Professional Documents
Culture Documents
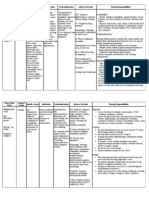
Drug Name Action Indication Contraindicat Ions Side Effects Nursing Considerations Generic
Uploaded by
Genevang Seaweeds0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views3 pagesThis document provides information on the drug digoxin including its action, indications, contraindications, side effects, and important nursing considerations. It also provides tables with the same information for the drugs captopril and furosemide. For digoxin, its main action is to increase the force of myocardial contraction and reduce heart conductivity. It is indicated for congestive heart failure and atrial fibrillation. Contraindications include digitalis toxicity. Important nursing considerations include monitoring for side effects and assessing electrolyte levels. The tables provide similar overviews of captopril as an ACE inhibitor and furosemide as a loop diuretic.
Original Description:
Furosemide and Captopril
Original Title
Drug study
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides information on the drug digoxin including its action, indications, contraindications, side effects, and important nursing considerations. It also provides tables with the same information for the drugs captopril and furosemide. For digoxin, its main action is to increase the force of myocardial contraction and reduce heart conductivity. It is indicated for congestive heart failure and atrial fibrillation. Contraindications include digitalis toxicity. Important nursing considerations include monitoring for side effects and assessing electrolyte levels. The tables provide similar overviews of captopril as an ACE inhibitor and furosemide as a loop diuretic.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views3 pagesDrug Name Action Indication Contraindicat Ions Side Effects Nursing Considerations Generic
Uploaded by
Genevang SeaweedsThis document provides information on the drug digoxin including its action, indications, contraindications, side effects, and important nursing considerations. It also provides tables with the same information for the drugs captopril and furosemide. For digoxin, its main action is to increase the force of myocardial contraction and reduce heart conductivity. It is indicated for congestive heart failure and atrial fibrillation. Contraindications include digitalis toxicity. Important nursing considerations include monitoring for side effects and assessing electrolyte levels. The tables provide similar overviews of captopril as an ACE inhibitor and furosemide as a loop diuretic.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
IX.
DRUG STUDIES
DRUG NAME ACTION INDICATION CONTRAINDICAT SIDE EFFECTS NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
IONS
Generic: Digoxin is a cardiac CHF Digitalis Extra History: Allergy to digitalis
glycoside which has Atrial toxicity, beats, preparations, ventricular
Digoxin positive inotropic fibrillatio ventricular anorexia, tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation,
activity characterized n tachycardia nausea heart block, sick sinus syndrome,
Brand: by an increase in the /fibrillation, and IHSS, acute MI, renal insufficiency,
force of myocardial obstructive vomiting. decreased K+, decreased Mg2+
Lanoxin contraction. It also cardiomyop increased Ca2+, pregnancy,
reduces the athy. lactation
Classification: conductivity of the Arrhythmias Physical: Weight; orientation, affect,
heart through the due to reflexes, vision; P, BP, baseline
Cardiac Glycoside atrioventricular (AV) accessory ECG, cardiac auscultation,
node. Digoxin also pathways peripheral pulses, peripheral
Dose: exerts direct action (e.g. Wolff- perfusion, edema; R, adventitious
on vascular smooth Parkinson- sounds; abdominal percussion,
Loading dose, 0.75– muscle and indirect White bowel sounds, liver evaluation;
1.25 mg PO effects mediated syndrome). urinary output; electrolyte levels,
primarily by the LFTs, renal function tests
Maintenance dose, autonomic nervous Report unusually slow pulse,
0.125–0.25 mg/day system and an
irregular pulse, rapid weight gain,
PO. increase in vagal
activity. loss of appetite, nausea, diarrhea,
vomiting, blurred or “yellow” vision,
unusual tiredness and weakness,
swelling of the ankles, legs or
fingers, difficulty breathing.
DRUG NAME ACTION INDICATION CONTRAINDICAT SIDE EFFECTS NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
IONS
Generic: Blocks ACE from Treatment of Contraindicate Tachycardi Assessment
converting hypertension d with allergy a
Captopril angiotensin I to alone or in to captopril, Dry mouth History: Allergy to captopril, history
angiotensin II, a combination history of GI Upset of angioedema, impaired renal
Brand: powerful with thiazide- angiodema. function, CHF, salt or volume
vasoconstrictor, type \u2022 Use depletion, pregnancy, lactation
Capoten, leading to diuretics cautiously Physical: Skin color, lesions, turgor;
decreased blood with impaired T; P, BP, peripheral perfusion;
Classification: pressure, decreased renal mucous membranes, bowel
aldosterone function; sounds, liver evaluation; urinalysis,
ACE inhibitor, secretion, a small Treatment of CHF; salt or LFTs, renal function tests, CBC
Antihypertensive increase in serum CHF in volume and differential
potassium levels, patients depletion,
Dose: and sodium and fluid unresponsiv Administer 1 hr before meals
loss; increased e to
Heart failure Initial: prostaglandin conventional Monitor patient closely for fall in BP
6.25-12.5 mg 2-3 synthesis also may therapy; secondary to reduction in fluid
times/day. be involved in the used with volume (due to excessive
antihypertensive diuretics and perspiration, and dehydration,
Max: 50 mg 3 action. digitalis vomiting, or diarrhea); excessive
times/day. hypotension may occur.
