Professional Documents
Culture Documents
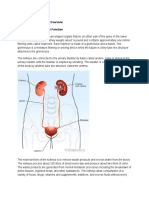
Causes: Normal Kidney vs. Diseased Kidney
Uploaded by
Abdel Azim Mohamed0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views4 pagespharma
Original Title
Kidney
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views4 pagesCauses: Normal Kidney vs. Diseased Kidney
Uploaded by
Abdel Azim MohamedYou are on page 1of 4
Causes
Normal kidney vs. diseased kidney
Polycystic kidney
Chronic kidney disease occurs when a disease or condition impairs kidney
function, causing kidney damage to worsen over several months or years.
Diseases and conditions that cause chronic kidney disease include:
Type 1 or type 2 diabetes
High blood pressure
Glomerulonephritis (gloe-mer-u-low-nuh-FRY-tis), an inflammation of the
kidney's filtering units (glomeruli)
Interstitial nephritis (in-tur-STISH-ul nuh-FRY-tis), an inflammation of the
kidney's tubules and surrounding structures
Polycystic kidney disease
Prolonged obstruction of the urinary tract, from conditions such as enlarged
prostate, kidney stones and some cancers
Vesicoureteral (ves-ih-koe-yoo-REE-tur-ul) reflux, a condition that causes
urine to back up into your kidneys
Recurrent kidney infection, also called pyelonephritis (pie-uh-low-nuh-FRY-
tis)
Risk factors
Factors that may increase your risk of chronic kidney disease include:
Diabetes
High blood pressure
Heart and blood vessel (cardiovascular) disease
Smoking
Obesity
Being African-American, Native American or Asian-American
Family history of kidney disease
Abnormal kidney structure
Older age
What is chronic kidney disease (CKD)?
Chronic kidney disease includes conditions that damage your kidneys and
decrease their ability to keep you healthy by doing the jobs listed. If kidney
disease gets worse, wastes can build to high levels in your blood and make you
feel sick. You may develop complications like high blood pressure, anemia (low
blood count), weak bones, poor nutritional health and nerve damage. Also,
kidney disease increases your risk of having heart and blood vessel disease.
These problems may happen slowly over a long period of time. Chronic kidney
disease may be caused by diabetes, high blood pressure and other disorders.
Early detection and treatment can often keep chronic kidney disease from getting
worse. When kidney disease progresses, it may eventually lead to kidney failure,
which requires dialysis or a kidney transplant to maintain life.
The Facts About Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
30 million American adults have CKD and millions of others are at
increased risk.
Early detection can help prevent the progression of kidney disease to
kidney failure.
Heart disease is the major cause of death for all people with CKD.
Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) is the best estimate of kidney function.
Hypertension causes CKD and CKD causes hypertension.
Persistent proteinuria (protein in the urine) means CKD is present.
High risk groups include those with diabetes, hypertension and family
history of kidney failure.
African Americans, Hispanics, Pacific Islanders, American Indians and
Seniors are at increased risk.
Two simple tests can detect CKD: blood pressure, urine albumin and
serum creatinine.
What causes CKD?
The two main causes of chronic kidney disease are diabetes and high blood
pressure, which are responsible for up to two-thirds of the cases. Diabetes
happens when your blood sugar is too high, causing damage to many organs in
your body, including the kidneys and heart, as well as blood vessels, nerves and
eyes. High blood pressure, or hypertension, occurs when the pressure of your
blood against the walls of your blood vessels increases. If uncontrolled, or poorly
controlled, high blood pressure can be a leading cause of heart attacks, strokes
and chronic kidney disease. Also, chronic kidney disease can cause high blood
pressure.
Other conditions that affect the kidneys are:
Glomerulonephritis, a group of diseases that cause inflammation and
damage to the kidney's filtering units. These disorders are the third most
common type of kidney disease.
Inherited diseases, such as polycystic kidney disease, which causes large
cysts to form in the kidneys and damage the surrounding tissue.
Malformations that occur as a baby develops in its mother's womb. For
example, a narrowing may occur that prevents normal outflow of urine and
causes urine to flow back up to the kidney. This causes infections and
may damage the kidneys.
Lupus and other diseases that affect the body's immune system.
