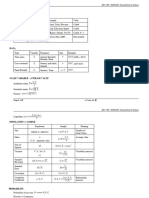
box-plot median=(Q3-Q1)/2 the middle age, middle line in the box. Mean=sum/number, average age, diagram long line. Each quartile contains
about 25% data. IQR the box at the middle, about 50% population. Q3-Q1=IQR=50% ppl age range. Mode=most occurring number. Range=most ppl
lies in this range. Box width=sample number. Outliers=very few exceptional ages. Draw conclusions.
Histogram frequency distribution of xxx. No age under 0. Standard Deviation 誤差 whether the data are close to the average or spread out.
1 1
Popu SD: σ = √ ∑N
i=1(xi − μ)
2 Sample SD: s = √ ∑ni=1(xi − μ)2
N n−1
Mosaic Plot % in col and row. 0 不再上下 95%的機會內
∑(x−x̅)(y−y̅) ̂−y)2
∑(y SSE
Y=β0 (Estimate 下的 intercept)+ b1 (estimate 下的 x)x; b1 = ; b0 =ŷ − b1 x; Stand Error = RMSE = se = √ = √MSE = √
∑(x−x̅)2 n−2 n−2
SSR ∑(y ̅)2
̂−y
R2 = = ;% of variation in y explained by x. How well fit line predicted tips by bills.
SST ̅)2
∑(y−y
(1−R2 )(n−1)
R2a ⅆj =1 − ( ) ; 同上 but more about how useful variable are to model.
n−k−1
Least Square=minimizing the sum of Square Error to find a fit line. RMSE smaller=smaller error
b1 −0
T-test: H0 : β1 = 0 H1 : β1 ≠ 0; β1 = x 旁數字; t = = t-Ratio 數字; t-ratio big, p-value small, Reject H0 , Claiming no rela.
(sb1 )=(Stanⅆarⅆ Error 下的 X)
Betw x & y.
F-test: H0 : β1 = 0 H1 : β1 ≠ 0; F=MSR/MSE=(SSR/1)/(SSE/n-2) = F Ratio 的數字;F 大 p 小, Reject H0 , Claiming no rela. Betw x & y.
Confidence Interval=a range of value, whether 95 % of the CI catches μ population true mean. Why not 5%? Because we’re doing a sample
σ σ
simulation. CI = x̅ ± z0.025 =x̅ ± 1.96 套 standard dev 和 n; z0.025 =1.96; 95%; α = 0.05
√n √n
better alternative of p-values are t-value, z-value, R^2, or you can compare Pvalue with alpha. Direct comparison has its advantages in relativism.
Pvalue indicate how incompatible the data are and don’t measure the probability that the hypothesis is true, it don’t measure an effect or result.
CLT-SD known,distribution of sample mean becomes normal as n gets larger. ŷ = y̅
只在交叉點上 Estimate Std T Ratio Probt
(slop) Error
DF S of S Mean S F-Ratio Intercept b0 / =
Model K SSR MSR MSR/MSE X1 x1 / =
X2 x2 / =
Error n-(k+1) SSE MSE=SSE/n-(k+1) Prob>F
C Total n-1 SST <.0001
n n n
SST=SSR+SSE=∑i=1(yi − y̅)2 = ∑i=1(yi − ŷ)2 + ∑i=1(ŷi − y̅)2 ŷ=b0 + b, x1 + b2 x2 + b3 x3
You might also like
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Simple Linear RegressionDocument5 pagesSimple Linear RegressionLincolnNo ratings yet
- Stat 5002 Final Exam Formulas W 21Document7 pagesStat 5002 Final Exam Formulas W 21PaolaCastelwhiteNo ratings yet
- Δ f f Δ f f: Median=L+ n f f XiDocument3 pagesΔ f f Δ f f: Median=L+ n f f XiAshekin MahadiNo ratings yet
- Regression Midterm SheetDocument10 pagesRegression Midterm SheetEllianna BrandelNo ratings yet
- Statistics - Dispersion - Week 4Document4 pagesStatistics - Dispersion - Week 4Austin Capal Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 7 Solution Numerical MethodsDocument12 pagesProblem Set 7 Solution Numerical MethodsAriyan JahanyarNo ratings yet
- 02 EstimationDocument20 pages02 EstimationchebudeNo ratings yet
