Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 viewsAbstract - Essentials For Selecting Antimicrobial Therapy For Intra-Abdominal Infections.
Abstract - Essentials For Selecting Antimicrobial Therapy For Intra-Abdominal Infections.
Uploaded by
MarinSelecting Antimicrobial Therapy for Intra-Abdominal Infections.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5819)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Study of Hematological Parameters in Patients With Non-Hematological Malignancies and Their Correlation With Stage of The DiseaseDocument7 pagesStudy of Hematological Parameters in Patients With Non-Hematological Malignancies and Their Correlation With Stage of The DiseaseIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- BSE Nadzor I Ocena Rizika PDFDocument714 pagesBSE Nadzor I Ocena Rizika PDFEkatarina EkatarinaNo ratings yet
- DR Tarek Tawfik Amin: Professor of Epidemiology Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University, EgyptDocument33 pagesDR Tarek Tawfik Amin: Professor of Epidemiology Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University, Egyptchipta lestariNo ratings yet
- Acupressure Massage For AscitesDocument4 pagesAcupressure Massage For Ascitessaif ahmedNo ratings yet
- HydrocortisoneDocument2 pagesHydrocortisoneMaggieNo ratings yet
- L1 Hypo, Hyperthyroidism and Hashimoto ThyroiditisDocument12 pagesL1 Hypo, Hyperthyroidism and Hashimoto ThyroiditisSivaNo ratings yet
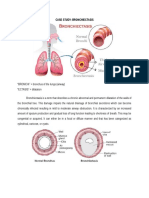
- Case Study: BronchiectasisDocument5 pagesCase Study: BronchiectasisHanna Mae HernandezNo ratings yet
- Jawaban Compound Exercise 2Document4 pagesJawaban Compound Exercise 2Evoria ManurungNo ratings yet
- DR Putut B - Slide-Diagnostic Challenges in Functional Dyspepsia - (PIN PAPDI 2019) - PDFDocument24 pagesDR Putut B - Slide-Diagnostic Challenges in Functional Dyspepsia - (PIN PAPDI 2019) - PDFMuhammad Ahmad bin makruf syammakuNo ratings yet
- Bioterrorism - A Public Health Perspective-DikonversiDocument9 pagesBioterrorism - A Public Health Perspective-DikonversiFira LasenaNo ratings yet
- Health DLP STAGES OF INFECTIONDocument9 pagesHealth DLP STAGES OF INFECTIONmarielabianaNo ratings yet
- ECDA - Letter To Parents 8 Feb 2020Document3 pagesECDA - Letter To Parents 8 Feb 2020Vinchy WinchyNo ratings yet
- 2019 Disease Detectives Case StudyDocument8 pages2019 Disease Detectives Case StudyFat NachoNo ratings yet
- Stampede M0 ASTRO Presentation Sept 2014Document24 pagesStampede M0 ASTRO Presentation Sept 2014Prof_Nick_JamesNo ratings yet
- Medical Application Form PDFDocument3 pagesMedical Application Form PDFHumanNo ratings yet
- Tugas Bahasa Inggris Mandiri Speech Class Program Gouty ArthritisDocument3 pagesTugas Bahasa Inggris Mandiri Speech Class Program Gouty ArthritisWisnu 12No ratings yet
- GP Eudor WEB MN3011250ENC 002.pdf - en PDFDocument32 pagesGP Eudor WEB MN3011250ENC 002.pdf - en PDFmysterix01No ratings yet
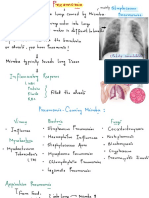
- PneumoniaDocument5 pagesPneumoniarjshubhNo ratings yet
- DNB Pediatrics Question BankDocument25 pagesDNB Pediatrics Question Bankshalpraba100% (1)
- Final Infection Exam Sarina Bakhtiarian 1801853Document12 pagesFinal Infection Exam Sarina Bakhtiarian 1801853Top MusicNo ratings yet
- DISEASES Kawasaki, RHD, Is HPN)Document9 pagesDISEASES Kawasaki, RHD, Is HPN)jenn212No ratings yet
- AnthraxDocument2 pagesAnthraxAmon Jnr KamungarangaNo ratings yet
- Craniosynostosis Research PresentationDocument12 pagesCraniosynostosis Research PresentationPaul MarjiNo ratings yet
- Fibroscan Interpretation - Guide 2020Document2 pagesFibroscan Interpretation - Guide 2020Faisal BaigNo ratings yet
- CDC Guidelines For Isolation Precautions in HospitalsDocument5 pagesCDC Guidelines For Isolation Precautions in HospitalsReamonn Vincent DantesNo ratings yet
- Problem PrioritizationDocument1 pageProblem PrioritizationFlauros Ryu JabienNo ratings yet
- NCP CervicalDocument4 pagesNCP CervicalZaira Kim93% (14)
- Swarnamalini Kathirvel (U3193222) :::: Patient Age / Sex 24 Y / Female BranchDocument1 pageSwarnamalini Kathirvel (U3193222) :::: Patient Age / Sex 24 Y / Female BranchswarnamaliniNo ratings yet
- A Visit To The Doctor - EnfermeriaDocument4 pagesA Visit To The Doctor - EnfermeriaSILVIA MARIELA LLAMOCA LIMACHENo ratings yet
- Cefuroxime Axetil (Oral)Document2 pagesCefuroxime Axetil (Oral)STORAGE FILENo ratings yet
Abstract - Essentials For Selecting Antimicrobial Therapy For Intra-Abdominal Infections.
