Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EXERCISE
Uploaded by
Fikry FakhrudinOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
EXERCISE
Uploaded by
Fikry FakhrudinCopyright:
Available Formats
EXERCISE
TIME AND COST OPTIMIZATION
UNDERGRADUATE PROGRAM
Day / date : Thursday / October 4th, 2018
Duration : 90 minutes
Lecturer : Cahyono Bintang Nurcahyo, ST, MT
TIME COST TRADE OFF
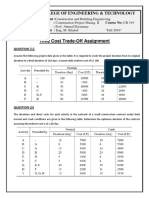
1. The table below provide information on activities, predecessors, normal duration, normal cost, crash duration,
and crash cost for a project.
Activities Predecessors Normal Normal Cost Crash Crash Cost
Duration Duration
(days) (Rp) (days) (Rp)
A - 50 50.000 35 72.500
B A 40 60.000 35 70.000
C A 20 45.000 10 55.000
D B 50 65.000 40 72.500
E C 60 85.000 45 115.000
F D,E 60 70.000 40 80.000
Indirect Cost = Rp 1.000 / day
Example to calculate Cost Slope for A is (72.500-50.000)/(50-35) = Rp1.500/day
a. Draw a network diagram from the preceding information, then define the critical path !
b. Calculate cost slope for each activity !
c. Use the information contained above to compress one time unit per move using the least cost method.
Reduce the schedule until you reach the crash point of the network.
For each move identify what activity(s) was crashed, the adjusted total cost, and explain your choice if
you have to choose between activities that cost the same.
d. Draw a project cost-duration graph !
e. What is the optimum cost-time schedule for the project ?
You might also like
- Earned Value ManagementDocument4 pagesEarned Value ManagementKuntzNo ratings yet
- Navfac 7.1-2005Document391 pagesNavfac 7.1-2005Saed Asiabi100% (1)
- (Project Title) : Earned Value Analysis ReportDocument4 pages(Project Title) : Earned Value Analysis ReportbolsamirNo ratings yet
- Problem 12-2 To 6Document3 pagesProblem 12-2 To 6MYCO PONCE PAQUENo ratings yet
- (Project Title) : Earned Value Analysis ReportDocument4 pages(Project Title) : Earned Value Analysis ReportccemilovaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Cost Behavior and Estimation - With AnswersDocument6 pagesModule 2 - Cost Behavior and Estimation - With AnswersKelvin CulajaráNo ratings yet
- Excel Seminar Break-Even AnalysisDocument6 pagesExcel Seminar Break-Even AnalysisKim CarreraNo ratings yet
- Assignment Time Cost Trade-OffDocument4 pagesAssignment Time Cost Trade-OffASAD ULLAHNo ratings yet
- INdu ASDocument7 pagesINdu ASbelaynehNo ratings yet
- PM Sheet 4Document2 pagesPM Sheet 4Samer TarekNo ratings yet
- Project EBTM3103 Assignment 2Document11 pagesProject EBTM3103 Assignment 2kruban0% (1)
- Project ManagementDocument11 pagesProject ManagementkrubanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 28855Document3 pagesAssignment 4 28855abbiha.mustafamalikNo ratings yet
- Project Management Techniques and SchedulingDocument4 pagesProject Management Techniques and SchedulingAjay MeenaNo ratings yet
- Project Management 2019Document5 pagesProject Management 2019AARTI MaidNo ratings yet
- EXAMINATION I NAME ANALYSISDocument4 pagesEXAMINATION I NAME ANALYSISlolaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 7Document17 pagesAssignment 7Arif AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Generated Through CPM (New Then Crashing)Document14 pagesGenerated Through CPM (New Then Crashing)Aiman BaigNo ratings yet
- Latihan Soal Akuntansi BiayaDocument5 pagesLatihan Soal Akuntansi Biayaaufa alfayedhaNo ratings yet
- discussion5_1Document8 pagesdiscussion5_1diristiNo ratings yet
- Project Crashing Time-Cost Tradeoff AnalysisDocument23 pagesProject Crashing Time-Cost Tradeoff AnalysisPuteri IntanNo ratings yet
- TD - Gestion-De Projet-1Document2 pagesTD - Gestion-De Projet-1Chanten NanNo ratings yet
- Part Two Demand AnalysisDocument9 pagesPart Two Demand AnalysisBrent PogiNo ratings yet
- ST - Mary's University: Department of Marketing ManagementDocument6 pagesST - Mary's University: Department of Marketing ManagementIsrael Ad FernandoNo ratings yet
- Time-Cost TradeoffDocument24 pagesTime-Cost Tradeoffمحمد بركاتNo ratings yet
- IEDA 2010 Assignment 2_Solution (2)Document5 pagesIEDA 2010 Assignment 2_Solution (2)Norris wongNo ratings yet
- Tahun Penjualan Harga A B C A B: Y (Estimasi PJL)Document3 pagesTahun Penjualan Harga A B C A B: Y (Estimasi PJL)Ratna KurniawatiNo ratings yet
- Digital Assignment - Software EngineeringDocument1 pageDigital Assignment - Software EngineeringAvk Aryan Vishant KulshreshthaNo ratings yet