Reduce dosage in patients with
impaired renal function
DRUG NAME ACTION INDICATION CONTRAINDI SIDE NURSING CONSIDERATION
CATIONS EFFECTS
Inhibits reabsorption of -CHF -Allergy to - decreased BP 1. increased risk of photosensitivity, use
Na & Cl in the ascending sulfonylureas sunscreens
Generic loop of henle and distal -Hypertension -
Name: renal tubule, interfering -anuria Hyperglycemia 2. high dosages of IV may cause ototoxicity
-Edema
Furosemide with the Cl-binding co- -hepatic coma - Decreased 3. A precipitate may form if mixed with gentamicin,
transport system, hence, potassium netilmicin, milnirone, in either D5W or PNSS
causing increase -severe levels
excretion of water, electrolyte 4. Note closely for signs and symptoms of vascular
Brand Name: depletion thrombosis, embolism, circulatory collapse
sodium, chloride,
Lasix magnesium, and calcium.
5. take on the morning with empty stomach to
enhance absorption and avoid interruption of sleep.
May take with food or milk to lessen GI upset.
Classification Absorption: Fairly rapidly
absorbed from the GI 7. Report if presence of adverse reaction
Loop Diuretic tract (oral).
8. Record BP and wights; report any gain of
Distribution: Crosses the
>2lb/day or >5-10 lb per week.
placenta and enters
Dosing: breast milk. Protein- 9. supplement with vegetables and fruits that are
binding: 99%. high in potassium such as banana, potatoes,
14 mg per tab, Excretion: Via urine (as
mangoes, oranges, peaches or dried dates.
1 tab OD PO unchanged); 2 hr
(elimination half-life), may 10. NSAIDs and Beta-blockers may cause sodium
be prolonged in neonates retention.
and renal and hepatic
impairment.
You might also like
- Antihypertensive - ABCDDocument5 pagesAntihypertensive - ABCDTingCheung100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyMarc Daryl MendozaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyDanica Kate GalleonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study-CardioDocument7 pagesDrug Study-CardioCharmaine ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- KaliumDocument2 pagesKaliumJustine Kaye Iballa HarligaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyAnne Marie BuenvenidaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Colleen S. de La Rosa BSN IiiDocument2 pagesDrug Study: Colleen S. de La Rosa BSN IiiColleen De la RosaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyKeanu PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Name Classificatio N Action Indication Contraindicati ON Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibilities Generic: Captopril MIDocument4 pagesName Classificatio N Action Indication Contraindicati ON Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibilities Generic: Captopril MIHarvey BanagNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyJenniferValmocenaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyKeanu PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Amlodipine Drug StudyDocument2 pagesAmlodipine Drug StudyJoseph Dann Enero Jr.100% (3)
- Drug Study of FurosemideDocument5 pagesDrug Study of FurosemideAntonette Lei100% (1)
- Drug Study orDocument5 pagesDrug Study orRalph Elvin MacanlalayNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Brand Name: Cardizem Generic Name: Diltiazem Drug Classification: Calcium Channel BlockersDocument2 pagesCollege of Nursing: Brand Name: Cardizem Generic Name: Diltiazem Drug Classification: Calcium Channel BlockersChristine Pialan SalimbagatNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyhitorixxivNo ratings yet
- Categorize The Treatment Options For Patients With Existing Medical ConditionDocument3 pagesCategorize The Treatment Options For Patients With Existing Medical ConditionMicah LatosaNo ratings yet
- Drug LordsDocument25 pagesDrug LordsGlen DaleNo ratings yet
- HF and CAD Case ScenarioDocument17 pagesHF and CAD Case ScenarioElla Neiza AngelesNo ratings yet
- Calcium Gluconate Drug StudyDocument4 pagesCalcium Gluconate Drug StudyAngelou Joefred CongresoNo ratings yet
- EnalaprilDocument2 pagesEnalaprilpinksapphire929100% (2)
- Drug Study - Nifedipine PODocument1 pageDrug Study - Nifedipine POJet BautistaNo ratings yet
- Lizzie Heisler - Hypertension MedsDocument2 pagesLizzie Heisler - Hypertension MedsTricia Kaye IblanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Assess AnginaDocument3 pagesDrug Study: Assess Anginadeo_gratias14No ratings yet
