Professional Documents
Culture Documents
8 Classes of Vegetables
8 Classes of Vegetables
Uploaded by
ashiah syen pirante0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageThis document outlines 8 classes of vegetables: BFF (bulb, flower, fruit), L8R (leafy, root), and SST (seeds, stems, tubers). It provides examples for each class such as onions and garlic for bulbs, lettuce and cabbage for leafy greens, and corn and peas for seeds. The document also notes that vegetables provide vitamins, minerals, fiber, and some protein and that deeper colored vegetables contain more vitamin A while vitamin C is water soluble and lost during boiling.
Original Description:
.
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document outlines 8 classes of vegetables: BFF (bulb, flower, fruit), L8R (leafy, root), and SST (seeds, stems, tubers). It provides examples for each class such as onions and garlic for bulbs, lettuce and cabbage for leafy greens, and corn and peas for seeds. The document also notes that vegetables provide vitamins, minerals, fiber, and some protein and that deeper colored vegetables contain more vitamin A while vitamin C is water soluble and lost during boiling.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 page8 Classes of Vegetables
8 Classes of Vegetables
Uploaded by
ashiah syen piranteThis document outlines 8 classes of vegetables: BFF (bulb, flower, fruit), L8R (leafy, root), and SST (seeds, stems, tubers). It provides examples for each class such as onions and garlic for bulbs, lettuce and cabbage for leafy greens, and corn and peas for seeds. The document also notes that vegetables provide vitamins, minerals, fiber, and some protein and that deeper colored vegetables contain more vitamin A while vitamin C is water soluble and lost during boiling.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
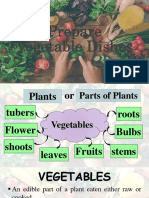
8 CLASSES OF VEGETABLES
A. BFF
1. BULB
2. FLOWER
3. FRUIT
EXAMPLES –
Bulb – onion, garlic, leek
Flower – cauliflower, broccoli
Fruit – tomato, squash, cucumber, eggplant
B. L8R
1. LEAFY
2. ROOT
EXAMPLES –
Leafy – lettuce, cabbage, spinach, arugula
Root – carrot, beet, radish, turnip, parsnip
C. SST
1. SEEDS
2. STEMS
3. TUBERS
EXAMPLES –
Seeds – corn, peas, beans
Stems – celery, asparagus
Tubers – potatoes, sweet potatoes (fat, underground stems of plant)
NUTRITIONAL VALUE OF VEGETABLES
1. Vegetables contribute vitamins, minerals, and fiber as well as some
incomplete protein.
2. The deeper the color, the more Vitamin A is present (Vitamin A is fat-
soluble).
3. Vitamin C is water-soluble and is lost during boiling.
You might also like
- Prepare Vegetable and Seafood DishesDocument120 pagesPrepare Vegetable and Seafood DishesJoeven Pantaleon67% (3)
- COOKERY10Document38 pagesCOOKERY10Jenalyn CarbonquilloNo ratings yet
- TLE 10 2nd Quarter Week 1 2Document10 pagesTLE 10 2nd Quarter Week 1 2zyra layagNo ratings yet
- Classifications of VegetablesDocument3 pagesClassifications of Vegetablesjessy maeNo ratings yet
- LESSON 1 PREPARE VEGETABLE DISHES OverviDocument12 pagesLESSON 1 PREPARE VEGETABLE DISHES OverviKeym Garcia Galvez IIINo ratings yet
- Cookery10vegetables 190117235613Document43 pagesCookery10vegetables 190117235613Meach CallejoNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 CookeryDocument18 pagesMODULE 1 CookeryMaribel B GarciaNo ratings yet
- TLE ASSIGNMENT March 22, 2023Document3 pagesTLE ASSIGNMENT March 22, 2023Ernest LucesNo ratings yet
- Prepare Vegetable Mise en PlaceDocument15 pagesPrepare Vegetable Mise en PlaceGrechie CortelNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-11-02 at 5.46.06 PMDocument10 pagesScreenshot 2023-11-02 at 5.46.06 PMShanara YzhiiNo ratings yet
- Vegetable LectureDocument3 pagesVegetable LectureimranNo ratings yet
- Tl.e 10 Week 7&8Document18 pagesTl.e 10 Week 7&8Christian BastonaNo ratings yet
- Q2 L1 - Perform Mise'en PlaceDocument10 pagesQ2 L1 - Perform Mise'en PlacePaolo Olivas100% (1)
- Horticulture NoteDocument17 pagesHorticulture NoteAzeem goriNo ratings yet
- LM - Cookery Quarter 2.1Document50 pagesLM - Cookery Quarter 2.1shprimero2020No ratings yet
- U5-L1 Vegetable Dishes in Culinary ArtsDocument15 pagesU5-L1 Vegetable Dishes in Culinary ArtsMary Grace Magadia PilarNo ratings yet
- File 1084457310Document278 pagesFile 1084457310Carlito Luces Jr.No ratings yet
- Unit 2 Agr-105Document85 pagesUnit 2 Agr-105RY4NNo ratings yet
- LAS 10 m1Document7 pagesLAS 10 m1Song Joong WeiNo ratings yet
