Professional Documents
Culture Documents
S Block Elements
Uploaded by
19ucha023 19ucha0230 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
162 views11 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
162 views11 pagesS Block Elements
Uploaded by
19ucha023 19ucha023Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
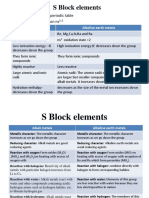
S Block elements
• Group 1 and 2 of the periodic table
• Electronic configuration ns1-2
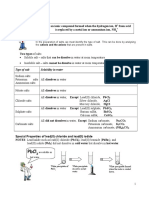
Alkali metals Alkaline earth metals
Li, Na K, Rb, Cs and Fr Be, Mg,Ca,Sr,Ba and Ra
ns1 oxidation state +1 ns2 oxidation state +2
Low ionisation energy –IE High ionisation energy:IE decreases down the group
decreases down the group
They form ionic They form ionic compounds
compounds
Highly reactive Less reactive
Large atomic and ionic Atomic radii: The atomic radii of alkaline earth metals
radii are larger but smaller compared to corresponding
alkali metals. It increases down the group
Hydration enthalpy- decreases as the size of the metal ion increases down
decreases down the group the group.
S Block elements
Alkali metals Alkaline earth metals
Metallic character: The metallic character Metallic character: The metallic character
increases as we go down the group increases as we go down the group
Reducing character: Alkali metals are good Reducing character: Alkaline earth metals are
reducing agents weak reducing agents
Reaction with oxygen Form oxides (M2O) Reaction with oxygen Form oxides (MO) on
,(MO2) and (M2O2)on heating with excess of heating with excess of oxygen with exception of
oxygen with Ba and Ra which form peroxides (MO2)
Reaction with halogens: Reactivity of alkali Reaction with halogen: combine directly with
metals with particular halogen increases from halogen to form corresponding halides.
Li to Cs.
Reaction with water: Alkali metals react with Reaction with water: Elements of this group
water and other compounds containing acidic are less reactive with water because they are
hydrogen atoms such as hydrogen halides, etc. less electropositive in nature
to liberate hydrogen gas
Reaction with hydrogen: Alkali metals react Reaction with hydrogen: The members of this
with dry hydrogen at about 673 K to form group except Be combine with hydrogen
crystalline hydrides which are ionic in nature directly upon heating to form metal hydrides.
and have high melting points.
S Block elements
Alkali metals Alkaline earth metals
Flame coloration :Li-crimson;Na-yellow;k-lilac; Flame coloration: Ca: brick red; Sr-crimson;Ba-
Rb-red violet; Cs-blue apple green;ra-crimson
Photoelectric effect -Cs
Biological importance of sodium and Biological importance of Ca and Mg
potassium: Na+ help to regulate flow of water Mg2+ act as cofactor for all enzymes that
across the cell membranes, transportation of utilize ATP.
sugars and amino acids inside the cells. K+ Mg2+ is present in chlorophyll pigment found
together Na+ are responsible for transmission of in green plants.
nerve signals and maintenance of ionic gradient Ca2+are required for bone formation, blood
across the cell. K+ activate many enzymes, and clotting and are required to trigger the
help in the oxidation of glucose contraction of muscles. They also regulate
Forms complexes: crown ethers, cryptates heart beat.
cryptands
LiOH-CO2absorptin in submarine, Li2CO3- Be-moderator in nuclear reactor ;Mg-
depressive psychosis drug,Li alkys-alkylating deoxidiser, milk of magnesia-medicine as an
agent ;(LiH,NaH,KH,LiAlH4) –reducing agent antidote;Ca-bones;CaCO3 –cement and glass
industry; BaSO4-barium meal -diagnosis
S Block
Alkali metals
elements
Alkaline earth metals
LiH-source of H2military applications ,Na- CaO –quicklime; used in cement, glass and
coolant; NaCl-iodised salt,NaHCO3 baking softening of water, Bordeaux mixture asa
soda,Na2CO3 glass industry,NaOH-paper and fungicide
textile inustry,Na2SO4 –paper and glass industry
KCl,K2SO4,KNO3-fertilizer;KMnO4-oxidising
agent; KNO3- explosive, KBr-photography;KO2-
breathing mask; K2CO3- ceramics, Rb and Cs-
scavenger of O2 and photoelectric cell
Oxides of Alkali metals
Normal oxides-monoxides of the type M2O(M=Li,Na,K,Rb and Cs)
Li2O and Na2O are white solid; K2O is yellow; Rb2O-bright yellow ;Cs2O-orange.