- Personal Task 1 June 1, 2020Document3 pagesPersonal Task 1 June 1, 2020Mohammad NaumanNo ratings yet
- Jawaban Quiz 4 - Investasi Proyek Dan KeuanganDocument5 pagesJawaban Quiz 4 - Investasi Proyek Dan KeuanganAlin SuarliakNo ratings yet
- Critical path analysis and resource levelingDocument4 pagesCritical path analysis and resource levelingstephanieNo ratings yet
- Tarea 9.1 Problemas Evaluación Proyectos 1 Loera CoronadoDocument12 pagesTarea 9.1 Problemas Evaluación Proyectos 1 Loera CoronadoBrandon LoeraNo ratings yet
- Material Budget (RS.)Document6 pagesMaterial Budget (RS.)James WisleyNo ratings yet
- Project Management AssessmentDocument2 pagesProject Management AssessmentChristopher RajkumarNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Laboratory Exercise 1Document10 pagesModule 2 - Laboratory Exercise 1Joana TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Particulars SQ FT Rate Amount (RS)Document4 pagesParticulars SQ FT Rate Amount (RS)deekaayNo ratings yet
- Specialization: - Project Management: Indian School of Management and StudiesDocument7 pagesSpecialization: - Project Management: Indian School of Management and StudiesRiyas PerumbadanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Cashing ProjectDocument2 pagesAssignment 2 Cashing ProjectHernan Ochoa0% (1)
- FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT Assignment 2Document14 pagesFINANCIAL MANAGEMENT Assignment 2dangerous saifNo ratings yet
- Accounts - FIFO and WA For FinalDocument11 pagesAccounts - FIFO and WA For FinalRohan SinghNo ratings yet
- Me 5.4 RMDocument12 pagesMe 5.4 RMPawan NayakNo ratings yet
- SamigroupDocument9 pagesSamigroupsamidan tubeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Investment AppraisalDocument43 pagesIntroduction To Investment AppraisalNURAIN HANIS BINTI ARIFFNo ratings yet
- PMD 913 - Module 4 - A5 EVA ExampleDocument3 pagesPMD 913 - Module 4 - A5 EVA ExampleAbdallah HabeebNo ratings yet
- MS Practice SetsDocument2 pagesMS Practice SetsKindred WolfeNo ratings yet
- 2.94 Exercise Line BalancingDocument3 pages2.94 Exercise Line BalancingJia Xin TanNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Accounting Chapter 12 Lower of Cost and Net Realizable ValueDocument11 pagesIntermediate Accounting Chapter 12 Lower of Cost and Net Realizable ValueBlue SkyNo ratings yet
- Reg No: 189282J Y.A.P.M Yahampath: Calculation of RevenueDocument2 pagesReg No: 189282J Y.A.P.M Yahampath: Calculation of Revenuece badullaNo ratings yet
- PM Practice SumsDocument3 pagesPM Practice Sumstanuj28blrNo ratings yet
- ABS Problems (1-2)Document3 pagesABS Problems (1-2)dewlate abinaNo ratings yet
- Assignment #04 - Time-Cost Optimization Methods and CrashingDocument1 pageAssignment #04 - Time-Cost Optimization Methods and CrashingKaushal KumarNo ratings yet
- (Project Title) : Earned Value Analysis ReportDocument6 pages(Project Title) : Earned Value Analysis Reportpabon90503No ratings yet
- Chapter9 10Document5 pagesChapter9 10Nyan Lynn HtunNo ratings yet
- Alvaro, Fernel Jean C. AE212-1741 TTHS 3-5PM Exercise 8-2. Joint Cost AllocationDocument4 pagesAlvaro, Fernel Jean C. AE212-1741 TTHS 3-5PM Exercise 8-2. Joint Cost AllocationNhel AlvaroNo ratings yet
- Fin Strategy Ass 1Document3 pagesFin Strategy Ass 1mqondisi nkabindeNo ratings yet
- Earned Value ManagementDocument4 pagesEarned Value Management20105167No ratings yet
- Project Management: Network TechniqueDocument5 pagesProject Management: Network TechniqueKAWSER RAFINo ratings yet
- Multiply and Divide by 10, 100, 1000 4444Document2 pagesMultiply and Divide by 10, 100, 1000 4444hazem mohraNo ratings yet
- C B FC 20% A: Debt RatioDocument4 pagesC B FC 20% A: Debt Ratiojohn condesNo ratings yet
- MPK - 03 Pemangku KepentinganDocument16 pagesMPK - 03 Pemangku KepentinganFikry FakhrudinNo ratings yet
- Schedule of Performances and EventsDocument11 pagesSchedule of Performances and EventsFikry FakhrudinNo ratings yet
- Smart Investing Choosing Investment StockDocument31 pagesSmart Investing Choosing Investment StockFikry FakhrudinNo ratings yet
- GayaDocument18 pagesGayaFikry FakhrudinNo ratings yet
- Artificial Ground Freezing in Geotechnical EngineeringDocument12 pagesArtificial Ground Freezing in Geotechnical EngineeringFikry Fakhrudin0% (1)
- CorelDRAW Graphics Suite X7Document1 pageCorelDRAW Graphics Suite X7Fikry FakhrudinNo ratings yet
- Table: Element Forces - Frames Frame Station Outputcase Casetype P V2 V3 TDocument10 pagesTable: Element Forces - Frames Frame Station Outputcase Casetype P V2 V3 TFikry FakhrudinNo ratings yet