Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 1 Aircraft Structures
Uploaded by
Mochammad Fajri MuharamCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 1 Aircraft Structures
Uploaded by
Mochammad Fajri MuharamCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 1 Aircraft Structures
General
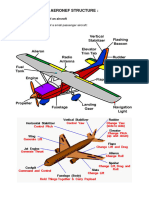
An aircraft is a device that is used for, or is intended to be used for, flight in the air.
Major categories of aircraft are airplane, rotorcraft, glider, and lighter-than-air vehicles.
[Figure 1-11]
the airframe of aircraft; specifically, the fuselage, booms, nacelles, cowlings, fairings, airfoil surfaces,
and landing gear.
One, two, or three sets of wings have all been successfully utilized. [Figure 1-12]
The airframe of a fixed-wing aircraft consists of five principal units: the fuselage, wings, stabilizers,
flight control surfaces, and landing gear. [Figure 1-13]
Helicopter airframes consist of the fuselage, main rotor and related gearbox, tail rotor (on
helicopters with a single main rotor), and the landing gear.
Airframe structural components are constructed from a wide variety of materials.
wood.
Steel tubing and the most common material, aluminum, followed.
composite materials.
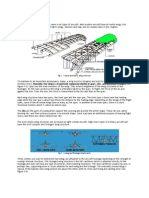
Structural members of an aircraft’s fuselage include
stringers, longerons, ribs, bulkheads, and more.
The main structural member in a wing is called the wing spar.
The skin of aircraft can also be made from a variety of materials, ranging from impregnated fabric to
plywood, aluminum, or composites.
airframe and its components are joined by rivets, bolts, screws, and other fasteners. Welding,
adhesives, and special bonding techniques are also used
You might also like
- Pilot's Encyclopedia of Aeronautical Knowledge: Federal Aviation AdministrationFrom EverandPilot's Encyclopedia of Aeronautical Knowledge: Federal Aviation AdministrationRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (17)
- Helicopter Flying Handbook (2024): FAA-H-8083-21BFrom EverandHelicopter Flying Handbook (2024): FAA-H-8083-21BRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Figure 1. Examples of Different Categories of Aircraft, Clockwise From Top Left: Lighter-Than-Air, Glider, Rotorcraft, and AirplaneDocument2 pagesFigure 1. Examples of Different Categories of Aircraft, Clockwise From Top Left: Lighter-Than-Air, Glider, Rotorcraft, and AirplaneAli ÇakircaNo ratings yet
- Aircraft StructuresDocument3 pagesAircraft StructuresAli ÇakircaNo ratings yet
- TPK Slide 2 Lazuardy Daring 2021Document19 pagesTPK Slide 2 Lazuardy Daring 2021Renanto SuryadinataNo ratings yet
- Design & Analysis of Aircraft Wing...Document66 pagesDesign & Analysis of Aircraft Wing...Mohammed Ibrahim Khan100% (1)
- Ringka, Dzharl - Activity 1Document3 pagesRingka, Dzharl - Activity 1Dzharl RingkaNo ratings yet
- 14014A ch4Document26 pages14014A ch4Sajjad ShamimNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Basic Construction: Learning ObjectivesDocument26 pagesAircraft Basic Construction: Learning ObjectivesdanishNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Construction and Materials1Document4 pagesAircraft Construction and Materials1govindarajan017No ratings yet
- Numerical Analysis of Wing Spar DesignDocument63 pagesNumerical Analysis of Wing Spar DesignManepalli Harshavardhanan100% (1)
- Aircraft Structure - 1 - IntroDocument13 pagesAircraft Structure - 1 - IntroAkash KaarthikNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Construction and MaterialsDocument4 pagesAircraft Construction and Materialsgalaxy_hypeNo ratings yet
- Chap 2 Aeronefs StructureDocument7 pagesChap 2 Aeronefs Structureismain.niniNo ratings yet
- 7an6.3 Maintenance of Airframe and Systems Design Unit I&iiDocument56 pages7an6.3 Maintenance of Airframe and Systems Design Unit I&iipriyankaNo ratings yet
- Wing Chapter-3Document77 pagesWing Chapter-3Abel BatuNo ratings yet
- Aircraft StructuresDocument6 pagesAircraft StructuresFurkanNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Structure 2Document4 pagesAircraft Structure 2raj mohanNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Structure - An Introduction To Major Airplane ComponentsDocument9 pagesAircraft Structure - An Introduction To Major Airplane ComponentsPj BaroesNo ratings yet
- Basic Aircraft StructureDocument47 pagesBasic Aircraft Structurekhagendrakryadav100% (7)
- Aeronautical Structures PDFDocument56 pagesAeronautical Structures PDFGiovanni OrnelasNo ratings yet
- The WingsDocument5 pagesThe WingsVelupucharla Saiprasad ReddyNo ratings yet
- DDDocument2 pagesDDAli ÇakircaNo ratings yet
- Aircraft StructureDocument10 pagesAircraft StructureAdi Putra100% (1)
