Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Food Production With Ans PDF
Uploaded by
sarvesh kumarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Food Production With Ans PDF
Uploaded by
sarvesh kumarCopyright:
Available Formats
Q.1 List the selection criteria for Fish.
Ans= To check the freshness of a fish, one must take into account certain characteristics the fish must have.
Some of the criteria which can help up select fresh fish are:
The eyes: must be full, moist, bright and rounded. Avoid fish with opaque, dry, wrinkled or concave eyes.
The gills: must be clean, red and shiny, without grey traces or mud residues.
The body: must be tight, smooth and almost hard, not loose, soft or deformed.
The skin: must be shiny and moist to the touch. It mustn’t be dry or dull.
Any other natural marking or coloring must also not be dull.
For example, fish such as red mullet must have a bright rosé-red color,
trout must have rainbow colorings and salmon must be bright silver.
The smell: fresh fish smell of freshness and the sea, not fishy.
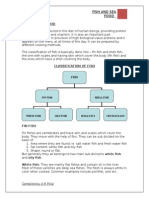
Q.2 Classify fish with an example of each category.
Ans= Fish are broadly classified as Finfish and Shellfish
Finfish
Finfish are divided into white fish and oil-rich fish.
White Fish
White fish are sometimes referred to as "lean fish" because all the oils are contained in the liver,
which is removed during gutting. White fish are further sub-divided into:
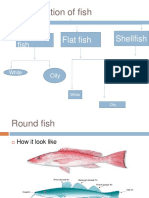
Round White Fish
Examples include cod, haddock, hake and pollock
Flat White Fish
Examples include plaice, lemon sole, brill, turbot, black sole are common examples of this category
Cartilaginous Fish
Ray, rock salmon and shark are examples
Oil-Rich Fish
Oil-rich fish are so called because the oils are distributed throughout the flesh of the fish.
Mackerel, herring, salmon and trout are common examples.
Occasionally you will find fish classified in a different way: Demersal and Pelagic Fish.
Demersal fish are those which live on or near the sea bed.
Round and flat white fish fall into this category.
Pelagic fish swim in mid-waters or near the surface.
Oil-rich fish such as mackerel, herring and tuna are common examples.
Shellfish
Shellfish are broadly divided into two main categories: Molluscs and Crustaceans.
Molluscs
Molluscs can be divided into three categories:
Uni-valve Molluscs
Uni-valve molluscs are those with one shell – periwinkle and whelks.
file:///C/Users/DJ%20ASHOK%20RAJ/Documents/food%20production%20with%20Ans.txt[5/10/2019 7:46:21 AM]
Bi-valve Molluscs
Bi-valve molluscs are those with two shells hinged at one end – mussels, oysters and scallops are good examples.
Cephalopods
This type of shellfish has no outer shell, but just a single internal one called a pen. Examples include squid and
cuttlefish.
Crustaceans
Crustaceans are more mobile creatures with hard segmented shells and flexible joints. Examples include prawns,
shrimp, crab and lobster.
Q.3 List the differences between a sauce and a gravy.
Ans= Gravy: Gravy is a sauce made from meat juices, usually combined with a liquid such as chicken or beef
broth, wine or milk and thickened with flour, cornstarch, or some other thickening agent.
A gravy may also be the simple juices left in the pan after the meat, poultry, or fish has been cooked.
Learn how to make Perfect Turkey Gravy.
Sauce: The word “sauce” is a French word that means a relish to make our food more appetizing.
Sauces are liquid or semi-liquid foods devised to make other foods look, smell, and taste better,
and hence be more easily digested and more beneficial.
Because of the lack of refrigeration in the early days of cooking, meat, poultry, fish, and seafood didn’t last long.
Sauces and gravies were used to mask the flavor of tainted foods.
Q.4 Give two derivatives each of basic mother sauces.
Ans= The 5 French Mother Sauces
1. Béchamel
This is roux whisked with milk or other dairy to make a white sauce.
Ever made macaroni and cheese or chicken pot pie? The base of both these dishes is béchamel.
By itself, béchamel is quite bland,
which is why it is usually cooked with other ingredients and not used as a finishing sauce.
2. Velouté
A velouté is a light roux whisked with chicken, turkey, fish or any other clear stock.
The resulting sauce takes on the flavor of the stock, and the name is derived from the French word for velvet,
which aptly describes this smooth but light and delicate sauce.
It is usually served over fish or poultry that has been delicately cooked, like by poaching or steaming.
