Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hazard Risk Assessment Procedure
Uploaded by
Satyajit DangeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hazard Risk Assessment Procedure
Uploaded by
Satyajit DangeCopyright:
Available Formats
IMS (QEHS) Procedure EHS Procedure No.
: EHS/P/00
Issue: 01, Issue Date: 01/06/2016
TITLE: Hazard Identification, Risk Assessment & Rev.: 00, Rev. Date: Nil
Determining controls.
Reference: OHSAS 18001:2007 Clause No.: 4.3.1 Page No.: 1 of 3
1 Purpose : To identify the occupational health and safety (OHS)hazards, and the
Associated risks and determination of necessary controls for the
significant risks associated with hazards
2 Scope : All functions pertaining to Engineering, Project & commissioning and
application of product.
3 Definition : Hazard: Source or situation with a potential to harm in terms of injury or
ill heath, damage to property, damage to workplace environment, or a
combination of these.
Risk: Combination of the likelihood and consequences of a specified
hazardous event occurring.
Risk Assessment – is the process of evaluating the probability and
consequences of Injury or illness arising from exposure to an identified
hazard.
Hazard Control – Hazard Control is the minimization of risk associated
with an identified hazard to bring down the risk up to acceptable level.
4 Reference : IMS (EHS) Manual Doc. No. IMS-01.
5 Responsibility : MR, EHS Committee & Departmental Heads, Safety Officer
6. Process – Description & Interfaces
1. The departmental team along with MR & HOD identifies the hazards associated with
each & every activity, product, services & Processes including new development/ over which it
may be expected to have control and/or can influence.
2. Classification of work activities
A necessary preliminary to Risk Assessment is to prepare a list of work activities, to group them
in a rational and manageable way, and to gather necessary information about them. It is vital to
incline, for example, infrequent maintenance task, as well as day-to-day production work.
3. Work activities Information requires
Information required for work activities should but are not limited to include items for following.
a. Task being carried out, is Routine or Non Routine task, their duration and frequency;
b. Location (s) where the work is carried out;
c. Who normally/ occasionally carries out the task;
d. Who else may be affected by the work (for example visitor, subcontractors,
the public);
e. Training that personnel have received about the tasks;
f. Written system of work and/ or permit to work procedure prepared for the
tasks;
g. Plant and machinery that may be used;
h. Powered hand tools that may be used;
i. Manufacturers and suppliers instructions for operation and maintenance of plant
ISO 14001:2004 & OHSAS
Prepared by DMR 18001:2007 Approved by MR & GM-QA
IMS (QEHS) Procedure EHS Procedure No.: EHS/P/00
Issue: 01, Issue Date: 01/06/2016
TITLE: Hazard Identification, Risk Assessment & Rev.: 00, Rev. Date: Nil
Determining controls.
Reference: OHSAS 18001:2007 Clause No.: 4.3.1 Page No.: 1 of 3
machinery and power / hand tools.
j. Size shape, surface characters and weight of material that might be handled
k. Distance and heights of the place where material have to be by handled.
l. Services used (for example compressed air)
m. Substances used or encountered during the work.
n. Physical form of substances used or encountered (fumes, gas, vapour, liquid, dust,
powder, solid )
o. Content and recommendations of safety data sheets relating to substances used or
encountered content.
p. Control measures believed to be in place. Availability monitoring data gain as a result of
information from within and outside the organization, incident accident and ill health
experience associated with work being done, equipment and substances used, and
4. Identify hazards & severity of harm
Identify all hazards relating to each work activity. Consider who might be harmed and how, &
what might be damaged.
Broad categories of hazards.
a) Mechanical
b) Electrical
c) Radiation
d) Substances
e) Fire & Explosion
Severity of harm ranging from slightly to very harmful
i.) Slightly harmful, for example –
A superficial injury minor cut and bruises eyes irritation from dust.
Nuisances and irritation (for example headache) ill health leading to temporary
discomfort.
ii) Harmful, for example
Lacerations, burns
Minor fractures
Deafness, dermatitis
Work related upper limb disorders and,
iii) Extremely harmful, for example.
