Professional Documents
Culture Documents
7 Steps of Writing A LP
Uploaded by
Sera MystOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
7 Steps of Writing A LP
Uploaded by
Sera MystCopyright:
Available Formats
Step 1: Check prior knowledge
This activity will allow students to begin to identify present perfect tense in
a natural way: by reading a conversation topic in which this tense naturally
appears.
Hand out copies of the script below.
Select two students to read the parts out loud.
Write on the board: Present perfect is used to:
Discuss the three main ways in which present perfect was used in the
above conversation. Be sure to number the three ways. Ask students
to give examples.
Students’ prior knowledge:
- Form: S + HAS/ HAVE + P2
- Usages, Signals
Step 2: Define the teaching objectives
(a) Learning:
By the end of lesson, students will be able to understand when to use the past
simple and when to use the present perfect and proceduce examples of
present perfect tense.
(b) Action:
By the end of lesson, students will be able to write or describe their
experience up to the present.
Practice and develop speaking skills
Step 3: Prioritise the information
(a) Essential information: Students must know all the forms, usages, signals of
Present perfect tense, and identify when to use the past simple and when to
use the present perfect.
(b) Related information: students should know the pronunciation of verbs in P.P
form, and learn more new vocabulary.
(c) Complementary information: students could know more about background
knowledge from conversations, exercises.
Step 4: Arrange the order of content
The logical order of this lesson is to move from that which is known to that
which is unknown.
Firstly, warm-up activity is to check students’ prior knowledge
Secondly, Presentation is to teach students about Present perfect tense.
Thirdly, practice using Present perfect tense by doing exercises
Finally, projects, conversations help students practice and develop
more speaking skill.
Step 5: Selecting of the resources:
Bring printed handouts for students
Preparing flashcards with irregular verbs on them
Experiences students worksheet
Prepare students worksheets
Prepare projectors
Bring a print out of the slides in case there is a problem with the
computer
Step 6: Selecting the teaching techniques:
Brainstorming :
Ask your students to share some of the things they or their family
members do every week.
Have them talk about the actions using complete sentences. For
example, a student may share: I go to school.Dad does the dishes.
Write some of the sentences on the board (verbatim, even if they
contain mistakes).
Have volunteers read the examples and correct any mistakes they
notice. To help them, you can ask a guiding question such as: Does
anything sound weird when you read it out loud?
Explain the different participles that a verb can have. If a verb
describes an activity that's currently taking place (e.g. jumping), then
it's a present participle. It if describes an action that's already
happened, it's a past participle(e.g. jumped).
Let them know that you can tell whether a verb is regular or irregular
based on its past participle. If a verb's past participle ends in -ed (e.g.
laughed), then it's a regular verb. If it doesn't end in -ed (e.g. ran),
then it's an irregular verb.
Questions and answer
Ask the questions to check whether students have understood the
information
Encouraging students to ask questions, this helps to clear up any
misunderstandings
Games: “The excellent story writer”
Place students into groups of three.
Ask them to use their irregular verbs to create sentences in present
perfect tense.
Let them know that these sentences will need to be compiled into a
short story.
Once they've finished, have each group come up to the front of the
room and tell their story.