Obstructions caused by problems like kidney stones, tumors or an
enlarged prostate gland in men.
Repeated urinary infections.
https://www.kidney.org/atoz/content/about-chronic-kidney-disease
https://www.kidney.org/kidneydisease/howkidneyswrk normal functions
https://www.ajkd.org/
You might also like
- Renal Diet Cookbook: 100 Simple & Delicious Kidney-Friendly Recipes To Manage Kidney Disease (CKD) And Avoid Dialysis (The Kidney Disease Cookbook)From EverandRenal Diet Cookbook: 100 Simple & Delicious Kidney-Friendly Recipes To Manage Kidney Disease (CKD) And Avoid Dialysis (The Kidney Disease Cookbook)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Polycystic Kidneys, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesFrom EverandPolycystic Kidneys, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument55 pagesChronic Kidney DiseaseBentoys Street100% (1)
- CKD CaseDocument2 pagesCKD CasePatricia Kaye Tayag CastroNo ratings yet
- Additional Research in CKD - SALES&CABANDODocument8 pagesAdditional Research in CKD - SALES&CABANDOShirryley R. SalesNo ratings yet
- The Facts About Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) : Back To TopDocument9 pagesThe Facts About Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) : Back To Top2netvelasquezNo ratings yet
- About Chronic Kidney Disease - National Kidney FoundationDocument3 pagesAbout Chronic Kidney Disease - National Kidney FoundationTiyang Solo TigoNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney FailureDocument21 pagesChronic Kidney FailurePatrick John AsperillaNo ratings yet
- Normal Kidneys and Their Function: Chronic Kidney Disease OverviewDocument12 pagesNormal Kidneys and Their Function: Chronic Kidney Disease OverviewLouie Collado100% (1)
- Case Study For Chronic Renal FailureDocument6 pagesCase Study For Chronic Renal FailureGabbii CincoNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument8 pagesChronic Kidney DiseaseSally MavyNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease OverviewDocument15 pagesChronic Kidney Disease Overviewjames100% (1)
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument3 pagesChronic Kidney DiseaseGen Paulo EstoyaNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument20 pagesChronic Kidney DiseasePappu HSD VenkateshNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal FailureDocument7 pagesChronic Renal FailureMary Jane Tiangson100% (1)
- CaseStudy ChronicRenalFailureDocument29 pagesCaseStudy ChronicRenalFailureCarlcedrick ManlapusNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument8 pagesChronic Kidney DiseaseAyiessa_AJNo ratings yet
- CKD - Case PresDocument29 pagesCKD - Case PresChristine Joy Ilao PasnoNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument27 pagesChronic Kidney DiseaseGloria KikiNo ratings yet
- What Is Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) ?: Diabetes High Blood PressureDocument4 pagesWhat Is Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) ?: Diabetes High Blood Pressureawana1991No ratings yet
- ColDocument40 pagesCol12F 24 Renu SinghNo ratings yet
- End Stage Renal DiseaseDocument62 pagesEnd Stage Renal DiseaseMae Navidas DigdiganNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease OverviewDocument28 pagesChronic Kidney Disease Overviewomie22100% (9)
- I. Data Table A. Physical Properties: Experiment No. 6 UrineDocument6 pagesI. Data Table A. Physical Properties: Experiment No. 6 UrineTyn TynNo ratings yet
- DialysisDocument34 pagesDialysisAntonio Junior CastroNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument7 pagesChronic Kidney DiseasejprakashjjNo ratings yet