3. Espagnole
Sauce espagnole is a basic brown sauce. It’s made of brown beef or veal stock, tomato puree, and browned mirepoix,
all thickened with a very dark brown roux. This sauce is sometimes used at the foundation for boeuf bourguinon and
demi-glace.
4. Sauce Tomat
This is made by cooking tomatoes down into a thick sauce but used to also be thickened with roux.
Unlike more modern-day tomato sauces, the classic French tomato sauce is flavored with pork and aromatic vegetables.
5. Hollandaise
This is the one mother sauce not thickened by a roux. Instead, it’s thickened by an emulsion of egg yolk and melted
butter,
which means it’s a stable mixture of two things that usually normally can’t blend together.
This is a very delicate sauce because the emulsion can easily break, and rich hollandaise is usually used as a dipping
sauce for asparagus
or a finishing sauce for dishes like eggs Benedict.
file:///C/Users/DJ%20ASHOK%20RAJ/Documents/food%20production%20with%20Ans.txt[5/10/2019 7:46:21 AM]
Q.5 Define soups.
Ans= a liquid dish, typically savoury and made by boiling meat, fish, or vegetables etc. in stock or water.
1.Clear Soups
Broth soup
Consommes
2.Thick Soups
Cream Soups
Veloute-based soups
3.Puree Soups
Bisques
Chowders
Cold Soups
1.Clear Soups
When you think of clear soups you think of light soups or mild-flavored soups.
Most clear soups include broths and bouillons made from meats, poultry, game, fish or vegetables.
There are also consommes, which are stock or broths that are clarified to remove impurities.
We are going to explore a bit more about the different types of soups that everyone needs to know if they are serious
about cooking.
2.Thick Soups
There are generally two different types of thick soups: Cream veloute-based soups and puree soups.
Cream veloute-based soups are thickened with a roux, while puree soups rely on a puree of the main ingredient for
thickening.
But in certain ways, the two soups are very similar. Some puree soups are finished with cream,
and rice or potatoes may be used to help thicken the soup.
3.Pureed Soups
Pureed types of soup are often very hearty and full of flavor.
They are healthy and include an impressive amount of vitamins and nutrition.
The best explanation of puree types of soup is to cook starchy vegetables or legumes (Or both!) in a stock or broth, and
then pureeing the ingredients.
It is always recommended when pureeing the ingredients to use a portion of the liquid and add it slowly to get the
desired thickness.
Q.6 Name and explain the different classical cuts of fish.
Ans= Whole Fish or Round Fish or Fish in the Round -
Whole head on with viscera (guts), tail, everything intact.
Dressed Fish - Whole head on, tail, everything except that it has the viscera (guts) removed.
Pan-Dressed Fish - This is a Dressed fish which has its fins, tail, and head removed.
H&G (Headed & Gutted) Fish - Whole, head-off, gutted.
Bullets or Rounds - H&G with fins and tail removed.
Top Back Loin - Taken from larger fish like Tuna, Swordfish, etc, this is the back loin without the belly portion. No
bones.
Loin - This is the prime part of a fillet from a large round fish.
It is the part of the fillet which is above the spine, sometimes called the top back loin.
Loins are typically cut from fish like Tuna, Swordfish, and Marlin.
Fillet - A fillet is an entire side of a fish with the backbone out. Round fish yield two fillets (one from each side).
Flat fish yield 4 fillets (2 from each side). Fillets from larger fish can be further portioned into supremes or
file:///C/Users/DJ%20ASHOK%20RAJ/Documents/food%20production%20with%20Ans.txt[5/10/2019 7:46:21 AM]
escalopes.
They may be skin-on or skin-off.
Fletch - A Fletch is part of a large Fillet from a large flatfish. It can be half, quarter, or less of the full fillet.
Steak or Darne - Is a thick, cross-section cut from a round fish, perpendicular to the spine. Steaks often retain part of
the backbone.
Supreme - A supreme is a prime boneless cut from a fillet or loin which is cut either as a block-cut or
bias-cut, and is considered the best and choicest cut of fish.
Also called a pavé, a supreme cut removes all bones in the filet.
Tronçon - This is a steak-cut (bone-in) from a flatfish such as flounder, halibut, sole, or turbot. In the US these are
called a Steak cut.
Paupiette - A paupiette is a fillet that is stuffed and rolled.
Cravatte - A cravatte is a fillet tied into a knot.
