Professional Documents
Culture Documents
16IJPHY343 C.done
Uploaded by
MiaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
16IJPHY343 C.done
Uploaded by
MiaCopyright:
Available Formats
Int J Physiother.
Vol 3(1), 94-99, February (2016) ISSN: 2348 - 8336
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
EFFECT OF MCKENZIE METHOD WITH TENS ON LUM-
IJPHY
BAR RADICULOPATHY – A RANDOMIZED CONTROLLED
TRIAL
¹Jay Indravadan Patel
*2
Prem Kumar B N
3
Dr. Ravish V N
ABSTRACT
Background: Lumbar radiculopathy is a disease of the spinal nerve root generally accompanied by radicular pain in
dermatomal distribution and/or neurologic symptoms. The previous studies were focusing on finding the disability
and pain caused due to Lumbar Radiculopathy. This study is focusing on the disability, pain, range of motion of the
spine and SLR. The objective of the study is to evaluate the effectiveness of Mckenzie method with TENS on reducing
symptoms and disability of Lumbar radiculopathy.
Methods: In the present prospective study patients with Lumbar radicular pain due to disc herniation or prolapse at
level L4, L5 & S1 were randomized into two groups – Group A and Group B. the study included 40 patients, with 20 in
each group. The selection criteria was based on the following - with age group 22-55years, both sexes – male and female,
with radicular pain in L4, L5 & S1 dermatomes, disabling leg pain for 6-12 weeks duration, evidence of disc herniation
confirmed on MR imaging. The radicular pain was measured using the SLR test, pain was measured using the VAS scale
of 0 – 100, disability was measured using the MODI and Lumbar Spine ROM was measured using the MMST. Group-A
were treated with McKenzie methods with TENS and Group-B were treated with general exercise with TENS.
Results: This study showed that there was a significant reduction of pain on the VAS, improvement in SLR, lumbar
spine range of motion using MMST and disability using MODI for both the groups. The statistical analysis found that
experimental group showed earlier control of all the outcome measures when compared to controlled group at the end
of the 6th week.
Conclusion: After 6 weeks of Mckenzie method with TENS intervention for 30 minutes for 5 days in week the statis-
tical analysis concluded that the experimental group had significantly faster rates of reducing the symptoms of lumbar
radiculopathy and reducing the disability due to lumbar radiculopathy.
Keywords: Lumbar radiculopathy, Disc herniation, Mckenzie Method, TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stim-
ulation), L4, L5
Received 16th January 2016, revised 30th January 2016, accepted 06th February 2016
10.15621/ijphy/2016/v3i1/88919
www.ijphy.org
¹Post Graduate student,
Kempegowda Institute of Physiotherapy,
Bangalore CORRESPONDING AUTHOR
²Assistant Professor, *2
Prem Kumar .B .N
Kempegowda Institute of Physiotherapy,
Bangalore Mailing address: 2476, 7th cross,
³Associate Professor, 7th B Main, R.P.C. layout,
Kempegowda Institute of Medical Sciences, Vijayanagar-2nd stage,
Bangalore Bangalore-560 104. India
Int J Physiother 2016; 3(1) Page | 94
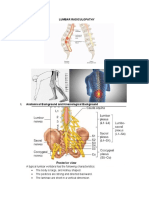
INTRODUCTION loads acting upon a normal disk is now excessive loads on
Lumbar radiculopathy is a disease of the spinal nerve root a compromised disk. At this point the degenerative process
generally accompanied by radicular pain in dermatomal is accelerated [9].
distribution and/or neurologic symptoms [1]. Low back Treatment for Lumbar radiculopathy includes physical
pain is the most common problem affecting both genders therapy, coping skills, medical treatment, yoga therapy,
and most of the ages. Incidence of which is around 85% surgical treatment, etc. It seems that Mckenzie method
of the population. It is termed as chronic after 3 months helps to centralize the pain radiating down the leg. It works
because most normal connective tissue heal within 6-12 on the passive/active extension of the patient which will
weeks. Only few cases of back pain are due to specific causes centralize the pain to the back [10]. As per the traditional
but most cases are non-specific. Along with pain sensation physiotherapy treatment, traction, TENS and general
patients also encountered with problems of reduced lumbar exercises has been advised for patients with lumbar
flexibility and reduced flexion. Researchers also indicate radiculopathy [11, 12]. TENS is an apparatus used to
the significance of the paraspinal and deep lumbar muscles relieve pain by way of stimulating the nerve via electrodes
as important stabilizers Repetitive flexion is a frequent transcutaneously [13].
insult to the back. This generally occurs in occupation like This study was implemented to know the effects of
such as building work, gardening, and house-work etc. this Mckenzie Method with TENS in early recovery from
results in shortening and tightening of anterior soft tissues symptoms of lumbar radiculopathy and also to know the
and lengthening and weakening of the posterior elements. effects of Mckenzie Method with TENS in reducing the
In some cases there is a chance of Lumbar disc herniation. disability.
