Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CH 3 Ok
Uploaded by
usman afzalOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CH 3 Ok
Uploaded by
usman afzalCopyright:
Available Formats
CH # 3
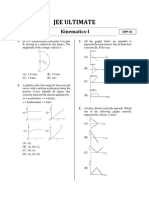
Q.1: Choose the correct option:
10
i. If unequal displacements are covered in equal intervals of time then velocity is said to be:
(A) Instantaneous (B) Linear (C) Uniform (D) Variable
ii. If average as well as instantaneous acceleration are same then acceleration is said to be:
(A) Instantaneous (B) Linear (C) Uniform (D) Variable
iii. Acceleration in the body is said to be _________ when its v-t graph is parallel to x-axis.
(A) Zero (B) Maximum (C) positive (D) Negative
iv. Which of the following is unit of linear momentum?
(A) N s (B) kg m s-1 (C) Both ‘a’ & ‘b’ (D) N s-1
v. Range of projectile for _________________ angles is same.
(A) Right (B) Complimentary (C) Supplementary (D) Acute
vi. At maximum height of projectile, velocity is:
(A) Minimum (B) Zero (C) Maximum (D) Along y-axis
vii. The angle at which maximum height and range of projectile become equal is:
(A) 760 (B) 450 (C) 900 (D) 00
viii. Which of the following remains constant during projectile motion?
(A) vx (B) ax (C) ay (D) All of these
ix. When we apply the brakes of car then velocity and acceleration become:
(A) Parallel (B) Anti-parallel (C) perpendicular (D) None of these
x. If the velocity of projectile is doubled then range becomes:
(A) Double (B) Half (C) 4 times (D) ¼ times
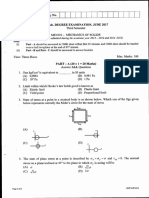
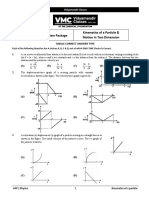
Q.2: Answer the following short questions.
12
i. Motion with constant velocity is a special case of motion with constant acceleration. Is this statement true?
Discuss.
ii. At what point or points in its path does a projectile have its minimum speed, its maximum speed?
iii. What is meant by Range of projectile? Derive a relation to find it.
iv. Explain the difference between elastic and inelastic collision. How would a bouncing ball behave in both
cases?
v. Write the working principle of rocket propulsion?
vi. If a moving car has uniform velocity then what will be its v-t graph? Write down characteristics of that graph
as well.
Q.3: Answer the following Long question.
i. Write a note on elastic collision in 1 D and prove speed of approach is equal to speed of sepration. 05
ii. A truck weighing 2500kg and moving with a velocity of 21 ms -1 collides with stationary car weighing
1000kg. The truck and the car move together after the impact. Calculate their common velocity. 03
You might also like
- Epis Topics BookDocument3 pagesEpis Topics BookabdullahrafiquempqNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 CompleteDocument2 pagesChapter 3 CompleteUsman Chughtai100% (1)
- 2013 Csec Physics Paper 1 PDFDocument12 pages2013 Csec Physics Paper 1 PDFNarvelle FerdinandNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 27 Sept 2023Document11 pagesAdobe Scan 27 Sept 2023s.piwal2002No ratings yet
- Pre Board Physics 11thDocument2 pagesPre Board Physics 11thSyed Raza Hassan GardeziNo ratings yet
- Test Chapter 1+2+3 B (Topper) DoneDocument2 pagesTest Chapter 1+2+3 B (Topper) DoneAzhar Riaz HunjraNo ratings yet
- 65b7475502df180018e5ac9d - ## - Kinematics DPP 05Document3 pages65b7475502df180018e5ac9d - ## - Kinematics DPP 05anupamasingh281984No ratings yet
- 11 PHYSICS Pre Board PaperDocument3 pages11 PHYSICS Pre Board PapershoaibNo ratings yet
- Test Chapter 1+2+3 A (Topper) DoneDocument3 pagesTest Chapter 1+2+3 A (Topper) DoneAzhar Riaz HunjraNo ratings yet
- CSEC Physics June 2013 P1Document12 pagesCSEC Physics June 2013 P1Leeyos78% (9)
