Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CRA - Hydrogen Peroxide PDF
Uploaded by
Rohan PanditOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CRA - Hydrogen Peroxide PDF
Uploaded by
Rohan PanditCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemical Risk Assessment
Worksheet
INTRODUCTION
The questions in this Worksheet are designed to prompt you to think about the risks you face when
using chemicals and whether you believe the current controls will adequately protect you. You should
not proceed with the use of a product if you believe it is unsafe.
There are two elements to the Risk Assessment: You will need a Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for the
product (obtained from Chem Alert or from the supplier); and you will need to consider circumstances
of use in your area. Complete the Risk Assessment in consultation with your supervisor.
SECTION 1: SUMMARY (from SDS)
Chemical / Product Name Storage Location
HYDROGEN PEROXIDE Building: 205 Room:
Manufacturer / Supplier Lab for Intended Use
ELITE SURFACE TECHNOLOGIES Building: 205 Room: 001
Safety Data Sheet Hazardous and Dangerous Goods
Is a current SDS Available? (You must obtain it) Is the chemical classified as Hazardous?
Yes No Yes No
Assessment Date: Is the chemical classified as Dangerous Goods?
16/4/2016 Yes No (if applicable)
Class: Sub Class:
Assessor Supervisor
Rohan Pandit Dr Tushar Sen
SECTION 2: USE
Task Description: Handling: Before use carefully read the product label. Use of
(Including any storage or disposal requirements) safe work practices are recommended to avoid eye or skin
contact and inhalation. Observe good personal hygiene,
including washing hands before eating. Prohibit eating,
drinking and smoking in contaminated areas.
Storage: Store in a cool, dry, well ventilated area, removed
from incompatible substances and foodstuffs. Ensure
containers are adequately labelled, protected from physical
damage and sealed when not in use. Large storage areas
should have appropriate ventilation systems. Store below
24°C.
Concentration: 100 Quantity: Duration 2 days Frequency twice
(%) (including units) of Use: of Use:
Note: Substances that are not classified as a Hazardous Substance or Dangerous Good require
no further assessment (i.e. you do not need to compete the remaining sections).
SECTION 3: HOW CAN EXPOSURE OCCUR?
Dermal (Skin): Eyes: Inhalation: Ingestion: Injection:
Solid Dust Vapour Dust Pressure
Aerosol Aerosol Aerosols Aerosols Sharp objects
Liquid Liquid Gas Liquid Open wounds
Dust Hygiene
Worksheet Page 1 of 4 Health and Safety
Chemical Risk Assessment Form Rev 2.0 issued: 21 April 2016
Uncontrolled document when printed Review: 13 February 2015
Who is potentially exposed? : Students, Lab Staff
(e.g. Students, Lab Staff, Researchers, Others)
SECTION 4: POTENTIAL HEALTH EFFECTS
Acute (Immediate) Effects Chronic (Delayed) Effects
Eye and skin Irritant / Corrosion Sensitising Agent (Skin/Inhalation)
Central Nervous System Carcinogenic
Asphyxiant (Inhalation) Liver/Kidney Disease
Respiratory Tract Irritant Brain/Nerve Disease
Toxic by Skin Exposure Respiratory Disease
Toxic by Ingestion Reproductive System Disease
Other (Specify): Other (Specify):
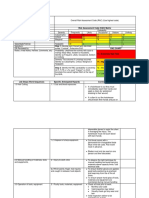
SECTION 5: RISK RANKING WITH EXISTING CONTROLS IN PLACE
Risk Matrix
LIKELIHOOD DESCRIPTION
The event may Not expected The event The event will The event is expected
LIKELIHOOD occur only in but the event could occur probably occur to occur or has
exceptional may occur at at some time in most occurred and is
circumstances some time circumstances continuing to impact
IMPACTS Likelihood Level
Health and Safety Rare Unlikely Possible Likely Almost Certain
Fatality
Critical
Permanent Total Extreme
Disability
CONSEQUENCE DESCRIPTION
Significant/extensive
injury or illness.
Major
Permanent Partial
High
Consequence Level
Disability
Serious injury or
illness.
Moderate
Lost time injury >10
Medium
days
Injury or illness
requiring medical
treatment Minor
Low
Lost time injury <10
days
Injury or illness
requiring First Aid
treatment Insignificant
No lost time injury
days
Worksheet Page 2 of 4 Health and Safety
Chemical Risk Assessment Rev 2.0 issued: 21 April 2016
Uncontrolled document when printed Review: 13 February 2015
So the questions are: based on the above matrix:
What could be the consequences? Corrosive. This product has the potential to cause adverse
health effects. Use safe work practices to avoid eye or skin
contact and inhalation. Over exposure may result in severe
and permanent eye, skin and respiratory damage. Upon
dilution, the potential for corrosive effects may be reduced..
Eye Irritant - Corrosive. Contact may result in irritation,
lacrimation, pain, redness, corneal burns and possible
permanent damage.
Inhalation- Corrosive - toxic. Over exposure may result in
mucous membrane irritation of the respiratory tract, coughing
and possible burns. High level exposure may result in
ulceration of the respiratory tract, breathing difficulties,
chemical pneumonitis and pulmonary oedema.
Skin – Corrosive Irritant. Contact may result in irritation,
redness, pain, rash, dermatitis and possible burns.
Ingestion - Harmful. Ingestion of large quantities may result in
vomiting, acidosis, bloody diarrhoea and shock. In some
cases, necrosis and haemorrhage of the gastrointestinal tract,
liver damage and death may occur. Scarring of the
gastrointestinal tract may occur in non-fatal cases.
