Professional Documents
Culture Documents
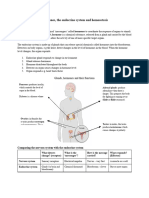
Homeostasis Poster
Uploaded by
api-375178914Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Homeostasis Poster
Uploaded by
api-375178914Copyright:
Available Formats
Blood Pressure Homeostasis
Abstract:
Methods and Materials:
When the human body’s blood pressure spike or lowers, it will return back to homeostasis. One
Materials:
way to test this is by measuring blood pressure before, right after and then after waiting to recover
3 Male Test subjects (Ages ranging from 15-16)
from exercise. The results all followed the same pattern, the blood pressure before was at
Sphygmomanometer - Blood Pressure Monitor
homeostasis and it increased due to the exercise. Then dropped back to homeostasis about 10
Methods:
minutes after exercising.This shows how the human body maintains homeostasis in blood pressure.
3 main stages in experiment
Introduction: Homeostasis is the equilibrium of the body and its systems. The brain can
Control: This was a measure of blood pressure while going through a typical day and
involuntarily (meaning that you don’t have to think about it) manage its functions to keep its
completing work.
systems and functions stable using the hormone ANP (Derreck Chu on Youtube). More
Active:
specifically, it can control the blood vessels’ and arteries’ dilation to keep our blood pressure in
A measurement of blood pressure was taken 10 minutes prior to running 100 yards.
check. It is known that this takes place but to prove it, more experimentation was needed. Our
A measurement of blood pressure was taken following shortly after running 100
experiments capture everyday life, spikes of activity, and the dips while one rests. In the
yards.
experiments, we expect blood pressure to change then change back to normal shortly after.
A measurement of blood pressure was taken 10 minutes after running 100 yards
Discussion/Conclusion:
Resting:
The research confirmed the hypothesis that although it may spike or dip, blood pressure will always
A measurement of blood pressure was taken 10 minutes prior to resting for 15
return to a safe and stable level due to homeostasis. Seeing as the control for participant 1 was 128/83,
minutes.
the measure while running spiked to 144/76 then in ten minutes returned back to 121/73. Following
A measurement of blood pressure was taken shortly after the 15 minute resting
this, the resting measurement was 102/62, where an obvious dip in blood pressure occurred. 10 minutes
period.
later and the blood pressure rose back to a level near the control. Participants 2 and 3 showed similar
A measurement of blood pressure was taken shortly after the 15 minute resting
patterns of blood pressure readings while put through the same test under the same conditions. The
period.
tests went well aside from not following the instrustructions for the sphygmomanometer initially,
which caused tests to be redone. The numbers seen are correct while tests were done
Participant Control -10 min 100 yrd 10 min -10 min Rest for 15 10 min
References:
Dash min
- “#BPraisers: Things That Raise Your Blood Pressure.” About Heart Attacks,
www.heart.org/en/health-topics/high-blood-pressure/the-facts-about-high-blood-pressure/bpr
1 128/83 128/83 144/76 121/73 121/73 102/62 115/79 aisers-things-that-raise-your-blood-pressure.
- Chopra, Sandeep et al. “Neuroendocrine regulation of blood pressure” Indian journal of
2 115/71 115/71 137/77 113/69 73/53 106/59 144/90 endocrinology and metabolism vol. 15 Suppl 4,Suppl4 (2011): S281-8.
- “Blood Pressure Homeostasis.” YouTube, YouTube, 18 Dec. 2016, youtu.be/j6VzjaOwg0g.
