Professional Documents
Culture Documents
mạch điện tử Chapter2 Quiz
Uploaded by
Ma Trix0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views17 pagestài liệu mạch điện tử chương 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documenttài liệu mạch điện tử chương 2
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views17 pagesmạch điện tử Chapter2 Quiz
Uploaded by
Ma Trixtài liệu mạch điện tử chương 2
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 17
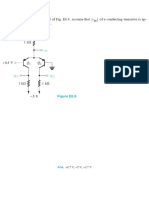
The transistor in the circuit of Fig. 6.14(a) has B= 100 and exhibits ag, of 0.7 V at i,=1 mA. Design the
circuit so that a current of 2 mA flows through the collector and a voltage of +5 V appears at the collector.
+15 V
Re
Figure 6.14 Circuit for Example 62.
Refer to Fig. 6.14(b). We note at the outset that since we are required to design for V,=+5 V. the CBJ
will be reverse biased and the BIT will be operating in the active mode. To obtain a voltage V.=+5 V.
the voltage drop across R, must be 15 — 5 = 10 V. Now, since I, = 2 mA, the value of R, should be
selected according to
Ro 5kQ
2mA
Since vg = 0.7 Vat ip= 1 mA, the value of vpe at ip = 2 mA is
Ver
Since the base is at 0 V, the emitter voltage should be
Vp = -O.71TV
For 8 = 100. @ = 100/101 = 0.99. Thus the emitter current should be
2 mA,
@ 099
Now the valne required for R, can be determined from
= (C15)
7.07 kQ
2.02
This completes the design. We should note, however, that the calculations above were made with a
degree of precision that is usually neither necessary nor justified in practice in view. for instance. of the
expected tolerances of component values, Nevertheless, we chose to do the design precisely in order to
illustrate the various steps involved.
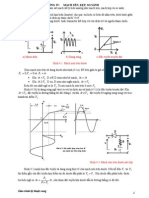
In the circuit shown in Fig. E6.13, the voltage at the emitter was measured and found to be
~0.7 V. If 8 =50. find I,. Jp. Ie. and Vo.
+10V
-10V Figure £6.13
You might also like
- Chapter5 KDCSATDocument28 pagesChapter5 KDCSATMa TrixNo ratings yet
- mạch điện tử Chapter 1Document40 pagesmạch điện tử Chapter 1Ma TrixNo ratings yet
- Bài Giải Phần Truyền SóngDocument11 pagesBài Giải Phần Truyền SóngMa TrixNo ratings yet
- Chapter4 QuizDocument3 pagesChapter4 QuizMa TrixNo ratings yet
- Quan Ly Du An Cho Ky SuDocument264 pagesQuan Ly Du An Cho Ky SuMa TrixNo ratings yet
- Chuong IvDocument15 pagesChuong IvMa TrixNo ratings yet
- Chuong IvDocument15 pagesChuong IvMa TrixNo ratings yet
- CH - NG IDocument17 pagesCH - NG IMa TrixNo ratings yet
- CH - NG IiiDocument15 pagesCH - NG IiiMa TrixNo ratings yet
- CH - NG IiDocument11 pagesCH - NG IiMa TrixNo ratings yet
- BCTN Bai4Document7 pagesBCTN Bai4Ma TrixNo ratings yet
- Cau Kien Dien TuDocument176 pagesCau Kien Dien TuMa TrixNo ratings yet
- Bai TNCSTD 1Document18 pagesBai TNCSTD 1Trần Thanh HoàngNo ratings yet
- TNTLS2013Document56 pagesTNTLS2013Huy VoNo ratings yet
- VXL BT CH1Document7 pagesVXL BT CH1Ma TrixNo ratings yet