Approximately 2% of the general population presents with MATERIAL AND METHOD
low back pain a presenting complaint [1,2,3]. It is estimated
that up to 70% of the population will experience back pain Design: A randomized experimental study. Setting and
sometime in their life [1,2,3]. Dilliance reported that in Participants: The study included 40 samples referred from
79% men and 89% women the specific cause were known Kempegowda Institute of Medical Sciences both from
[4]. They also noted that 40% of those reporting of low Orthopedics OPD and Physiotherapy OPD with ethical
back pain also reported lumbar radiculopathy. However, clearance. Sample was randomized into two groups with
clinically significant lumbar radiculopathy due to lumbar equal size. Selection criteria was based on the following -
disc prolapse occurs in 4 – 6% of the population. The with age group 22-55years, both sexes, male and female,
people affected are most commonly below 40 years who with radicular pain in L4, L5 & S1 dermatomes, disabling
are in economically productive age group. Hence, low leg pain for 6-12 weeks duration, evidence of disc herniation
back pain affects the socio – economic status of a region confirmed on MR imaging.
significantly [1,2,3]. Epidemiological studies have shown INTERVENTION
that 50 – 80% of the population is affected by low back Subjects referred from the Orthopaedic OPD and
pain once in life time [5]. It is surprising how many people Physiotherapy OPD was divided into 2 groups by asking
claim to know all the correct procedures for reaching and/ them to pick up chits from a box which is written as Group
or lifting objects, and yet they don’t actually internalize and A or Group B. Each group will consist of 20 samples.
use those safety procedures. ‘Picking up a mug of coffee GROUP A which is an experimental group will receive
from the opposite side of a table’, for example, can produce Mckenzie Exercises along with TENS (Transcutaneous
more force against the intervertebral discs than lifting a Electrical Nerve Stimulation). GROUP B which is a
20 pound weight next to one’s body [6]. Approximately Controlled Group will receive General Exercises with
two thirds of adults will suffer at some time in their life TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation).
[7]. LDH results in clinical evidence of Radiculopathy,
Mckenzie exercise:
and if conservative treatment such as medication and
physical therapy fails, diskectomy often is recommended • Reduction of derangement
[8]. Degenerative joint changes are not limited to synovial • Maintenance of reduction
joint though, and in the spine they commonly occur at the • Recovery of function
intervertebral disk articulations. The intervertebral disc • Prevention of recurrence
changes include alterations in volume, shape, structure, Correction of Posture: The patients sitting posture has
and composition. Although there is not a 100% correlation to be corrected. The patient will be made to sit in the
between the presence of degenerative disk disease and arm and back rest chair with the support of the pillow
pain complaints, the structural alterations will decrease behind the back.
motion and alter the mechanical properties of the spine. Lying in Prone: The patient will made to lie prone on
The intervertebral disk undergoes marked changes with the treatment couch by turning the head to one side
age. The most significant alterations occur in the nucleus and arms at the side.
pulposus. The number of cells and the concentration of Lying - Prone Extension: The patient will be made to
proteoglycans & water decrease. Once enough structural lie in the prone position. Post this patient will be asked
breakdowns occurs, what once were normal mechanical to take the support of the elbows and lift the upper
Int J Physiother 2016; 3(1) Page | 95
trunk. This will acquire the position of prone extension RESULTS
with elbow support In this study with 40 Subjects who were randomized in to
Extension in lying: The patient will be asked to assume two groups with 20 in Group A (Mckenzie method and
the prone on elbows with extension of the spine and TENS) and 20 in Group B (general exercises and TENS)
then made to extent the elbows so the extension in were undertaken to find out the effect of Mckenzie method
prone on hand position is acquired. with TENS on lumbar radiculopathy.