Step 7. Estimating the segment times:
Introduction (10 minutes)
Explicit Instruction/Teacher modeling (5 minutes)
Guided Practice (10 minutes)
Independent working time (10 minutes)
Assessment (5 minutes)
Review and closing ( 5 minutes)
You might also like
- Activity Type: Several Short Speaking Activities Level: A2+ Age: Teenage/AdultDocument6 pagesActivity Type: Several Short Speaking Activities Level: A2+ Age: Teenage/AdultAgung AdyatmikaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 2Document3 pagesLesson Plan 2api-283392025No ratings yet
- Listening Subskills 2Document5 pagesListening Subskills 2Ngân TrầnNo ratings yet
- On-Line Course - Units Grammar ExpressDocument10 pagesOn-Line Course - Units Grammar ExpresserickperdomoNo ratings yet
- STEPP Lesson Plan Form: Content Standard(s) Addressed by This LessonDocument6 pagesSTEPP Lesson Plan Form: Content Standard(s) Addressed by This Lessonapi-264548225No ratings yet
- Lesson Planning Form For Accessible Instruction - Calvin College Education ProgramDocument5 pagesLesson Planning Form For Accessible Instruction - Calvin College Education Programapi-336528722No ratings yet
- Verbs and Their TensesDocument5 pagesVerbs and Their TensesPurisima D. BagsawanNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Foldable Perfect Tenses Jennifer Swain ADocument3 pagesLesson Plan Foldable Perfect Tenses Jennifer Swain Aapi-233370840No ratings yet
- Cursul de Pregătire Pentru TitularizareDocument12 pagesCursul de Pregătire Pentru TitularizareAnonymous Wfl201YbYo100% (1)
- Handouts - Grammar Workshop Winter 2012cDocument6 pagesHandouts - Grammar Workshop Winter 2012csocallifeNo ratings yet
- Imperfectlessonplan 5Document3 pagesImperfectlessonplan 5api-284249375No ratings yet
- Assure Model Instructional Plan Draft 2Document7 pagesAssure Model Instructional Plan Draft 2api-505405562No ratings yet
- Anecdotes Get Everyone Talking: Anecdotes and English Language TeachingDocument3 pagesAnecdotes Get Everyone Talking: Anecdotes and English Language Teachingsarah rasydNo ratings yet
- Anecdotes Get Everyone TalkingDocument3 pagesAnecdotes Get Everyone Talkingsarah rasydNo ratings yet
- ASSURE Model Instructional PlanDocument9 pagesASSURE Model Instructional Planapi-340857409No ratings yet
- Presenting and Practising LanguageDocument5 pagesPresenting and Practising Languagevalerika1989100% (1)
- Strategies and Examples in Teaching ListeningDocument4 pagesStrategies and Examples in Teaching Listeningcastrokathlynjoy24No ratings yet
- Living Forever Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesLiving Forever Lesson Planapi-425637153No ratings yet
- Language Arts Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesLanguage Arts Lesson Planapi-240544643No ratings yet
- TEFL SSummaryDocument4 pagesTEFL SSummarymariaNo ratings yet
- Lesson materials. Board game (printDocument20 pagesLesson materials. Board game (printJonny xiluNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan GrammarDocument5 pagesLesson Plan GrammarPierre Noumbissi Teaching Portfolio Capstone 2 Final Project.No ratings yet
- Flipped Grammar LessonDocument5 pagesFlipped Grammar Lessonapi-268373101100% (1)
- Lesson Plan - Prepositional PhrasesDocument3 pagesLesson Plan - Prepositional Phrasesapi-2135472360% (1)
- Teaching English Language Skills TechniquesDocument11 pagesTeaching English Language Skills TechniquesIoana IonitaNo ratings yet
- HW5e PreIntermediate TG Unit01 PDFDocument13 pagesHW5e PreIntermediate TG Unit01 PDFMatheus PereiraNo ratings yet
- Headway5thEd Pre Intermediate TeachersGuideDocument150 pagesHeadway5thEd Pre Intermediate TeachersGuideAmbra FerrarottoNo ratings yet
- Flipped Lesson 1Document19 pagesFlipped Lesson 1api-325261291No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 2 WeeblyDocument4 pagesLesson Plan 2 Weeblyapi-284602462No ratings yet