- Amt 4101 Activity 2Document15 pagesAmt 4101 Activity 2Brendan Lewis DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Notes - FundamentalsDocument19 pagesPreliminary Notes - Fundamentalssarathkumar sebastinNo ratings yet
- 1 - BasicAircraftStructure Ver2007Document49 pages1 - BasicAircraftStructure Ver2007Chalvin NapitupuluNo ratings yet
- Aircraft StructureDocument11 pagesAircraft StructureVagesh VagesNo ratings yet
- Acft StructureDocument58 pagesAcft Structurejocampo.aceserphNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Structures I Chapter-1Document163 pagesAircraft Structures I Chapter-1Ejigayehu Lemma100% (1)
- Parts of AircraftDocument27 pagesParts of Aircrafthuseyinova747No ratings yet
- Air Craft Manufacturing Process: Internship Report Air Craft Research and Design CentreDocument49 pagesAir Craft Manufacturing Process: Internship Report Air Craft Research and Design CentreNikhil Chandra RNo ratings yet
- FuselageDocument4 pagesFuselageByron Chicaiza0% (1)
- Aircraft Components Manual Amt 628Document17 pagesAircraft Components Manual Amt 628Carl Vincent SurnitNo ratings yet
- Aeronautical Project Report On Aircraft StructureDocument12 pagesAeronautical Project Report On Aircraft StructuresumanbabaNo ratings yet
- Eoa NotesDocument45 pagesEoa NotesPrabu MariNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Structural Analysis (Omar)Document12 pagesAircraft Structural Analysis (Omar)ja_mufc_scribdNo ratings yet
- SS An Sem 2 2 1Document4 pagesSS An Sem 2 2 1Alexia-Maria AposticaNo ratings yet
- FUSELAGEDocument2 pagesFUSELAGEEster Souza100% (1)
- Aircraft Systems: The Parts of An AirplaneDocument11 pagesAircraft Systems: The Parts of An AirplaneTariq TaeemNo ratings yet
- Basic Construction of AircraftDocument25 pagesBasic Construction of Aircraftshibin874141No ratings yet
- AirplaneDocument1 pageAirplaneLNNo ratings yet
- Basicaircraftstructure 110325070203 Phpapp02Document36 pagesBasicaircraftstructure 110325070203 Phpapp02yinkaakins2001No ratings yet
- 1 - BasicAircraftStructure Ver2007 - 2017-18 PDFDocument49 pages1 - BasicAircraftStructure Ver2007 - 2017-18 PDFAndhika Prahasta Djaya100% (2)
- Chapter 3 2023Document10 pagesChapter 3 2023ismain.niniNo ratings yet
- Structural ComponentsDocument29 pagesStructural ComponentsCed SisonNo ratings yet
- Aircraft StructuresDocument3 pagesAircraft StructuresVarun Karthikeyan ShettyNo ratings yet
- Flight Control SurfacesDocument28 pagesFlight Control Surfacesjan paul de leonNo ratings yet
- Acp033 Vol4Document104 pagesAcp033 Vol4Marcus Drago100% (1)
- EOA NotesDocument15 pagesEOA NotesIswarya ThiyagarajanNo ratings yet
- Aircraft BasicsDocument8 pagesAircraft BasicsSantosh Patil Sunny100% (1)
- Basicaircraftstructure 110325070203 Phpapp02Document36 pagesBasicaircraftstructure 110325070203 Phpapp02Kv PavanNo ratings yet
- Types of Aircraft WingsDocument3 pagesTypes of Aircraft WingsAshley Anthony XhigahNo ratings yet
- Ve Unit 4Document16 pagesVe Unit 4vamshimohanNo ratings yet
- Landing Gear Arrangement - 5 Main Components of An AircraftDocument8 pagesLanding Gear Arrangement - 5 Main Components of An AircraftSuVam LeoChanNo ratings yet
- نسخة مضغوطة من Final Project 2Document10 pagesنسخة مضغوطة من Final Project 2sq.vp76No ratings yet
- Aircraft StructureDocument5 pagesAircraft Structuremaverick72270% (1)
- Cambridge Airplane LoadsDocument10 pagesCambridge Airplane LoadsSafdar JuttNo ratings yet
- Fleet Planning Workshop: ProspectusDocument8 pagesFleet Planning Workshop: ProspectusMochammad Fajri MuharamNo ratings yet
- Process of Invention14Document10 pagesProcess of Invention14Mochammad Fajri MuharamNo ratings yet
- Sertif 1 SyaifullahDocument1 pageSertif 1 SyaifullahMochammad Fajri MuharamNo ratings yet
- Inspeksi TeknikDocument7 pagesInspeksi TeknikMochammad Fajri MuharamNo ratings yet
- SI 8900-5.14 Amdt. 1 Edition 2 - English Language Proficiency TestingDocument68 pagesSI 8900-5.14 Amdt. 1 Edition 2 - English Language Proficiency TestingMochammad Fajri MuharamNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Materials: NAMA: Mochammad Fajri Muharam NPM: 40403116026 Prodi: Airframe 2016Document1 pageAircraft Materials: NAMA: Mochammad Fajri Muharam NPM: 40403116026 Prodi: Airframe 2016Mochammad Fajri MuharamNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Gas Turbine 2 - Presentation 4Document31 pagesAircraft Gas Turbine 2 - Presentation 4Mochammad Fajri MuharamNo ratings yet
- Aircraft HardwareDocument57 pagesAircraft HardwareMochammad Fajri MuharamNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Electrical Dan Electronics Xi 4Document46 pagesAircraft Electrical Dan Electronics Xi 4Mochammad Fajri MuharamNo ratings yet
- EquationsDocument24 pagesEquationsMochammad Fajri MuharamNo ratings yet
- Baja Karbon (Carbon Steels)Document25 pagesBaja Karbon (Carbon Steels)Mochammad Fajri MuharamNo ratings yet