Extension Lying with Belt Fixation: The above position
is made and a belt fixed to the couch is used to stabilize In the evaluation of VAS, (Table-1, Graph-1) the mean and
the pelvic lifting. standard deviation with 20 subjects in Group A (Mckenzie
Extension in standing: In this the patient stand in the Method +TENS), in the pre test (6.20±1.85), the mean
normal position. The patient is then instructed to do and standard deviation at the end of 2nd week (4.65±1.49),
extension of the spine. the mean and standard deviation at the end of 4th week
(2.55±1.36) and the mean and standard deviation at the
General Exercises: end of the 6th week of the pain is significantly reduced to
• Back extensors (supine): Patient will stay supine lying (1.75±1.33).
with knee flexed. Then the trunk is lifted to neutral The mean and standard deviation with 20 subjects in Group
position. B (general exercise and TENS), in the pre-test (6.65±1.42),
• Back extensors (prone): Patient will be lying in prone the mean and standard deviation at the end of 2nd week
position with pillow under the stomach. The patient (5.70±1.59), the mean and standard deviation at the end of
is then instructed to lift the trunk to neutral position. 4th week (4.35±1.39) and the mean and standard deviation
• Back Extensors (kneeling): Patient will do 4 point at the end of the 6th week of the pain is significantly reduced
kneeling and then attempt to lift alternate leg and arm to (3.15±1.59).
in extension
• Back extensors (standing): patient will do active Table-1: Evaluation of Pain on VAS.
extension of the back in standing
VAS Group A Group B P value
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS):
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) a 1st day 6.20±1.85 6.65±1.42 0.395
dual channel unit will be used. One channel is placed
paraspinally at the level of origin of the sciatic nerve 2nd week 4.65±1.49 5.70±1.59 0.038*
(L4, L5, S1, S2 and S3) and a second channel at the site
of referred pain (e.g. Posterior thigh). The machine is on 4th week 2.55±1.36 4.35±1.39 <0.001**
with High TENS (frequency of 100Hz & pulse duration of
150µs) for a duration of 30 minutes. 6th week 1.75±1.33 3.15±1.59 0.005**
Dosage: Graph 1: Representation of VAS
Mckenzie Exercises and TENS = 5 days a week. 9 Group A
General Exercises and TENS = 5 days a week. Group B
8
Outcome measures: The improvement is measured by long 7
– arm goniometer for straight leg raise, visual analog scale
6
for the pain, inch tape for lumbar spine range of motion
VAS Score
and disability by MODI on the 1st day (pre test) then assess 5
on the 2nd week(15th day),4th week(28th day) and on the 6th 4
week(42 days, post-test). 3
Data Analysis: Descriptive statistical analysis has been 2
carried out in the present study. Results on continuous 1
measurements are presented on Mean ± SD (Min-Max) 0
and results on categorical measurements are presented 1st day 2nd week 4th week 6th week
in Number (%). Significance is assessed at 5 % level of In the evaluation of SLR (Table-2, Graph-2), the mean and
significance. Student t test (two tailed, independent) has standard deviation with 20 subjects in Group A (Mckenzie
been used to find the significance of study parameters method and TENS), in the pre-test (52.00±6.96), the mean
on continuous scale between two groups Inter group and standard deviation at the end of 2ndweek (62.00±6.16),
analysis) on metric parameters and Student t test (two the mean and standard deviation at the end of 4th week
tailed, dependent) has been used to find the significance (73.00±9.22) and the mean and standard deviation at
of study parameters on continuous scale with in each the end of the 6th week of the Straight Leg Raise Score is
group. Chi-square/ Fisher Exact test has been used to find significantly increased to (76.50±11.37).
the significance of study parameters on categorical scale
The mean and standard deviation with 20 subjects in
between experimental and controlled group.
Group B
Int J Physiother 2016; 3(1) Page | 96
(General Exercise and TENS), in the pre-test (48.00±9.52), Graph 3: Representation of Lumbar spine ROM.
the mean and standard deviation at the end of 2ndweek 8 Group A
(50.00±10.26), the mean and standard deviation at the Group B
7
end of 4thweek (60.00±12.15)and the mean and standard
deviation at the end of the 6th week of the Straight Leg 6
Raise Score is significantly increased to (63.95±11.89). 5
LS ROM
Table 2: Evaluation of SLR 4
3
SLR Group A Group B P value
2
1 day st
52.00±6.96 48.00±9.52 0.137 1
2nd week 62.00±6.16 50.00±10.26 <0.001** 0
1st day 2nd week 4th week 6th week
4th week 73.00±9.22 60.00±12.15 <0.001** In the evaluation of MODI score (Table-4,Graph-4), the
mean and standard deviation with 20 subjects in Group A
6th week 76.50±11.37 63.95±11.89 0.002** (Mckenzie Method +TENS), in the pre-test (50.20±12.48n),
Graph 2: Representation of SLR the mean and standard deviation at the end of 2ndweek
(37.30±9.41), the mean and standard deviation at the end of
100 Group A
Group B
4thweek (26.75±9.14) and the mean and standard deviation
90
at the end of the 6th week the MODI Score is significantly
80
reduced to (18.25±9.71).