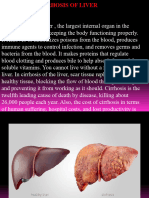
- Chirosis HepaticDocument8 pagesChirosis HepaticCikalHrNo ratings yet
- Kidney DisorderDocument5 pagesKidney DisorderTWINKLE MAE EGAYNo ratings yet
- Renal Failure NoteDocument27 pagesRenal Failure Notechiemerieagana3No ratings yet
- Kimmelstiel-Wilson Syndrome BDocument13 pagesKimmelstiel-Wilson Syndrome BRanela Kwinkee Pastor SalazarNo ratings yet
- Cirrhosis of The Liver: CausesDocument6 pagesCirrhosis of The Liver: CausespakdejackNo ratings yet
- Kidney FailureDocument2 pagesKidney Failuredanee しNo ratings yet
- Avi Suarez Case StudyDocument7 pagesAvi Suarez Case StudyIva Abigail EspinoNo ratings yet
- Non Communicable Disease Grade 7Document4 pagesNon Communicable Disease Grade 7Joshua RamirezNo ratings yet
- End-Stage Renal DiseaseDocument7 pagesEnd-Stage Renal Diseasemarvin de castroNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument4 pagesIntroductionCristina L. JaysonNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument11 pagesChronic Kidney DiseaseMah AlfaroNo ratings yet
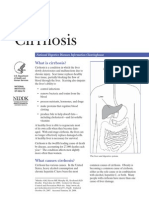
- Cirrhosis: On This PageDocument23 pagesCirrhosis: On This PageHasna FauziyahNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument5 pagesChronic Kidney DiseaseFaye R. PelayoNo ratings yet
- Rajashree 12Document13 pagesRajashree 12Rakesh BarmanNo ratings yet
- By3 Safaa Mohammed Abd-Elghany: V Nder SupervisionDocument13 pagesBy3 Safaa Mohammed Abd-Elghany: V Nder SupervisiontrrdsNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis Diabetic NephropathyDocument6 pagesCase Analysis Diabetic NephropathyJassel EscobarNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal FailureDocument26 pagesChronic Renal FailureRemington Thomas II100% (5)
- Continue RENALDocument8 pagesContinue RENALLeofe CorregidorNo ratings yet
- Ôm Ôm Ôm ÔmDocument7 pagesÔm Ôm Ôm ÔmMr-Ms KoobecafNo ratings yet
- Ôm Ôm Ôm ÔmDocument7 pagesÔm Ôm Ôm ÔmMr-Ms KoobecafNo ratings yet
- Deborah Mukendenge Mujinga Nurs201Document6 pagesDeborah Mukendenge Mujinga Nurs201Lois MpangaNo ratings yet
- Chronic Glumerulonephritis HandoutsDocument8 pagesChronic Glumerulonephritis HandoutsLanzen DragneelNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal FailureDocument4 pagesChronic Renal FailureHercy Emarie AnabeNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease (Chronic Renal Failure)Document9 pagesChronic Kidney Disease (Chronic Renal Failure)Meet NarulaNo ratings yet
- ESRDDocument10 pagesESRDKayle Irah CaburnayNo ratings yet
- Kidneydiseasesppt 190920122127Document10 pagesKidneydiseasesppt 190920122127shazinahmedsirajNo ratings yet
- NephritisDocument16 pagesNephritisyikesNo ratings yet
- Kidney DiseaseDocument33 pagesKidney DiseaseRezin JNo ratings yet
- Kidney Failure FactsDocument19 pagesKidney Failure Factss.khan9211rediffmail.comNo ratings yet
- Filling Machine in CapsuleDocument9 pagesFilling Machine in Capsuleomer hushyarNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument10 pagesBiologyZack Leaf HendersonNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument54 pagesChronic Kidney DiseaseJosh Matthew RosalesNo ratings yet
- Spectrum September KidneyDocument29 pagesSpectrum September KidneyParth LandeNo ratings yet
- Nephrotic SyndromeDocument8 pagesNephrotic SyndromeKanmani AniNo ratings yet
- PETE 4090-Unconventional Hydrocarbon Reservoirs Course SyllabusDocument4 pagesPETE 4090-Unconventional Hydrocarbon Reservoirs Course SyllabusAbdel Azim MohamedNo ratings yet
- Abdelazim Mohamed Abdelazim CV - Vesion One.16-2-2021 PDF 2Document3 pagesAbdelazim Mohamed Abdelazim CV - Vesion One.16-2-2021 PDF 2Abdel Azim MohamedNo ratings yet
- Chapter.7 CRUDE OIL TREATING SYSTEMS (Q&A)Document3 pagesChapter.7 CRUDE OIL TREATING SYSTEMS (Q&A)Abdel Azim MohamedNo ratings yet
- FUE - (Non Technical Session) - 1-Mar-22Document1 pageFUE - (Non Technical Session) - 1-Mar-22Abdel Azim MohamedNo ratings yet
- Write Short Notes About Sieve Analysis, and It Can Be Used For Describing The Formation Sand Sorting, Explain With SketchDocument16 pagesWrite Short Notes About Sieve Analysis, and It Can Be Used For Describing The Formation Sand Sorting, Explain With SketchAbdel Azim MohamedNo ratings yet
- Rig Site Calculations For Drilling OperationsDocument15 pagesRig Site Calculations For Drilling OperationsAbdel Azim MohamedNo ratings yet
- 10 1002-Asjc 1992figure19920001Document1 page10 1002-Asjc 1992figure19920001Abdel Azim MohamedNo ratings yet
- Drill Bit SelectionDocument10 pagesDrill Bit SelectionAbdel Azim MohamedNo ratings yet
- What Is Sweep Efficiency? and What Is The Main Difference Between Arial, Vertical and Volumetric Sweep Efficiency?Document4 pagesWhat Is Sweep Efficiency? and What Is The Main Difference Between Arial, Vertical and Volumetric Sweep Efficiency?Abdel Azim MohamedNo ratings yet
- InnovEgypt Project Deliverables Team Name Group No.Document15 pagesInnovEgypt Project Deliverables Team Name Group No.Abdel Azim MohamedNo ratings yet
- Land Rigs Equipment List Template - OZDocument50 pagesLand Rigs Equipment List Template - OZAbdel Azim MohamedNo ratings yet
- Drilling r1Document12 pagesDrilling r1Abdel Azim MohamedNo ratings yet
- Matlab Workshop OnlineDocument5 pagesMatlab Workshop OnlineAbdel Azim MohamedNo ratings yet
- Reservoir Engineering 1 Course (1 Ed.)Document43 pagesReservoir Engineering 1 Course (1 Ed.)Abdel Azim MohamedNo ratings yet
- Adsorbed Free: 1. What Are The Organic Shale Reservoirs? Give at Least 4 CharacteristicsDocument5 pagesAdsorbed Free: 1. What Are The Organic Shale Reservoirs? Give at Least 4 CharacteristicsAbdel Azim MohamedNo ratings yet
- Rig Select2020Document3 pagesRig Select2020Abdel Azim MohamedNo ratings yet
- What Is Sweep Efficiency? and What Is The Main Difference Between Arial, Vertical and Volumetric Sweep Efficiency?Document4 pagesWhat Is Sweep Efficiency? and What Is The Main Difference Between Arial, Vertical and Volumetric Sweep Efficiency?Abdel Azim MohamedNo ratings yet
- 1112 GGDocument29 pages1112 GGAbdel Azim MohamedNo ratings yet
- - A soil particle is found to be subjected to a, and a - Find by using the the the place of with respect to the major principal stresses, and also find τmaxDocument1 page- A soil particle is found to be subjected to a, and a - Find by using the the the place of with respect to the major principal stresses, and also find τmaxAbdel Azim MohamedNo ratings yet
- 8 Man-Basic Open Hole ServicesDocument18 pages8 Man-Basic Open Hole ServicesAbdel Azim MohamedNo ratings yet
- Research About/well Perforation Presented by /: Abdelazim Mohamed Abdelazim Mohamed Afify (20152304)Document30 pagesResearch About/well Perforation Presented by /: Abdelazim Mohamed Abdelazim Mohamed Afify (20152304)Abdel Azim MohamedNo ratings yet
- N.ocr 1Document1 pageN.ocr 1Abdelazim MohamedNo ratings yet
- Chapter (2) - Air Pollution PDFDocument31 pagesChapter (2) - Air Pollution PDFAbdel Azim MohamedNo ratings yet
- Chapter (3) - Climate ChangeDocument25 pagesChapter (3) - Climate ChangeAbdel Azim MohamedNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4.docx - ESP dESIGN PDFDocument7 pagesAssignment 4.docx - ESP dESIGN PDFAbdel Azim MohamedNo ratings yet