3 129/69 129/69 142/71 115/55 115/55 100/65 116/72
You might also like
- Homeostasis PosterDocument1 pageHomeostasis Posterapi-375897947No ratings yet
- High Blood Pressure: Safe alternatives without drugsFrom EverandHigh Blood Pressure: Safe alternatives without drugsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Lab Report On Blood PressureDocument2 pagesLab Report On Blood PressureToni Calsado50% (2)
- Blood Pressure PosterDocument1 pageBlood Pressure Posterapi-385956544No ratings yet
- Sofia Sanchez - 4Document8 pagesSofia Sanchez - 4api-553676905No ratings yet
- ResearchDocument4 pagesResearchapi-389089120No ratings yet
- Lab Report AnatomyDocument7 pagesLab Report Anatomyapi-339983508No ratings yet
- AP Lab 10Document8 pagesAP Lab 10Julian TanjuakioNo ratings yet
- ResearchDocument3 pagesResearchapi-386487682No ratings yet
- Bio Lab 11Document5 pagesBio Lab 11Sarah JaglalNo ratings yet
- Activity 18 - GerenteDocument3 pagesActivity 18 - GerenteFLORENCE GERENTENo ratings yet
- Pranjal Parmar. Comparison of The Effect of Isometric Exercise of Upper Limb On Vitals Between Young Males and FemalesDocument13 pagesPranjal Parmar. Comparison of The Effect of Isometric Exercise of Upper Limb On Vitals Between Young Males and FemalesDr. Krishna N. SharmaNo ratings yet
- Heart Rate Design Lab 1Document4 pagesHeart Rate Design Lab 1Alexandra McGinnNo ratings yet
- Harvard Step Test ProcedureDocument31 pagesHarvard Step Test ProcedureMaria Pauline100% (1)
- Stress TestDocument2 pagesStress TestDavid GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis Lab ActivityDocument2 pagesHomeostasis Lab ActivityMARY GLORY IGNACIONo ratings yet
- Homeostasis Lab ActivityDocument2 pagesHomeostasis Lab ActivityMARY GLORY IGNACIONo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure Homeostasis PosterDocument1 pageBlood Pressure Homeostasis Posterapi-352673659No ratings yet
- ENLS Case Study FDAR AMALDocument3 pagesENLS Case Study FDAR AMALAMAL ALI HASSANNo ratings yet
- Heartbeat HomeostasisDocument1 pageHeartbeat Homeostasisapi-296692561No ratings yet
- Jurnal GerontikDocument3 pagesJurnal GerontikCarla NasbarNo ratings yet
- Hormones, The Endocrine System and HomeostasisDocument5 pagesHormones, The Endocrine System and Homeostasischiusavi77No ratings yet
- What To Expect During A Myocardial Perfusion ScanDocument2 pagesWhat To Expect During A Myocardial Perfusion ScanR K PathamNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Breaths Per Minute On Heart RateDocument7 pagesThe Effect of Breaths Per Minute On Heart RateJorge AscencioNo ratings yet
- Equipment Used in Exercise Physiology and Its UsesDocument55 pagesEquipment Used in Exercise Physiology and Its UsesAkshayNo ratings yet
- PDF HeDocument13 pagesPDF Heapi-169518406No ratings yet
- FundaDocument5 pagesFundaGreggy Francisco LaraNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis LabDocument6 pagesHomeostasis LabNaiomiNo ratings yet
- Effects CaffeineDocument18 pagesEffects CaffeineYacine LyazidiNo ratings yet
- Vital Sign Na (1) by ZWBDocument52 pagesVital Sign Na (1) by ZWBAshraf Ali100% (1)
- Vital Signs (BHW Training) 2Document31 pagesVital Signs (BHW Training) 2Yathziel Meow100% (4)
- The Effects of Verapamil SR and Bisoprolol On Reducing The Sympathetic Nervous System's ActivitDocument4 pagesThe Effects of Verapamil SR and Bisoprolol On Reducing The Sympathetic Nervous System's ActivitDian Sekar LarassatiNo ratings yet
- HILOT WELLNESS MASSAGE NC II 2nd TopicDocument17 pagesHILOT WELLNESS MASSAGE NC II 2nd TopicClydie Joy100% (2)
- Module 1Document6 pagesModule 1api-569816669No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Doppler Scan and Stress TestingDocument10 pagesNursing Care Plan For Doppler Scan and Stress TestingAmy Rose AbuevaNo ratings yet
- Feedback MechanismDocument4 pagesFeedback MechanismMelvin Razon Espinola Jr.No ratings yet