Metallic oxides are basic. They react with water
Li2O +H2O → 2 LiOH the hydroxides are called alkalis.
Na2O+H2O→ 2 NaOH
Peroxides
of the type M2O2 (-O-O-)2-diamagnetic and good oxidising agents. They react
with water to form H2O2 Li2O +H2O → LiOH + H2O2
S Block elements
Good oxidizing agents
Al →Al2O3 CO →CO2
Cr(III) →Cr(VI)
Na2O2 +O2→ 2NaO2
Superoxide (O2)-
Na2O2 + O2 → 2 NaO2( 4500 C and 300atm)
K, Rb,Cs form superoxides at ordinary pressure of O2
Paramagnetic in nature .they are strong oxidising agents than peroxides . With water or acid they
produce H2O2 and O2
2KO2 +2H2O →2KOH +H2O2 +O2
KO2 is used -space capsules /submarines - breathing masks to produce O2
4KO2 +2CO2→2K2CO3 +O2
4KO2 +4 CO2 +2H2O →4KHCO3+3O2
Sesquioxide
K.Rb,Cs form another type oxide M2O3 called sesquioxide. They are not stable. They are
paramagnetic in nature
S Block elements
Hydroxides: All alkali metals form hydroxides of the type MOH. They are formed on
dissolving M2O with water .They are basic, strong electrolytes-undergo dissociation
MOH → OH-+M+
They react with acids to form salts
NaOH +HCl→ NaCl +H2O
They react with alcohol to form alkoxide
ROH +MOH → RO-M+ + H2O
They absorb CO2 and H2S
NaOH +CO2 →NaHCO3
They react with Al2O3
Al2O3 +2NaOH → NaAlO2
Alkalis attack glass
SiO2 + 2NaOH → Na2SiO3 +H2O
S Block elements
Halides
They are stable compounds They have rock salt type structure. NaCl forms FCC, CsCl,
CsBr and CsI have a Body centered cubic structure . The halides are ionic except LiI
which is covalent. They have high electrical conductivity. They exhibit high negative
enthalpies of formation
NaCl +H2SO4 → NaHSO4 +HCl
Preparation
M2O + 2HX → 2MX + H2O
M2CO3+ 2HX → 2MX + CO2 + H2O
Poly halides MI3 KI +I2 → KI3
RbI3,CsI3 are anhydrous and crystalline. RbBr3,CsBr3 are also known.
NaCl KCl CsCl
S Block elements
Carbonates and bicarbonates
Alkali metals form carbonates of the type M2CO3. bicarbonates of the two MHCO3.
Na2CO3and NaHCO3 are industrially important.
Na2CO3 + CO2 + H2O → 2NaHCO3 it reacts with acids
NaHCO3 +HCl → NaCl + CO2↑+ H2O
N heating
NaHCO3→Na2CO3 + CO2↑+ H2O as it produces CO2↑with ease it is used in fire
extinguishers. . Alkali metal carbonates except Li2CO3 are soluble in water. Anhydrous
Na2CO3 .10 H2O soda ash (washing soda).
