0% found this document useful (0 votes)
274 views21 pagesA 10 GHZ Frequency-Drift Temperature Compensated LC Vco With Fast-Setting Low-Noise Voltage Regulator in 0.13 Um Cmos
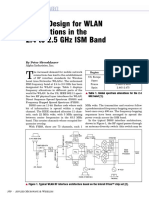
This document summarizes a 10 GHz LC VCO with temperature compensation and fast settling voltage regulation implemented in 0.13 um CMOS. Key features include a frequency coverage of 10.63-12.33 GHz, phase noise of -103.9 dBc/Hz at 1 MHz offset, and temperature drift reduced to 10.5 MHz from -61.6 MHz with compensation. The VCO is integrated with a low noise voltage regulator to minimize supply noise contributions.
Uploaded by
kidusCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
274 views21 pagesA 10 GHZ Frequency-Drift Temperature Compensated LC Vco With Fast-Setting Low-Noise Voltage Regulator in 0.13 Um Cmos
This document summarizes a 10 GHz LC VCO with temperature compensation and fast settling voltage regulation implemented in 0.13 um CMOS. Key features include a frequency coverage of 10.63-12.33 GHz, phase noise of -103.9 dBc/Hz at 1 MHz offset, and temperature drift reduced to 10.5 MHz from -61.6 MHz with compensation. The VCO is integrated with a low noise voltage regulator to minimize supply noise contributions.
Uploaded by
kidusCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd