Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Thorax
Uploaded by
Hayatul AkmaLia0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pagemnj
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentmnj
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageThorax
Uploaded by
Hayatul AkmaLiamnj
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Background
Cardiogenic pulmonary edema (CPE) is defined as pulmonary edema due to
increased capillary hydrostatic pressure secondary to elevated pulmonary
venous pressure. CPE reflects the accumulation of fluid with a low-protein
content in the lung interstitium and alveoli as a result of cardiac dysfunction
(see the image below). (See Etiology.)
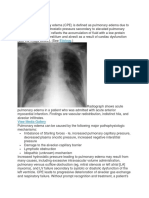
Radiograph shows acute
pulmonary edema in a patient who was admitted with acute anterior
myocardial infarction. Findings are vascular redistribution, indistinct hila, and
alveolar infiltrates.
View Media Gallery
You might also like
- Edema Pulmonar AgudaDocument4 pagesEdema Pulmonar AgudaAna Belén Artero CastañoNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Edema: Moderator - Asso Prof DR Arun Kumar Presentor - DR Kannan GDocument39 pagesPulmonary Edema: Moderator - Asso Prof DR Arun Kumar Presentor - DR Kannan GGrace JasminNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Cardiogenic Pulmonary EdemaDocument13 pagesPathophysiology of Cardiogenic Pulmonary EdemaIrina DuceacNo ratings yet
- Edema Pulmo: Putri Fadhila Nugraheni - 30101507538Document8 pagesEdema Pulmo: Putri Fadhila Nugraheni - 30101507538putriNo ratings yet
- Background: EtiologyDocument5 pagesBackground: Etiologylia lykimNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Edema: Dr. Harsh Pandya R1 Under Guidance of DR - Nipa Nayak M.D. Asso. ProfDocument49 pagesPulmonary Edema: Dr. Harsh Pandya R1 Under Guidance of DR - Nipa Nayak M.D. Asso. ProfKrisno ParammanganNo ratings yet
- Noncardiogenic Pulmonary EdemaDocument12 pagesNoncardiogenic Pulmonary EdemaIrina DuceacNo ratings yet
- PT precautionsDocument2 pagesPT precautionsfarhanah ariffinNo ratings yet
- Acute Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure (AHRF, ARDS) - Critical Care Medicine - MSD Manual Professional EditionDocument11 pagesAcute Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure (AHRF, ARDS) - Critical Care Medicine - MSD Manual Professional Editionpeterpavel112No ratings yet
- Jacobs 2015Document6 pagesJacobs 2015rani tiaraNo ratings yet
- Noncardiogenic Pumonary EdemaDocument15 pagesNoncardiogenic Pumonary EdemaAnonymous OlS0WZwNo ratings yet
- Edema Paru Kardiogenik Akut Kak TiaraDocument8 pagesEdema Paru Kardiogenik Akut Kak TiaraTyara LarisaNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary EdemaDocument20 pagesPulmonary EdemaMohmmad Lateef GanieNo ratings yet
- Sclerodactyly, and Telangiectasis) Syndrome Accompany-: Cor PulmonaleDocument2 pagesSclerodactyly, and Telangiectasis) Syndrome Accompany-: Cor PulmonaledivinaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema - UpToDateDocument14 pagesPathophysiology of Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema - UpToDateStefani AtlleNo ratings yet
- Thorax 1Document9 pagesThorax 1Ferry Ferdiansyah HidayatNo ratings yet
- Management of Pulmonary EdemaDocument42 pagesManagement of Pulmonary Edemaademato4real576No ratings yet
- Acute Interstitial Pulmonary Edema Power Point FixDocument29 pagesAcute Interstitial Pulmonary Edema Power Point FixnandablaguNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema - UpToDateDocument9 pagesPathophysiology of Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema - UpToDateRoberto López MataNo ratings yet
- LI 8 - Differential Diagnosis of Acute Heart FailureDocument11 pagesLI 8 - Differential Diagnosis of Acute Heart Failure19-034 Jefry Junaidi PurbaNo ratings yet
- Acute Pulmonary SovianDocument9 pagesAcute Pulmonary SovianGP KRWNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Edema - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocument7 pagesPulmonary Edema - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfriyanasirNo ratings yet