Hydrides
Alkali metals form hydrides of he type MH. They are ionic in nature. They acts as good
reducing agents(Reference ionic hydrides)
S Block elements
Important compounds of alkaline earth metals
Oxides- All alkaline earth metals tend to form monoxide (MO) except beryllium
2Ba +O2→2BaO. ;2Mg +O2→2MgO
Nitrate ,Carbonates ,sulphates and hydroxides on heating produce the oxides
Ba(NO3)2 → BaO ; SrSO4 →SrO ;Ca(OH)2→CaO,white solid soluble in water forming
hydroxides. good conductors of heat, chemically inert, electrical insulator
MO+H2O →M(OH)2 ;dissolve in acid to give salt
BeO +HCl → BeCl2 ; BeO +NaOH →Na2BeO2(odium beryllate)
BaO +H2SO4→ BaSO4 ; CaO used in cement, glass industry, softening of water
Peroxides: Except be other metals form peroxides of the type MO2
Ca(OH)2 +H2O2 →CaO2;BaO →BaO2; in the presence of H+ peroxides form hydrogen
peroxide BaO2 +HCl →H2O2 +BaCl2
Hydroxides all metals except Be form hydroxides of the type M(OH)2
MO+H2O →M(OH)2 ;Be(OH)2 is amphoteric all other hydroxides are basic, Ca(OH)2 is
lime water, Ba(OH)2 is baryta used for detecting CO2; Ca(OH)2 + CO2 →Ca(HCO3)
( soluble)
S block elements
Carbonates CaCO3 most important –limestone ,they are slightly soluble in water
,solubility decreases down the group, they undergo thermal decomposition
BaCO3 → BaO + CO2↑ ; BaCO3 most stable and BeCO3 is least stable ;hydration
energy is maximum for BeO. Solubility can be explained based on hydration energy.
Be2+ has the highest hydration energy. M(HCO3)2 unlike alkali metals exist in solution
Sulphates all metals form sulphates MSO4; CaSO4.2H2O –gypsum; CaSO4.1/2H2O
plaster of paris.
Preparation: BaCl2 + H2SO4→BaSO4 sulphates are white solids sparingly soluble in
water; MgSO4 →MgO +SO3 ;BaSO4 +4C → BaS +4CO
Halides They form halides of the type MX2 ; all halides are soluble in water,fluorides
are least soluble. Chlorides ,bromides and iodides of Mg,Ca,Sr,Ba are ionic
chlorides are well known.BeCl2 is a linear molecule with sp hybridization. They are
hygroscopic and form hydrates .BeCl2 behaves as Lewis acids
Ca+HCl →BaCl2; CaCO3 +HCL
S Block elements
Hydrides
They form hydrides of the type MH2. BeH2 and MgH2 are covalent hydrides. They are
polymeric in nature. All other alkaline earth metal hydrides are ionic in nature
(Reference Hydrides)
You might also like
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Notes GoodDocument21 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes Notes GoodAnitesh DharamNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Notes Ch10 Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument7 pages12 Chemistry Notes Ch10 Haloalkanes and HaloarenesShouvik sinhaNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Impq CH10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes 02Document47 pages12 Chemistry Impq CH10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes 02Swaroop SurendraNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument2 pagesHaloalkanes and HaloarenesVisakh Suku SNo ratings yet
- HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES (FULLY SOLVED) FOR CBSE (IIT-JEE) EXAMS (2021-2022Document38 pagesHALOALKANES AND HALOARENES (FULLY SOLVED) FOR CBSE (IIT-JEE) EXAMS (2021-2022Ananth DharanidharanNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes QDocument7 pagesHaloalkanes Qlucylovesbooks6770No ratings yet
- Mrs. Preetha - Haloalkanes and Haloarenes - WS005Document4 pagesMrs. Preetha - Haloalkanes and Haloarenes - WS005Vikram MishraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument24 pagesChapter 10 Haloalkanes and HaloarenesSuhas GowdaNo ratings yet