70
The mean and standard deviation with 20 subjects in Group
SLR Score
60
50
B (General exercise + TENS), in the pre-test (54.40±11.62),
40
the mean and standard deviation at the end of 2ndweek
30
(44.00±11.95), the mean and standard deviation at the
end of 4th week (36.35±10.39) and the mean and standard
20
deviation at the end of the 6th week the MODI Score is
10
significantly increased to (29.70±10.07).
0
1st day 2nd week 4th week 6th week
Table 4: Evaluation of MODI
In the evaluation of lumbar spine range of motion (Table-
MODI Group A Group B P value
3,Graph-3), the mean and standard deviation with 20
subjects in Group A (Mckenzie method+TENS), in the 1st day 50.20±12.48 54.40±11.62 0.278
pre-test (4.70±1.08), the mean and standard deviation at
the end of 2ndweek (5.45±1.23), the mean and standard 2nd week 37.30±9.41 44.00±11.95 0.056+
deviation at the end of 4th week (6.65±0.81)and the mean
and standard deviation at the end of the 6th week of the 4th week 26.75±9.14 36.35±10.39 0.004**
Lumbar spine range of motion is significantly increased to
(6.75±0.72). 6th week 18.25±9.71 29.70±10.07 0.001**
The mean and standard deviation with 20 subjects in Graph 4: Representation of MODI
Group B (General Exercise and TENS), in the pre-test 70 Group A
(4.30±1.29), the mean and standard deviation at the end of Group B
2ndweek (4.25±1.12), the mean and standard deviation at 60
the end of 4thweek (4.70±1.22) and the mean and standard 50
deviation at the end of the 6th week of the Lumbar spine
MODI Score
range of motion is significantly increased to (5.20±0.69). 40
Table 3: Evaluation of Lumbar spine ROM 30
LS ROM Group A Group B P value 20
10
1st day 4.70±1.08 4.30±1.29 0.259
0
2nd week 5.45±1.23 4.25±1.12 0.003** 1st day 2nd week 4th week 6th week
The statistical analysis of VAS, SLRT, MMST and
4th week 6.65±0.81 4.70±1.22 <0.001**
MODI showed significant reduction of pain, disability,
6th week 6.75±0.72 5.20±0.69 <0.001** improvement in SLR and range of motion in Group-A than
Group-B.
Int J Physiother 2016; 3(1) Page | 97
DISCUSSION REFERENCES
This study was implemented to know the effects of [1] Joel A. Delisa, Bruce M. Gans. Nicolas E. Walsh,
Mckenzie method with TENS in early recovery from William L. Bockenek, Walter R. Fontera, Steve R.
symptoms of lumbar radiculopathy and also to know the Geiringer, Lynn H. Gerber, William S. Pease, Lawrance
effects of Mckenzie method with TENS in reducing the R. Robinson, Jay Smith, Todd P. Stitik, Ross O. Zafonte.
disability. The pre-treatment assessment was taken by Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation. Principles and
using the following outcome measures – VAS, MMST, Practice. Low Back Pain, 4th edition; 2005.
SLR, MODI and their assessment was repeated 2, 4, 6 week [2] MD S. Terry Canale. Campbell Operative Orthopedics.
respectively According to the results obtained by VAS, SLR, 10th Edi; 2003.
MMST, MODI the changes in 2nd, 4th and 6th week showed [3] Abramovitz ZN, Neff S. Lumbar Disc Surgery. Results
there is improvement in both the groups. Following the of prospective lumbar Discectomy study of joint section
statistical analysis, experimental group showed early on disorders of spine of peripheral nerves of American
recovery than controlled group. The VAS score at the Association of Neurological surgeons and Congress of
pre-test was 6.20±1.85 and was decreased to 1.75±1.33 at neurological Surgeons. Neurosurgery.1991; 29(2):301-
the end of the 6th week, the outcome measures based on 08, 1991.
percentage change of VAS is significant for experimental [4] Finesson B E. Lumbar disc excision – Schidesk H.K.,
group The SLR score at the pre-test was 52.00±6.96 and Sweet W.H. (Eds). Operative Neurosurgical Technique.
was increased to 76.50±11.37 at the end of the 6th week, the 3rd Edi; 1995.
outcome measures based on percentage change of SLR is [5] Descarreaux M, Jean Sebastein Blouin, Marc Drolet,
significant for experimental group The MMST score at the Stanislas Papadimitriou, Normand Teasdale. Efficacy
pre-test was 4.70±1.08 and was increased to 6.75±0.72 at of preventive spinal manipulation for chronic low back
the end of the 6th week, the outcome measures based on pain and related disabilities. A Preliminary study. J
percentage difference of the pre and post tests for MMST is Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2004; 27(8):509-14.
