Professional Documents
Culture Documents
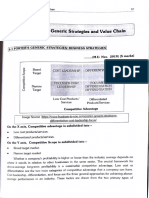
Cost Focus-Firm Strives To Create A Cost 2. Differentiation Focus - Seeks To
Uploaded by
caicaiiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cost Focus-Firm Strives To Create A Cost 2. Differentiation Focus - Seeks To
Uploaded by
caicaiiCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 5: Business-Level Strategy Too much differentiation
Too high a price premium
Generic Strategies (F-O-D) Differentiation that is easily imitated
- Presented by Michael Porter Dilution of brand identification through
- Basic type of business level strategies based product-line extensions
on breadth of target market and type of Perceptions of differentiation that vary
competitive advantage between buyers and sellers
a. Focus Strategy Combination Strategies: Overall Low Cost and
- Based on the choice of narrow competitive Differentiation
scope within an industry - Firm’s integrations of various strategies to
1. Cost Focus- firm strives to create a cost provide multiple types of value to customers
advantage; difference in cost behavior - GOAL: provide unique value to customers in
2. Differentiation Focus- seeks to an efficient manner
differentiate in its target market; special
needs of buyer in other segments FOUR APPROACHES
- Potential Pitfalls 1. Adopting Automated and Flexible
Cost advantages may erode within Manufacturing Systems
the narrow segment Mass Communication- firm’s ability to
Product and service offerings that are manufacture unique products in small
highly focused are subject to quantities at low cost
competition from new entrants and 2. Using Data analytics
from imitation Big Bang- collecting and analyzing data
Focusers can become too focused to on their customers
satisfy buyer needs 3. Exploiting the profit pool concept
Profit pool- total profits in an industry at
b. Overall Cost Leadership all points along the industry’s value chain
- Appeal to the industrywide market using a 4. Coordinating the extended value chain
competitive advantage based on low cost
- Experience Curve: factor that is central to an - Potential Pitfalls
overall cost leadership strategy Failing to attain both strategies and
: decline in the unit costs of possibly ending up neither, leaving
production as cumulative output the firm “stuck in the middle”
increases Underestimating challenges and
: developed by Boston expenses associate with coordinating
Consulting Group value-creating activities in the
- To generate above-average performance a extended value chain
firm must attain Miscalculating sources of revenue
competitive parity and profit pools in the firm’s industry
A firm’s achievement of
similarity, or “on par”, with INDUSTRY LIFE-CYCLE STAGES: Strategic
competitors with respect to Implications
the generic strategies - Refers to the stages of introduction, growth,
- Potential Pitfalls maturity, and decline that occur over the life
Too much focus on one or few value on an industry
chain activities
Increase in the cost of the inputs on INTRODUCTION STAGE
which the advantage is based - First stage of the life cycle
Strategy that can be imitated too - Characteristics:
easily Products are unfamiliar to the
Lack of parity on differentiation customer
Reduced Flexibility Poorly defined market segments
Obsolescence of the basis of cost Unspecified product features
advantage Low sales growth
Rapid technological change
c. Differentiation Strategy Operating losses
- Based on creating differences in the firm’s Need for financial support
product or service offering by creating - Challenges:
something that is perceived industrywide as Developing the product and finding a
unique and valued by customers way to get users to try it
- Potential Pitfalls
Generating enough exposure
Uniqueness that is not valuable
- Reversing performance decline and
GROWTH STAGE reinvigorating growth toward profitability
- Second stage of the life cycle - May occur at any stage in the life cycle but is
- Characteristics: most likely to occur during maturity or decline
Strong increases in sales
Growing competition THREE STRATEGIES
Developing brand recognition a. Asset and Cost Surgery
