Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit-1 Bits PDF
Uploaded by
REVANTH KUMAR K0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views4 pagesOriginal Title
UNIT-1 BITS.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views4 pagesUnit-1 Bits PDF
Uploaded by
REVANTH KUMAR KCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
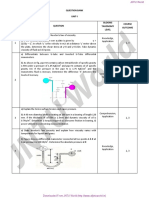
Fluid Mechanics
Unit-I
For a Newtonian fluid
Shear stress is proportional to Shear stress is proportional to rate
A. B.
shear strain of shear strain
1. Rate of shear stress is Rate of shear stress is
C. proportional to shear strain D. proportional to rate of shear
strain
E. All the above F. None of the above
The increase in temperature
Increases the viscosity of a Decreases the viscosity of a liquid
A. liquid and decreases the B. and increases the viscosity of a
2. viscosity of a gas gas
Increases the viscosity of both Decreases the viscosity of both a
C. D.
a liquid and a gas liquid and a gas
E. All the above F. None of the above
If a uniform solid body weighs 50 N in air and 30 N in water, its specific gravity is
A. 1.5 B. 1.67
3.
C. 2.5 D. 3.0
E. 5.0 F. None of the above
An oil has a kinematic viscosity of 1.25E–4 m2/s and a specific gravity of 0.80. What
is its dynamic (absolute) viscosity in kg/(m · s)?
4. A. 0.08 B. 0.10
C. 0.125 D. 1.0
E. 1.25 F. None of the above
5. Consider a soap bubble of diameter 3 mm. If the surface tension coefficient is 0.072
N/m and external pressure is 0 Pa gage, what is the bubble’s internal gage pressure?
A. -24 Pa B. 48 Pa
C. 96 Pa D. 192 Pa
E. -192 Pa F. None of the above
6. Two parallel plates, one moving at 4 m/s and the other fixed, are separated by a 5-
mm-thick layer of oil of specific gravity 0.80 and kinematic viscosity 1.25E−4 m2/s.
What is the average shear stress in the oil in Pa?
A. 80 B. 100
C. 125 D. 160
E. 200 F. None of the above
7. Buoyancy force is equal to
A. Resultant force on the body B. Resultant force acting on a
due to the surrounding fluid floating body
C. Weight of the fluid displaced D. Force necessary to maintain
by the solid body equilibrium of a submerged body
E. All the above F. None of the above
8. Which of the following pressure units represents least pressure?
A. Millibar B. Millimeter of mercury
C. N/mm2 D. Kgf/cm2
E. All the above F. None of the above
9. The centre of pressure will coincide with the CG if a plane surface is
A. Vertical B. Horizontal
C. Immersed in a gas D. Inclined
E. All the above F. None of the above
10. If the volume of a liquid weighing 3000 kg is 4 cubic meters, 0.75 is its
A. Specific mass B. Specific gravity
C. Specific weight D. Specific volume
E. All the above F. None of the above
11. ______________________= Local atmospheric pressure + ____________________.
12. ______________ is the pressure measured by a device with respect to local
atmospheric pressure.
13. Stoke is the unit of __________________________________.
14. ___________ is the force of attraction between the molecules of different liquids.
15. ___________________ is used to measure local atmospheric pressure.
16. Compressibility is the reciprocal of ___________________________.
17. The point of application of total pressure or static force on the surface is known as
_______________________.
18. The ratio of pressures between two points A and B located respectively at depths
0.5 m and 2 m below of water in a tank is _______________.
19. ____________________ is the measure of liquids tendency to take a spherical
shape, caused by the mutual attraction of the liquid molecules.
20. _________________ is the pressure at which a liquid boils and is in equilibrium
with its own vapour.