significant for experimental group The MODI value at the [6] Pamela K Lavangie, Cynthia C Norkin; Joint structure
pre-test was 50.20±12.48 and was reduced to 18.25±9.71 and function- A comprehensive ananlysis; Jaypee
at the end of the 6th week, the outcome measures based on brothers; 2nd edition; 1998.
percentage change of MODI is significant for experimental [7] Alon Rabin, Peter C. Gerszten, Pat Karausky, Clareann
group The VAS score at the pre-test was 6.65±1.42 and H. Bunker. The sensitivity of the seated Straight –
was decreased to 3.15±1.79 at the end of the 6th week, the Leg Raise Test Compared with the Supine Straight-
outcome measures based on percentage change of VAS is Leg Raise Test in Patients Presenting with Magnetic
significant for controlled group. The SLR score at the pre- Resonance Imaging Evidence of Lumbar Nerve Root
test was 48.00±9.52 and was increased to 63.95±11.89 at Compression. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2007;88(7):840-
the end of the 6th week, the outcome measures based on 3.
percentage change of SLR is significant. The MMST score at [8] Andrew J. Hahne, Jon J Ford. Functional restoration
the pre-test was 4.30±1.29 and was increased to 5.20±0.69 for a chronic lumbar disk extrusion with associated
at the end of the 6th week, the outcome measures based radiculopathy. Phys Ther. 2006;86(12):1668-80.
on percentage difference of the pre and post tests for [9] Catherine Goodman, William Boissonnault, Kenda
MMST is significant. The MODI value at the pre-test was Fuller Gary L Soderberg. Pathology: Implications for
54.40±11.62 and was reduced to 29.70±10.07 at the end of the Physical Therapist. 2nd Edition;1986.
the 6th week, the outcome measures based on percentage [10] Donelson R, Silva G, and Murphy K. The centralization
change of MODI is significant. phenomenon: its usefulness in evaluating and treating
CONCLUSION referred pain. Spine. 1990;15(3):211-3.
[11] Jorn Rittweger, MD, Karsten Just, MD, Katjakautzsch,
Results showed that there was a significant reduction Ms Psych. Treatment of Chronic low back pain with
of pain on the VAS, improvement in SLR, Lumbar spine lumbar extension and whole body vibration exercise.
range of motion Using MMST and disability using MODI Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002;27(17):1829-34.
for both the groups. It is found from the statistical analysis [12] Gladys L. Y. Cheing, Amy Y. Y. Tsui, Sing Kai Lo,
that experimental group showed earlier control of all the Christina W. Y. Hui-Chan. Optimal stimulation
outcome measures when compared to controlled group at duration of TENS in the management of osteoarthritis
the end of the 6th week. of knee pain. J Rehabil Med. 2003;35(2):62-8.
Acknowledgement [13] Brian M. Busanich; Susan D. Verscheure. Does
I would like thank Prof. Dr. J N Sridharamurthy (HOD) Mckenzie therapy Improve Outcomes For back Pain?
Department of orthopaedics and Prof. Dr. I. Suresh, Journal of Athletic Training. 2006:41(1):117-19.
Department of orthopaedics for their support for
conducting the study.
Int J Physiother 2016; 3(1) Page | 98
Citation
Jay Indravadan Patel, Prem Kumar B N, & Ravish V N. (2016). EFFECT OF MCKENZIE METHOD WITH TENS ON
LUMBAR RADICULOPATHY – A RANDOMIZED CONTROLLED TRIAL. International Journal of Physiotherapy,
3(1), 94-99.