Need for financing complementary b. Selective product and market pruning
value-chain activities c. Piecemeal productivity improvements
MATURITY STAGE
- Third stage in the life cycle
- Characteristics:
Slowing demand growth
Saturated markets
Direct competition
Price competition
Strategic emphasis on efficient
operations
- Two positioning strategies to affect customer
mental shifts are
Reverse Positioning- break in the
industry tendency to continuously
augment products by offering
products with fewer product attributes
and lower prices
Breakaway Positioning- break in the
industry tendency to incrementally
improve products along specific
dimensions by offering products that
are still in the industry but are
perceived by customers as being
different
DECLINE STAGE
- Fourth stage in the life cycle
- Characteristics:
Falling sales and profits
Increasing price competition
Industry consolidation
- Firm’s strategic options become dependent on
the actions of rivals
FOUR BASIC STRATEGIES
a. Maintaining: keeping a product going
without significantly reducing marketing
support, technological development and
other investments, in hopes that rivals will
soon exit the market
b. Harvesting: obtaining as much profit as
possible in the short to medium term and
requires that costs be reduced quickly
c. Exiting the Market: dropping the product
from a firm’s portfolio
d. Consolidation: firm’s acquiring or merging
with other firms in an industry in order to
enhance market power and gain valuable
assets
TURNAROUND STRATEGIES
You might also like
- 07 DCF Steel Dynamics AfterDocument2 pages07 DCF Steel Dynamics AfterJack JacintoNo ratings yet
- Agricultural tax exemptions quizDocument19 pagesAgricultural tax exemptions quizJona Celle Castillo100% (1)
- Internal Environment Analysis and Competitive StrategiesDocument38 pagesInternal Environment Analysis and Competitive StrategiesBINEY SINGH RCBSNo ratings yet
- Memorandum of Agreement (Pineridge)Document2 pagesMemorandum of Agreement (Pineridge)caicaiiNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Justice State Regional Prosecutor San Fernando, La Union Marielle QuilacioDocument20 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Justice State Regional Prosecutor San Fernando, La Union Marielle QuilaciocaicaiiNo ratings yet
- Steps Amendment at SECDocument1 pageSteps Amendment at SECcaicaiiNo ratings yet
- HBR's 10 Must Reads on Strategy (including featured article "What Is Strategy?" by Michael E. Porter)From EverandHBR's 10 Must Reads on Strategy (including featured article "What Is Strategy?" by Michael E. Porter)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (25)
- Australian Valuation Handbook 2436862Document770 pagesAustralian Valuation Handbook 2436862jfpansard7730100% (1)
- Business Level StrategyDocument29 pagesBusiness Level StrategyNusrat Jahan NishatNo ratings yet
- The Profit Zone (Review and Analysis of Slywotzky and Morrison's Book)From EverandThe Profit Zone (Review and Analysis of Slywotzky and Morrison's Book)No ratings yet
- Crim. Case No: 43504-R NPS Docket No.: I-17-INV-19-0238 For: Violation of Sec. 5 (I) of R.A. 9262Document10 pagesCrim. Case No: 43504-R NPS Docket No.: I-17-INV-19-0238 For: Violation of Sec. 5 (I) of R.A. 9262caicaiiNo ratings yet
- Petition For Voluntary Dissolution - AVIDocument2 pagesPetition For Voluntary Dissolution - AVIcaicaii75% (4)
- Business Strategies (Bus Pol) Week 8Document51 pagesBusiness Strategies (Bus Pol) Week 8Melanie Cruz ConventoNo ratings yet
- JA of Janice Psychologist DraftDocument11 pagesJA of Janice Psychologist DraftcaicaiiNo ratings yet
- JA of Janice Psychologist DraftDocument11 pagesJA of Janice Psychologist DraftcaicaiiNo ratings yet
- Secretary's Certificate Get GISDocument1 pageSecretary's Certificate Get GIScaicaiiNo ratings yet
- Secretary's Certificate Get GISDocument1 pageSecretary's Certificate Get GIScaicaiiNo ratings yet
- Competitive StrategyDocument14 pagesCompetitive Strategyragini sriNo ratings yet
- R12 Year Ending Proces in GLDocument2 pagesR12 Year Ending Proces in GLsureshNo ratings yet
- Cost Leadership, Differentiation and Niche Strategies AssignmentDocument19 pagesCost Leadership, Differentiation and Niche Strategies AssignmentDoris AchengNo ratings yet