Amputation major fractures
Poisonings multiple injuries
Fatal injuries
Occupational cancer other severely life shorting diseases and
5. Likelihood of harm
When seeking to establish likelihood of harm the adequacy of control measures already
ISO 14001:2004 & OHSAS
Prepared by DMR 18001:2007 Approved by MR & GM-QA
IMS (QEHS) Procedure EHS Procedure No.: EHS/P/00
Issue: 01, Issue Date: 01/06/2016
TITLE: Hazard Identification, Risk Assessment & Rev.: 00, Rev. Date: Nil
Determining controls.
Reference: OHSAS 18001:2007 Clause No.: 4.3.1 Page No.: 1 of 3
implemented and complied with needs to be considered. Here legal requirements and codes of
practice are good guides covering controls of specific hazards. The following issues should then
typically to be considered in addition to the work activity information in
a) Protection afforded by personal protective equipment and uses rate of PPEs
b) Frequency and duration of exposure to the hazard.
c) Failure of service for example electricity and water.
d) Failure of plant and machinery components and safety devices.
e) Exposure to the elements.
6. Estimate the risks (the likelihood and severity of harm) from each hazardous event
Determine risk: make a subjective estimate of risk associated with each hazard assuming that
planned or existing controls are in place. Assessors should also consider the effectiveness of their
failure.
7. Decide if the risk is Not significant (i.e. Acceptable) for this purpose an acceptable risk
criteria has been evolved which takes into consideration the legal requirements and other norms
in that activity. While identifying occupational health & safety OHS hazards and risk during initial
OHS review, the following criteria shall be considered :
a. All activities where previous records of accidents occurred.
b. Inputs from regular safety audits.
c. All activity routine & non routine, where substantial hazards and risks are
involved.
d. Evaluation of feedback from investigation of previous incident.
e. Activities of all personnel having access to the work places (including
subcontractors and visitors).
8. The cut off score decided for significance of Risk if Probability X Consequence score
rating is more than or equal to 10. ( 40% of total score).
9. All scores which are equal to or above bench mark level (i.e.10) are treated as significant
Risks. Those activities where the score is below bench mark level are on the watch list, and are
controlled operationally
10. Based on the P x C analysis the cutoff point is bench marked as significant/critical
hazards. All scores which are above benchmark are treated as Significant Hazards.
11. Conduct brain storming/discussion to apply the evaluation criteria for evaluating all the
identified OHS risks.
12. Treat any of the OHS risks falling under legal compliance on significant. The OHS risk
having a score above benchmark is considered significant.
13. Based on above prepare a list of significant OHS risk, those will be considered in setting
ISO 14001:2004 & OHSAS
Prepared by DMR 18001:2007 Approved by MR & GM-QA
IMS (QEHS) Procedure EHS Procedure No.: EHS/P/00
Issue: 01, Issue Date: 01/06/2016
TITLE: Hazard Identification, Risk Assessment & Rev.: 00, Rev. Date: Nil
Determining controls.
Reference: OHSAS 18001:2007 Clause No.: 4.3.1 Page No.: 1 of 3
adjectives, targets and controls.
Qualitative Measures of Consequence or Impact (SEVERITY)
Level Descriptor Example Detail Description
1 Insignificant No injuries, low financial loss.
2 Minor FIRST aid treatment case, ill health for short duration, on-site
release immediately constrained, medium financial loss.
3 Moderate Medical treatment required, Reversible ill health for long time,
on-site release contained with outside assistance, high financial
loss.
4 Major Extensive injuries, Amputation, Irreversible Ill health, loss of
production capability, off-site release with no detrimental
effects, major financial loss.
5 Catastrophic Death, toxic release off-site with detrimental effects, huge
financial loss.
Level Descriptor Example Detail Description
5 Almost Impact may occur in any time in ongoing process.
Certain /
Continuous /
Most likely
4 Likely / Expected to occur at least once in a half year
Frequent
3 Possible Expected to occur at least once in a year
2 Remote Expected to occur at least once in a 5 years
1 Rare / May occur only in exceptional circumstances. Not heard till now /
Improbable Highly unlikely.