- Ways To Measure Blood PressureDocument2 pagesWays To Measure Blood PressureMuhammad RifaiNo ratings yet
- Lab Report - Circulation and RespirationDocument4 pagesLab Report - Circulation and RespirationSimranNo ratings yet
- How Heart Rate Maintains HomeostasisDocument4 pagesHow Heart Rate Maintains Homeostasisapi-375163452No ratings yet
- BCS KardiovaskulerDocument37 pagesBCS KardiovaskulerhragunathanNo ratings yet
- Testing Lab 1Document8 pagesTesting Lab 1api-704464346No ratings yet
- VITAL SIGNS ReviewDocument4 pagesVITAL SIGNS ReviewA CNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Parameters 6 1Document12 pagesCardiovascular Parameters 6 14dkh9jx7fsNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System ActivityDocument7 pagesCirculatory System ActivityReginald MalibiranNo ratings yet
- Cardiorespiratory FitnessDocument44 pagesCardiorespiratory FitnesssuperallNo ratings yet
- Cape Exercise LabDocument2 pagesCape Exercise Labanisa aliNo ratings yet
- The Adrenal GlandsDocument6 pagesThe Adrenal GlandsNICOLAENo ratings yet
- Homeostasis Lab (Developed by Kelly Perry) Introduction: Homeostasis (Greek For "Staying The Same") Is A Process by Which The Body MaintainsDocument3 pagesHomeostasis Lab (Developed by Kelly Perry) Introduction: Homeostasis (Greek For "Staying The Same") Is A Process by Which The Body MaintainsCatherine JacksonNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis ProjectDocument2 pagesHomeostasis Projectapi-302340711No ratings yet
- Effect of Water Temperature and Voluntary Drinking On The Post Rehydration SweatingDocument5 pagesEffect of Water Temperature and Voluntary Drinking On The Post Rehydration SweatingJames_FogalNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure ProjectDocument3 pagesBlood Pressure ProjectjademvdfNo ratings yet
- Step Test LabDocument3 pagesStep Test Labapi-287068011No ratings yet
- Bio PulseDocument2 pagesBio PulseAliyah DumontNo ratings yet
- Hypertension Related To Faulty Eating Habits As Evidence My Blood Pressure of 13080.Document2 pagesHypertension Related To Faulty Eating Habits As Evidence My Blood Pressure of 13080.Senyorita KHayeNo ratings yet
- HR 102054Document3 pagesHR 102054smithsashay74No ratings yet
- Oberoi International School: Summative: Effect of Posture & Activity On Pulse RateDocument11 pagesOberoi International School: Summative: Effect of Posture & Activity On Pulse RateParashie SidhwaniNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure Manual: 110/40 (Me) 110/30 (Sidney) 100/60 (Virginia)Document3 pagesBlood Pressure Manual: 110/40 (Me) 110/30 (Sidney) 100/60 (Virginia)api-346905466No ratings yet
- Sport & Exercise PhysiologyDocument24 pagesSport & Exercise PhysiologyDeclan SavageNo ratings yet
- Script in VITAL SIGNS Preparation 1. AssessDocument6 pagesScript in VITAL SIGNS Preparation 1. AssessJeizel IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Good Copy of Life Cycle of The BicycleDocument5 pagesGood Copy of Life Cycle of The Bicycleapi-376822573No ratings yet
- Jake Hobson - Classification Scheme - Final TakeDocument3 pagesJake Hobson - Classification Scheme - Final Takeapi-375178914No ratings yet
- Survey Results GraphsDocument6 pagesSurvey Results Graphsapi-375178914No ratings yet
- Jake Hobson - Classification Scheme - First TakeDocument3 pagesJake Hobson - Classification Scheme - First Takeapi-375178914No ratings yet
- Jake Hobson - Classification Scheme Designs Selection 1Document3 pagesJake Hobson - Classification Scheme Designs Selection 1api-375178914No ratings yet
- Jake Hobson - 3 Design Possibilities - Conceptual Sketches and DrawingsDocument3 pagesJake Hobson - 3 Design Possibilities - Conceptual Sketches and Drawingsapi-375178914No ratings yet
