Professional Documents
Culture Documents
AverageTrueRange PDF
AverageTrueRange PDF
Uploaded by
Theodoros MaragakisOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
AverageTrueRange PDF
AverageTrueRange PDF
Uploaded by
Theodoros MaragakisCopyright:
Available Formats
Stocks & Commodities V.
20:3 (76-79): Working Money: Average True Range by Sharon Yamanaka
TRADER’S NOTEBOOK WORKING-MONEY.COM
Average True Range
Average or extraordinary, “true range”
is often referred to in stocks and
commodities trading. But what is it?
by Sharon Yamanaka
rader, author, and technician J.
T
Welles Wilder developed average
true range (ATR) in the 1970s as a
measurement of price volatility.
Wilder believed that the range was
directly proportional to volatility,
and that range — the high and low of a stock for
a given period, be it intraday, daily, weekly, or
monthly — was indicative of a trend. If the volatility of a stock volatility, would be included in the true range.
increased, it was entering a trend, and if it slowed down, it For some stocks and commodities, during volatile times,
suggested a reversal. He further refined the trading range, this would be fairly significant. For example, a stock
calling it a true range when he included changes in price that closing at $10, then opening the next day at $12, that
occurred from the previous day’s close rather than starting traded between the opening $12 and $12.50, would only
from the opening price. Such things as after-hours show a 0.5 range, whereas the stock had actually risen 2.5
announcements that would predispose the market to open points from the day before.
higher or lower next day would not be accounted for. The price There are three different scenarios you will encounter
range for the day would increase, and that difference, or higher when calculating true range (Figure 1):
True range is the greatest distance between
Yesterday's
close
Today's high
Today's high
True True
Range Range
True
Range
Today's low Today's low
Yesterday's C. Today's low and
A. Today's high close yesterday's close
and today's low,
B. Today's high and FIGURE 1: There are three possible
yesterday's close, or scenarios when calculating true range.
Copyright © Technical Analysis Inc. www.Traders.com
Stocks & Commodities V. 20:3 (76-79): Working Money: Average True Range by Sharon Yamanaka
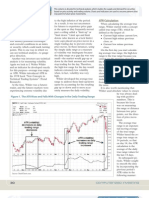
FIGURE 2: Ford Motor Co. (F) with ATR on the top,
B–trend
and the parabolic stop and reverse (SAR), Wilder’s slowly consolidating
volatility indicator, shown as the dotted lines. As the
stock begins to trend in mid-August, ATR shoots up A
from a low of 0.50 to almost 0.90 in a week’s time.
Note also there is a divergence — ATR is going up as Signals low of
consolidation period.
the stock trends down. May be ready to trend.
ATR AS AN INDICATOR
Average true range (ATR) is often used
as an indicator, but is not one itself. It
doesn’t necessarily predict anything,
but extremes in activity can indicate a
STOCKCHARTS.COM
change in a stock’s movement; higher
ATRs can mean a stock is trending, and
lower A TR s could indicate a
consolidation in price. Whether the
stock is trending up or down, the range
is always positive. This is because true range is calculated as
an absolute value, meaning that the smaller price (opening or
closing) will be subtracted from the larger, therefore always FIGURE 3: General Dynamics Corp. (GD). With an ATR of 3.28, this
assuring a positive number. stock is showing more volatility than Ford. If you want to place a stop
Figure 2 is Ford (F) with a low ATR and Figure 3 is General on this stock, you should give it more leeway than a stop placed on
Dynamics (GD), the ATR of which is relatively higher. Note Ford. Ford is trading at about a fourth of the dollar amount of GD ($22
also the pre– and post–September 11th trading patterns. versus $85), so multiplying the ATR of 16 by four would produce an
ATR of 2.4, still much lower than GD’s 3.28 mark.