- Hand-Out For The Class G-10 Caregiving 4th QuarterDocument5 pagesHand-Out For The Class G-10 Caregiving 4th QuarterLovely PajaresNo ratings yet
- 3.prepare Vegetable DishesDocument38 pages3.prepare Vegetable DishesaileenNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Prepare Vegetable Dishes Tlte10Document5 pagesLesson 1 Prepare Vegetable Dishes Tlte10Kimby VentuzoNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Cookery 12Document5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Cookery 12Danica Joy Penion GarlitNo ratings yet
- Tlefop Note Fruitandvegetables Group4Document13 pagesTlefop Note Fruitandvegetables Group4janlorainelumogdangNo ratings yet
- Cookery 10 Quarter 2 m1Document37 pagesCookery 10 Quarter 2 m1Jennifer CarpioNo ratings yet
- Reprt in TVLDocument29 pagesReprt in TVLriejinesaldivar250No ratings yet
- Vegetables ProductionDocument35 pagesVegetables Productionสวแส เำครNo ratings yet
- He ReviewerDocument14 pagesHe Reviewerxls.cineNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 Lesson 1 Misen Place Charlene With Signature 1Document16 pagesQuarter 2 Lesson 1 Misen Place Charlene With Signature 1Joseph Jucons C. SantosNo ratings yet
- Compendium Cookery 10Document54 pagesCompendium Cookery 10RYAN PADERONo ratings yet
- Class: Reported By: Aaron Mathew Ragadio and Lyka Verone RamosDocument34 pagesClass: Reported By: Aaron Mathew Ragadio and Lyka Verone RamosAaron Mathew VRagadioNo ratings yet
- Module 6Document43 pagesModule 6Juan Miguel ArceoNo ratings yet
- q2 Module Ks3 Grade10 CookeryDocument67 pagesq2 Module Ks3 Grade10 Cookerylinarubino351No ratings yet
- Beige and Pink Playful Guess The Vegetables Game Presentation 20240208 104140 0000Document28 pagesBeige and Pink Playful Guess The Vegetables Game Presentation 20240208 104140 0000Conavil TamponNo ratings yet
- Cookery 10: Department of Education SptveDocument10 pagesCookery 10: Department of Education Sptveienna morsNo ratings yet
- Caregiving 10 ModuleDocument38 pagesCaregiving 10 ModuleLerie Carpentero100% (2)
- TLE 10-Cookery - Q2 - W1-2 - M1 - LDS - Principles-of-Preparing-Vegetables - JRA-RTPDocument7 pagesTLE 10-Cookery - Q2 - W1-2 - M1 - LDS - Principles-of-Preparing-Vegetables - JRA-RTPEDMARK PONCENo ratings yet
- Cucumber Beetle08Document7 pagesCucumber Beetle08Hinniss1No ratings yet
- Quarter 3 Week 5 ModuleDocument6 pagesQuarter 3 Week 5 ModuleHace Zhell MacasioNo ratings yet
- Nutrient SymptomsDocument6 pagesNutrient SymptomsLovely PriyaNo ratings yet
- T1.10 Mineral NutritionDocument10 pagesT1.10 Mineral NutritionKudaNo ratings yet
- Clasification of VegetablesDocument10 pagesClasification of VegetablesRonald CortezanoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Prepare Vegetable DishesDocument108 pagesLesson 1 Prepare Vegetable DishesRonald Serrano100% (3)
- Presentation Nutrient Uptaked by Plant RootsDocument60 pagesPresentation Nutrient Uptaked by Plant RootsHasbullah ZawawiNo ratings yet
- Module 3. Grow SeedlingsDocument46 pagesModule 3. Grow SeedlingsRommel Sacramento100% (1)
- l2 Quarter 2 Week 1 - Prepare Mise en PlaceDocument38 pagesl2 Quarter 2 Week 1 - Prepare Mise en PlaceGwyneth VicenteNo ratings yet
- Bert MAjor Final Pest of CropDocument21 pagesBert MAjor Final Pest of CropJohn Vincent D. ReyesNo ratings yet
- Cookery 10 q3 Lesson 1Document30 pagesCookery 10 q3 Lesson 1John Albert Tubillo ChingNo ratings yet
- StylishDocument14 pagesStylishVăn Chương LêNo ratings yet
- CarrotDocument15 pagesCarrotKhushbu kholiya (SBSR Assistant Professor)No ratings yet
- 4 How Sustainable Is Organic Agriculture in The Phils Rodel G. Maghirang Et AlDocument13 pages4 How Sustainable Is Organic Agriculture in The Phils Rodel G. Maghirang Et AlAbner Obniala Venus Jr.No ratings yet
- Gloria Alberto PDFDocument7 pagesGloria Alberto PDFGabriela AlbertoNo ratings yet
- Module 3. Grow SeedlingsDocument48 pagesModule 3. Grow SeedlingsEva NolascoNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 LESSON: Produce Vegetables Module 3: Growing SeedlingsDocument45 pagesQuarter 2 LESSON: Produce Vegetables Module 3: Growing SeedlingsPENTIL HIGH SCHOOLNo ratings yet
- VegetablesDocument49 pagesVegetablesJaine LuzNo ratings yet
- Q2 LAP 1 Perfom Mise en Place Daisy E. VillareteDocument13 pagesQ2 LAP 1 Perfom Mise en Place Daisy E. VillareteJhoana Paula EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- As growing your exceptional vegetable garden: Little tricks and ancient secretsFrom EverandAs growing your exceptional vegetable garden: Little tricks and ancient secretsNo ratings yet