- QP 1098Document10 pagesQP 1098Anshul ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- 2nd Year Physics Important MCQs Solved - Ratta - PKDocument1 page2nd Year Physics Important MCQs Solved - Ratta - PKEmma SwanNo ratings yet
- The Roots Science Academy Pind Dadan KhanDocument2 pagesThe Roots Science Academy Pind Dadan KhanAnonymous 117cflkW9WNo ratings yet
- Ch#1 To 6 - Test - Ist (1st Half)Document2 pagesCh#1 To 6 - Test - Ist (1st Half)QamarNo ratings yet
- Ist Year FLP 2 Physics CompleteDocument2 pagesIst Year FLP 2 Physics CompleteRana Hassan Tariq100% (1)
- 1.bernoulli's Equation Cannot Be Applied When The Flow IsDocument9 pages1.bernoulli's Equation Cannot Be Applied When The Flow IssureshkumarNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamics - Problem Sheet Level 1Document4 pagesAerodynamics - Problem Sheet Level 1Komal joshi100% (1)
- Smart Test Series: 1-Circle The Correct Answer. (12x1 12)Document4 pagesSmart Test Series: 1-Circle The Correct Answer. (12x1 12)Shaban BukhariNo ratings yet
- Motion Inn 2DDocument10 pagesMotion Inn 2Dbishnuprasadmohapatra01No ratings yet
- NK C SI R: Rigid Body Dynamics, Home Work Sheet-7Document2 pagesNK C SI R: Rigid Body Dynamics, Home Work Sheet-7Nilakantha PradhanNo ratings yet
- Circular MotionDocument3 pagesCircular MotionUncle IrodovNo ratings yet
- Kinematics-1 01 Most Important Concepts DPPDocument4 pagesKinematics-1 01 Most Important Concepts DPPNishant KumarNo ratings yet
- Class 11 PhysicsDocument3 pagesClass 11 PhysicsMask Man LifeNo ratings yet
- West Bengal University of Technology EC-604ADocument4 pagesWest Bengal University of Technology EC-604Asomething creativeNo ratings yet
- IX Science Chapter 08 AssignmentDocument8 pagesIX Science Chapter 08 AssignmentARPIT SINGHNo ratings yet
- Exercise - II: (A) Moment of InertiaDocument3 pagesExercise - II: (A) Moment of InertiaAnant DwivediNo ratings yet
- KEY Answer For I-PUC DPU Model Paper - 2023-24Document11 pagesKEY Answer For I-PUC DPU Model Paper - 2023-24jolylife1No ratings yet
- Nust Engineering Sample Paper 01Document19 pagesNust Engineering Sample Paper 01Bilal NasirNo ratings yet
- Motion in A Plane: Chapter FourDocument10 pagesMotion in A Plane: Chapter FourAbhik SarkarNo ratings yet
- Career Channel: Engineering Sample Admission Test 01Document10 pagesCareer Channel: Engineering Sample Admission Test 01Uzair KhanNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering R AGOR Objective TypeDocument831 pagesCivil Engineering R AGOR Objective TypeJohn Carlo SabadoNo ratings yet
- Part-A Single Correct Choice Type (1-5) : MST (Km+Vector)Document4 pagesPart-A Single Correct Choice Type (1-5) : MST (Km+Vector)AtulNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Half Yearly (2023-24)Document4 pagesClass 11 Half Yearly (2023-24)shivkarnwal2No ratings yet
- 11TH Midterm23-24Document3 pages11TH Midterm23-24mohammedsahal734No ratings yet
- Grade/Section: 9 Student Name/RCN - Total Marks: 55 Subject: Computer ScienceDocument4 pagesGrade/Section: 9 Student Name/RCN - Total Marks: 55 Subject: Computer ScienceRania CatoNo ratings yet
- 11th Physics FB MCQs With KeysDocument29 pages11th Physics FB MCQs With Keyssamyafarooq504No ratings yet
- Rotational Mechanics - 4Document5 pagesRotational Mechanics - 4hrishik guptaNo ratings yet
- Half Yearly Paper Physics Class-Xi M.Makrs-60 Questions 1 To 20 (1 Marks)Document6 pagesHalf Yearly Paper Physics Class-Xi M.Makrs-60 Questions 1 To 20 (1 Marks)Darth VaderNo ratings yet
- XII 22.02.2020 (CH#17 Relativity)Document5 pagesXII 22.02.2020 (CH#17 Relativity)Kamran AliNo ratings yet
- Vectors TestDocument5 pagesVectors TestNaveed AhmedNo ratings yet
- Past PaperDocument17 pagesPast Paperamohid751No ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Motion - ObjDocument3 pagesChapter 8 - Motion - ObjShubh tiwari TiwariNo ratings yet