Copyright © Technical Analysis Inc. www.Traders.com
Stocks & Commodities V. 20:3 (76-79): Working Money: Average True Range by Sharon Yamanaka
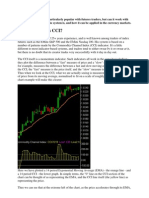
J. Welles Wilder himself used ATR as the basis for his stocks. A true range of 1.0 is a smaller percentage
volatility system. Called parabolic stop and reverse (SAR) change for a $90 stock than for a $20 one.
because of the rounded curve it produces, this trend-following 2. When a stock is in its lower ATR range, it is a sign that
system uses a trailing stop to generate its entry and exit the stock is consolidating, or trading within a narrow price
signals. SAR is a common indicator and can be found on the range. This can be followed by a continuation of the stock
larger charting websites such as BigCharts and in the direction it had previously been going, or it could
StockCharts.com. Its attraction is that its initial stop is placed signal a reversal. By the time the ATR begins to rise,
far away from the entry point and allows a certain amount of meaning the day’s trading range is increasing, it should be
leeway for the trade to develop. Later, as the stock advances clear which way the stock is going, and you can buy, sell,
and becomes profitable, the stop is constantly recalculated so or short accordingly.
that it becomes tighter and tighter, allowing less volatility (and
therefore loss) on a profitable trade. You can see how closely 3. When a stock is in its upper ATR range, it’s a sign of
SAR hugs the stock price during the consolidation period high volatility and suggests a stock is trending. Since
between June and August in the chart of Ford, and how far trends tend to be sporadic and short-lived, the higher end
away it gets when the stock is trending during October. of the range may signal an end to the trend. If you own an
upwardly trending stock, you might consider selling. If the
THE BIG GAP stock is trending down, you might consider buying once
Figures 2 and 3 clearly show different trading patterns before the stock consolidates.
and after the September 11th attacks. General Dynamics 4. Sometimes you’ll notice that the ATR and stock price
(Figure 3), an aerospace company with defense contracts, aren’t going up or down at the same time. Instead, their
looks like a completely different stock once Wall Street movements are mirroring each other, one going up while the
started trading again on September 17. This is very apparent other goes down. This divergence occurs because true range
on the average true range. It goes from looking like a relief map is an absolute value (and thus always a positive number).
of the Great Plains to the white cliffs of Dover. On its When the ATR is going up and the stock price down, the
September 17th opening, GD gapped upward from its stock is in a downtrend. When the ATR is going down and the
September 10th closing price of 75.97 to a high of 86.60. Later stock price is high, it is going into a consolidation period.
the stock lost ground, reaching This makes it slightly different
a low of 80.77 and closing at from most oscillator-type
82.90. The true range for the ATR reflects the trading range, and indicators where upper limits
day was 10.63, up from the 1.5 knowing this can allow you to more signal overbought territory and
ATR prior to September 11. lower limits, oversold.
Ford (Figure 2) more
accurately buy and sell into trends
conventionally gapped as well as set stops. ATR AND STOPS
downward, following the ATR as an indicator has its
overall market trend, hitting a limitations, and there are
new low, recovering, and then bouncing like a seismograph certainly other, more sophisticated ones to choose from. ATR
registering aftershocks, which is perhaps after all what may tell you a stock is consolidating or trending and that’s a lot
really happened. Each reversal was shorter than the previous right there, but it doesn’t provide buy/sell signals.
one, gradually settling into a trading range. The ATR also So what is it good for? Stops! As former STOCKS &
reflects this movement, peaking at 1.00 during the initial COMMODITIES editor John Sweeney once wrote, stops are
big opening gap downward, and then slowly drifting toward like forward passes in football: Three things can happen to
a low of 0.6. you and two of them are bad. Of course, the best option would
be to never trigger the stop in the first place, but at some point
CALCULATING ATR a trade will go against you. You can use the ATR to place stops,
Like any other average, ATR is calculated by picking a time increasing your chances of having only the necessary stop-
period — 14 days is commonly used — and adding the loss enacted, as opposed to getting stopped out prematurely
present day’s true range to that of the previous 13 days, then from a winning trade.