- All EXam Data - RevisedDocument108 pagesAll EXam Data - RevisedTesfaye Belaye100% (2)
- TAXATION REFORMSDocument27 pagesTAXATION REFORMSCaranay BillyNo ratings yet
- Financial Projections and AssumptionsDocument15 pagesFinancial Projections and AssumptionsAbigail GeronimoNo ratings yet
- The Five Generic CompetitiveDocument31 pagesThe Five Generic Competitiveeva mriNo ratings yet
- Directors Approve Voluntary DissolutionDocument3 pagesDirectors Approve Voluntary DissolutioncaicaiiNo ratings yet
- Directors Approve Voluntary DissolutionDocument3 pagesDirectors Approve Voluntary DissolutioncaicaiiNo ratings yet
- Court Documents Detail Domestic Abuse CaseDocument13 pagesCourt Documents Detail Domestic Abuse CasecaicaiiNo ratings yet
- Court Documents Detail Domestic Abuse CaseDocument13 pagesCourt Documents Detail Domestic Abuse CasecaicaiiNo ratings yet
- Court Documents Detail Domestic Abuse CaseDocument13 pagesCourt Documents Detail Domestic Abuse CasecaicaiiNo ratings yet
- Deed of DonationDocument2 pagesDeed of Donationkentclark03No ratings yet
- Deed of DonationDocument2 pagesDeed of Donationkentclark03No ratings yet
- Deed of DonationDocument2 pagesDeed of Donationkentclark03No ratings yet
- Deed of DonationDocument2 pagesDeed of Donationkentclark03No ratings yet
- SBA Notes Chapter 8Document3 pagesSBA Notes Chapter 8Aira Santos VibarNo ratings yet
- Competitive Strategy and Industry Analysis: A La Michael PorterDocument4 pagesCompetitive Strategy and Industry Analysis: A La Michael PorterDaria TomescuNo ratings yet
- BusinessStrategy 9 18 07Document26 pagesBusinessStrategy 9 18 07bananibeheraNo ratings yet
- Strategic ManagementDocument8 pagesStrategic Managementphamtra241998No ratings yet
- 1ps-Business Level StrategyDocument2 pages1ps-Business Level StrategyI Nyoman Sujana GiriNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management Guide for Business Level StrategyDocument28 pagesStrategic Management Guide for Business Level StrategyPrime Johnson FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management Part 5Document7 pagesStrategic Management Part 5aansh rajNo ratings yet
- Business 87 PDFDocument1 pageBusiness 87 PDFLissa MontielNo ratings yet
- STRATEGIC CHOICES: COST LEADERSHIP VS DIFFERENTIATIONDocument118 pagesSTRATEGIC CHOICES: COST LEADERSHIP VS DIFFERENTIATIONAdarsh DashNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Business Strategies and Their Marketing ImplicationDocument29 pagesChapter 3 Business Strategies and Their Marketing ImplicationkarolinNo ratings yet
- Business Strategy N ModelsDocument1 pageBusiness Strategy N ModelsLasitha NawarathnaNo ratings yet
- Strategic Chapter 5Document61 pagesStrategic Chapter 5Ketema AsfawNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management and CompetitivenessDocument3 pagesStrategic Management and CompetitivenessStephanie Nicole DiputadoNo ratings yet
- SM_Functional Level StratDocument26 pagesSM_Functional Level StratAkshat TiwariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document26 pagesChapter 10LumongtadJoanMaeNo ratings yet
- Module III Strategy Formulation UpdatedDocument19 pagesModule III Strategy Formulation Updatedmacs emsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Functional Level StrategyDocument26 pagesChapter 5 - Functional Level StrategyNetsanet Workineh ነፃነት ወርቅነህNo ratings yet
- CBMEC 102 Strategic Management Study Guide Module 05Document11 pagesCBMEC 102 Strategic Management Study Guide Module 05ambitchous19No ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Managing ProductDocument14 pagesLesson 2 Managing ProductCOCONUTNo ratings yet
- Production and Efficiency Strategies ChapterDocument26 pagesProduction and Efficiency Strategies ChapterKalkidanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 MAKING STRATEGIC DECISIONSDocument41 pagesLecture 4 MAKING STRATEGIC DECISIONSJon KrusinskiNo ratings yet
- Functional Level Strategy: Strategic ManagementDocument26 pagesFunctional Level Strategy: Strategic ManagementYvhette Mycah GodaNo ratings yet
- Mastrat MidtermDocument18 pagesMastrat MidtermMae TndnNo ratings yet