- Jake Hobson - Experiments Tests Plan and Set-UpDocument8 pagesJake Hobson - Experiments Tests Plan and Set-Upapi-375178914No ratings yet
- Cooper Hochman - 4 To 6 Pages Initial ProposalDocument6 pagesCooper Hochman - 4 To 6 Pages Initial Proposalapi-389074434No ratings yet
- Demands and Wishes UpdateDocument2 pagesDemands and Wishes Updateapi-375178914No ratings yet
- Wat-Er We Drinking PresentationDocument33 pagesWat-Er We Drinking Presentationapi-375178914No ratings yet
- Chem ArtDocument10 pagesChem Artapi-375178914No ratings yet
- Blood Pressure Research ArticleDocument3 pagesBlood Pressure Research Articleapi-375178914No ratings yet
- Bicyclean Commuter Bikes Stem Capstone Project - Google FormsDocument6 pagesBicyclean Commuter Bikes Stem Capstone Project - Google Formsapi-375178914No ratings yet
- Biofuel 1Document17 pagesBiofuel 1api-375178914No ratings yet
- Ecology ProjectDocument14 pagesEcology Projectapi-376381619No ratings yet
- Murder MysteryDocument11 pagesMurder Mysteryapi-375178914No ratings yet
- InstrumentsDocument2 pagesInstrumentsapi-375178914No ratings yet
- Energy Justification 2018 6 2f7thDocument11 pagesEnergy Justification 2018 6 2f7thapi-375178431No ratings yet
- Stem Hyundai Car Presentation 1Document11 pagesStem Hyundai Car Presentation 1api-375178914No ratings yet
- Giant OtterDocument39 pagesGiant Otterapi-375178914No ratings yet
- Alzheimers DiseaseDocument5 pagesAlzheimers Diseaseapi-376804623No ratings yet
- Planting The Seeds of StemDocument16 pagesPlanting The Seeds of Stemapi-376400809No ratings yet
- SMMGDocument9 pagesSMMGapi-375178914No ratings yet
- Proof of Efficacy DocumentDocument4 pagesProof of Efficacy Documentapi-375178914No ratings yet
- Arcade Rube Goldberg MachineDocument5 pagesArcade Rube Goldberg Machineapi-375178914No ratings yet
- Weed PreventionDocument3 pagesWeed Preventionapi-375178914No ratings yet
- Current COPD TreatmentsDocument5 pagesCurrent COPD Treatmentssmashraf2100% (1)
- LacrisertDocument4 pagesLacrisertChindra Sebaly PutryNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Depth Imaging Optical Coherence TomographyDocument10 pagesEnhanced Depth Imaging Optical Coherence TomographyKaran KumarswamyNo ratings yet
- Ministry of Health and Family Welfare Pregnancy GuidelinesDocument173 pagesMinistry of Health and Family Welfare Pregnancy GuidelinesKhushi GuptaNo ratings yet
- TOMS Giving-Report 2013Document13 pagesTOMS Giving-Report 2013Inglorious KunalNo ratings yet
- HCFA 2008 Annual ReportDocument16 pagesHCFA 2008 Annual ReportHCFAMANo ratings yet
- PNB - Oriental Royal MEDICLAIM ProspectusDocument10 pagesPNB - Oriental Royal MEDICLAIM ProspectusKkaran SinghNo ratings yet
- For Website All Questions PDFDocument26 pagesFor Website All Questions PDFAyyaz HussainNo ratings yet
- Nueva Ecija University of Science and Technology: Case 7Document7 pagesNueva Ecija University of Science and Technology: Case 7jomariNo ratings yet
- Dyspepsia: Group 3ADocument14 pagesDyspepsia: Group 3AAradhanaRamchandaniNo ratings yet
- The Interaction Between Blood Pressure and Biryani LovingDocument3 pagesThe Interaction Between Blood Pressure and Biryani LovingrizkiyatulNo ratings yet
- Classic Imaging Signs A Guide To The Whole Body - 1stDocument382 pagesClassic Imaging Signs A Guide To The Whole Body - 1stclaudiuNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure: Caroline L. Guglielmetti RN, BSNDocument19 pagesCongestive Heart Failure: Caroline L. Guglielmetti RN, BSNbudoy00No ratings yet
- NURS FPX 6412 Assessment 1 Policy and Guidelines For The Informatics Staff - Making Decisions To Use Informatics Systems in PracticeDocument5 pagesNURS FPX 6412 Assessment 1 Policy and Guidelines For The Informatics Staff - Making Decisions To Use Informatics Systems in PracticeCarolyn HarkerNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Kinesiotaping Therapy in Sciatic Patients in Pregnancy Due To Lumbar Disc Herniation According To Mckenzie's Extension Back ExerciseDocument3 pagesThe Effect of Kinesiotaping Therapy in Sciatic Patients in Pregnancy Due To Lumbar Disc Herniation According To Mckenzie's Extension Back ExerciseAna Lu LoboNo ratings yet