dividing by 14. This would be your initial ATR: Average true range is often used in calculations for various
other technical analysis systems, most notably Wilder’s own
ATR= (13 previous ATR + today’s true range)/14 parabolic SAR, which uses ATR as the basis for its stop-and-
reversal calculations. Figure 3 shows GD in an ATR in a
When using ATR as an indicator, you need to follow a few consolidation period from May through August, but the
rules: parabolic SAR derived from ATR is actively trading the stock
1. When used as an indicator, ATR’s actual dollar amount (albeit for a loss) in that same time period. Unfortunately, one
is not significant. Higher-priced stocks should have of the drawbacks of the parabolic stop and reverse is that it
higher true ranges than similar ranges in lower-priced doesn’t trade well during consolidation periods. This is because
Copyright © Technical Analysis Inc. www.Traders.com
Stocks & Commodities V. 20:3 (76-79): Working Money: Average True Range by Sharon Yamanaka
it sells at the bottom of the trading range and buys back, in the with an optimization value for Ford. Rather than roughly
reversal, at the top. So, rather than using SAR as a trading halving the difference, a $0.20 cushion was added to Ford’s
system, it can be used more effectively to place stops. It is ATR, putting the stop at $24.15. Interestingly, MetaStock
recalculated daily and is useful for a fairly active investor. It optimized between zero and $0.20 for Ford, meaning very
is also effective for shorting stocks. little cushion was needed to place an effective stop. Even a
A simpler way to set stops is to use the ATR as a trading very simple system that went in when the stock rose above the
channel, and place the stop just outside of the average day’s ATR and sold when it fell below did better than buy and hold.
trading range. Stops are often set at some generic point, such It yielded a 275% gain, versus 107% for buy and hold.
as at a 5% loss on the investment. If you bought $5,000 worth
of Ford stock at $25/share during the consolidation period CONCLUSION
occurring in mid-July, a 5% stop-loss would have been ATR is a durable meat-and-potatoes type of indicator that can
placed at $23.75. The calculations for that are: serve you well in your investing ventures. Range and volatility
are fundamental concepts in technical analysis and true range
$5,000 @ $25/share = 200 shares
comes up frequently, not only as a concept but also as the
5% of $5,000 = $250
underlying calculation, in more complex indicators. ATR
$5,000 - $250 = $4,750
reflects the trading range, and knowing this can allow you to
$4,750/200 shares = $23.75 stop-loss
more accurately buy and sell into trends as well as set stops.
The ATR at this time was 0.65, which means the stop-loss
would be $24.35. This is higher than the $23.75 stop-loss RELATED READING
calculated by using percentage, so one option would be to Wilder, J. Welles [1978]. New Concepts In Technical Trading
halve the difference and set the stop at $24. This should save Systems, Trend Research.
you a little money if the stock takes an unexpected dip.
Further research on the subject using MetaStock came up †See Traders’ Glossary for definition S&C
Copyright © Technical Analysis Inc. www.Traders.com
Article copyright 2012 by Technical Analysis Inc. Reprinted from the March 2002 issue with permission
from Stocks & Commodities Magazine.
The statements and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author. Fidelity Investments
cannot guarantee the accuracy or completeness of any statements or data.