- K7 Curve FittingDocument36 pagesK7 Curve FittingMuhammad IkramullahNo ratings yet
- Lecture 15 PDFDocument28 pagesLecture 15 PDFĐăng HảiNo ratings yet
- Formulas and Tables For GerstmanDocument10 pagesFormulas and Tables For GerstmanAlex RobertsNo ratings yet
- Corr and RegressDocument30 pagesCorr and RegressgraCENo ratings yet
- Regression AnalysisDocument280 pagesRegression AnalysisA.Benhari100% (1)
- CHP 3 PDFDocument31 pagesCHP 3 PDFRibuNo ratings yet
- Ss-Chapter 12: Sampling: Final and Initial Sample Size DeterminationDocument14 pagesSs-Chapter 12: Sampling: Final and Initial Sample Size Determination1517 Nahin IslamNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Multiple Linear Regression ModelDocument11 pages3.1 Multiple Linear Regression ModelMaria Paola Velasquez RoyNo ratings yet
- Linear RegressionDocument27 pagesLinear RegressionAmit SinghNo ratings yet
- Range SD VarianceDocument8 pagesRange SD VarianceSyed UzairNo ratings yet
- Chapter FourDocument21 pagesChapter Fourbeshahashenafe20No ratings yet
- Regression - Miembro, Jomin Dennis M.Document17 pagesRegression - Miembro, Jomin Dennis M.Jomin Dennis MiembroNo ratings yet
- mcd1110 Sample Test 2b 2012 02Document19 pagesmcd1110 Sample Test 2b 2012 02dharma alexanderNo ratings yet
- Notes 1Document23 pagesNotes 1Daniel Fortes ManoelNo ratings yet
- University of Palestine Gaza Strip Civil Engineering College Numerical Analysis CIVL 3309 Dr. Suhail LubbadDocument19 pagesUniversity of Palestine Gaza Strip Civil Engineering College Numerical Analysis CIVL 3309 Dr. Suhail LubbadHazem AlmasryNo ratings yet
- MultivariableRegression SummaryDocument15 pagesMultivariableRegression SummaryAlada manaNo ratings yet
- Maxima and MinimaDocument12 pagesMaxima and MinimaJoey GuarinNo ratings yet
- Reliance JIODocument69 pagesReliance JIOPriyanka KumariNo ratings yet
- ECON1150 Lec 01Document5 pagesECON1150 Lec 01vietthu35No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document67 pagesChapter 3MUHAMMAD IMRAN HAKIM BIN SULAIMAN STUDENTNo ratings yet
- HW 03 SolDocument9 pagesHW 03 SolfdfNo ratings yet
- 120MP Lecture 23 PREDICTION: Model and AssumptionsDocument4 pages120MP Lecture 23 PREDICTION: Model and AssumptionsLexNo ratings yet
- - DC.docx Ii7 y n.3 i Ju吗 你 那 有 44。很 他。。 。 。 1st k8bDocument10 pages- DC.docx Ii7 y n.3 i Ju吗 你 那 有 44。很 他。。 。 。 1st k8bumaima khanNo ratings yet
- Formula StablesDocument29 pagesFormula StablesRobert ChapmanNo ratings yet
- 02data Part2Document34 pages02data Part2baigsalman251No ratings yet
- : µ = 0 vs H: µ 6= 0. Previous work shows that σ = 2. A change in BMI of 1.5 is considered important to detect (if the true effect size is 1.5 or higherDocument5 pages: µ = 0 vs H: µ 6= 0. Previous work shows that σ = 2. A change in BMI of 1.5 is considered important to detect (if the true effect size is 1.5 or higherShreyas SatardekarNo ratings yet
- MAS202 - Assignment 2: Exercise 1Document16 pagesMAS202 - Assignment 2: Exercise 1Tran Thu Hang (K15 HL)No ratings yet
- Presented By:: Moiz Khan Esha Saeed Iqra Rafique Sidra SattarDocument27 pagesPresented By:: Moiz Khan Esha Saeed Iqra Rafique Sidra SattarMoiz khanNo ratings yet