- I PU MCQs FinalDocument48 pagesI PU MCQs Finalshaziyabanu1764No ratings yet
- Physics 11th Test No 4 CH 5 Start To Rotational K.EDocument2 pagesPhysics 11th Test No 4 CH 5 Start To Rotational K.EatfaNo ratings yet
- Test - Kinematics - 1Document7 pagesTest - Kinematics - 1Sankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- ME 2001 Unsolved PDFDocument13 pagesME 2001 Unsolved PDFSathya ThyaguNo ratings yet
- XI' Physics Examination 2022: Section A' (Multiple Choice Questions)Document4 pagesXI' Physics Examination 2022: Section A' (Multiple Choice Questions)Muneeb AlamNo ratings yet
- KEY Answer For PU Board Model Paper PU - 1-2022Document12 pagesKEY Answer For PU Board Model Paper PU - 1-2022Kabir SehdevNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 02 Sept 2023Document6 pagesAdobe Scan 02 Sept 2023Divyesh .RNo ratings yet
- LPP - Kinematics: 8 Ms V 2ms ADocument5 pagesLPP - Kinematics: 8 Ms V 2ms AMuffadal AlaviNo ratings yet
- Physics Set 1Document4 pagesPhysics Set 1raha78056No ratings yet
- Objective PhysicsDocument4 pagesObjective PhysicsleoyodapieNo ratings yet
- Physics - Sept - Class 11Document2 pagesPhysics - Sept - Class 11bishoppairisdeadNo ratings yet
- QP Class 11Document2 pagesQP Class 11gkr94No ratings yet
- (I) (Id Hours: Jio (C)Document6 pages(I) (Id Hours: Jio (C)Arjun OrcsNo ratings yet
- Ans KeyDocument5 pagesAns KeyVignesh SNo ratings yet
- Week 01 Motion WorksheetDocument4 pagesWeek 01 Motion WorksheetKrystian BonghanoyNo ratings yet
- Advanced Problem Package Kinematics of A Particle & Motion in Two DimensionDocument166 pagesAdvanced Problem Package Kinematics of A Particle & Motion in Two DimensionSachin100% (1)
- 11th Boost Sample MedicalDocument16 pages11th Boost Sample MedicalmadhavNo ratings yet
- Chapter Review - University Physics Volume 1conceptual Questions - OpenStaxDocument2 pagesChapter Review - University Physics Volume 1conceptual Questions - OpenStaxsanmohdNo ratings yet
- Water Hammer: Design CriteriaDocument3 pagesWater Hammer: Design CriteriamazharimechNo ratings yet
- UV Spectroscopy by Group 5Document5 pagesUV Spectroscopy by Group 5kurrupp k.pNo ratings yet
- 8K LightDocument47 pages8K Lightraba10067% (3)
- Kinematics Pratics Problems DPPDocument3 pagesKinematics Pratics Problems DPPShahil AhmedNo ratings yet
- All SheetsDocument22 pagesAll Sheetsأمل عبد اللهNo ratings yet
- Phy ProjectDocument18 pagesPhy Projectdevendra kasoteNo ratings yet
- EWP Independent Study Booklet III (Wave Properties)Document34 pagesEWP Independent Study Booklet III (Wave Properties)navNo ratings yet
- Dual Nature of Matter and Radiation PDFDocument49 pagesDual Nature of Matter and Radiation PDFabhishekNo ratings yet
- B Motion in A Straight LineDocument24 pagesB Motion in A Straight Linef20230069No ratings yet
- Comsar-Circ.25 - Procedure For Responding To DSC Distress Alerts by ShipsDocument3 pagesComsar-Circ.25 - Procedure For Responding To DSC Distress Alerts by ShipsNicolasMaregaNo ratings yet
- Module2 - Transmission LineDocument43 pagesModule2 - Transmission LineAbhinav MauryaNo ratings yet
- Numericcals LaserDocument13 pagesNumericcals LaserTanawush89% (9)
- Paper Paper Paper Paper PaperDocument6 pagesPaper Paper Paper Paper PaperResearch1 amtdcNo ratings yet
- Physics LASER DIFFRACTIONDocument13 pagesPhysics LASER DIFFRACTIONDisha DineshNo ratings yet
- G8 - Q1 - Slem - 4.1 Sound Gallego Approvedformat 1Document11 pagesG8 - Q1 - Slem - 4.1 Sound Gallego Approvedformat 1Juliana RoseNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic TestingDocument153 pagesUltrasonic Testinglucky kakanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 Fluid Kinematics (Chapter 3)Document5 pagesTutorial 3 Fluid Kinematics (Chapter 3)Naser KhalidNo ratings yet