620108
1
You might also like
- Diamant Capital Full Strategy BreakdownDocument20 pagesDiamant Capital Full Strategy BreakdownSepa Log100% (4)
- ATR Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesATR Cheat SheetOlalekan Akinola100% (1)
- Interview With Andrew Cardwell On RSIDocument27 pagesInterview With Andrew Cardwell On RSIpsoonek86% (7)
- Vijay Final Year ProjectDocument55 pagesVijay Final Year ProjectSau100% (1)
- Jason Perl Interview ExpertDocument2 pagesJason Perl Interview ExpertmoongraberNo ratings yet
- Jeff Cooper - The 5 Day Momentum MethodDocument57 pagesJeff Cooper - The 5 Day Momentum Methodfaces of war100% (3)
- Reverse Engineering MACDDocument1 pageReverse Engineering MACDNiltonNo ratings yet
- Calhoun ADX Breakout ScanDocument5 pagesCalhoun ADX Breakout Scanedsnake80% (5)
- Common Rsi StrategyDocument43 pagesCommon Rsi StrategyMukeshBhardwaj100% (1)
- Reverse Engineering RSIDocument7 pagesReverse Engineering RSIalpepezNo ratings yet
- Bobble Pattern Ebook PDFDocument12 pagesBobble Pattern Ebook PDFmiralemh100% (1)
- Commodity Channel IndexDocument5 pagesCommodity Channel Indextamas_orban4546No ratings yet
- Jan L Arps - Surfing The Market Waves - The Swing Trader'sDocument37 pagesJan L Arps - Surfing The Market Waves - The Swing Trader'sapi-3776228100% (3)
- Charles Lebeau Day Trading Systems & MethodsDocument45 pagesCharles Lebeau Day Trading Systems & MethodsAlex NikovskiNo ratings yet
- Average True RangeDocument5 pagesAverage True RangeZoltán NagyNo ratings yet
- Trading Tips 10 - Algorithmic Trading With Renko Charts PDFDocument19 pagesTrading Tips 10 - Algorithmic Trading With Renko Charts PDFswetha reddy100% (1)
- Average True Range AtrDocument2 pagesAverage True Range AtrHimanshu AggarwalNo ratings yet
- AtrDocument5 pagesAtrErezwa100% (2)
- DMI LectureDocument24 pagesDMI Lecture_karr99100% (1)
- Tushare Chande Momentum PDFDocument3 pagesTushare Chande Momentum PDFloshudeNo ratings yet
- Bar Pattern - Keeping It SimpleDocument6 pagesBar Pattern - Keeping It SimpleNihilisticDelusion100% (1)
- Reversal Patterns: Part 2Document17 pagesReversal Patterns: Part 2Oxford Capital Strategies LtdNo ratings yet
- Elder Stock Finder ManualDocument29 pagesElder Stock Finder ManualRafael MunhozNo ratings yet
- The Link Between Bollinger Bands Amp Cci PDFDocument5 pagesThe Link Between Bollinger Bands Amp Cci PDFbhupendra investorNo ratings yet
- Detrended Price OscillatorDocument15 pagesDetrended Price Oscillatorsagarmkale4395100% (1)
- DMI Directional Movement IndexDocument8 pagesDMI Directional Movement Indexmontu9100% (1)
- ConnorsRSI Pullbacks GuidebookDocument46 pagesConnorsRSI Pullbacks GuidebookBill Hunter80% (5)
- Using Trailing Stops: in A Trading SystemDocument5 pagesUsing Trailing Stops: in A Trading SystemNitin Chanduka100% (1)
- A Volatility Based Momentum Indicator For Traders - Steve Roehling - MediumDocument7 pagesA Volatility Based Momentum Indicator For Traders - Steve Roehling - MediumcidsantNo ratings yet
- CME Keltner ChannelsDocument26 pagesCME Keltner ChannelsA Paulo SilvaNo ratings yet
- Adaptive RSIDocument3 pagesAdaptive RSIRay WoolsonNo ratings yet
- Tradingstrategyguides All Strategies Forex Strategies Indicator Strategies Indicators 0 CommentsDocument5 pagesTradingstrategyguides All Strategies Forex Strategies Indicator Strategies Indicators 0 CommentsLucaNo ratings yet
- Bollinger BandsDocument16 pagesBollinger BandsNikolaos Fyntas0% (1)
- Solid Swing Trading Concepts Ebook PDFDocument16 pagesSolid Swing Trading Concepts Ebook PDFemirav2No ratings yet
- Find A Trend With The Partial RetraceDocument8 pagesFind A Trend With The Partial RetraceVibhats VibhorNo ratings yet