Delice - Delice is a fillet that is neatly stuffed and folded.
Goujons - Strips 2" x ¼" from the fillets of small fish such as sole or plaice.
En Tresse - A braided or platted fillet.
Butterfly Fillets - Used with small fish like trout, sardines, mackerel or herring, this cut is made by leaving the two
fillets attached by the skin.
Thus you get the whole fish minus the head and rib bones.
Canoe Fillets - Same as a butterfly fillet except that the head is left on.
Q.7 Draw a neat diagram and label the different cuts of lamb/mutton.
Ans=
file:///C/Users/DJ%20ASHOK%20RAJ/Documents/food%20production%20with%20Ans.txt[5/10/2019 7:46:21 AM]
You might also like
- Seafood DishesDocument10 pagesSeafood DishesArmie LandritoNo ratings yet
- Terminologies, Cooking Methods and TechniquesDocument200 pagesTerminologies, Cooking Methods and TechniquesAle Grace100% (1)
- Let's: Fish!Document58 pagesLet's: Fish!raphaelNo ratings yet
- Basic Stocks, Soups & SaucesDocument11 pagesBasic Stocks, Soups & SaucesJoshua GalpoNo ratings yet
- Cookery Week 11 To 20 by Liesly TohoyDocument17 pagesCookery Week 11 To 20 by Liesly TohoyPeter Rey SabanalNo ratings yet
- FLRegKey RegDocument2 pagesFLRegKey RegIngram29% (14)
- URBVNFIT Plant Based Meal PlanDocument16 pagesURBVNFIT Plant Based Meal PlanMami Chulaaa100% (1)
- Fish and ShellfishDocument60 pagesFish and ShellfishTristhan Carl SolosaNo ratings yet
- Fish - Grade 9Document3 pagesFish - Grade 9lil sister and cousinNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Types of Seafoods: Report By: Lex Cabrera & Jeremy FelicianoDocument30 pagesLesson 3 - Types of Seafoods: Report By: Lex Cabrera & Jeremy FelicianoRhea CaasiNo ratings yet
- What Is Fish CuttingDocument26 pagesWhat Is Fish CuttingGeorgia Grant100% (2)
- FISH and SHELLFISHDocument61 pagesFISH and SHELLFISHMaricel Sanchez - Costillas71% (7)
- Evaluation of FoodDocument3 pagesEvaluation of Foodsarvesh kumarNo ratings yet
- Stock Making in DetailDocument6 pagesStock Making in DetailZIO HrtdNo ratings yet
- Preparing Fish & Seafood DishesDocument59 pagesPreparing Fish & Seafood DishesSan Isidro Agnes0% (1)
- My PPT Fish and ShellfishDocument44 pagesMy PPT Fish and Shellfishkrestina lacamra50% (2)
- Basic Fish Cooking Methods: A No Frills Guide to Preparing Fresh FishFrom EverandBasic Fish Cooking Methods: A No Frills Guide to Preparing Fresh FishNo ratings yet
- Fish and Sea FoodDocument9 pagesFish and Sea Fooditzmeaneesh50% (2)
- Silver and Pre Plated ServiceDocument11 pagesSilver and Pre Plated Servicesarvesh kumarNo ratings yet
- Silver and Pre Plated ServiceDocument11 pagesSilver and Pre Plated Servicesarvesh kumarNo ratings yet
- Tle Reviewer 3rd QTR PDFDocument8 pagesTle Reviewer 3rd QTR PDFJasmine AlbaNo ratings yet
- Fish CookeryDocument6 pagesFish Cookerygauravkrishana28No ratings yet
- Cookery ReviewerDocument8 pagesCookery ReviewerolmoguezmarcelleneNo ratings yet
- BF2 Laboratory Egg FishDocument3 pagesBF2 Laboratory Egg FishBernadette YurongNo ratings yet
- Fish NewDocument6 pagesFish NewUP TO DATE VIDEOSNo ratings yet
- Fish NewDocument6 pagesFish NewUP TO DATE VIDEOSNo ratings yet
- Classification of FishDocument10 pagesClassification of FishDebjyoti BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- FishDocument42 pagesFishRanjit KarkiNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Fin Fish and Shell FishDocument6 pagesDifference Between Fin Fish and Shell FishRhoan TibayanNo ratings yet