- Science 7 Lesson PlanDocument39 pagesScience 7 Lesson PlanIra MontillaNo ratings yet
- Lady Bug Revolution ActivityDocument1 pageLady Bug Revolution ActivityAngelica LorenzoNo ratings yet
- ICSE Sample Papers For Class 7 Physics Paper 1 (2021-2022)Document10 pagesICSE Sample Papers For Class 7 Physics Paper 1 (2021-2022)bhaskar51178No ratings yet
- Brief History Twentieth Century Danger SignDocument14 pagesBrief History Twentieth Century Danger SignBill GeerhartNo ratings yet
- Experimental Investigations On A Standing-Wave Thermoacoustic EngineDocument96 pagesExperimental Investigations On A Standing-Wave Thermoacoustic EngineMahmoud Shaaban100% (2)
- Open Channel FlowDocument161 pagesOpen Channel FlowJuan HeroNo ratings yet
- Me303 HW9Document2 pagesMe303 HW9T uohzNo ratings yet
- HEAT ExchangersDocument27 pagesHEAT ExchangersBeatriceNo ratings yet
- Propagation Over A Plane EarthDocument5 pagesPropagation Over A Plane EarthMohana ManasaNo ratings yet
- Bandwidth TheoremDocument9 pagesBandwidth TheoremJoel50% (2)
- Written Work2Document2 pagesWritten Work2John Robert Dayrit VenturaNo ratings yet
- Mental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorFrom EverandMental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- A Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormFrom EverandA Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Basic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeFrom EverandBasic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Build a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.From EverandBuild a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsFrom EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Fluent in 3 Months: How Anyone at Any Age Can Learn to Speak Any Language from Anywhere in the WorldFrom EverandFluent in 3 Months: How Anyone at Any Age Can Learn to Speak Any Language from Anywhere in the WorldRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (80)
- Calculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeFrom EverandCalculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Mathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingFrom EverandMathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Mental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)From EverandMental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)No ratings yet
- Images of Mathematics Viewed Through Number, Algebra, and GeometryFrom EverandImages of Mathematics Viewed Through Number, Algebra, and GeometryNo ratings yet
- ParaPro Assessment Preparation 2023-2024: Study Guide with 300 Practice Questions and Answers for the ETS Praxis Test (Paraprofessional Exam Prep)From EverandParaPro Assessment Preparation 2023-2024: Study Guide with 300 Practice Questions and Answers for the ETS Praxis Test (Paraprofessional Exam Prep)No ratings yet
- Math Workshop, Grade K: A Framework for Guided Math and Independent PracticeFrom EverandMath Workshop, Grade K: A Framework for Guided Math and Independent PracticeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- How Math Explains the World: A Guide to the Power of Numbers, from Car Repair to Modern PhysicsFrom EverandHow Math Explains the World: A Guide to the Power of Numbers, from Car Repair to Modern PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (9)
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- A Guide to Success with Math: An Interactive Approach to Understanding and Teaching Orton Gillingham MathFrom EverandA Guide to Success with Math: An Interactive Approach to Understanding and Teaching Orton Gillingham MathRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)