Int J Physiother 2016; 3(1) Page | 99
You might also like
- Heavy HandsDocument8 pagesHeavy HandsPicklehead McSpazatronNo ratings yet
- Victimology exam questions and answersDocument3 pagesVictimology exam questions and answersSubhojit Das0% (1)
- Hazardous Waste ManagementDocument8 pagesHazardous Waste Managementmateenmohamed100% (1)
- Word form siêu khó làm chao đảo thế giới ảo (nguồn tổng hợpDocument9 pagesWord form siêu khó làm chao đảo thế giới ảo (nguồn tổng hợpVu Ngoc Quynh AnhNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Soap MakingDocument6 pagesLab Report Soap MakingAmihanNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Spinal Exercises On H-Reflex in Subjects With Lumbosacral RadiculopathyDocument5 pagesThe Effect of Spinal Exercises On H-Reflex in Subjects With Lumbosacral RadiculopathyInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- تنزيلDocument7 pagesتنزيلDr Abdallah BahaaNo ratings yet
- Mccre Esh 2013Document1 pageMccre Esh 2013Francisco Javier Luza RamosNo ratings yet
- McKenzie therapy and lumbar strengthening for low back painDocument5 pagesMcKenzie therapy and lumbar strengthening for low back painSahithya MNo ratings yet
- PQ Art 37583-10Document7 pagesPQ Art 37583-10Vinay KumarNo ratings yet
- Added Effect of Muscle Energy TechniqueDocument6 pagesAdded Effect of Muscle Energy Techniquesriram gopalNo ratings yet
- Piriformis Syndrome Treatment EffectivenessDocument5 pagesPiriformis Syndrome Treatment EffectivenessPraktek Fisioterapi Mitra SempajaNo ratings yet
- Conventional Therapy Versus Positional Release Technique in The Treatment of Chronic Low Back DysfunctionDocument7 pagesConventional Therapy Versus Positional Release Technique in The Treatment of Chronic Low Back DysfunctionEmad Eldin Mohamed AbdelatiefNo ratings yet
- 166-Article Text-300-1-10-20190603Document4 pages166-Article Text-300-1-10-20190603Achmad JunaidiNo ratings yet
- RSW in LBP RCTDocument10 pagesRSW in LBP RCTNakarit SangsirinawinNo ratings yet
- Physiotheorpy File Black and WhiteDocument84 pagesPhysiotheorpy File Black and WhitesatishNo ratings yet
- Lumbar RadiculopatyDocument8 pagesLumbar RadiculopatyRiri NandaNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Myofascial Release and Muscle Energy Technique On Pectoralis Minor Length in Subjects With Shoulder Impingement Syndrome A Comparative StudyDocument10 pagesEffectiveness of Myofascial Release and Muscle Energy Technique On Pectoralis Minor Length in Subjects With Shoulder Impingement Syndrome A Comparative StudyInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study To Determine The Efficacy of Routine Physical Therapy Treatment With and Without Kaltenborn Mobilization On Pain and Shoulder Mobility in Frozen Shoulder PatientsDocument4 pagesA Comparative Study To Determine The Efficacy of Routine Physical Therapy Treatment With and Without Kaltenborn Mobilization On Pain and Shoulder Mobility in Frozen Shoulder Patientsfi.afifah NurNo ratings yet
- Bachelor of PhysiotherapyDocument9 pagesBachelor of Physiotherapyanushka.ganasanNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study To Find Out The Effects of Capsular Stretching Over Muscle Energy Technique in The Management of Frozen ShoulderDocument50 pagesA Comparative Study To Find Out The Effects of Capsular Stretching Over Muscle Energy Technique in The Management of Frozen ShoulderjojiNo ratings yet
- # SMWLMDocument9 pages# SMWLMMahmoud Abo AlfaNo ratings yet
- An Adherent Nerve Root - Classification and Exercise Therapy in A PatientDocument4 pagesAn Adherent Nerve Root - Classification and Exercise Therapy in A PatientPablo Zamora MillanNo ratings yet
- Asj 2020 0146Document6 pagesAsj 2020 0146Mandeep JangraNo ratings yet
- Sanjana S. Zad, Pragati PatilDocument15 pagesSanjana S. Zad, Pragati PatilAquaNo ratings yet
- To Analyse The Short Term Effect of Upper Trapezius Inhibition Taping in Patients With Mechanical Neck PainDocument8 pagesTo Analyse The Short Term Effect of Upper Trapezius Inhibition Taping in Patients With Mechanical Neck PainDr. Krishna N. SharmaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal SF 2Document4 pagesJurnal SF 2inunk xiNo ratings yet
- Evidence-Based PT for Cervical RadiculopathyDocument9 pagesEvidence-Based PT for Cervical RadiculopathyDr Abdallah BahaaNo ratings yet
