Professional Documents
Culture Documents
S-Block Elements
Uploaded by
Rishabh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views1 pageS block
Original Title
7
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentS block
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views1 pageS-Block Elements
Uploaded by
RishabhS block
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
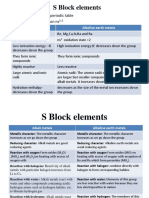
s-BLOCK ELEMENTS
Be(OH)2 < Mg(OH)2 < Ca(OH)2 < Sr(OH)2 < Ba(OH)2
Be(OH)2 reacts with acids as well as base, due to their
amphoteric nature. Other hydroxides react with acids
only.
(iv) Halides / Chlorides : (iv) Halides / Chlorides :
(1) Alkali metals directly combine with halogen to form (1) All these metals react with halogens to form MX2 type
halides (MX), which are ionic compounds. halides (BeCl2, MgCl2, CaCl2, SrCl2, BaCl2)
(2) Hydrolysis of Halides : The ionic compounds get (2) Ba turns on coming on contact with chlorine.
dissolved in water, while the covalent compounds get (3) Covalent character of these halides decreases from
Hydrolysed. Ionic character increases from LiCl to CsCl. BeCl2 to BaCl2. Therefore, the amount of hydrolysis also
Therefore, the amount of hydrolysis of decreases from decreases from BeCl2 to BaCl2. Only BeCl2 and MgCl2
LiCl to CsCl. get hydrolysed due to their covalent nature .Other halides
(3) LiCl gets hydrolysed due to its covalent nature. do not get hydrolysed.
Decreasing order of these halides in undergoing Hydrolysis is as follows :
hydrolysis is as follows " BeCl2 > MgCl2 > CaCl2 > SrCl2 > BaCl2
LiCl > NaCl > KCl > RbCl > CsCl
(v) Metal carbonates (v) Metal carbonates :
(1) All these metals from M2CO3 type carbonates. (1) All these metals form MCO3 type carbonates
(Li2CO3, Na2CO3, K2CO3, Rb2CO3, Cs2CO3) (BeCO3, MgCO3, CaCO3, SrCO3, BaCO3)
(2) Li2CO3 is least stable out of all these carbonates, (2) BeCO3 is least stable out of all these carbonates
because it is covalent and decomposes to Li2O and because it is covalent and decomposes to BeO and
CO2 at low temperature. Order of their stability is as CO2 at low temperature. Order of their stability is as
follows : follows.
Li2CO3 < Na2CO3 < K2CO3 < Rb2CO3 < Cs2CO3 BeCO3 < MgCO3 < CaCO3 < SrCO3 < BaCO3
(3) Stability of carbonates of IA group metals > stability of (3) Stability of Carbonates of IIA group metals < stability
carbonates of IIA group metals. of carbonates of IA group metals.
(vi) Nitrides : (vi) Nitrides :
Among all alkali metals, only lithium directly combines Only Be and Mg (and to some extent Ca) burn in N2 to
with nitrogen to form nitride. Other alkali meta ls combine form nitrides (M3N2), which decomposes to give NH3.
indirectly with nitrogen, because Li3N is covalent and 3Mg + N2 → Mg3N2
as the metallic character increases, the tendency of Mg3N2 + 6H2O → 3Mg(OH)2 + 2NH3
donating electron and forming ionic bond increases. Due
to which strength of metal nitrogen bond decreases
(vii) Sulphates : (vii) Sulphates :
Li2SO4 , Na2SO4 < K2SO4 < RbSO3 < Cs2SO4 Solubility of Sulphates : Their hydration energy is high
due to small size of Be+2 and Mg+2 and it overcomes
the lattice energy. This is the reason why
BeSO4 > MgSO4 > CaSO4 > SrSO4 > BaSO4
Increasing order of thermal stability
(viii) Nitrates : BeSO4 < MgSO4 < CaSO4 < SrSO4 < BaSO4
LiNO3 decomposes to Li2O at low temperature, whereas (viii) Nitrates :
NaNO3 gets decomposed to NaNO2 These metals also form M(NO3)2 and allnitrates give
oxides on decomposition.