Total Risk Score (R) = Probability (P) x Severity (S) x Nos. of persons affected (N)
Note : If Risk assessment score is ≥ 10, then it is considered as Significant risk
ISO 14001:2004 & OHSAS
Prepared by DMR 18001:2007 Approved by MR & GM-QA
14. Activities with Significant Risks are controlled through additional control like Engineering
Control, operational control procedure or management programs, provision of PPE as a last line
of defense in order to control these aspects and the resultant impacts. The programs are
expected to eliminate or bring within the impacts to acceptable limits.
15. MR, Core committee will prepare a composite list of significant Risk for the entire unit
based on the document prepared by the various individual department.
16. Each department plans their objective and targets based on the significant risks which
also include all the legislative/regulatory requirements.
17. The document is updated by departmental heads annually or whenever there is a
change in the procedures/process conditions, or legislative/regulatory requirements or the
results of the measurements and monitoring are not in line with the requirement.
18. The above procedure is repeated once in year or whenever there are changes in
processes.
19. Any new/modified or changed OHS hazards and risks, introduction of new processes,
activity, chemicals, any change in process, activity within the company shall be identified and
included in the record of OHS hazards and associated risks for risk assessment as per the
procedures.
20. Management Review meeting ensures the monitoring and control. All individual
department heads maintain relevant records.
21. The hazards are identified, analyzed and recorded in the format XYZ/EOHS/F/00/00 .
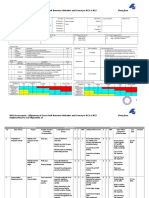
22. The identification of hazard, assessment of risk and determination of controls register
(HIRA register) is maintained (KDL/EOHSD/03).
23. Summary of Significant Risks (i.e. Risks which are not acceptable) is maintained in
xyz/EOHS/F/0/00
1. Control of Environmental Aspects
By individual HOD as detailed in the process description.
2. Records
a. Aspect-Impact, Hazard-Risk analyses record.
b. Composite list of significant aspect of entire organization.
8.0 Records
a. Legal Register (VW-F-13).
You might also like
- Mock Drill TemplateDocument7 pagesMock Drill TemplateAnkurNo ratings yet
- Training On ISO 14001, Clause No.: 6.1.2 Environmental Aspects (AI)Document37 pagesTraining On ISO 14001, Clause No.: 6.1.2 Environmental Aspects (AI)sankusi_rkflNo ratings yet
- HIRA TemplatesDocument12 pagesHIRA Templatesvictor100% (1)
- HIRA Risk AssessmentDocument25 pagesHIRA Risk AssessmentSuraj PantNo ratings yet
- OCP For EHSDocument29 pagesOCP For EHSAtul Sharma100% (2)
- Contractor's EHSS Evaluation by PMT EHSS PK CLC Project FMO Jan 2020Document5 pagesContractor's EHSS Evaluation by PMT EHSS PK CLC Project FMO Jan 2020ManPower RecruitingNo ratings yet
- Monthly HSE Performance ReportDocument9 pagesMonthly HSE Performance ReportHemant HoneyNo ratings yet
- HSE Permit to Work ProcedureDocument2 pagesHSE Permit to Work Procedureवात्सल्य कृतार्थNo ratings yet
- Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment for Loading and Off-Loading with Truck Mounted CraneDocument5 pagesHazard Identification and Risk Assessment for Loading and Off-Loading with Truck Mounted CraneGerrit100% (1)