- Williams %R - The BigTrends WayDocument7 pagesWilliams %R - The BigTrends WaybigtrendsNo ratings yet
- Technical Trading StrategyDocument2 pagesTechnical Trading StrategyTommy LohNo ratings yet
- Trading ATR - Part 3Document3 pagesTrading ATR - Part 3Raja RajNo ratings yet
- Basic Patterns and Terminology: by James L. O'ConnellDocument29 pagesBasic Patterns and Terminology: by James L. O'ConnellSribd_No ratings yet
- BigTrends Price Headleys Simple Trading System1Document10 pagesBigTrends Price Headleys Simple Trading System1emirav2No ratings yet
- J. Welles Wilder, Jr. - Volatility BreakoutDocument8 pagesJ. Welles Wilder, Jr. - Volatility BreakoutOxford Capital Strategies Ltd0% (2)
- Volatility Illuminated by Mark WhistlerDocument363 pagesVolatility Illuminated by Mark Whistlerlion07100% (2)
- Bill Williams Fractals Description of Fractals IndicatorDocument3 pagesBill Williams Fractals Description of Fractals IndicatorMichael MarioNo ratings yet
- 39-Trade Breakouts and Retracements With TMVDocument7 pages39-Trade Breakouts and Retracements With TMVfredtag4393No ratings yet
- Arm's Short Term Trading Index (TRIN)Document9 pagesArm's Short Term Trading Index (TRIN)Nabamita Pyne100% (1)
- Relative Strength Index, or RSI, Is A Popular Indicator Developed by A Technical AnalystDocument2 pagesRelative Strength Index, or RSI, Is A Popular Indicator Developed by A Technical AnalystvvpvarunNo ratings yet
- Precise Exits Entries ManualDocument44 pagesPrecise Exits Entries ManualAdil Bensellam100% (10)
- Defining The Bull & BearDocument8 pagesDefining The Bull & BearNo NameNo ratings yet
- Safezone Stops: Free Download Subscribe Education Trading Diary Forum HelpDocument6 pagesSafezone Stops: Free Download Subscribe Education Trading Diary Forum HelpPapy RysNo ratings yet
- Andrew Abraham - Trading The Trend PDFDocument3 pagesAndrew Abraham - Trading The Trend PDFJ4NY4R100% (1)
- Hull Moving AverageDocument19 pagesHull Moving Averagecsp_675491100% (3)
- Chande T.S.-Adapting Moving Averages To Market Volatility (1992) PDFDocument12 pagesChande T.S.-Adapting Moving Averages To Market Volatility (1992) PDFNguyễn Hoàng PhongNo ratings yet
- Rsi-R2 Super Rsi FaqDocument14 pagesRsi-R2 Super Rsi FaqSapta WirmanNo ratings yet
- Channel Breakouts: Part 1: EntriesDocument5 pagesChannel Breakouts: Part 1: EntriesdavyhuangNo ratings yet
- HowITradeGaps 030213Document31 pagesHowITradeGaps 030213edscribeNo ratings yet
- Multiple Time Frame Analysis for Beginner TradersFrom EverandMultiple Time Frame Analysis for Beginner TradersRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Lifespan Investing: Building the Best Portfolio for Every Stage of Your LifeFrom EverandLifespan Investing: Building the Best Portfolio for Every Stage of Your LifeNo ratings yet
- Options for Risk-Free Portfolios: Profiting with Dividend Collar StrategiesFrom EverandOptions for Risk-Free Portfolios: Profiting with Dividend Collar StrategiesNo ratings yet
- Trend Trading for a Living: Learn the Skills and Gain the Confidence to Trade for a LivingFrom EverandTrend Trading for a Living: Learn the Skills and Gain the Confidence to Trade for a LivingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 5 Minutes a Week Winning Strategies: Trading SPY in Bull & Bear MarketFrom Everand5 Minutes a Week Winning Strategies: Trading SPY in Bull & Bear MarketRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Using ADX To Trade BreakoutsDocument44 pagesUsing ADX To Trade BreakoutsKrisMo Da100% (15)
- Expo14 ADX PowerTrendsDocument67 pagesExpo14 ADX PowerTrendsZoltán Nagy0% (1)