- BN2102 7-10Document24 pagesBN2102 7-10Jiayao HuangNo ratings yet
- Examen Metodos NumericosDocument17 pagesExamen Metodos Numericos阿人个人No ratings yet
- Lecture 11 RegressionDocument53 pagesLecture 11 RegressionKaanNo ratings yet
- Linear RegressionDocument228 pagesLinear Regressionkeyyongpark100% (2)
- Statistics 221 Summary of MaterialDocument5 pagesStatistics 221 Summary of MaterialJames McQueenNo ratings yet
- ML Midsem 2018 SolutionsDocument7 pagesML Midsem 2018 SolutionsAniket VermaNo ratings yet
- StatsDocument2 pagesStatsEmmanuel OppongNo ratings yet
- Csmodel NotesDocument79 pagesCsmodel NotesbrentsoanNo ratings yet
- Range (R) Highest Value Lowest ValueDocument5 pagesRange (R) Highest Value Lowest ValueNor AmirNo ratings yet
- STA101 Formula SheetDocument4 pagesSTA101 Formula SheetConner BiekerNo ratings yet
- Cambridge AS Biology 9700 Practical NotesDocument2 pagesCambridge AS Biology 9700 Practical NotesSafiya Naina100% (1)
- Materi StatistikaDocument16 pagesMateri Statistikashinta chanNo ratings yet
- Stats Formula SheetDocument5 pagesStats Formula Sheetmsmithmail21No ratings yet
- Sampling Distribution & Distribusi Normal: Dr. Sunarjo, DR, MS, MSCDocument15 pagesSampling Distribution & Distribusi Normal: Dr. Sunarjo, DR, MS, MSCslayerfishNo ratings yet
- RegrionDocument19 pagesRegrionBiplove PokhrelNo ratings yet
- Measure of DispersionDocument4 pagesMeasure of DispersionFurqan ShoukatNo ratings yet
- CE304-Unit 5-Lect1-Jumah2018Document10 pagesCE304-Unit 5-Lect1-Jumah2018محمد بركاتNo ratings yet
- Topic 6B RegressionDocument13 pagesTopic 6B RegressionMATHAVAN A L KRISHNANNo ratings yet
- Process Capability: Evaluate The Process From Accuracy of Parts Machine Repeatability Tool Life Program CoolantDocument17 pagesProcess Capability: Evaluate The Process From Accuracy of Parts Machine Repeatability Tool Life Program CoolantAgung KaswadiNo ratings yet
- Unit 6Document8 pagesUnit 6Mahesh GandikotaNo ratings yet
- Linear Regression Analysis For STARDEX: Trend CalculationDocument6 pagesLinear Regression Analysis For STARDEX: Trend CalculationSrinivasu UpparapalliNo ratings yet
- Linear Regression NotesDocument25 pagesLinear Regression NotesAnusha BiswasNo ratings yet
- Assignment7 SolutionsDocument7 pagesAssignment7 SolutionsMicklengeNo ratings yet
- Data Admin 601 Syllabus Spring 2018Document6 pagesData Admin 601 Syllabus Spring 2018Jen ChangNo ratings yet
- Data Driven Decision RegressionDocument3 pagesData Driven Decision RegressionJen ChangNo ratings yet
- Data Driven Decision Hw2Document2 pagesData Driven Decision Hw2Jen ChangNo ratings yet
- Pobability Exercise 1Document2 pagesPobability Exercise 1Jen ChangNo ratings yet
- Assignment Cluster P209#3Document1 pageAssignment Cluster P209#3Jen ChangNo ratings yet
- Final Exam SP '18Document6 pagesFinal Exam SP '18Jen ChangNo ratings yet
- Jackson Electrodynamics, Notes 1Document5 pagesJackson Electrodynamics, Notes 1Tianyi ZhangNo ratings yet
- Inverse Trig Function Dr. Maslan Osman UtmDocument28 pagesInverse Trig Function Dr. Maslan Osman UtmZazliana IzattiNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study Between Experimental and Theoretical Buckling Load For Hollow Steel ColumnDocument7 pagesA Comparative Study Between Experimental and Theoretical Buckling Load For Hollow Steel ColumnSaurabh SahuNo ratings yet