- MKM 302: Product Management: Unit 6: Developing Product StrategyDocument3 pagesMKM 302: Product Management: Unit 6: Developing Product StrategyPlatero RolandNo ratings yet
- Strama Reviewer For MTDocument4 pagesStrama Reviewer For MTDawn BitangcorNo ratings yet
- SBAN11B MODULE 5 Porters Generic Market AnalysisDocument3 pagesSBAN11B MODULE 5 Porters Generic Market AnalysisFrancis Ryan PorquezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document7 pagesChapter 5ERICKA MAE NATONo ratings yet
- Competitive and Functional StrategiesDocument20 pagesCompetitive and Functional StrategiesprabodhNo ratings yet
- Olympus Optical - SCM Group7Document16 pagesOlympus Optical - SCM Group7Raksha SarafNo ratings yet
- Guru Jambheshwar University of Science and Technology: Haryana School of BusinessDocument27 pagesGuru Jambheshwar University of Science and Technology: Haryana School of Businessarvind singhalNo ratings yet
- Mcgraw Hill/IrwinDocument19 pagesMcgraw Hill/IrwinAnh TaNo ratings yet
- Part Three: Business Marketing ProgrammingDocument26 pagesPart Three: Business Marketing ProgrammingCandra GirinataNo ratings yet
- FORECASTING TECHNIQUESDocument24 pagesFORECASTING TECHNIQUESsoulniacsipamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 STRATEGIC FORMULATIONDocument5 pagesChapter 5 STRATEGIC FORMULATIONJohn ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Daily Wear: Business Management and StrategyDocument7 pagesDaily Wear: Business Management and StrategyMuhammad ArslanNo ratings yet
- MM 1 Session 18 Dr.s.saibabaDocument33 pagesMM 1 Session 18 Dr.s.saibabasovinahalli 1234No ratings yet
- SM 6 AlternativesDocument36 pagesSM 6 AlternativesCGM MechanicalNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Strategy FormulationDocument14 pagesModule 3 - Strategy FormulationRonald Reagan AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Stratman MidtermsDocument5 pagesStratman MidtermsAngel CortezNo ratings yet
- Corporate Level Strategy Lecture Slides 2009.10Document37 pagesCorporate Level Strategy Lecture Slides 2009.10Priya BalasubramanianNo ratings yet
- 1 - Strategic Management and Stategic CompetitivenessDocument3 pages1 - Strategic Management and Stategic CompetitivenessStephanie Nicole DiputadoNo ratings yet
- A Group10 3MDocument11 pagesA Group10 3MVeni GuptaNo ratings yet
- Business Level Strategies: After Studying This Chapter, You Will Be Able ToDocument32 pagesBusiness Level Strategies: After Studying This Chapter, You Will Be Able ToBhai LangurNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4b: Functional Level StrategyDocument26 pagesChapter 4b: Functional Level StrategyBerhanu ShancoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - The Five Generic Competitive Strategies - Orbegoso, Aira Coleen R.Document26 pagesChapter 5 - The Five Generic Competitive Strategies - Orbegoso, Aira Coleen R.Coleen OrbegosoNo ratings yet
- 669368-Ubv2916u - Deem DilemmaDocument9 pages669368-Ubv2916u - Deem Dilemmarsnagpal2006No ratings yet
- Porter's Generic StrategiesDocument3 pagesPorter's Generic StrategiesCarolina Ocampo GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Alternative Approaches To Achieving Competitive AdvantageDocument11 pagesAlternative Approaches To Achieving Competitive AdvantageMitzukiNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management - Key Concepts for Competitive AdvantageDocument20 pagesStrategic Management - Key Concepts for Competitive AdvantageMayur ParvaniNo ratings yet
- Business Level Strategies: After Studying This Chapter, You Will Be Able ToDocument30 pagesBusiness Level Strategies: After Studying This Chapter, You Will Be Able Tovaibhav sharmaNo ratings yet
- Strategic ManagementDocument2 pagesStrategic ManagementMangesh pandeyNo ratings yet
- First: Generic Strategies Generic Competitive Strategies:: Product DifferentiationDocument8 pagesFirst: Generic Strategies Generic Competitive Strategies:: Product DifferentiationYousab KaldasNo ratings yet
- Formal resignation letter from service staff at ChowkingDocument1 pageFormal resignation letter from service staff at ChowkingcaicaiiNo ratings yet
- Philippine lawyer affidavit oath ceremonyDocument1 pagePhilippine lawyer affidavit oath ceremonycaicaiiNo ratings yet