- Instructional Plan 4Document7 pagesInstructional Plan 4api-314976210No ratings yet
- Lecture Unit 3 Mod 3Document26 pagesLecture Unit 3 Mod 3del420No ratings yet
- Reflective Lesson Plan 1Document5 pagesReflective Lesson Plan 1straitmi100% (1)
- Unit Part 2Document6 pagesUnit Part 2api-547144460No ratings yet
- Chapter Five Teaching Language ComponentsDocument45 pagesChapter Five Teaching Language ComponentsElmin Josephine tambingNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Adapted For MllsDocument4 pagesLesson Plan Adapted For Mllsapi-667037729No ratings yet
- Flipped Lesson: Mad (Libs) For Nouns and VerbsDocument6 pagesFlipped Lesson: Mad (Libs) For Nouns and Verbsapi-323813187No ratings yet
- French 3 LessonsDocument10 pagesFrench 3 Lessonsapi-242011178No ratings yet
- How-To Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesHow-To Lesson Planapi-276590409No ratings yet
- All About Me Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesAll About Me Lesson PlanBettiana GarciaNo ratings yet
- ? To Improve WritingDocument5 pages? To Improve WritingReda AlsadekNo ratings yet
- On Line Course - Units Grammar ExpressDocument4 pagesOn Line Course - Units Grammar ExpresserickperdomoNo ratings yet
- Educ 302 - Lesson 4Document3 pagesEduc 302 - Lesson 4api-339064965No ratings yet
- Dictations Please Improves Listening, Spelling, and VocabularyDocument3 pagesDictations Please Improves Listening, Spelling, and VocabularyHaniza AnyssNo ratings yet
- Edtpa-Aligned Lesson For All ClassesDocument12 pagesEdtpa-Aligned Lesson For All Classesapi-267736442No ratings yet
- Millicent Atkins School of Education: Common Lesson Plan TemplateDocument6 pagesMillicent Atkins School of Education: Common Lesson Plan Templateapi-382117266No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Observation 1Document6 pagesLesson Plan Observation 1api-702381076No ratings yet
- Activities To Encourage Speaking FluencyDocument5 pagesActivities To Encourage Speaking FluencyZainab ShdefatNo ratings yet
- Tài liệu kỹ thuật 2 chỉnh sửa 2014 2Document60 pagesTài liệu kỹ thuật 2 chỉnh sửa 2014 2englishdept.fansipanschoolNo ratings yet
- Grammar TeachingDocument6 pagesGrammar TeachingMiryam Niño PuelloNo ratings yet
- Mary Mistretta's Retrofit Assignment: Original Lesson PlanDocument9 pagesMary Mistretta's Retrofit Assignment: Original Lesson Planmist2662No ratings yet
- Edss 511 - 1st Lesson Unit PlanDocument4 pagesEdss 511 - 1st Lesson Unit Planapi-246041784No ratings yet
- Travel Unit Lesson Plan 2Document4 pagesTravel Unit Lesson Plan 2api-524805491No ratings yet
- How To Teach Prepositions of PlaceDocument4 pagesHow To Teach Prepositions of Placeapi-252821028No ratings yet
- College of Saint Mary Lesson Plan Format With Lesson ReflectionDocument13 pagesCollege of Saint Mary Lesson Plan Format With Lesson Reflectionapi-280302462No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 3 Educ 302Document8 pagesLesson Plan 3 Educ 302api-315445685No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan-Extemporaneous SpeechesDocument4 pagesLesson Plan-Extemporaneous SpeechesAmelyn Goco Mañoso100% (1)
- Extemporaneous Speeches: 6 Steps to SuccessDocument4 pagesExtemporaneous Speeches: 6 Steps to SuccessOwaidah Marcaban MacabangonNo ratings yet
- Numbers of Students: 8-14 Time of Activity: 50 MinDocument2 pagesNumbers of Students: 8-14 Time of Activity: 50 MinbokriNo ratings yet
- Activities For The Language ClassroomDocument65 pagesActivities For The Language ClassroomSk.Monirul Alam100% (10)
- AmerContribDickey67 86Document20 pagesAmerContribDickey67 86meph666269No ratings yet
- Hindi For Non-Hindi Speaking People by Kavita KumarDocument482 pagesHindi For Non-Hindi Speaking People by Kavita KumarAmardeep Hindi Diction Classes95% (19)