- To_Compare_the_Effects_of_Maitland_MobilizationDocument4 pagesTo_Compare_the_Effects_of_Maitland_MobilizationravichandragoudaNo ratings yet
- Anusha Article IJIRMFDocument5 pagesAnusha Article IJIRMFAnusha SampathNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Spencer Muscle Energy Technique On Periarthritis ShoulderDocument5 pagesEffectiveness of Spencer Muscle Energy Technique On Periarthritis Shoulderplaboni banerjeeNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Manual Traction and Other Physiotherapy Treatment in The Management of Painful Cervical RadiculopathyDocument5 pagesEffectiveness of Manual Traction and Other Physiotherapy Treatment in The Management of Painful Cervical RadiculopathyAgus Dwiyana NMNo ratings yet
- 1260-Article Text-5244-1-10-20221110Document26 pages1260-Article Text-5244-1-10-20221110Salma AfifiNo ratings yet
- Lumbopelvic Stabilization Exercises and Mckenzie Method in Low Back Pain Due To Disc Protrusion: A Blind Randomized Clinical TrialDocument12 pagesLumbopelvic Stabilization Exercises and Mckenzie Method in Low Back Pain Due To Disc Protrusion: A Blind Randomized Clinical TrialZahra SativaniNo ratings yet
- Moore 2013Document9 pagesMoore 2013Andrés MardonesNo ratings yet
- Satpute 2018Document9 pagesSatpute 2018Mahmoud Abo AlfaNo ratings yet
- Giray 2019Document13 pagesGiray 2019Felix LoaizaNo ratings yet
- 72-Article Text-135-1-10-20190522 PDFDocument7 pages72-Article Text-135-1-10-20190522 PDFestherNo ratings yet
- 72-Article Text-135-1-10-20190522 PDFDocument7 pages72-Article Text-135-1-10-20190522 PDFestherNo ratings yet
- Chronic Back PainDocument6 pagesChronic Back PaininnyNo ratings yet
- 291-297 Jopct1Document7 pages291-297 Jopct1efi hudriahNo ratings yet
- Bowen Back Pain WSN-93-2018-81-94Document14 pagesBowen Back Pain WSN-93-2018-81-94Saleha TariqNo ratings yet
- A Structured Physiotherapy Treatment Model Can Provide Rapid Relief To Patients Who Qualify For Lumbar Disc Surgery: A Prospective Cohort StudyDocument8 pagesA Structured Physiotherapy Treatment Model Can Provide Rapid Relief To Patients Who Qualify For Lumbar Disc Surgery: A Prospective Cohort StudyQuiroprácticaParaTodosNo ratings yet
- Background:: TH ST THDocument6 pagesBackground:: TH ST THRahayu WindariNo ratings yet
- Lumbar Traction for Herniated Disc Pain ReliefDocument7 pagesLumbar Traction for Herniated Disc Pain ReliefRanier Atienza MagcawasNo ratings yet
- Lumbar Radiculopathy Medback Castillo Mendez EDITEDDocument12 pagesLumbar Radiculopathy Medback Castillo Mendez EDITEDSteve ColbertNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Tens Versus Intermittent CervicalDocument6 pagesEffectiveness of Tens Versus Intermittent CervicalshindyNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Addition Kinesio Taping To Mckenzie Exercise in Patient With Chronic Mechanical Low Back PainDocument4 pagesThe Effect of Addition Kinesio Taping To Mckenzie Exercise in Patient With Chronic Mechanical Low Back PainRama BayuNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0003999319303892 MainDocument8 pages1 s2.0 S0003999319303892 MainRizkyrafiqoh afdinNo ratings yet
- Efficacy of Tens Vs PNF in Relieving Acute Cervical Osteoarthritic PainDocument10 pagesEfficacy of Tens Vs PNF in Relieving Acute Cervical Osteoarthritic PainTJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Effect of Positional Release Technique in Subjects With Subacute TrapezitisDocument9 pagesEffect of Positional Release Technique in Subjects With Subacute TrapezitisijphyNo ratings yet
- Low Back PainDocument10 pagesLow Back PainValeria AlfaroNo ratings yet
- Yo MPDocument4 pagesYo MPRo KohnNo ratings yet
- ptrs009 03 03 PDFDocument6 pagesptrs009 03 03 PDFGusti Ayu KrisnayantiNo ratings yet
- Aluko2013 2Document11 pagesAluko2013 2Dr Ahmed NabilNo ratings yet
- PNF Ombro 04Document10 pagesPNF Ombro 04Isaias AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- 73-Article Text-137-1-10-20190522 PDFDocument11 pages73-Article Text-137-1-10-20190522 PDFestherNo ratings yet
- Chapter - IDocument34 pagesChapter - ImohiiieNo ratings yet
- Chiropractic & OsteopathyDocument10 pagesChiropractic & OsteopathyjebabalanNo ratings yet