- Telangana State Paramedical Board: Top Priority ExaminationsDocument21 pagesTelangana State Paramedical Board: Top Priority ExaminationsManojNo ratings yet
- Redefining Susceptibility Testing Categories S, I and R.: Gunnar Kahlmeter and The EUCAST Steering CommitteeDocument54 pagesRedefining Susceptibility Testing Categories S, I and R.: Gunnar Kahlmeter and The EUCAST Steering CommitteeRuth RachitaNo ratings yet
- Cytology Project in 18 PageDocument17 pagesCytology Project in 18 PageAnil Amrawanshi67% (3)
- International Journal of Women's Dermatology: Mohsen Baghchechi, Jeffery Dunn, Navin Jaipaul, Sharon E. JacobDocument5 pagesInternational Journal of Women's Dermatology: Mohsen Baghchechi, Jeffery Dunn, Navin Jaipaul, Sharon E. JacobR JNo ratings yet
- Biosafety and BiosecurityDocument39 pagesBiosafety and BiosecurityAlliah Angelica NavalNo ratings yet
- Post Anesthesia Care UnitDocument19 pagesPost Anesthesia Care UnitRizqidio LarisoNo ratings yet
- Nice Guidelines For VteDocument512 pagesNice Guidelines For VtesilcmtgNo ratings yet
- Joint Statement On Red Light and Siren Operations With LogosDocument4 pagesJoint Statement On Red Light and Siren Operations With LogosepraetorianNo ratings yet
- Nurs362 Professional Development PlanDocument4 pagesNurs362 Professional Development Planapi-272566401No ratings yet
- Clinical Pearls in NephrologyDocument5 pagesClinical Pearls in NephrologyEdmilson R. LimaNo ratings yet
- Management of CholeraDocument69 pagesManagement of CholeraNatalia LawrenceNo ratings yet
- Instruction For Collection of Microbiology PDFDocument8 pagesInstruction For Collection of Microbiology PDFAbu KaramNo ratings yet
- Garcin2018 PDFDocument9 pagesGarcin2018 PDFjoao marcelo lealNo ratings yet
- Iloilo Doctors' Hospital, Inc. Department of Internal MedicineDocument10 pagesIloilo Doctors' Hospital, Inc. Department of Internal MedicineAllison Eunice ServandoNo ratings yet
- Scabies.: Vanessa ChelimoDocument19 pagesScabies.: Vanessa ChelimoAlvin OmondiNo ratings yet
- Boundless: Upgrade Your Brain, Optimize Your Body & Defy AgingFrom EverandBoundless: Upgrade Your Brain, Optimize Your Body & Defy AgingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (66)
- Relentless: From Good to Great to UnstoppableFrom EverandRelentless: From Good to Great to UnstoppableRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (783)
- Weight Lifting Is a Waste of Time: So Is Cardio, and There’s a Better Way to Have the Body You WantFrom EverandWeight Lifting Is a Waste of Time: So Is Cardio, and There’s a Better Way to Have the Body You WantRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (38)
- Peak: The New Science of Athletic Performance That is Revolutionizing SportsFrom EverandPeak: The New Science of Athletic Performance That is Revolutionizing SportsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (95)
- Muscle for Life: Get Lean, Strong, and Healthy at Any Age!From EverandMuscle for Life: Get Lean, Strong, and Healthy at Any Age!Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (22)
- Power of 10: The Once-A-Week Slow Motion Fitness RevolutionFrom EverandPower of 10: The Once-A-Week Slow Motion Fitness RevolutionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (11)
- Aging Backwards: Reverse the Aging Process and Look 10 Years Younger in 30 Minutes a DayFrom EverandAging Backwards: Reverse the Aging Process and Look 10 Years Younger in 30 Minutes a DayNo ratings yet
- Chair Yoga: Sit, Stretch, and Strengthen Your Way to a Happier, Healthier YouFrom EverandChair Yoga: Sit, Stretch, and Strengthen Your Way to a Happier, Healthier YouRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (5)