- Sheet PET 512 PDFDocument1 pageSheet PET 512 PDFAbdel Azim MohamedNo ratings yet
- Sheet PET 512 PDFDocument1 pageSheet PET 512 PDFAbdel Azim MohamedNo ratings yet
- CT Lec1Document24 pagesCT Lec1Abdel Azim MohamedNo ratings yet
- Chapter (2) - Air Pollution PDFDocument31 pagesChapter (2) - Air Pollution PDFAbdel Azim MohamedNo ratings yet
- Well Perforation MeDocument19 pagesWell Perforation MeAbdel Azim MohamedNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic NursingDocument21 pagesOrthopedic NursingCris Constantino San JuanNo ratings yet
- Mom WP Med RPTDocument1 pageMom WP Med RPTravi kumar v100% (1)
- Bleeding Per RectumeDocument35 pagesBleeding Per RectumetharakaNo ratings yet
- Review 2Document12 pagesReview 2Christine Rubio100% (1)
- DermatologyDocument23 pagesDermatologyAntung AlangdeoNo ratings yet
- Coding For Lab SvcsDocument54 pagesCoding For Lab SvcsTintinNo ratings yet
- Healthy Body CompositionDocument18 pagesHealthy Body CompositionSDasdaDsadsaNo ratings yet
- 2012 UpmcccanualreportDocument70 pages2012 Upmcccanualreportapi-290001443No ratings yet
- Chemicals Safety PresentationDocument39 pagesChemicals Safety Presentatione cube100% (1)
- Brachy Quality GuideDocument270 pagesBrachy Quality GuideTejinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Physical Assessment DaraDocument3 pagesPhysical Assessment DaraMichael Bon MargajaNo ratings yet
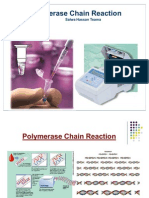
- Polymerase Chain Reaction: Salwa Hassan TeamaDocument56 pagesPolymerase Chain Reaction: Salwa Hassan TeamaSamiksha SharmaNo ratings yet
- AstroDiagonosis CancerDocument31 pagesAstroDiagonosis CancerOvn MurthyNo ratings yet
- FilgrastimDocument3 pagesFilgrastimfransiscaNo ratings yet
- Care of Clients With Problems in Perception and CoordinationDocument44 pagesCare of Clients With Problems in Perception and CoordinationmikErlhNo ratings yet
- Textbook of Clinical Occupational and Environmental MedicineDocument4 pagesTextbook of Clinical Occupational and Environmental MedicineAmos SiraitNo ratings yet
- Induction of LabourDocument8 pagesInduction of Labourgeorgeloto12100% (1)
- List of Eponyms in MedicineDocument12 pagesList of Eponyms in MedicinePavan V RaiNo ratings yet
- Classification of Periodontal Diseases and Conditions 2018Document15 pagesClassification of Periodontal Diseases and Conditions 2018Jean DatorNo ratings yet
- Red Book Atlas of Pediatric Infectious Diseases 3rd EditionDocument786 pagesRed Book Atlas of Pediatric Infectious Diseases 3rd EditionAaron Elvir100% (2)
- Medical Anthropology and The World System 2004Document440 pagesMedical Anthropology and The World System 2004Maya Yuda100% (1)
- Summerassignment2 SurvivalofsickestDocument3 pagesSummerassignment2 Survivalofsickestapi-196665276No ratings yet
- Sveučilište U Mostaru (Napisi Puno Ime Fakulteta I Smjer Ako To Nesto Ima)Document7 pagesSveučilište U Mostaru (Napisi Puno Ime Fakulteta I Smjer Ako To Nesto Ima)Lucija PavkovicNo ratings yet
- Ganglion Impar Block2Document4 pagesGanglion Impar Block2Rindy Bukand RindiNo ratings yet
- Protocol Standing Order TBDocument33 pagesProtocol Standing Order TByuniNo ratings yet
- Breast MassesDocument12 pagesBreast MassesTrivedi NisargNo ratings yet
- 1201 Alodine, AKA DX 503Document7 pages1201 Alodine, AKA DX 503Mark Evan SalutinNo ratings yet
- 5096 w09 Ms 2Document7 pages5096 w09 Ms 2Asiff MohammedNo ratings yet
- Color and LearningDocument9 pagesColor and LearningRodrigo HolguínNo ratings yet
- Emerging Biopharmas Contribution To InnovationDocument60 pagesEmerging Biopharmas Contribution To InnovationGene ParksNo ratings yet