- P O S T (Post) : Ositive Perational Afety Arget Score CardDocument2 pagesP O S T (Post) : Ositive Perational Afety Arget Score CardekoimampNo ratings yet
- Monthwise EHS theme planDocument6 pagesMonthwise EHS theme planSafety DeptNo ratings yet
- PUR-LS-01 List of Approved Supplier-11082020Document5 pagesPUR-LS-01 List of Approved Supplier-11082020shobha shelarNo ratings yet
- Health Safety & Environment WI - C PDFDocument134 pagesHealth Safety & Environment WI - C PDFNilesh DeoreNo ratings yet
- GEN-005 Low Pressure Turbine and Generator Coupling and Decoupling Alignment CheckDocument3 pagesGEN-005 Low Pressure Turbine and Generator Coupling and Decoupling Alignment Checkacanbasri1980No ratings yet
- 022 - Compressed Gas Cylinder - HandlingDocument3 pages022 - Compressed Gas Cylinder - HandlingAbhijit JanaNo ratings yet
- Bajaj Electricals LTD: Minutes of Meeting (Safety Committee)Document3 pagesBajaj Electricals LTD: Minutes of Meeting (Safety Committee)anil kumar100% (1)
- Annual Safety Activity Plan of UAIL Site, Rev.-03Document1 pageAnnual Safety Activity Plan of UAIL Site, Rev.-03Sheikh AshfaqueNo ratings yet
- Aspect Impact Analysis QADocument1 pageAspect Impact Analysis QAAtul SharmaNo ratings yet
- HIRA FormatDocument2 pagesHIRA FormatSachin Yashwant kumbharNo ratings yet
- FRM-EHS-PRO-05 Hazard Identification & Risk Assessment (HIRA)Document1 pageFRM-EHS-PRO-05 Hazard Identification & Risk Assessment (HIRA)Venkatesan DNo ratings yet
- December 2019 EHS Calendar with Daily Safety ActivitiesDocument1 pageDecember 2019 EHS Calendar with Daily Safety ActivitiesSiddharth RanaNo ratings yet
- Daily HSEReport FormatDocument7 pagesDaily HSEReport Formatsufiyan sskNo ratings yet
- MMY Environment Aspect & Significant Impact (EASI) RegisterDocument11 pagesMMY Environment Aspect & Significant Impact (EASI) RegisterThirumaran MuthusamyNo ratings yet
- Incidents By Root Causes Tools Equipment TrainingDocument5 pagesIncidents By Root Causes Tools Equipment TrainingvictorNo ratings yet
- Safety Dash BoardDocument1 pageSafety Dash BoardSandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- HSE Program 2016 ReviewDocument4 pagesHSE Program 2016 ReviewNurAjiNo ratings yet
- Safety Committee ConstitutionDocument3 pagesSafety Committee ConstitutionHarsh VaidyaNo ratings yet
- Health and Safety EssentialsDocument29 pagesHealth and Safety EssentialsAbdelRahman AbdelRazek RashwanNo ratings yet
- HEO Monthly HSE Perfomance Report 24 FeDocument11 pagesHEO Monthly HSE Perfomance Report 24 Feabdulla kasim100% (1)
- Rimal Global Technical Services LLC.: HSE Management System ProcedureDocument1 pageRimal Global Technical Services LLC.: HSE Management System ProcedureSreekumarNo ratings yet
- Incident Reporting Form (Ir 01) : Fatality Lti I RWC Accident NEAR MissDocument1 pageIncident Reporting Form (Ir 01) : Fatality Lti I RWC Accident NEAR Missmuhammadumar412296No ratings yet
- Rameshwer Lal Gadri - Safety KPIs For FY 2021-22Document7 pagesRameshwer Lal Gadri - Safety KPIs For FY 2021-22Nikhil VaidyaNo ratings yet
- OCP For Welding - Gas CuttingDocument2 pagesOCP For Welding - Gas Cuttingravikpandey100% (2)
- Sinai Fields HSE Annual Report 2004Document15 pagesSinai Fields HSE Annual Report 2004HosamMohamedNo ratings yet
- Brand Analysis India Private Limited Risk Assessment: Risk Risk Impact C I A Risk Value Threat Miltigation PlanDocument2 pagesBrand Analysis India Private Limited Risk Assessment: Risk Risk Impact C I A Risk Value Threat Miltigation PlanTrivesh SNo ratings yet