- ALCALOSIS RESPIRATORIA - VeterinariaDocument8 pagesALCALOSIS RESPIRATORIA - VeterinariaAlanNo ratings yet
- Edema ParuDocument4 pagesEdema ParuSri BayaniNo ratings yet
- Noncardiogenic Pulmonary EdemaDocument19 pagesNoncardiogenic Pulmonary EdemaCláudio CalixtoNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Edema II: Noncardiogenic Pulmonary EdemaDocument31 pagesPulmonary Edema II: Noncardiogenic Pulmonary EdemaGita Helvia SariNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary EmbolismDocument14 pagesPulmonary EmbolismAngel Naypes ReyesNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Edema: Dr. Harsh Pandya R1 Under Guidance of DR - Nipa Nayak M.D. Asso. ProfDocument49 pagesPulmonary Edema: Dr. Harsh Pandya R1 Under Guidance of DR - Nipa Nayak M.D. Asso. ProfSef NengkoNo ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory Failure 1Document7 pagesAcute Respiratory Failure 1Trish 0019No ratings yet
- Pediatric Respiratory Failure: Signs and SymptomsDocument23 pagesPediatric Respiratory Failure: Signs and SymptomsAjp Ryuzaki CaesarNo ratings yet
- 3487 VJXHXVDocument13 pages3487 VJXHXVمحمد عقيليNo ratings yet
- Histo and Anatomy (Lungs) : Capillary PressureDocument1 pageHisto and Anatomy (Lungs) : Capillary PressureAthena BorjaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Failure: Dr. Sat Sharma Univ of ManitobaDocument38 pagesRespiratory Failure: Dr. Sat Sharma Univ of ManitobaGonzalo Venegas RojasNo ratings yet
- Cor PulmonaleDocument14 pagesCor PulmonaleEvangelin MelvinNo ratings yet
- ALCALOSIS RESPIRATORIA - Veterinaria PDFDocument6 pagesALCALOSIS RESPIRATORIA - Veterinaria PDFAlanNo ratings yet
- Presentasi Radiologi Edema ParuDocument19 pagesPresentasi Radiologi Edema ParuFia100% (1)
- Acute Respiratory Distress SyndromeDocument18 pagesAcute Respiratory Distress SyndromeFasiha SamiNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Leukostasis Mimicking Pulmonary Embolism: Case of The MonthDocument4 pagesPulmonary Leukostasis Mimicking Pulmonary Embolism: Case of The MonthkaremiaNo ratings yet
- Acute Pulmonary OdemaDocument9 pagesAcute Pulmonary OdemaAnonymous ysrxggk21cNo ratings yet
- Respiratory FailureDocument39 pagesRespiratory FailureMuntasir BashirNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary EdemaDocument47 pagesPulmonary Edemamaeliszxc kimNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Pulmonary Emergencies: Causes and TreatmentsDocument7 pagesPediatric Pulmonary Emergencies: Causes and TreatmentsLucas AresNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts Pulmonary EdemaDocument24 pagesBasic Concepts Pulmonary EdemaRangga SaputraNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Respiratory FailureDocument6 pagesPathophysiology of Respiratory FailurevidagurlNo ratings yet
- Cor Pulmonale An Overview 2003Document12 pagesCor Pulmonale An Overview 2003Ade Cahyo IslamiNo ratings yet
- LP Edema ParuDocument10 pagesLP Edema ParuRama DeniNo ratings yet
- Under Supervision DR/ Mariam Sabry: Ulmonary DemaDocument28 pagesUnder Supervision DR/ Mariam Sabry: Ulmonary DemaMohamed ElsyaedNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Respiratory FunctionDocument4 pagesAssessment of Respiratory FunctionCristine Dominique E. DonaireNo ratings yet
- Flash Pulmonary EdemaDocument11 pagesFlash Pulmonary EdemaEda SopNo ratings yet
- M V ICU: Echanical Entilation INDocument82 pagesM V ICU: Echanical Entilation INabhilashreddy45No ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis of PULMONARY EDEMADocument3 pagesDifferential Diagnosis of PULMONARY EDEMAHY Hong YiNo ratings yet
- Chest Pain and Dyspnea CausesDocument12 pagesChest Pain and Dyspnea CausesAmi DhaniaNo ratings yet
- Definition of Noncardiogenic Pulmonary Edemanoncardiogenic Pulmonary Edema Is IdentifiedDocument35 pagesDefinition of Noncardiogenic Pulmonary Edemanoncardiogenic Pulmonary Edema Is IdentifiedAya EyadNo ratings yet