- The Short-Term Efficacy of Laser Brace ADocument6 pagesThe Short-Term Efficacy of Laser Brace AHevin GokulNo ratings yet
- 8Document1 page8Daniel GuevaraNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Two Intensities of Massage On H-Reflex AmplitudeDocument11 pagesThe Effect of Two Intensities of Massage On H-Reflex AmplitudeMiki ShimizuNo ratings yet
- Effect of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy On The Shoulder Joint Functional Status of Patients With Calcific TendinitisDocument3 pagesEffect of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy On The Shoulder Joint Functional Status of Patients With Calcific Tendinitisginamilena90No ratings yet
- The Impact of Novel Inflammation-Preserving TreatmDocument11 pagesThe Impact of Novel Inflammation-Preserving TreatmlalyphyocentroNo ratings yet
- Interventional Radiology of the Spine: Image-Guided Pain TherapyFrom EverandInterventional Radiology of the Spine: Image-Guided Pain TherapyJ. Kevin McGrawNo ratings yet
- Physical therapy evaluation and treatment plan templateDocument1 pagePhysical therapy evaluation and treatment plan templateMiaNo ratings yet
- 16IJPHY343 C.doneDocument6 pages16IJPHY343 C.doneMiaNo ratings yet
- PEDro ScaleDocument2 pagesPEDro Scalesweetpudding0% (1)
- Home Exercise ProgramDocument2 pagesHome Exercise ProgramMiaNo ratings yet
- Project ManagementDocument54 pagesProject ManagementJustin PauNo ratings yet
- An Abrupt Transformation of Phobic Behavior After A Post-Retrieval Amnesic AgentDocument7 pagesAn Abrupt Transformation of Phobic Behavior After A Post-Retrieval Amnesic AgentOlivera Novakovic100% (1)
- DMLCIIDocument2 pagesDMLCIIVu Tung LinhNo ratings yet
- Yee Mee Sticker (Final)Document4 pagesYee Mee Sticker (Final)SARAH JANENo ratings yet
- Ntrs 415b Case Study Paper FinalDocument29 pagesNtrs 415b Case Study Paper Finalapi-287590844100% (1)
- Think Nursing! ReportDocument20 pagesThink Nursing! ReportRobert Fraser RNNo ratings yet
- When Learning and Remembering Compete: A Functional MRI StudyDocument5 pagesWhen Learning and Remembering Compete: A Functional MRI Studyclaire_thixtonNo ratings yet
- A Case Report of Evans SyndromeDocument5 pagesA Case Report of Evans SyndromecatNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Lagos DocumentaryDocument6 pagesWelcome To Lagos DocumentaryDede SonntagNo ratings yet
- Reflection'brain On FireDocument2 pagesReflection'brain On FireJevelyn AgdolNo ratings yet
- Office Memorandum No. 09 SDO CSFP TASK FORCE COVID 19Document4 pagesOffice Memorandum No. 09 SDO CSFP TASK FORCE COVID 19Dally AudiaNo ratings yet
- BENEDICT JORDAN L. LIMOS ENVIRONMENTAL AND SANITARY ENGINEERING PROFILEDocument2 pagesBENEDICT JORDAN L. LIMOS ENVIRONMENTAL AND SANITARY ENGINEERING PROFILEMaria Theresa LimosNo ratings yet
- Agenda Zoonotic Influenza Webinar - 8-9 May 2023Document2 pagesAgenda Zoonotic Influenza Webinar - 8-9 May 2023haniefahmadNo ratings yet
- Frenillo LingualDocument9 pagesFrenillo LingualJosé DavidNo ratings yet
- Mayne Pharma Annual Report 2012Document78 pagesMayne Pharma Annual Report 2012Deepa DevanathanNo ratings yet
- Choice of A Baby Boy or GirlDocument3 pagesChoice of A Baby Boy or GirljulietanclNo ratings yet
- About Exercise ProgramsDocument3 pagesAbout Exercise Programsriann leigh TrangiaNo ratings yet
- - annona-squamosa-leaves-extract-a-potential-dog-gel-soap-ingredient-for-eradication-of-ticks-đã chuyển đổiDocument8 pages- annona-squamosa-leaves-extract-a-potential-dog-gel-soap-ingredient-for-eradication-of-ticks-đã chuyển đổiMỹ LiênNo ratings yet
- ECG Signal Final Project-1Document9 pagesECG Signal Final Project-1Sejal NagbhidkarNo ratings yet
- Crystal pH Guide: Common & Uncommon CrystalsDocument4 pagesCrystal pH Guide: Common & Uncommon CrystalsyholicNo ratings yet
- Final MHA Thesis, Getachew L.Document62 pagesFinal MHA Thesis, Getachew L.Ochom Yar RiamNo ratings yet
- EBP Literature Searching SkillsDocument47 pagesEBP Literature Searching SkillsAndi sutandiNo ratings yet
- Q SourcingDocument20 pagesQ Sourcingkabuye mauroNo ratings yet
- Luyen Thi Bai Tap Doc HieuDocument3 pagesLuyen Thi Bai Tap Doc HieuChi MinhNo ratings yet
- Panel Hospital List IGIDocument6 pagesPanel Hospital List IGIAbdul RahmanNo ratings yet