- MERCADODocument104 pagesMERCADOlodelyn caguilloNo ratings yet
- Schaums Quick Guide To Writing Research PapersDocument7 pagesSchaums Quick Guide To Writing Research Papersgvznen5k100% (1)
- Chapter 17-Some Auxiliary, Defective, Model and Semi Model VerbsDocument74 pagesChapter 17-Some Auxiliary, Defective, Model and Semi Model VerbszubayersumaNo ratings yet
- All English TensesDocument5 pagesAll English TensesIkramNo ratings yet
- DutchDocument58 pagesDutchAndreea DanielaNo ratings yet
- Universal Academy Dehradun Syllabus For The Session Class-5: English Hindi Pt1:LitDocument2 pagesUniversal Academy Dehradun Syllabus For The Session Class-5: English Hindi Pt1:LitmohdtariqkhanNo ratings yet
- GrammarDocument10 pagesGrammarАрина ВдовинаNo ratings yet
- Aptitude Day04 EnglishDocument79 pagesAptitude Day04 EnglishVipul PatilNo ratings yet
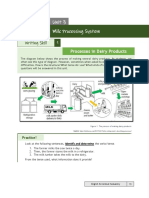
- Unit 3 Milk Processing System: Writing SkillDocument7 pagesUnit 3 Milk Processing System: Writing SkillKafana Salsabilla100% (1)
- 1 Mod 208Document39 pages1 Mod 208SIC SmandaNo ratings yet
- English Speaking Course FinalDocument97 pagesEnglish Speaking Course Finalfarheen shaikhNo ratings yet
- Test On The Simple Tense (Grammar Test)Document3 pagesTest On The Simple Tense (Grammar Test)Fatima Quiroz pardoNo ratings yet
- Exercitii Verbe ModaleDocument5 pagesExercitii Verbe ModaleNatalia Midvichi100% (1)
- Meeting 2 Past Continuous Dan Recount TextDocument4 pagesMeeting 2 Past Continuous Dan Recount TextSepram HijrinNo ratings yet
- News item structureDocument7 pagesNews item structureLamia DeareniNo ratings yet
- Tenses Upgrade Your GrammarDocument23 pagesTenses Upgrade Your Grammarrup 144fpsNo ratings yet
- Suggestions: ShouldDocument3 pagesSuggestions: ShouldEsther Arum Galih RahayuNo ratings yet
- Lightweight introduction to Communicative English GrammarDocument42 pagesLightweight introduction to Communicative English Grammarsdenhelle100% (1)
- Old English DialectsDocument20 pagesOld English Dialectsfiremaster2207100% (1)
- Present Simple and Adverbs of Frequency Colour and Greyscale Version Key IncludedDocument3 pagesPresent Simple and Adverbs of Frequency Colour and Greyscale Version Key IncludedPatrícia RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Skill & strategy of structure & writing of TOEFLDocument12 pagesSkill & strategy of structure & writing of TOEFLVita Dwi SakundianaNo ratings yet
- Infinitive (Verb 1) Past Tense (Verb 2) Past Participle (Verb 3) ArtiDocument12 pagesInfinitive (Verb 1) Past Tense (Verb 2) Past Participle (Verb 3) ArtiMaya putrinya radjaNo ratings yet
- Key To Junior English For China For Tibetan StudentsDocument267 pagesKey To Junior English For China For Tibetan StudentskoknorNo ratings yet
- If This Paper Were in Chinese, Would Chinese People Understand the Title? An Exploration of Whorfian Claims About the Chinese Language If This Paper Were in Chinese, Would Chinese People Understand the Title? An Exploration of Whorfian Claims About the Chinese Language If This PaperDocument69 pagesIf This Paper Were in Chinese, Would Chinese People Understand the Title? An Exploration of Whorfian Claims About the Chinese Language If This Paper Were in Chinese, Would Chinese People Understand the Title? An Exploration of Whorfian Claims About the Chinese Language If This PaperDavid MoserNo ratings yet
- Block Universe - Bradford SkowDocument26 pagesBlock Universe - Bradford Skowjosephcs22No ratings yet
- Improve Your PunctuationDocument177 pagesImprove Your PunctuationRienne BinksNo ratings yet
- Tuisyen BiDocument134 pagesTuisyen BiwanieNo ratings yet
- Raise vs. Rise Grammar GuideDocument3 pagesRaise vs. Rise Grammar GuideGabriel BispoNo ratings yet