- Symptoms and Signs: Pulmonary Edema (American English), or Oedema (Document4 pagesSymptoms and Signs: Pulmonary Edema (American English), or Oedema (contentseeker3401No ratings yet
- Cor PulDocument11 pagesCor PulMariani AniNo ratings yet
- NURS 19 Pulmonary Edema, Hemorrhage, Cardiac Arrest Midterm ExamDocument6 pagesNURS 19 Pulmonary Edema, Hemorrhage, Cardiac Arrest Midterm ExamSN BundleNo ratings yet
- ARDS SLHDocument43 pagesARDS SLHYamto TlNo ratings yet
- ARDSDocument22 pagesARDSELDHOSE RAJUNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Hemorrhage-1Document20 pagesPulmonary Hemorrhage-1ELDHOSE RAJUNo ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory Distress SyndromeDocument36 pagesAcute Respiratory Distress Syndromedr9348345000No ratings yet
- CoronaDocument1 pageCoronaHayatul AkmaLiaNo ratings yet
- Background: Download The PDF For The Full ArticleDocument1 pageBackground: Download The PDF For The Full ArticleHayatul AkmaLiaNo ratings yet
- Managing Acute Pulmonary OedemaDocument8 pagesManaging Acute Pulmonary OedemaHayatul AkmaLiaNo ratings yet
- Corona VirusDocument2 pagesCorona VirusHayatul AkmaLiaNo ratings yet
- Ileus and Bowel Obstruction Guide for Cancer PatientsDocument5 pagesIleus and Bowel Obstruction Guide for Cancer PatientsHayatul AkmaLiaNo ratings yet
- This Article Has No Abstract The First 100 Words Appear BelowDocument1 pageThis Article Has No Abstract The First 100 Words Appear BelowHayatul AkmaLiaNo ratings yet
- Metabolic EncephalopathyDocument26 pagesMetabolic Encephalopathywirdahaja100% (3)
- Management of Status Epilepticus in Children: Clinical MedicineDocument19 pagesManagement of Status Epilepticus in Children: Clinical MedicineDienda AleashaNo ratings yet
- Ethical Drug: ThesaurusDocument1 pageEthical Drug: ThesaurusHayatul AkmaLiaNo ratings yet
- ENT Emergencies - DR Azwar Ridwan, SP - THT-KLDocument51 pagesENT Emergencies - DR Azwar Ridwan, SP - THT-KLHayatul AkmaLiaNo ratings yet
- Blood Gases SlideDocument17 pagesBlood Gases SlideHayatul AkmaLiaNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Is An Infection That Inflames The Air Sacs in One or Both LungsDocument2 pagesPneumonia Is An Infection That Inflames The Air Sacs in One or Both LungsHayatul AkmaLiaNo ratings yet
- ENT Emergencies - DR Azwar Ridwan, SP - THT-KLDocument51 pagesENT Emergencies - DR Azwar Ridwan, SP - THT-KLHayatul AkmaLiaNo ratings yet
- Critically Ill Patient Transport: A Guide for Medical TeamsDocument26 pagesCritically Ill Patient Transport: A Guide for Medical TeamsHayatul AkmaLia0% (1)
- Gawat Darurat Bedah - DR Munthadar, SP.B, SP - BaDocument25 pagesGawat Darurat Bedah - DR Munthadar, SP.B, SP - BaHayatul AkmaLiaNo ratings yet
- Metabolic EncephalopathyDocument26 pagesMetabolic Encephalopathywirdahaja100% (3)
- Neuro EmergencyDocument53 pagesNeuro EmergencyHayatul AkmaLiaNo ratings yet
- Basic Life Support Provider CourseDocument33 pagesBasic Life Support Provider CoursemedmnhmNo ratings yet
- Host ParasiteDocument24 pagesHost ParasiteHayatul AkmaLiaNo ratings yet
- ENT Emergencies - DR Azwar Ridwan, SP - THT-KLDocument51 pagesENT Emergencies - DR Azwar Ridwan, SP - THT-KLHayatul AkmaLiaNo ratings yet
- Mekanisme Pertahanan Inang THD Bakteri Dan VirusDocument87 pagesMekanisme Pertahanan Inang THD Bakteri Dan VirusHayatul AkmaLiaNo ratings yet
- Risk Stratification of AHF Patients JournalDocument10 pagesRisk Stratification of AHF Patients JournalHayatul AkmaLiaNo ratings yet
- Acute Gastrointestinal EmergenciesDocument25 pagesAcute Gastrointestinal EmergenciesHayatul AkmaLiaNo ratings yet
- Ad Part 4Document16 pagesAd Part 4Flor OMNo ratings yet
- Rekap Pasien Bedah Digestive 24 September 2016Document8 pagesRekap Pasien Bedah Digestive 24 September 2016Hayatul AkmaLiaNo ratings yet
- Rekap Pasien Bedah Digestive 24 September 2016Document8 pagesRekap Pasien Bedah Digestive 24 September 2016Hayatul AkmaLiaNo ratings yet