- Original PDF Calculus Concepts and Contexts 4th Edition PDFDocument41 pagesOriginal PDF Calculus Concepts and Contexts 4th Edition PDFbert.roesch92897% (32)
- 1819 SM015 - 1 Solution Latihan Sem1Document15 pages1819 SM015 - 1 Solution Latihan Sem1Suha WzneNo ratings yet
- Top Expected Reasoning Questions For Bank Mains Exams PDFDocument119 pagesTop Expected Reasoning Questions For Bank Mains Exams PDFAdarshKumarNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of MachinesDocument8 pagesMechanics of MachinesSachi MensiNo ratings yet
- Danyal Education: Correct 117.9875 DecimalDocument20 pagesDanyal Education: Correct 117.9875 DecimalbrcraoNo ratings yet
- Cyborgs: The ArchetypeDocument32 pagesCyborgs: The ArchetypeMichał StojeckiNo ratings yet
- Finite Mixture Modelling Model Specification, Estimation & ApplicationDocument11 pagesFinite Mixture Modelling Model Specification, Estimation & ApplicationPepe Garcia EstebezNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Additional Mathematics Chapter 8 Circular MeasureDocument9 pagesForm 4 Additional Mathematics Chapter 8 Circular MeasureManisha Sekaran Muniandy80% (5)
- DicaDocument26 pagesDicaganga_ch1No ratings yet
- Elg 3126Document6 pagesElg 3126Serigne Saliou Mbacke SourangNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesLesson PlanAnn Francis SalonNo ratings yet
- Programming in C PDFDocument177 pagesProgramming in C PDFRameshNo ratings yet
- Course Description CatalogDocument56 pagesCourse Description CatalogstefNo ratings yet
- Khubaib Agha - Add Maths Form IIIDocument7 pagesKhubaib Agha - Add Maths Form IIIKhubaib AghaNo ratings yet
- Demand Estimation & Forecasting: Ninth Edition Ninth EditionDocument17 pagesDemand Estimation & Forecasting: Ninth Edition Ninth EditionRogelio VasquezNo ratings yet
- AWS90 Ch05 ModalDocument24 pagesAWS90 Ch05 ModalCinitha ANo ratings yet
- Teacher's Resource Book 3Document348 pagesTeacher's Resource Book 3Sarim Shah54% (28)
- SIPNAYANDocument4 pagesSIPNAYANApril Jane Buñag SanchezNo ratings yet
- Human Movement Science: Paul S. GlazierDocument18 pagesHuman Movement Science: Paul S. GlazierNICOLÁS ANDRÉS AYELEF PARRAGUEZNo ratings yet
- Normalization A Preprocessing StageDocument5 pagesNormalization A Preprocessing StageTanzeel HassanNo ratings yet
- FEM AssignmentDocument8 pagesFEM AssignmentVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- Fea Module 1Document56 pagesFea Module 1NAVADE SATISHNo ratings yet
- Apu Carc 03 LMCDocument5 pagesApu Carc 03 LMCRaifKhan0% (3)
- Tractor Systems Controls PDFDocument88 pagesTractor Systems Controls PDFSARGEN SARENNo ratings yet
- Programming QuestionsDocument2 pagesProgramming QuestionsAhmad AhmadNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving & Decision Making (HBO)Document5 pagesProblem Solving & Decision Making (HBO)Leofold Laluna Salas Jr.No ratings yet
- CH5100 Peristaltic FlowDocument21 pagesCH5100 Peristaltic FlowashuiskeshavNo ratings yet