You might also like
- S-Block Elements Alkaline Earth Metals PropertiesDocument9 pagesS-Block Elements Alkaline Earth Metals PropertiesKunwarNo ratings yet
- s-Block Elements ReviewDocument12 pagess-Block Elements ReviewGaurav ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- S-Block Elements L7Document11 pagesS-Block Elements L7Aryaman VyasNo ratings yet
- S BlockDocument5 pagesS Blockaxiom8750No ratings yet
- Alkaline Earth MetalsDocument12 pagesAlkaline Earth Metalselango achamNo ratings yet
- S-Block ElementsDocument17 pagesS-Block ElementsPiggu SurfersNo ratings yet
- X DZaa ZQAr X1 PA9 EUG2 R MDocument22 pagesX DZaa ZQAr X1 PA9 EUG2 R MSubhashakti BeheraNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2023 S-Block Elements Revision Notes - Free PDF DownloadDocument12 pagesJEE Main 2023 S-Block Elements Revision Notes - Free PDF DownloadRuhaan Bansal, 11B2, 51No ratings yet
- S Block ElementsDocument11 pagesS Block Elements19ucha023 19ucha023No ratings yet
- Sblock NotesDocument22 pagesSblock NotesLaukikNo ratings yet
- S Block (Landscape)Document8 pagesS Block (Landscape)Drastic Pranksters Inc.No ratings yet
- S - and P-Block ElementsDocument8 pagesS - and P-Block Elementssameenrashid410No ratings yet
- S Block QuestionsDocument9 pagesS Block QuestionsZaid KhanNo ratings yet
- Alkali Metals: Properties and ReactionsDocument22 pagesAlkali Metals: Properties and ReactionsRoshita G PillaiNo ratings yet
- Group 1-2Document22 pagesGroup 1-2Gudia kumariNo ratings yet
- S-Block Lecture NotesDocument43 pagesS-Block Lecture NotesIchhpilani KabirNo ratings yet
- Chemical PropertiesDocument1 pageChemical PropertiesRishabhNo ratings yet
- New Approach to Studying Inorganic ChemistryDocument47 pagesNew Approach to Studying Inorganic ChemistryAshik jhaNo ratings yet
- S-Block ElementDocument31 pagesS-Block ElementSiva ChamlingNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Properties of s-Block ElementsDocument29 pagesPhysical and Chemical Properties of s-Block ElementsRobiul AlomNo ratings yet
- S Bllock - 4 RevisedDocument3 pagesS Bllock - 4 RevisedAbhiNo ratings yet
- Spodumene Lial (Sio) Petalite (Lial (Si O), Lepidolite K (Li, Al) (Al, Si, RB) O (F, Oh)Document16 pagesSpodumene Lial (Sio) Petalite (Lial (Si O), Lepidolite K (Li, Al) (Al, Si, RB) O (F, Oh)dannyNo ratings yet
- (Ix) Hydrides: (1) (2) (Ix) Hydrides: (1) : Behaviour of Lithium Different From Other Alkali MetalsDocument1 page(Ix) Hydrides: (1) (2) (Ix) Hydrides: (1) : Behaviour of Lithium Different From Other Alkali MetalsRishabhNo ratings yet
- 7 PDFDocument1 page7 PDFRishabhNo ratings yet
- Alkali Metals and Their CompoundsDocument47 pagesAlkali Metals and Their CompoundsDhruv SainiNo ratings yet
- Wa0008.Document24 pagesWa0008.Meenakshi SuhagNo ratings yet
- VIII Chemistry The S-Block Elements IIT Material (30.11.2022)Document9 pagesVIII Chemistry The S-Block Elements IIT Material (30.11.2022)Jameer ShaikNo ratings yet
- S&P Block PDFDocument1 pageS&P Block PDFvrtbhgmngfNo ratings yet
- CH5 Alkaline and Alkaline Earth Metals-1Document20 pagesCH5 Alkaline and Alkaline Earth Metals-1Fikremariam TsegayeNo ratings yet
- S&P Block PDFDocument1 pageS&P Block PDFvrtbhgmngfNo ratings yet
- Group 12Document23 pagesGroup 12Miniatur IniNo ratings yet