- Iso 45001-2018Document19 pagesIso 45001-2018Scientific KingNo ratings yet
- Report On Mock DrillDocument6 pagesReport On Mock Drillakshay aryaNo ratings yet
- OCP - 15 - GrindingDocument2 pagesOCP - 15 - GrindingNagendra Kumar Singh100% (1)
- HIRADocument6 pagesHIRAvijay kumar singhNo ratings yet
- L&T Chennai Metro Noise Monitoring ReportDocument1 pageL&T Chennai Metro Noise Monitoring Reportsalman farisNo ratings yet
- Oil India Limited: Onshore Emergency Response PlanDocument23 pagesOil India Limited: Onshore Emergency Response Planaji sathyanandanNo ratings yet
- HSE Monthly MeetingDocument16 pagesHSE Monthly MeetingsajidNo ratings yet
- Procedure For Accident Incident and Near MissDocument2 pagesProcedure For Accident Incident and Near MissrgmNo ratings yet
- Aspect-Impact Rating Sheet (Airs) : Department/ Section/ Unit: Process, Building and UtilitiesDocument4 pagesAspect-Impact Rating Sheet (Airs) : Department/ Section/ Unit: Process, Building and UtilitiesSir ZenNo ratings yet
- KPI Submission (October)Document3 pagesKPI Submission (October)Htoo Htoo KyawNo ratings yet
- July-2023 DLPS Corporate HSE Monthly Report (Statistics)Document1 pageJuly-2023 DLPS Corporate HSE Monthly Report (Statistics)DLPS HSENo ratings yet
- Sample Form-HIRARC 10.11.2010Document21 pagesSample Form-HIRARC 10.11.2010mrsmartguys100% (1)
- Environmental Aspect Impact RegisterDocument17 pagesEnvironmental Aspect Impact Registersyahir et0% (1)
- Jurong Island Cargo Tec RA Alignment of Cover Belt BC1 & BC2Document3 pagesJurong Island Cargo Tec RA Alignment of Cover Belt BC1 & BC2Anonymous kWfNFb100% (1)
- C - 6 Crane & Lifting Equipment StandartDocument4 pagesC - 6 Crane & Lifting Equipment StandartwawanNo ratings yet
- SHEQXel Performance Monitoring ToolDocument105 pagesSHEQXel Performance Monitoring ToolDanu HenantyoNo ratings yet
- Health, Safety and Environment Close-Out Report: Sno Corrective Actions Taken/Implemented Electrical SafetyDocument2 pagesHealth, Safety and Environment Close-Out Report: Sno Corrective Actions Taken/Implemented Electrical SafetyVijayakumar KarunanidhiNo ratings yet
- HSE Training History FormDocument4 pagesHSE Training History FormAnonymous 1wDPsonNo ratings yet
- Register of Hazards and Risks: (OHSAS 18001:2007)Document2 pagesRegister of Hazards and Risks: (OHSAS 18001:2007)Anonymous ZBMKga2LINo ratings yet
- Training Matrix Oct 12 v3 For Health and SafetyDocument3 pagesTraining Matrix Oct 12 v3 For Health and Safetyven1959No ratings yet
- EHS Calendar September 2019 Training Fire Safety PPE AuditsDocument1 pageEHS Calendar September 2019 Training Fire Safety PPE AuditsSiddharth RanaNo ratings yet
- ARA - For Emergency Diesel GeneratorDocument4 pagesARA - For Emergency Diesel GeneratorShaikh AftabNo ratings yet
- RiskAssessment For Precast Foundation and Road MarkingDocument13 pagesRiskAssessment For Precast Foundation and Road MarkingAneessh KumarNo ratings yet
- HSE Procedure For Environmental Aspects, Hazards, Evaluation of Impacts, Risks & Determination of Control MeasuresDocument19 pagesHSE Procedure For Environmental Aspects, Hazards, Evaluation of Impacts, Risks & Determination of Control MeasuresSafety IezzproNo ratings yet