Abstract - Essentials For Selecting Antimicrobial Therapy For Intra-Abdominal Infections.
Uploaded by
Marin0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views2 pagesSelecting Antimicrobial Therapy for Intra-Abdominal Infections.
Original Title
Abstract- Essentials for Selecting Antimicrobial Therapy for Intra-Abdominal Infections.
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSelecting Antimicrobial Therapy for Intra-Abdominal Infections.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views2 pagesAbstract - Essentials For Selecting Antimicrobial Therapy For Intra-Abdominal Infections.
Abstract - Essentials For Selecting Antimicrobial Therapy For Intra-Abdominal Infections.
Uploaded by
MarinSelecting Antimicrobial Therapy for Intra-Abdominal Infections.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Drugs. 2012 Apr 16;72(6):e17-32. doi: 10.2165/11599800-000000000-00000.
Essentials for selecting antimicrobial therapy for intra-
abdominal infections.
Blot S1, De Waele JJ, Vogelaers D.
Author information
1
Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences, Ghent University, Ghent, Belgium.
stijn.blot@UGent.be
Abstract
Intra-abdominal infection (IAI) is a complex disease entity in which different aspects must be
balanced in order to select the proper antimicrobial regimen and determine duration of therapy. A
current classification indicates different faces of peritonitis. Primary peritonitisimplies an intact
gastrointestinal tract without overt barrier disruption. Secondary peritonitis refers to localized or
diffuse peritoneal inflammation and abscess formation due to disruption of the anatomical barrier.
Tertiary peritonitis includes cases that cannot be solved by a single or even sequential surgical
intervention, often in combination with sequential courses of antimicrobial therapy. The most
frequently used classification distinguishes 'uncomplicated' and 'complicated' IAI. In
uncomplicated IAI, the infectious process is contained within a single organ, without anatomical
disruption. In complicated IAI, disease is extended, with either localized or generalized peritonitis.
However, there exists more than a single dimension of complexity in IAI, including severity of
disease expression through systemic inflammation. As the currently used classifications of IAI
often incite confusion by mixing elements of anatomical barrier disruption, severity of disease
expression and (the likelihood of) resistance involvement, we propose an alternative for the
current widely accepted classification. We suggest abandoning the terms 'uncomplicated' and
'complicated' IAI, as they merely confuse the issue. Furthermore, the term 'tertiary peritonitis'
should likewise be discarded, as this simply refers to treatment failure of
secondary peritonitis resulting in a state of persistent infection and/or inflammation. Hence,
anatomical disruption and disease severity should be separated into different phenotypes for the
same disease in combination with either presence or absence of risk factors for involvement of
pathogens that are not routinely covered in first-line antimicrobial regimens (Pseudomonas
aeruginosa, enterococci, Candida species and resistant pathogens). Generally, these risk factors
can be brought back to recent exposure to antimicrobial agents and substantial length of stay in
healthcare settings (5-7 days). As such, we developed a grid based on the different components
of the classification: (i) anatomical disruption; (ii) severity of disease expression; and (iii) either
community-acquired/early-onset healthcare-associated origin or healthcare-associated origin
and/or recent antimicrobial exposure. The grid allows physicians to define the index case of IAI in
a more unequivocal way and to select the most convenient empirical antimicrobial regimens. The
grid advises on the necessity of covering nosocomial Gram-negative bacteria (including P.
aeruginosa), enterococci and yeasts. The basis of antimicrobial therapy for IAI is that both Gram-
negative and anaerobic bacteria should always be covered. In recent years, some newer agents
such as doripenem, moxifloxacin and tigecycline have been added to the antimicrobial
armamentarium for IAI. For patients in whom the source can be adequately controlled,
antimicrobial therapy should be restricted to a short course (e.g. 3-7 days in peritonitis).