- Advanced Inorganic Chemistry - ROBERT L. CARTERDocument16 pagesAdvanced Inorganic Chemistry - ROBERT L. CARTERBRUNO RAMOS DE LIMANo ratings yet
- Revision Notes On S BlockDocument12 pagesRevision Notes On S Blockharpal_abhNo ratings yet
- Chemistry PresentationDocument43 pagesChemistry PresentationgabyyyyyyNo ratings yet
- Block NotesDocument8 pagesBlock Notesarjunrkumar2024No ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 6 Sem 2 04 Notes STPM 2014/2013Document27 pagesChemistry Form 6 Sem 2 04 Notes STPM 2014/2013Raj Nittiya SugumaranNo ratings yet
- Ores and Metallurgy-02 - Solved ProblemsDocument11 pagesOres and Metallurgy-02 - Solved ProblemsRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- 19 Jan S Block 2Document17 pages19 Jan S Block 2sachin anuseNo ratings yet
- Alkali Metals: Properties and Uses of Important CompoundsDocument16 pagesAlkali Metals: Properties and Uses of Important CompoundsANSHEEKA SINGHNo ratings yet
- Group 2A: Alkaline Earth MetalsDocument109 pagesGroup 2A: Alkaline Earth MetalsAnggunNo ratings yet
- Alkaline Earth Metals Properties and ExtractionDocument4 pagesAlkaline Earth Metals Properties and Extractionswamy ChinthalaNo ratings yet
- S Block ElementsDocument10 pagesS Block ElementsFilmodeNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Notes (Sem 2)Document7 pagesGroup 2 Notes (Sem 2)Geethanjali SivakumarNo ratings yet
- Group 2: 1. Physical Properties A. Effective Nuclear ChargeDocument5 pagesGroup 2: 1. Physical Properties A. Effective Nuclear Chargeyyy ntNo ratings yet
- The S-Block ElementsDocument34 pagesThe S-Block ElementsPrakhar TandonNo ratings yet
- 10 - Group 2Document20 pages10 - Group 2Soma Chowdhury RosyNo ratings yet
- Alkaline Earth Group: Pranjoto UtomoDocument46 pagesAlkaline Earth Group: Pranjoto UtomoSatria Adji PNo ratings yet
- Part 2 Lecture9Document21 pagesPart 2 Lecture9barry allenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18Document63 pagesChapter 18Amit KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Group 2Document8 pagesChapter 10 Group 2Vjayan DharmaNo ratings yet
- Diagonal Relationship Between Lithium and Magnesium: S-Block ElementsDocument1 pageDiagonal Relationship Between Lithium and Magnesium: S-Block ElementsRishabhNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Period II 1Document6 pagesChemistry of Period II 1zakNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - The Group 2 MetalsDocument4 pagesChapter 12 - The Group 2 MetalsrickyNo ratings yet
- The s-Block Elements Solutions (Set-1Document15 pagesThe s-Block Elements Solutions (Set-1VinayNo ratings yet
- CarbidesDocument5 pagesCarbidestania030206No ratings yet
- S Block 2Document3 pagesS Block 2AbhiNo ratings yet
- S Block ElementsDocument5 pagesS Block ElementsKhalid Thabit KampanjeNo ratings yet
- Preparation Properties Fi PDFDocument43 pagesPreparation Properties Fi PDFPlaying PUBGNo ratings yet
- SblockkkkDocument3 pagesSblockkkkKisha KhuranaNo ratings yet
- Discovery-Driven Growth: Rita Gunther Mcgrath Ian C. MacmillanDocument14 pagesDiscovery-Driven Growth: Rita Gunther Mcgrath Ian C. MacmillanRishabhNo ratings yet
- Get Placement Ready With KushalDocument7 pagesGet Placement Ready With KushalRishabhNo ratings yet
- 01 - Assignment TX Line SolutionsDocument4 pages01 - Assignment TX Line SolutionsRishabh100% (2)
- Lecture 2 - Principles of EconomicsDocument33 pagesLecture 2 - Principles of EconomicsRishabhNo ratings yet