- HaloalkanesDocument13 pagesHaloalkanesChingYan TanNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and Ketones ReactionsDocument9 pagesAldehydes and Ketones ReactionsKudzayi Tusaumwe100% (1)
- Haloalkanes & HaloarenesDocument28 pagesHaloalkanes & HaloarenesFam IlyNo ratings yet
- 20 HaloalkanesDocument7 pages20 HaloalkanesizabelNo ratings yet
- Topic 14.0: Haloalkanes (Alkyl Halides)Document12 pagesTopic 14.0: Haloalkanes (Alkyl Halides)Supia NazmaNo ratings yet
- Properties and Trends of s-Block ElementsDocument72 pagesProperties and Trends of s-Block ElementsashrafraziNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl Compounds: Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocument16 pagesCarbonyl Compounds: Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsRanit Mukherjee100% (1)
- Hydrogen and Its Compounds: ST THDocument8 pagesHydrogen and Its Compounds: ST THAravind NarasimhaluNo ratings yet
- Reactions of HaloalkanesDocument10 pagesReactions of Haloalkanesapi-504683923No ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument25 pagesElectrolysisMuhammad UmerNo ratings yet
- P BlockDocument52 pagesP BlockYogendra GangwarNo ratings yet
- Preparation and Characterization of Cobalt ComplexesDocument7 pagesPreparation and Characterization of Cobalt ComplexesIftitah HauriyahNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About SaltsDocument32 pagesEverything You Need to Know About SaltsSabriza Hassan Assa'ariNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument9 pagesHaloalkanes and HaloarenesManish kumarNo ratings yet
- Edexcel & Cambridge Syllabus: Unit 4: Carbonyl Compounds Alauddin Sir A & O Level Chemistry TeacherDocument8 pagesEdexcel & Cambridge Syllabus: Unit 4: Carbonyl Compounds Alauddin Sir A & O Level Chemistry TeacherMaliha Ishrat JarinNo ratings yet
- P Block2012 457Document143 pagesP Block2012 457Abhishek Bansal100% (1)
- Pdf-Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument159 pagesPdf-Haloalkanes and HaloarenesOmkar Singh Shekhawat100% (2)
- Acid Base LectureDocument9 pagesAcid Base LectureJulia Kropel'nytskaNo ratings yet
- Introduction to HydrogenDocument36 pagesIntroduction to HydrogenAryaman VyasNo ratings yet
- Coordination Chemistry JEE AdvancedDocument44 pagesCoordination Chemistry JEE AdvancedKartikey SharmaNo ratings yet
- 2023-24 Coordination CompoundsDocument36 pages2023-24 Coordination Compoundsthe Skulptor100% (1)
- Learn: Chapter-10 Haloalkanes & Haloarenes Class-XII Subject-ChemistryDocument32 pagesLearn: Chapter-10 Haloalkanes & Haloarenes Class-XII Subject-Chemistryprajaktac506No ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions NotesDocument141 pagesChemical Reactions Notesapi-182809945No ratings yet
- Chemistry PracticalDocument16 pagesChemistry PracticalmayashankarjhaNo ratings yet
- MCQ-S BlockDocument4 pagesMCQ-S Blocktgs100No ratings yet
- Hydrogen Class 11: Created By: Amir Husain, PGT CHEMISTRYDocument65 pagesHydrogen Class 11: Created By: Amir Husain, PGT CHEMISTRYBaljit SinghNo ratings yet
- 06 Chapter 1Document63 pages06 Chapter 1Dintakurthi PrasanthNo ratings yet
- Organometallic Transition Metal Catalysis: A Holistic Approach to Understanding and Predicting their MechanismsFrom EverandOrganometallic Transition Metal Catalysis: A Holistic Approach to Understanding and Predicting their MechanismsNo ratings yet
- HaloalkanesDocument12 pagesHaloalkanesMo_Bash1No ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-03 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Haloalkanes and Haloarenes)Document1 pageCbse Test Paper-03 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Haloalkanes and Haloarenes)Shreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class-12 Chemistry Quick Revision Notes on Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument6 pagesCBSE Class-12 Chemistry Quick Revision Notes on Haloalkanes and HaloarenesKunal ShahNo ratings yet