- Classification of Fish and Sea Foods According Their KindDocument6 pagesClassification of Fish and Sea Foods According Their KindDedan GideonNo ratings yet
- Classification of FishDocument16 pagesClassification of FishBharat NailwalNo ratings yet
- Quality of FishDocument90 pagesQuality of FishMario MelrickNo ratings yet
- Finfish and Shellfish CookeryDocument14 pagesFinfish and Shellfish CookeryBrianna GrahamNo ratings yet
- Classification of FishDocument16 pagesClassification of FishfelixrajasNo ratings yet
- Tle 10-Q4 L4 Preparation of Fish and Shellfish ProductsDocument83 pagesTle 10-Q4 L4 Preparation of Fish and Shellfish ProductsAdoree Ramos100% (1)
- nguyên lý nấu nướng khối lượng lớnDocument6 pagesnguyên lý nấu nướng khối lượng lớnNgọc HồngNo ratings yet
- TLE ReviewerDocument10 pagesTLE ReviewerAndrea JimenezNo ratings yet
- Butterfly FilletDocument16 pagesButterfly FilletBlake KamminNo ratings yet
- 3rd-Lesson 1Document23 pages3rd-Lesson 1Jardine BeneroNo ratings yet
- FishDocument6 pagesFishNeelesh KadamNo ratings yet
- Understanding Fish and ShellfishDocument45 pagesUnderstanding Fish and ShellfishCeejaay PelinaNo ratings yet
- Unit - 4 Le Poisson (Fish) PDFDocument12 pagesUnit - 4 Le Poisson (Fish) PDFDevil 4uNo ratings yet
- Rainbow Trout CultureDocument6 pagesRainbow Trout Cultureluis ruperto floresNo ratings yet
- SHS Stocks SoupsDocument38 pagesSHS Stocks SoupsLiam AngelesNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Lesson 1Document39 pagesGrade 8 Lesson 1Kyle Daphne SumpayNo ratings yet
- Task Sheet 5 Fish and Shellfish - Villanueva - Jonaver - C - Btvted - 2 - J - FSM - BDocument62 pagesTask Sheet 5 Fish and Shellfish - Villanueva - Jonaver - C - Btvted - 2 - J - FSM - BjohnpoulcebuNo ratings yet
- Q2 Module 6 Preparing and Cooking Seafood Dishes UPDATEDDocument52 pagesQ2 Module 6 Preparing and Cooking Seafood Dishes UPDATEDKim Russel AgpaoaNo ratings yet
- ColdmealsDocument4 pagesColdmealsOrlando PabloNo ratings yet
- FNH Part 4Document15 pagesFNH Part 4JessicaNo ratings yet
- Portfolio in Cookery: Maybelle A. Berano Grade 10 - Amity (1) Mrs. BallesterolDocument14 pagesPortfolio in Cookery: Maybelle A. Berano Grade 10 - Amity (1) Mrs. BallesterolMaybelle Atanoc BeranoNo ratings yet
- Anna TleDocument22 pagesAnna TleReigne AngcayaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 StocksDocument7 pagesChapter 1 StocksSandeep Kumar ThakurNo ratings yet
- Interview Questionnaire FinalDocument37 pagesInterview Questionnaire FinalKrishna ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- StockDocument17 pagesStockTenzin KesangNo ratings yet
- Fish CookeryDocument12 pagesFish Cookeryshagay.sheppy0106No ratings yet
- Handling and Storage of FishDocument14 pagesHandling and Storage of Fishelara diorNo ratings yet
- Preparing AppetizersDocument2 pagesPreparing AppetizersJappy CarberoNo ratings yet
- Elective 4Document10 pagesElective 4Rico EsponillaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document15 pagesChapter 5rhiantics_kram11100% (1)
- Cold Cuts: Farci: Terrines:: Pate Cooked in ADocument8 pagesCold Cuts: Farci: Terrines:: Pate Cooked in ANawed KhanNo ratings yet
- BF2 PT Fish&ShellfishDocument2 pagesBF2 PT Fish&ShellfishBernadette YurongNo ratings yet
- Hot MealDocument16 pagesHot MealJana Denissa NOTONo ratings yet
- Asynch Activity - Q1 - W7 (Saliente)Document3 pagesAsynch Activity - Q1 - W7 (Saliente)Daniela Marie SalienteNo ratings yet
- FN41.3.04.Meat, Poultry, and SeafoodDocument28 pagesFN41.3.04.Meat, Poultry, and SeafoodGeorgia GrantNo ratings yet