- 01 - Assignment TX LineDocument2 pages01 - Assignment TX LineRishabhNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Programming Questions PDFDocument10 pagesDynamic Programming Questions PDFSaurav AgarwalNo ratings yet
- MA 105: Calculus: Sudhir R. GhorpadeDocument16 pagesMA 105: Calculus: Sudhir R. GhorpadeRishabhNo ratings yet
- CH 12 NotesDocument3 pagesCH 12 NotesRishabhNo ratings yet
- Ultimate Java CheatSheetDocument4 pagesUltimate Java CheatSheetShubham SamratNo ratings yet
- Low-Impact Protection of The Built Environment From EarthquakesDocument1 pageLow-Impact Protection of The Built Environment From EarthquakesRishabhNo ratings yet
- 50+ Project Ideas For Resume ?Document10 pages50+ Project Ideas For Resume ?RishabhNo ratings yet
- C++ Interview QuestionsDocument22 pagesC++ Interview Questionslefela6421No ratings yet
- NEST - 13: Key To Set: ADocument2 pagesNEST - 13: Key To Set: Asandeep214400No ratings yet
- MA 105: Calculus: Sudhir R. GhorpadeDocument26 pagesMA 105: Calculus: Sudhir R. GhorpadeRishabhNo ratings yet
- Epsilon Ics DeltaDocument5 pagesEpsilon Ics DeltaIvan FadillahNo ratings yet
- Admission News 2019 PDFDocument1 pageAdmission News 2019 PDFRishabhNo ratings yet
- Autumn Mid-Semester Examination - 2019Document14 pagesAutumn Mid-Semester Examination - 2019RishabhNo ratings yet
- 001 Set 1 English Core PDFDocument12 pages001 Set 1 English Core PDFGurshaan Singh BajajNo ratings yet
- CamScanner Scans PDFs from PhotosDocument3 pagesCamScanner Scans PDFs from PhotosRishabhNo ratings yet
- Physics Imp Derivations + TheoryDocument6 pagesPhysics Imp Derivations + TheoryAL Surya67% (3)
- Noticeb 1532909749Document11 pagesNoticeb 1532909749RishabhNo ratings yet
- Rishabh JainDocument1 pageRishabh JainRishabhNo ratings yet
- Indian Institute of Technology BhubaneswarDocument1 pageIndian Institute of Technology BhubaneswarRishabhNo ratings yet
- ST ST ST Stoichiometr Oichiometr Oichiometr Oichiometry - 1 Y - 1 Y - 1 Y - 1Document2 pagesST ST ST Stoichiometr Oichiometr Oichiometr Oichiometry - 1 Y - 1 Y - 1 Y - 1RishabhNo ratings yet
- For More Important Questions Visit:: Matrices and DeterminantsDocument16 pagesFor More Important Questions Visit:: Matrices and DeterminantsRishabhNo ratings yet
- Expected Questions and Noteson The Invisible ManDocument14 pagesExpected Questions and Noteson The Invisible ManPrashant JainNo ratings yet
- Coordin Coordin Coordin Coordina A A Ation Compound Tion Compound Tion Compound Tion CompoundDocument2 pagesCoordin Coordin Coordin Coordina A A Ation Compound Tion Compound Tion Compound Tion CompoundRishabhNo ratings yet
- X SSTDocument2 pagesX SSTRishabhNo ratings yet
- For More Important Questions Visit:: Matrices and DeterminantsDocument16 pagesFor More Important Questions Visit:: Matrices and DeterminantsRishabhNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry: Theory and Exercise BookletDocument2 pagesThermochemistry: Theory and Exercise BookletRishabhNo ratings yet
- Basic Operator TranningDocument319 pagesBasic Operator TranningluisA1923No ratings yet
- Process Piping: - StructureDocument10 pagesProcess Piping: - StructureTawanda NyambiyaNo ratings yet
- Plant Adaptations in WaterDocument4 pagesPlant Adaptations in WaterAdelajaDalrympleNo ratings yet