- Lab Experiment 21 Report: Organic Chemistry Lab Tuesdays at 1:30Document4 pagesLab Experiment 21 Report: Organic Chemistry Lab Tuesdays at 1:30Johnathan DoeNo ratings yet
- Coordination Compound: IIT-JEE 2013Document50 pagesCoordination Compound: IIT-JEE 2013Utkarsh Agarwal100% (1)
- Experiment 4 Palvi FinalDocument8 pagesExperiment 4 Palvi FinalSara AliNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry ReactionDocument3 pagesOrganic Chemistry ReactionGAMEPORIUMNo ratings yet
- Name Reactions of Organic ChemistryDocument7 pagesName Reactions of Organic ChemistryNaynam SharmaNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Class XII - Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument8 pagesAssignment - Class XII - Haloalkanes and Haloarenesgarv khoslaNo ratings yet
- HaloalkanesDocument6 pagesHaloalkanesDoc_CrocNo ratings yet
- Iit Chemistry: NurtureDocument38 pagesIit Chemistry: NurtureKushagra PandeyNo ratings yet
- Coordination Compounds 1Document12 pagesCoordination Compounds 1Anonymous 8VJhV1eI2y100% (2)
- Fajan RulesDocument11 pagesFajan RulesSanjita mimNo ratings yet
- CrackingDocument5 pagesCrackingnorlin facultadNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes: Classification of Halogen DerivativesDocument16 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes: Classification of Halogen Derivativeskaushik247No ratings yet
- Kinetics Iodine Clock RXN Reportsheets PDFDocument13 pagesKinetics Iodine Clock RXN Reportsheets PDFElizabeth Polancos BruaNo ratings yet
- Reactive Intermediates: Arynes, Carbenes, and NitrenesDocument115 pagesReactive Intermediates: Arynes, Carbenes, and NitrenesMuhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- Hand-Out: Chemistry Chapter 4: Haloalkanes & HaloarenesDocument11 pagesHand-Out: Chemistry Chapter 4: Haloalkanes & HaloarenesLuisgarciaBerlangaNo ratings yet
- NamereactionorganicDocument13 pagesNamereactionorganicdeykrishna654100% (1)
- Molecular RearrangementsDocument158 pagesMolecular RearrangementsRamesh Katkam75% (4)
- Name ReactionsDocument10 pagesName ReactionsParam SoniNo ratings yet
- D and F Block Elements-1Document12 pagesD and F Block Elements-1ilias1973No ratings yet
- Preparative Methods in Solid State ChemistryFrom EverandPreparative Methods in Solid State ChemistryPaul HagenmullerNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution - Monitoring and Management A Case Study - DelhiDocument26 pagesAir Pollution - Monitoring and Management A Case Study - Delhi19ucha023 19ucha023No ratings yet
- Composition and Functions of BloodDocument17 pagesComposition and Functions of Blood19ucha023 19ucha023No ratings yet
- S Block ElementsDocument11 pagesS Block Elements19ucha023 19ucha023No ratings yet
- Understanding Air Pollution ModuleDocument25 pagesUnderstanding Air Pollution ModulegayneNo ratings yet
- Super StarDocument2 pagesSuper Star19ucha023 19ucha023No ratings yet
- Applications of Genetic Engineering: Medicine IndustriesDocument4 pagesApplications of Genetic Engineering: Medicine Industries19ucha023 19ucha023No ratings yet
- SorryDocument2 pagesSorry19ucha023 19ucha023No ratings yet
- Vehicular Pollution in IndiaDocument9 pagesVehicular Pollution in India19ucha023 19ucha023No ratings yet
- Welcome To Our Presentati OnDocument18 pagesWelcome To Our Presentati On19ucha023 19ucha023No ratings yet
- SL-Vehicular Air PollutionDocument5 pagesSL-Vehicular Air Pollution19ucha023 19ucha023No ratings yet