- Print MeDocument4 pagesPrint MeDoneva Lyn MedinaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - DigoxinDocument2 pagesDrug Study - DigoxinDanielle AglusolosNo ratings yet
- Electrolytes TableDocument4 pagesElectrolytes TableMeg NoriegaNo ratings yet
- Pharmasheet AMLODIPINE BESYLATEDocument3 pagesPharmasheet AMLODIPINE BESYLATEplokatzNo ratings yet
- Careplan Medication ListDocument17 pagesCareplan Medication ListGiorgia ScorsoneNo ratings yet
- Digoxin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDigoxin Drug StudyHarline GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyCheska Mae PalicNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Dosage/ Frequency / Timing/ Route Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindic Ation Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument3 pagesName of Drug Dosage/ Frequency / Timing/ Route Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindic Ation Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesphoebeNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyizzieliciousNo ratings yet
- Ace Inhibitors Simple NursingDocument2 pagesAce Inhibitors Simple NursingMM J30No ratings yet
- Drug Study Task 2Document94 pagesDrug Study Task 2ClaireNo ratings yet
- Drug Study D InsipidusDocument7 pagesDrug Study D InsipidusAisha MarieNo ratings yet
- Drug Studies and Health Teaching PlanDocument28 pagesDrug Studies and Health Teaching PlansfkjalkhsafgNo ratings yet
- Atropine Sulfate Indications: Adverse Effects: CNS: Headache, Ataxia, Contraindication: Assessment & Drug EffectsDocument4 pagesAtropine Sulfate Indications: Adverse Effects: CNS: Headache, Ataxia, Contraindication: Assessment & Drug EffectsMarie Kris Chua AbelleraNo ratings yet
- @ Shopwithkey On Etsy Perfusion Drug Classification ChartDocument8 pages@ Shopwithkey On Etsy Perfusion Drug Classification ChartSutanyaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudySocial BaeNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Labetalol Hydro ChlorideDocument6 pagesDrug Study: Labetalol Hydro ChlorideMark ToxNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY - Furosemide (Lasix)Document1 pageDRUG STUDY - Furosemide (Lasix)julesubayubay542876% (25)
- DRUG STUDY Furosemide LasixDocument1 pageDRUG STUDY Furosemide LasixG4 AMOYO ANGELICA NICOLENo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Losartan)Document1 pageDrug Study (Losartan)Baji ۦۦNo ratings yet
- Drugs Indications Actions Side Effects / Adverse Effects Nursing Consideration Patient TeachingDocument10 pagesDrugs Indications Actions Side Effects / Adverse Effects Nursing Consideration Patient TeachingTyrone IglesiasNo ratings yet
- TELMISARTANDocument8 pagesTELMISARTANCidny CalimagNo ratings yet
- Case Study: RLE DutyDocument12 pagesCase Study: RLE DutyEsther Ellise AbundoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studyunkown userNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY (Preeclampsia)Document11 pagesDRUG STUDY (Preeclampsia)Jobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Omeprazole & LosartanDocument4 pagesDrug Study - Omeprazole & LosartanCarla Tongson MaravillaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study MsDocument10 pagesDrug Study MsAbie Jewel Joy RoqueNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyBella Cy LopezNo ratings yet
- Sweet Glomerulus: A Case of Diabetic NephropathyDocument9 pagesSweet Glomerulus: A Case of Diabetic NephropathyRon OpulenciaNo ratings yet
- Reactions and Drug Interaction - Assess Patients and Family's Knowledge of Drug TherapyDocument3 pagesReactions and Drug Interaction - Assess Patients and Family's Knowledge of Drug Therapyelvie21No ratings yet
- Brand Name: Cardizem Generic Name: Diltiazem Drug Classification: Calcium Channel BlockersDocument2 pagesBrand Name: Cardizem Generic Name: Diltiazem Drug Classification: Calcium Channel BlockersChristine Pialan SalimbagatNo ratings yet
- Dolan Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDolan Drug StudyLian Robbie BautistaNo ratings yet
- Drug Name WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesDrug Name WPS OfficeCAMILLE GAIL HADJIRANINo ratings yet