Key
1. B 2. B 3. C 4. B 5. D
6. A 7. C 8. A 9. B 10. B
11. Atmospheric pressure, Gauge pressure 12. Gauge pressure
13. Kinematic viscosity 14. Adhesion
15. Barometer 16. Bulk modulus of elasticity
17. Centre of pressure 18. 1:4
19. Surface tension 20. Vapour pressure
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5807)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Subsurface Geology and Resource ExplorationDocument10 pagesSubsurface Geology and Resource ExplorationnisacoreNo ratings yet
- ESP - Electric Submersible Pumps Design, 11 Chapters Consolidated, Mohamed Dewidar 2013Document451 pagesESP - Electric Submersible Pumps Design, 11 Chapters Consolidated, Mohamed Dewidar 2013joreli100% (2)
- Boiler and Boiler CalculationsDocument7 pagesBoiler and Boiler CalculationsChaya Stia ClaluiNo ratings yet
- Catalogue TCG2032V16 4Document4 pagesCatalogue TCG2032V16 4Mizan SarkarNo ratings yet
- Philippine Clean Air ActDocument48 pagesPhilippine Clean Air ActMaria Lorna O BerionesNo ratings yet
- 1412TP 204 204Document8 pages1412TP 204 204Muhammad UmairNo ratings yet
- Process Data Sheet For Fired HeaterDocument8 pagesProcess Data Sheet For Fired HeaterBangkiyak LanangNo ratings yet
- Fire Pump Check ListDocument1 pageFire Pump Check ListArafat Robin100% (1)
- Owners Manual ASX 2018 PDFDocument514 pagesOwners Manual ASX 2018 PDFNikolaJakopovicNo ratings yet
- Aggregate Impact Value: Why This Test?Document2 pagesAggregate Impact Value: Why This Test?REVANTH KUMAR KNo ratings yet
- I-MID Examinations (Subjective Test) : BranchDocument1 pageI-MID Examinations (Subjective Test) : BranchREVANTH KUMAR KNo ratings yet
- I-MID Examinations (Subjective Test) : BranchDocument1 pageI-MID Examinations (Subjective Test) : BranchREVANTH KUMAR KNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machinery Question BankDocument9 pagesFluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machinery Question BankREVANTH KUMAR KNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics ObjectiveDocument7 pagesFluid Mechanics ObjectiveREVANTH KUMAR KNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machinery Question BankDocument9 pagesFluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machinery Question BankREVANTH KUMAR KNo ratings yet
- Documentation Guide LinesDocument5 pagesDocumentation Guide LinesREVANTH KUMAR KNo ratings yet
- Previous Papers 2Document28 pagesPrevious Papers 2REVANTH KUMAR KNo ratings yet
- Assignement 3 FMDocument3 pagesAssignement 3 FMREVANTH KUMAR KNo ratings yet
- RCC Question PaperDocument4 pagesRCC Question PaperREVANTH KUMAR KNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Durability Indices For High Performance Concrete Mix Design As Per ACI 211-1Document4 pagesEvaluation of Durability Indices For High Performance Concrete Mix Design As Per ACI 211-1REVANTH KUMAR KNo ratings yet
- Concrete Technology Quiz-1 Answer All The Following QuestionsDocument4 pagesConcrete Technology Quiz-1 Answer All The Following QuestionsREVANTH KUMAR KNo ratings yet
- 1996-ATO pdf1779920554Document1 page1996-ATO pdf1779920554Hector ManNo ratings yet
- Drilling Calculation SummaryDocument3 pagesDrilling Calculation SummaryBerat HasolliNo ratings yet
- AMCO - RBI Engineer - Mr. Syed Hameed HussainDocument4 pagesAMCO - RBI Engineer - Mr. Syed Hameed HussainOwais MalikNo ratings yet
- Manual WalingaDocument68 pagesManual WalingaFederico De MartiniNo ratings yet
- TDS - Total - Lubrilam S 20L - BP2 - 201412 - enDocument1 pageTDS - Total - Lubrilam S 20L - BP2 - 201412 - enVelibor KaranovicNo ratings yet
- Formation EvaluationDocument61 pagesFormation Evaluationabelgonca7869No ratings yet
- Folly Current - July 9, 2010Document15 pagesFolly Current - July 9, 2010Lucky_Dog_PublishingNo ratings yet
- Electric Heat ExchangerDocument2 pagesElectric Heat Exchangerhappale2002No ratings yet
- Flight 143Document5 pagesFlight 143blackwellbertNo ratings yet
- UNIT7L1 - 2S - Electronically Controlled Fuel SystemsDocument10 pagesUNIT7L1 - 2S - Electronically Controlled Fuel SystemsEbied Yousif AlyNo ratings yet
- PROBLEMS of Energy BallanceDocument35 pagesPROBLEMS of Energy BallanceDiah Wulan AyuningtiasNo ratings yet
- Exer 2 Internal Combustion EngineDocument6 pagesExer 2 Internal Combustion Enginesheil.cogayNo ratings yet
- Fluid Catalytic Cracking 2Document27 pagesFluid Catalytic Cracking 2PAWAR ROHAN RAMESHNo ratings yet
- Prashant Final Project-OnGCDocument127 pagesPrashant Final Project-OnGCvpceb22enNo ratings yet
- Cat Electronic Technician 2015A v1.0 Product Status ReportDocument5 pagesCat Electronic Technician 2015A v1.0 Product Status ReportVentsislav VenevNo ratings yet
- Document CepDocument7 pagesDocument CepShanzay DaudNo ratings yet
- Flow Through ChokeDocument7 pagesFlow Through ChokeShahzad AshrafNo ratings yet
- PETSOC-09-07-18 Gas Condensate Reservoir Performance PDFDocument7 pagesPETSOC-09-07-18 Gas Condensate Reservoir Performance PDFEduardo UstarezNo ratings yet
- Catalogo PrincipalDocument89 pagesCatalogo PrincipalJavierfox98100% (1)
- Graco Husky 3275 Diaphragm Pump Data SheetDocument8 pagesGraco Husky 3275 Diaphragm Pump Data SheetMROstop.comNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Centrifugal CompressorsDocument17 pagesPresentation On Centrifugal CompressorsakshayupadhyayNo ratings yet