- PHT 2Document49 pagesPHT 2Juliet Cayao SajolNo ratings yet
- Food & Beverage Service: Tobacco TobaccoDocument11 pagesFood & Beverage Service: Tobacco Tobaccosarvesh kumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document4 pagesChapter 1sarvesh kumar0% (1)
- Types of Accounts & DiscountDocument10 pagesTypes of Accounts & Discountsarvesh kumarNo ratings yet
- Bank Reconciliation Statement (BRS)Document2 pagesBank Reconciliation Statement (BRS)sarvesh kumarNo ratings yet
- 100 Calorie Food Portions ListDocument4 pages100 Calorie Food Portions Listfilipe.machazNo ratings yet
- Basic Vegan Gravy RecipeDocument1 pageBasic Vegan Gravy Recipelayehrockgothstar2295No ratings yet
- Y HB M College Cookbook 09Document61 pagesY HB M College Cookbook 09Shaikh MeenatullahNo ratings yet
- Dinner MenuDocument2 pagesDinner MenueatlocalmenusNo ratings yet
- Tonga Room RecipesDocument4 pagesTonga Room RecipesJesus AndradeNo ratings yet
- 2020 Sanchaya Food MenuDocument1 page2020 Sanchaya Food MenushinemgnptNo ratings yet
- ITC Rajputana in Room DiningDocument69 pagesITC Rajputana in Room DiningSatish MenonNo ratings yet
- Grand Menu Pepper Lunch MedanDocument1 pageGrand Menu Pepper Lunch MedanSemi Syaina AmandaNo ratings yet
- Barbeque NationDocument9 pagesBarbeque Nationjony048211No ratings yet
- q3 Module4 g12 CookeryDocument5 pagesq3 Module4 g12 Cookeryayra cyreneNo ratings yet
- Download pdf Calculus Graphical Numerical Algebraic 5Th Edition Ross L Finney ebook full chapterDocument53 pagesDownload pdf Calculus Graphical Numerical Algebraic 5Th Edition Ross L Finney ebook full chapterjulie.barnes770100% (1)
- 50 Kid Friendly Meal IdeasDocument2 pages50 Kid Friendly Meal IdeasMartha Patricia López PimentelNo ratings yet
- Apollo Fruit ProductsDocument13 pagesApollo Fruit ProductsAbhayaSimhaNo ratings yet
- Sweet Potato Chickpea Buddha BowlDocument2 pagesSweet Potato Chickpea Buddha BowlMegan WoodsonNo ratings yet
- Cookery10 Q3 W2Document4 pagesCookery10 Q3 W2Runa YomozukiNo ratings yet
- Chinese New Year 2023Document3 pagesChinese New Year 2023Jejen LenovoNo ratings yet
- Nutrition FactsDocument3 pagesNutrition FactsMARIELLE LOUISE JAMON ANDRADENo ratings yet
- Street Food MenuDocument43 pagesStreet Food MenuVu Le MinhNo ratings yet
- Written Questions: Prepare Vegetables, Eggs and Farinaceous Dishes - D1.HCC - CL2.18Document9 pagesWritten Questions: Prepare Vegetables, Eggs and Farinaceous Dishes - D1.HCC - CL2.18Billy MillennioNo ratings yet
- HM 111 Module FinalDocument18 pagesHM 111 Module FinalJonna NalanggayNo ratings yet
- BEEF BURGER PATTIES-reggie AspirasDocument2 pagesBEEF BURGER PATTIES-reggie AspirasRoland GarciaNo ratings yet
- E.-Cooking Verbs Is Fun.Document1 pageE.-Cooking Verbs Is Fun.Wilman Alvis GrandezNo ratings yet
- Chicken Makhani (Indian Butter Chicken) : Ingredients DirectionsDocument2 pagesChicken Makhani (Indian Butter Chicken) : Ingredients DirectionsFarruNo ratings yet
- Performance TAsk in MATHDocument25 pagesPerformance TAsk in MATHMelissa Marie CustodioNo ratings yet
- Cocktail Party Menu WebDocument3 pagesCocktail Party Menu Webapi-289211494No ratings yet
- I. Introduction & II. Market FeasibilityDocument34 pagesI. Introduction & II. Market FeasibilityEumar FabruadaNo ratings yet
- Prepare Hot and Cold MealsDocument6 pagesPrepare Hot and Cold MealsFame EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- PROMO Party PackageDocument3 pagesPROMO Party Packagechubaboinks100% (1)