- AWWA Standard List 2014Document3 pagesAWWA Standard List 2014VI King Pro100% (1)
- Controlled and Non-Controlled Type DepressuringDocument12 pagesControlled and Non-Controlled Type Depressuringgrimdorlf100% (1)
- Linatex Impact BarDocument3 pagesLinatex Impact BarNaveenNo ratings yet
- Casein PlasticDocument6 pagesCasein Plasticpiepie2No ratings yet
- PRODUCTION OF BIOETHANOL FROM POMELO (Citrus Maxima) PEEL (MANDIA) 2019Document60 pagesPRODUCTION OF BIOETHANOL FROM POMELO (Citrus Maxima) PEEL (MANDIA) 2019Carlo Quinsayas SablanNo ratings yet
- Chemicals Zetag MSDS LDP Zetag 3940 (US) - 1010Document6 pagesChemicals Zetag MSDS LDP Zetag 3940 (US) - 1010PromagEnviro.comNo ratings yet
- Low cost micropropagation of bananaDocument14 pagesLow cost micropropagation of bananaHabibullah KhanNo ratings yet
- A-Level Chemistry SyllabusDocument61 pagesA-Level Chemistry SyllabusLabiba GulNo ratings yet
- ClobazamDocument4 pagesClobazamLuwinda SariNo ratings yet
- 4th QUARTEST TEST SCIENCE 7Document6 pages4th QUARTEST TEST SCIENCE 7Geraldine Dioquino RosalesNo ratings yet
- Methods of Dna Extraction Presented By: Ayesha Kabeer: University of Gujrat Sialkot SubcampusDocument24 pagesMethods of Dna Extraction Presented By: Ayesha Kabeer: University of Gujrat Sialkot SubcampusDevill ShiverNo ratings yet
- Igcse Coordinated Sciences 0654 Combined Science 0 - 59cc8a591723ddab3bbdfff3 PDFDocument50 pagesIgcse Coordinated Sciences 0654 Combined Science 0 - 59cc8a591723ddab3bbdfff3 PDFBank Yossy WoluslaweNo ratings yet
- NACE Final MICRoundTableMPJanuary2014Feature PDFDocument10 pagesNACE Final MICRoundTableMPJanuary2014Feature PDFNestora Ruth DE Los Milagros Rojas GastuloNo ratings yet
- Brochure FX951Document3 pagesBrochure FX951Claudiu NistorescuNo ratings yet
- ch05 PDFDocument11 pagesch05 PDFKaren PedrazaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacognosy VII (Herbal Formulations & Complimentary Therapies)Document2 pagesPharmacognosy VII (Herbal Formulations & Complimentary Therapies)Nitin BirariNo ratings yet
- M1 W03 AnsDocument4 pagesM1 W03 AnsJoeNo ratings yet
- Bulking of SandDocument2 pagesBulking of SandEngr Sarang KhanNo ratings yet
- Water Soluble Polymer Flocculants Synthesis, PDFDocument43 pagesWater Soluble Polymer Flocculants Synthesis, PDFruizgj2011No ratings yet
- Bioline Pricing 2020Document4 pagesBioline Pricing 2020Asrul M FuadNo ratings yet
- Improve Your Paintings Luminous Watercolor Mixing Ewing Craftsy v1Document10 pagesImprove Your Paintings Luminous Watercolor Mixing Ewing Craftsy v1Raisona AlamNo ratings yet
- Raw Mill Area-HamzaDocument21 pagesRaw Mill Area-HamzaAdnan rasoolNo ratings yet
- Seismic Design and Retrofit of Piping Systems 7 02Document120 pagesSeismic Design and Retrofit of Piping Systems 7 02Jhe InibamNo ratings yet
- Mammalian Toxicology of Cetrimonium Chloride: Applicable To These Current Stepan ProductsDocument3 pagesMammalian Toxicology of Cetrimonium Chloride: Applicable To These Current Stepan Productsmohamed AdelNo ratings yet
- Silica Sols and Colloidal Silica 2007Document4 pagesSilica Sols and Colloidal Silica 2007veroniqueNo ratings yet
- Doxycycline SpecificationDocument2 pagesDoxycycline SpecificationKanokpol AphichoNo ratings yet
- Structure of Atoms and Symbols of ElementsDocument4 pagesStructure of Atoms and Symbols of ElementsWilrose BarbacionNo ratings yet