- Functional Training and Beyond: Building the Ultimate Superfunctional Body and MindFrom EverandFunctional Training and Beyond: Building the Ultimate Superfunctional Body and MindRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (1)
- Music For Healing: With Nature Sounds For Natural Healing Powers: Sounds Of Nature, Deep Sleep Music, Meditation, Relaxation, Healing MusicFrom EverandMusic For Healing: With Nature Sounds For Natural Healing Powers: Sounds Of Nature, Deep Sleep Music, Meditation, Relaxation, Healing MusicRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Strong Is the New Beautiful: Embrace Your Natural Beauty, Eat Clean, and Harness Your PowerFrom EverandStrong Is the New Beautiful: Embrace Your Natural Beauty, Eat Clean, and Harness Your PowerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Wall Pilates: Quick-and-Simple to Lose Weight and Stay Healthy. A 30-Day Journey with + 100 ExercisesFrom EverandWall Pilates: Quick-and-Simple to Lose Weight and Stay Healthy. A 30-Day Journey with + 100 ExercisesNo ratings yet
- Yamas & Niyamas: Exploring Yoga's Ethical PracticeFrom EverandYamas & Niyamas: Exploring Yoga's Ethical PracticeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- The Yogi Code: Seven Universal Laws of Infinite SuccessFrom EverandThe Yogi Code: Seven Universal Laws of Infinite SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (104)
- Whole Body Barefoot: Transitioning Well to Minimal FootwearFrom EverandWhole Body Barefoot: Transitioning Well to Minimal FootwearRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (16)
- SAS Training Manual: How to get fit enough to pass a special forces selection courseFrom EverandSAS Training Manual: How to get fit enough to pass a special forces selection courseRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: Built for This: The Quiet Strength of PowerliftingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: Built for This: The Quiet Strength of PowerliftingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (132)
- Body by Science: A Research Based Program for Strength Training, Body building, and Complete Fitness in 12 Minutes a WeekFrom EverandBody by Science: A Research Based Program for Strength Training, Body building, and Complete Fitness in 12 Minutes a WeekRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (84)
- Endure: Mind, Body, and the Curiously Elastic Limits of Human PerformanceFrom EverandEndure: Mind, Body, and the Curiously Elastic Limits of Human PerformanceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (237)
- The Power of Now by Eckhart Tolle: Summary and AnalysisFrom EverandThe Power of Now by Eckhart Tolle: Summary and AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (12)
- How To Walk Yourself Healthy And Happy: Discover the physical and mental benefits of regular walking.From EverandHow To Walk Yourself Healthy And Happy: Discover the physical and mental benefits of regular walking.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (11)
- Not a Diet Book: Take Control. Gain Confidence. Change Your Life.From EverandNot a Diet Book: Take Control. Gain Confidence. Change Your Life.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (124)
- You: Breathing Easy: Meditation and Breathing Techniques to Relax, Refresh and RevitalizeFrom EverandYou: Breathing Easy: Meditation and Breathing Techniques to Relax, Refresh and RevitalizeRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (5)
- Body by Science: A Research Based Program to Get the Results You Want in 12 Minutes a WeekFrom EverandBody by Science: A Research Based Program to Get the Results You Want in 12 Minutes a WeekRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (38)