- Distributor Logo: Henrietta's Store May 23,2020 Country Club Village, Baguio CityDocument4 pagesDistributor Logo: Henrietta's Store May 23,2020 Country Club Village, Baguio CitycaicaiiNo ratings yet
- Motion To Set Case For Family ConferenceDocument3 pagesMotion To Set Case For Family ConferencecaicaiiNo ratings yet
- Motion To Set Case For Family ConferenceDocument3 pagesMotion To Set Case For Family ConferencecaicaiiNo ratings yet
- Motion For LeaveDocument2 pagesMotion For LeaveRaffy RoncalesNo ratings yet
- Janice Katrina O. Castelo: 488074801.docx, Page 1 of 4Document4 pagesJanice Katrina O. Castelo: 488074801.docx, Page 1 of 4caicaiiNo ratings yet
- Tracking Number 126764530911 Delivery StatusDocument1 pageTracking Number 126764530911 Delivery StatuscaicaiiNo ratings yet
- Quilacio - PsychologistDocument1 pageQuilacio - PsychologistcaicaiiNo ratings yet
- Tracking Number: Date of Last Status Transaction StatusDocument1 pageTracking Number: Date of Last Status Transaction StatuscaicaiiNo ratings yet
- Protecting Property Rights Through Legal ActionDocument5 pagesProtecting Property Rights Through Legal ActioncaicaiiNo ratings yet
- Secretary'S Certificate: Republic of The Philippines) City of Baguio .) S.SDocument1 pageSecretary'S Certificate: Republic of The Philippines) City of Baguio .) S.ScaicaiiNo ratings yet
- AccountingDocument7 pagesAccountingDaniela Pedrosa100% (1)
- Accounting Equation Format - Superior ClampsDocument5 pagesAccounting Equation Format - Superior ClampsdeadNo ratings yet
- Ch3 Acct2105 UpDocument59 pagesCh3 Acct2105 Upgor jamNo ratings yet
- Negotiation Case Study FileDocument6 pagesNegotiation Case Study Filerajal11No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 CVPDocument81 pagesChapter 6 CVPPrometheus SmithNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Bond Portfolio Management - IRRM - Immunization and ALMDocument31 pagesLecture 5 - Bond Portfolio Management - IRRM - Immunization and ALMNguyễn Việt LêNo ratings yet
- Determinants of Corporate BorrowingDocument47 pagesDeterminants of Corporate Borrowingvidovdan9852No ratings yet
- CVP RelationshipDocument14 pagesCVP RelationshipSarith SagarNo ratings yet
- Revision Questions On Management AccountingDocument15 pagesRevision Questions On Management AccountingSyazliana Kasim100% (1)
- Job Order Costing: Process Cost SystemDocument11 pagesJob Order Costing: Process Cost SystemShiv AchariNo ratings yet
- Accounting Equation - Examples of Transactions Affecting Assets, Liabilities, CapitalDocument3 pagesAccounting Equation - Examples of Transactions Affecting Assets, Liabilities, Capitalmaheshbendigeri5945No ratings yet
- Savings Account Opening Application Form: MUFG Bank, LTDDocument24 pagesSavings Account Opening Application Form: MUFG Bank, LTDayuNo ratings yet
- NPC Online Course Guide: Basic Microeconomics Chapter 6Document3 pagesNPC Online Course Guide: Basic Microeconomics Chapter 6Micmic DTorresNo ratings yet
- 1-CIR Vs General Foods, Inc. - GR NO. 143672Document1 page1-CIR Vs General Foods, Inc. - GR NO. 143672Jason BUENANo ratings yet
- Goods and Services Tax Media and Entertainment SectorDocument28 pagesGoods and Services Tax Media and Entertainment SectorSanjog100% (1)
- Dividend Policy Research Article PDFDocument45 pagesDividend Policy Research Article PDFaruba anwarNo ratings yet
- © The Institute of Chartered Accountants of IndiaDocument8 pages© The Institute of Chartered Accountants of IndiaBKLMMDFKLFBNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement SAP ChinaDocument6 pagesFinancial Statement SAP ChinaSatyvir VermaNo ratings yet
- 251 0405Document23 pages251 0405api-27548664No ratings yet
- Belen'S: Sari-Sari StoreDocument21 pagesBelen'S: Sari-Sari StoreJPIA Scholastica DLSPNo ratings yet
- Kolkata Port Trust - Group 7Document11 pagesKolkata Port Trust - Group 7Rahul GautamNo ratings yet
- Senior Executive Title Operations Management in Tampa Bay FL Resume Mark WanichDocument2 pagesSenior Executive Title Operations Management in Tampa Bay FL Resume Mark WanichMarkWanichNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting Part 1Document5 pagesFinancial Accounting Part 1Christopher Price100% (1)