- Procedure For Identification of Environmental Aspects, Hazards, Evaluation of Impacts, Risks and Determination of Control MeasuresDocument10 pagesProcedure For Identification of Environmental Aspects, Hazards, Evaluation of Impacts, Risks and Determination of Control MeasuresradhouaneNo ratings yet
- ANSWERDocument1 pageANSWERengr valderrama adrianNo ratings yet
- 1.CEK LIST Syringe Pump PDFDocument1 page1.CEK LIST Syringe Pump PDFsri lestariNo ratings yet
- Nirosta 4104: Krupp EdelstahlprofileDocument2 pagesNirosta 4104: Krupp EdelstahlprofileLuis MayorgaNo ratings yet
- AVR520 Service ManualDocument160 pagesAVR520 Service ManualtlehotskyNo ratings yet
- Goldman+Sachs+Interview+Process My+CompilationDocument3 pagesGoldman+Sachs+Interview+Process My+CompilationPraveen NagarajanNo ratings yet
- Analisis Preventive Maintenance Pada Mesin Produksi Dengan Metode Fuzzy FMEA - JST (AutoRecovered)Document8 pagesAnalisis Preventive Maintenance Pada Mesin Produksi Dengan Metode Fuzzy FMEA - JST (AutoRecovered)RandisNo ratings yet
- Base Plate - MammutDocument8 pagesBase Plate - MammutAwais Hameed100% (1)
- 1 PBDocument12 pages1 PBRazan Nuhad Dzulfaqor razannuhad.2020No ratings yet
- Computer Masti Level 4Document129 pagesComputer Masti Level 4Rupesh Kumar Shah50% (2)
- Perceptons Neural NetworksDocument33 pagesPerceptons Neural Networksvasu_koneti5124No ratings yet
- Training Course BrochureDocument4 pagesTraining Course BrochureGodofredo PabloNo ratings yet
- Securiton Smoke Detector Performance DeclarationDocument2 pagesSecuriton Smoke Detector Performance DeclarationAnonymous YWmB9HDgNo ratings yet
- NV 8 Non Invasive Neonatal VentilatorDocument4 pagesNV 8 Non Invasive Neonatal Ventilatorchiraggala0% (1)
- HSBCDocument21 pagesHSBCHarsha SanapNo ratings yet
- Automatic Payment Program Run F110 - SAP TutorialDocument20 pagesAutomatic Payment Program Run F110 - SAP TutorialVenkateswarlu vNo ratings yet
- Quality Control Tools For Improving Processes: Supplement 6Document55 pagesQuality Control Tools For Improving Processes: Supplement 6janssen.villian3621No ratings yet
- Electrical OFFICE WAREHOUSE FREEWOOD - PERMIT 2 - Part3Document1 pageElectrical OFFICE WAREHOUSE FREEWOOD - PERMIT 2 - Part3David BarrientosNo ratings yet
- Nip Control - TheTextileMagazine-March 2021Document2 pagesNip Control - TheTextileMagazine-March 2021pravinthombreNo ratings yet
- Architectural Drawing TypesDocument28 pagesArchitectural Drawing TypesAr Ayoushika AbrolNo ratings yet
- Opisanie K Alcatel 1670 SMDocument6 pagesOpisanie K Alcatel 1670 SMsulomenNo ratings yet
- Log FileDocument4 pagesLog FileArquimedes FaquinoNo ratings yet
- Darul Mubarak Travel & Tours SDN BHDDocument30 pagesDarul Mubarak Travel & Tours SDN BHDNurulFarihahMohdZulkefleNo ratings yet
- Pressure Data Logger PDFDocument2 pagesPressure Data Logger PDFMuhammad Akbar WalennaNo ratings yet
- Pentium Processor Architecture Features and Performance OptimizationDocument18 pagesPentium Processor Architecture Features and Performance OptimizationJain Marshel BNo ratings yet
- STC 1000 Manual en EspanolDocument4 pagesSTC 1000 Manual en EspanolPancho Fer0% (1)
- Sales BOMDocument7 pagesSales BOMAravind SrirangapuriNo ratings yet
- CANalyzer Workshops Overview FactSheet enDocument2 pagesCANalyzer Workshops Overview FactSheet enPrasad GNo ratings yet
- Essay Tik TokDocument6 pagesEssay Tik TokEzayffa HizfarNo ratings yet
- RQD After 20 Years Deere 1989Document101 pagesRQD After 20 Years Deere 1989Johan Van Staveren100% (1)