- Related Laws Republic Act No 7277 IRR of The Magna Carta For Disabled PersonDocument23 pagesRelated Laws Republic Act No 7277 IRR of The Magna Carta For Disabled PersonGenevang SeaweedsNo ratings yet
- Complete Blood CountDocument10 pagesComplete Blood CountGenevang Seaweeds100% (1)
- Background: Disorders, Fourth Edition, Text Revision (DSM-IV-TR) As An AnxietyDocument21 pagesBackground: Disorders, Fourth Edition, Text Revision (DSM-IV-TR) As An AnxietyGenevang SeaweedsNo ratings yet
- Gynecological Instruments: Surgical Instruments Images & NamesDocument4 pagesGynecological Instruments: Surgical Instruments Images & NamesGenevang SeaweedsNo ratings yet
- Geographical Area - Tropical Islands in Thepacific (Philippines) and AsiaDocument1 pageGeographical Area - Tropical Islands in Thepacific (Philippines) and AsiaGenevang SeaweedsNo ratings yet
- SRS Cheat CodesDocument9 pagesSRS Cheat CodesnurhayatiNo ratings yet
- LP 1st ObservationDocument6 pagesLP 1st ObservationMichael AnoraNo ratings yet
- Standard Safety Practices Manual PDFDocument350 pagesStandard Safety Practices Manual PDFsithulibraNo ratings yet
- Ground Investigation ReportDocument49 pagesGround Investigation Reportjoemacx6624No ratings yet
- Object: Annex A, B, C DDocument74 pagesObject: Annex A, B, C DfjsdNo ratings yet
- THESISDocument44 pagesTHESISRowena Shaira AbellarNo ratings yet
- Aeration PaperDocument11 pagesAeration PapersehonoNo ratings yet
- Faculty Profile: Dr. Injam Siva ParvathiDocument9 pagesFaculty Profile: Dr. Injam Siva ParvathiMr. Y. RajeshNo ratings yet
- RediFlex Hoses Data SheetDocument2 pagesRediFlex Hoses Data SheetNordson Adhesive Dispensing SystemsNo ratings yet
- Design Analysis and Comparison Between The Conventional Materialswith Composite Material of The Leaf Springs Fmoa 1000127Document20 pagesDesign Analysis and Comparison Between The Conventional Materialswith Composite Material of The Leaf Springs Fmoa 1000127Anonymous oTrMzaNo ratings yet
- Edc Contractors Basic Safety Training: "New Normal" EditionDocument8 pagesEdc Contractors Basic Safety Training: "New Normal" EditionCharles Rommel TadoNo ratings yet
- G30 Developer MSDS ABDocument6 pagesG30 Developer MSDS ABramadhanNo ratings yet
- Naplan Year 9 PracticeDocument23 pagesNaplan Year 9 PracticetonynuganNo ratings yet
- ENDOCRINE-BOARD REVIEW Dr. SchearDocument57 pagesENDOCRINE-BOARD REVIEW Dr. SchearNayara PataroNo ratings yet
- CO Q1 TLE EPAS 7 8 Module 4 Preparing Technical DrawingsDocument47 pagesCO Q1 TLE EPAS 7 8 Module 4 Preparing Technical DrawingsNicky John Doroca Dela MercedNo ratings yet
- C8 Flyer 2021 Flyer 1Document7 pagesC8 Flyer 2021 Flyer 1SANKET MATHURNo ratings yet
- V260 Control ValveDocument12 pagesV260 Control ValvenwabukingzNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics - MKM - DLX - Parts - Catalogue MAR 14 PDFDocument33 pagesHydraulics - MKM - DLX - Parts - Catalogue MAR 14 PDFRS Rajib sarkerNo ratings yet
- HW - MainlineList - 2023 - FINAL 2 17 23 UPDATEDDocument9 pagesHW - MainlineList - 2023 - FINAL 2 17 23 UPDATEDJosé Mario González AlfaroNo ratings yet
- B.ing Wajib - XI IPA1-2Document3 pagesB.ing Wajib - XI IPA1-2iwan fals NurjaniNo ratings yet
- Plugs, Fuses and Household ElectricityDocument4 pagesPlugs, Fuses and Household ElectricityRonald HuynhNo ratings yet
- BBMP C&D Draft Notice 2014 (Updated)Document10 pagesBBMP C&D Draft Notice 2014 (Updated)PriankMathurNo ratings yet
- Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) and War-Related StressDocument56 pagesPosttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) and War-Related Stresshiggjp3No ratings yet
- Calculus II: Prepared By: Cathleen HoboDocument19 pagesCalculus II: Prepared By: Cathleen HoboEspinosa Teves FernanNo ratings yet
- High Risk Neonatal Nursing CareDocument40 pagesHigh Risk Neonatal Nursing Carecarol_cezar100% (2)
- Daitoumaru and Panstar GenieDocument41 pagesDaitoumaru and Panstar GeniePedroNo ratings yet
- Scripture Passages Suitable For Lectio Divina: 1 John 4:7-11Document2 pagesScripture Passages Suitable For Lectio Divina: 1 John 4:7-11Victor AugustoNo ratings yet
- INERT-SIEX 200-300 IG-100: Design ManualDocument54 pagesINERT-SIEX 200-300 IG-100: Design ManualSaleh Mohamed0% (1)
- Shipping Agents in SGDocument3 pagesShipping Agents in SGeason insightsNo ratings yet
- The Beginningof The Church.R.E.brownDocument4 pagesThe Beginningof The Church.R.E.brownnoquierodarinforNo ratings yet