- Relative Spread Strength As A Long-Term Cyclic Tool: Orex OcusDocument4 pagesRelative Spread Strength As A Long-Term Cyclic Tool: Orex OcusZoltán NagyNo ratings yet
- Woodies CCI 0Document3 pagesWoodies CCI 0Zoltán Nagy100% (1)
- How To Trade Flags (Continuation Patterns)Document3 pagesHow To Trade Flags (Continuation Patterns)alpepezNo ratings yet
- Impact of Financial Ratios and Technical Analysis On Stock Price Prediction Using Random ForestsDocument5 pagesImpact of Financial Ratios and Technical Analysis On Stock Price Prediction Using Random ForestsJames LiuNo ratings yet
- Hurst CyclesDocument5 pagesHurst CyclesTheodoros Maragakis100% (2)
- Order FlowDocument184 pagesOrder Flowvaclarush100% (11)
- 047126847X 1Document18 pages047126847X 197989No ratings yet
- Security Analysis and Portfolio ManagementDocument4 pagesSecurity Analysis and Portfolio ManagementSrinita MishraNo ratings yet
- All About Stock Market - Read ItDocument44 pagesAll About Stock Market - Read ItShekhar SumanNo ratings yet
- 3 Best Chart Patterns For Intraday Trading in ForexDocument15 pages3 Best Chart Patterns For Intraday Trading in ForexCheng80% (5)
- The Art of Chart Reading A Complete Guide For Day Traders and SwingDocument272 pagesThe Art of Chart Reading A Complete Guide For Day Traders and SwingJoan MontserratNo ratings yet
- The Secrets of Trading Chart Patterns Like The Pros11 Mar 24' Issue 044Document123 pagesThe Secrets of Trading Chart Patterns Like The Pros11 Mar 24' Issue 044VERO NICA100% (2)
- How To Identify Supply and DemaDocument16 pagesHow To Identify Supply and DemaEgyptian Treasure100% (1)
- Equity Research Fundamental and Technical Analysis and Its Impact On Stock Prices With Reliance MoneyDocument81 pagesEquity Research Fundamental and Technical Analysis and Its Impact On Stock Prices With Reliance MoneyRs rs100% (2)
- Why Technical Analysis Is 100% Bullshit - F.S. ComeauDocument28 pagesWhy Technical Analysis Is 100% Bullshit - F.S. ComeauOnepiece TsikenNo ratings yet
- Internship Final Report Guidelines For All MajorsDocument24 pagesInternship Final Report Guidelines For All MajorsTamzid Ahmed AnikNo ratings yet
- CMT Level I Sample Exam AnswersDocument14 pagesCMT Level I Sample Exam AnswersZahamish MalikNo ratings yet
- How To Trade Chart Patterns With Target and SL@Document39 pagesHow To Trade Chart Patterns With Target and SL@millat hossain100% (1)
- AssignmentDocument14 pagesAssignmentAhmed HassanNo ratings yet
- Stock Market ForecastingDocument18 pagesStock Market ForecastingOm Prakash100% (1)
- Effective Trading in Financial Markets Using Technical AnalysisDocument295 pagesEffective Trading in Financial Markets Using Technical AnalysissushilNo ratings yet
- A Study On Technical Analysis On Equity StockDocument3 pagesA Study On Technical Analysis On Equity StockN.MUTHUKUMARAN75% (4)
- Introduction To Technical A AnalysisDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Technical A AnalysisVedant MahajanNo ratings yet
- Basic Crypto Currency TradingDocument34 pagesBasic Crypto Currency TradingANo ratings yet
- Trading With The Time FactorDocument100 pagesTrading With The Time FactormghugaradareNo ratings yet
- 45504Document7 pages45504thilaksafaryNo ratings yet
- Charts, Trend and Trend Reversal PatternsDocument19 pagesCharts, Trend and Trend Reversal PatternsSatishKumarKNo ratings yet
- Optimization of MACD and RSI Indicators: An Empirical Study of Indian Equity Market For Profitable Investment DecisionsDocument13 pagesOptimization of MACD and RSI Indicators: An Empirical Study of Indian Equity Market For Profitable Investment Decisionsmonik shahNo ratings yet