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5819)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Study of Hematological Parameters in Patients With Non-Hematological Malignancies and Their Correlation With Stage of The DiseaseDocument7 pagesStudy of Hematological Parameters in Patients With Non-Hematological Malignancies and Their Correlation With Stage of The DiseaseIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- BSE Nadzor I Ocena Rizika PDFDocument714 pagesBSE Nadzor I Ocena Rizika PDFEkatarina EkatarinaNo ratings yet
- DR Tarek Tawfik Amin: Professor of Epidemiology Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University, EgyptDocument33 pagesDR Tarek Tawfik Amin: Professor of Epidemiology Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University, Egyptchipta lestariNo ratings yet
- Acupressure Massage For AscitesDocument4 pagesAcupressure Massage For Ascitessaif ahmedNo ratings yet
- HydrocortisoneDocument2 pagesHydrocortisoneMaggieNo ratings yet
- L1 Hypo, Hyperthyroidism and Hashimoto ThyroiditisDocument12 pagesL1 Hypo, Hyperthyroidism and Hashimoto ThyroiditisSivaNo ratings yet
- Case Study: BronchiectasisDocument5 pagesCase Study: BronchiectasisHanna Mae HernandezNo ratings yet
- Jawaban Compound Exercise 2Document4 pagesJawaban Compound Exercise 2Evoria ManurungNo ratings yet
- DR Putut B - Slide-Diagnostic Challenges in Functional Dyspepsia - (PIN PAPDI 2019) - PDFDocument24 pagesDR Putut B - Slide-Diagnostic Challenges in Functional Dyspepsia - (PIN PAPDI 2019) - PDFMuhammad Ahmad bin makruf syammakuNo ratings yet
- Bioterrorism - A Public Health Perspective-DikonversiDocument9 pagesBioterrorism - A Public Health Perspective-DikonversiFira LasenaNo ratings yet
- Health DLP STAGES OF INFECTIONDocument9 pagesHealth DLP STAGES OF INFECTIONmarielabianaNo ratings yet
- ECDA - Letter To Parents 8 Feb 2020Document3 pagesECDA - Letter To Parents 8 Feb 2020Vinchy WinchyNo ratings yet
- 2019 Disease Detectives Case StudyDocument8 pages2019 Disease Detectives Case StudyFat NachoNo ratings yet
- Stampede M0 ASTRO Presentation Sept 2014Document24 pagesStampede M0 ASTRO Presentation Sept 2014Prof_Nick_JamesNo ratings yet
- Medical Application Form PDFDocument3 pagesMedical Application Form PDFHumanNo ratings yet
- Tugas Bahasa Inggris Mandiri Speech Class Program Gouty ArthritisDocument3 pagesTugas Bahasa Inggris Mandiri Speech Class Program Gouty ArthritisWisnu 12No ratings yet
- GP Eudor WEB MN3011250ENC 002.pdf - en PDFDocument32 pagesGP Eudor WEB MN3011250ENC 002.pdf - en PDFmysterix01No ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument5 pagesPneumoniarjshubhNo ratings yet
- DNB Pediatrics Question BankDocument25 pagesDNB Pediatrics Question Bankshalpraba100% (1)
- Final Infection Exam Sarina Bakhtiarian 1801853Document12 pagesFinal Infection Exam Sarina Bakhtiarian 1801853Top MusicNo ratings yet
- DISEASES Kawasaki, RHD, Is HPN)Document9 pagesDISEASES Kawasaki, RHD, Is HPN)jenn212No ratings yet
- AnthraxDocument2 pagesAnthraxAmon Jnr KamungarangaNo ratings yet
- Craniosynostosis Research PresentationDocument12 pagesCraniosynostosis Research PresentationPaul MarjiNo ratings yet
- Fibroscan Interpretation - Guide 2020Document2 pagesFibroscan Interpretation - Guide 2020Faisal BaigNo ratings yet
- CDC Guidelines For Isolation Precautions in HospitalsDocument5 pagesCDC Guidelines For Isolation Precautions in HospitalsReamonn Vincent DantesNo ratings yet
- Problem PrioritizationDocument1 pageProblem PrioritizationFlauros Ryu JabienNo ratings yet
- NCP CervicalDocument4 pagesNCP CervicalZaira Kim93% (14)
- Swarnamalini Kathirvel (U3193222) :::: Patient Age / Sex 24 Y / Female BranchDocument1 pageSwarnamalini Kathirvel (U3193222) :::: Patient Age / Sex 24 Y / Female BranchswarnamaliniNo ratings yet
- A Visit To The Doctor - EnfermeriaDocument4 pagesA Visit To The Doctor - EnfermeriaSILVIA MARIELA LLAMOCA LIMACHENo ratings yet
- Cefuroxime Axetil (Oral)Document2 pagesCefuroxime Axetil (Oral)STORAGE FILENo ratings yet