- FT-IR Analysis of Hock ProcessDocument4 pagesFT-IR Analysis of Hock ProcessmohsengolestanzadehNo ratings yet
- Using Roger's Diffusion of Innovation Theory To Implement The Healthy Schools National AccreditationDocument6 pagesUsing Roger's Diffusion of Innovation Theory To Implement The Healthy Schools National AccreditationputriNo ratings yet
- 08 Ergonomics - 01Document35 pages08 Ergonomics - 01Cholan PillaiNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 2Document5 pagesLab Report 2adrianeNo ratings yet
- Shortened Dental Arch ConceptDocument3 pagesShortened Dental Arch ConceptVivek ShankarNo ratings yet
- MA Only Notice Explains Coverage ChangeDocument2 pagesMA Only Notice Explains Coverage ChangeAnonymous Zp7kAtNo ratings yet
- Manual de Reparacion TXV75Document16 pagesManual de Reparacion TXV75Ovh MaquinariasNo ratings yet
- Plasma MachiningDocument14 pagesPlasma MachiningMayankNo ratings yet
- OSHA Group Assigtment 1Document4 pagesOSHA Group Assigtment 1Muhammad SyahmiNo ratings yet
- Physics Radiant Energy Light: GE 143 Remote SensingDocument1 pagePhysics Radiant Energy Light: GE 143 Remote SensingPISALBO, JEXTER P.No ratings yet
- Self Esteem and The Real Body ImageDocument12 pagesSelf Esteem and The Real Body ImageChy Alcarde50% (2)
- Experiment # 04: Short-Circuit Test of Single Phase TransformerDocument5 pagesExperiment # 04: Short-Circuit Test of Single Phase TransformerNasir Ali / Lab Engineer, Electrical Engineering DepartmentNo ratings yet
- Sika Poxitar FDocument3 pagesSika Poxitar FBudhi KurniawanNo ratings yet
- CompostAGuideForUsing PDFDocument4 pagesCompostAGuideForUsing PDFmkmikmiNo ratings yet
- Devsecops Course Content: Module-1 Devops BasicsDocument3 pagesDevsecops Course Content: Module-1 Devops Basicshelo nameNo ratings yet
- Glycerol PDFDocument3 pagesGlycerol PDFTushar GaikarNo ratings yet
- State-wise list of 376 approved cold chain projectsDocument45 pagesState-wise list of 376 approved cold chain projectsUsha Hasini VelagapudiNo ratings yet
- NURS 366 Exam 1 Study Guide and RubricDocument7 pagesNURS 366 Exam 1 Study Guide and RubriccmpNo ratings yet
- Serving TechniquesDocument4 pagesServing TechniquesSindy FadyaNo ratings yet
- PT. Citilink Indonesia N P W P: 0 2 - 8 2 7 - 5 9 7 - 2 - 0 9 3 - 0 0 0 Jl. Raya Juanda Sawotratap Gedangan SidoarjoDocument2 pagesPT. Citilink Indonesia N P W P: 0 2 - 8 2 7 - 5 9 7 - 2 - 0 9 3 - 0 0 0 Jl. Raya Juanda Sawotratap Gedangan SidoarjoZemNo ratings yet
- Grooved Peg BoardDocument2 pagesGrooved Peg BoarddanifgNo ratings yet
- Ecodial Advance Calculation 4.1Document33 pagesEcodial Advance Calculation 4.1Youwan LeeNo ratings yet
- Lab Report P2 A1 - IDocument19 pagesLab Report P2 A1 - Inzirh 01No ratings yet
- How to Improve Your Self-Motivation Through Self-Confidence, Positive Thinking, Goal Setting and EnvironmentDocument21 pagesHow to Improve Your Self-Motivation Through Self-Confidence, Positive Thinking, Goal Setting and EnvironmentRose Anne100% (1)
- S35MC Engine Layout and Load DiagramsDocument17 pagesS35MC Engine Layout and Load DiagramsMuhammad AlfaniNo ratings yet
- Format Bahasa Inggeris UPSR 2016 ENGLISH (013) Section ADocument33 pagesFormat Bahasa Inggeris UPSR 2016 ENGLISH (013) Section AVINOTININo ratings yet
- Wo PRJ #304Document2 pagesWo PRJ #304Gigin PlusNo ratings yet
- Fire Safety in Public BuildingDocument48 pagesFire Safety in Public BuildingSamirsinh ParmarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document2 pagesChapter 6Zhane CruzNo ratings yet
- Stress and Coping in Families With Deaf Children: Terri Feher-Prout University of PittsburghDocument12 pagesStress and Coping in Families With Deaf Children: Terri Feher-Prout University of PittsburghGolfiNo ratings yet