What is the likelihood of that happening? rare
What is the risk rating? high
Note: If the rating is above LOW,
Risk Management action is required.
Worksheet Page 3 of 4 Health and Safety
Chemical Risk Assessment Rev 2.0 issued: 21 April 2016
Uncontrolled document when printed Review: 13 February 2015
Risk Management Action
Risk Level Response
Immediate action required to reduce exposure. A detailed mitigation plan must be developed,
Extreme implemented and monitored by senior management to reduce the risk to as low as reasonably
practicable.
A mitigation plan shall be developed and authorised by area manager or supervisor to reduce the
High risk to as low as reasonably practicable. The effectiveness of risk control strategies shall be
monitored and reported to management and relevant committee.
A mitigation plan shall be developed. Control strategies are implemented and periodically
Medium
monitored.
Manage by documented routine processes and procedures. Monitor periodically to determine
Low
situation changes which may affect the risk.
SECTION 6: REQUIRED CONTROL MEASURES TO REDUCE RISK
Control Example Intention to apply
1. Elimination Eliminate materials or elements of the process that carry
significant risk.
2. Substitution Substitute a safer chemical or safer process.
3. Isolation Barriers, enclosures, remote operation.
4. Engineering Local exhaust ventilation, dilution ventilation.
5. Administrative Supervision, use of safe work procedures, housekeeping,
organisation of work to limit contact, standards, training,
signage.
6. PPE Face shields, safety glasses, goggles, gloves, aprons.
SECTION 7: SPECIFIC ACTIONS TO REDUCE RISK
List specific actions that will be carried out for each of the controls you nominated in Section 6.
Control Action
1. Elimination
2. Substitution
3. Isolation
4. Engineering Making sure the work is carried out in a well ventilated area
5. Administrative Making sure all safe practices are followed
6. PPE All PPE will be worn at all times.
Note: If after the implementation of all of the controls above, the risks of using the assessed
chemical remain MODERATE or higher (based on the Risk Matrix in Section 5); expert
advice must be obtained so as to reduce risk before proceeding.
The Occupational Health and Safety Regulations (1996) require that Risk Assessments are retained.
Risk Assessments must be revised if procedures change and are to be reviewed every 5 years. Save a
copy of this Risk Assessment, to be retained in your area. Give it a unique name (eg CRA + product
name + your name). Send a copy to Health and Safety. Any queries should be directed to the Curtin
Health and Safety Ext. 4900.
Worksheet Page 4 of 4 Health and Safety
Chemical Risk Assessment Rev 2.0 issued: 21 April 2016
Uncontrolled document when printed Review: 13 February 2015
You might also like
- Working at Height Rescue Plan SampleDocument7 pagesWorking at Height Rescue Plan SampleAnvarsha SharafudheenNo ratings yet
- Steel Shield Temporary Fencing Risk Assessment and Method Statement For ErectionDocument7 pagesSteel Shield Temporary Fencing Risk Assessment and Method Statement For ErectionIrfan Prima AldiNo ratings yet
- Confined Space Entry - SH&E Risk Assessment: Middle EastDocument5 pagesConfined Space Entry - SH&E Risk Assessment: Middle EastyahiyaNo ratings yet
- Metamorphic RockDocument23 pagesMetamorphic RockShekel DeninoNo ratings yet
- Fire Fighting Mock Drill Report of Al KhuwaimaDocument8 pagesFire Fighting Mock Drill Report of Al KhuwaimaMobin Thomas AbrahamNo ratings yet
- HIRAC (Commissioning Operations)Document2 pagesHIRAC (Commissioning Operations)hendraNo ratings yet
- JSA For MobilizationDocument3 pagesJSA For MobilizationHossain amjad Hossain100% (1)
- Risk Assessment Ground Collapse 8Document5 pagesRisk Assessment Ground Collapse 8Ali Almarshad100% (1)
- FRM-2530-03 Daily Site Inspection Checkllist Ver - 00Document4 pagesFRM-2530-03 Daily Site Inspection Checkllist Ver - 00Ali KaziNo ratings yet
- 5-Star Safety and Health Management SystemDocument5 pages5-Star Safety and Health Management SystemSn Ahsan100% (1)
- SWMS - Blind IstallationDocument12 pagesSWMS - Blind IstallationParasNo ratings yet
- Scaffolding Inspection Checklist: Indus Motor Company LTDDocument1 pageScaffolding Inspection Checklist: Indus Motor Company LTDZain AhmedNo ratings yet
- COSHH Assessment FormDocument2 pagesCOSHH Assessment Formsupriyo sarkar100% (1)
- Risk Assessment - House and BuildingDocument1 pageRisk Assessment - House and Buildingnayanahari0% (1)
- 7-SOP06 - Working at Height Vers 1.1Document10 pages7-SOP06 - Working at Height Vers 1.1Reaz UddinNo ratings yet
- Jsa Tank CleaningDocument5 pagesJsa Tank CleaningASLAM MULANINo ratings yet
- Personal Protective EquipmentDocument1 pagePersonal Protective EquipmentFrancois Johannes BrinkNo ratings yet
- Construction Site Inspection Check List ALMCDocument2 pagesConstruction Site Inspection Check List ALMCAmeerHamzaWarraichNo ratings yet
- RA - 14 - For Waterproofing Membrane ApplicationDocument13 pagesRA - 14 - For Waterproofing Membrane ApplicationIbrahim EsmatNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment Non Routine - General JobDocument42 pagesRisk Assessment Non Routine - General JobGanesh Murugesan0% (1)
- Baseline Risk Assessment: Phindile Kula (Project Coordinator)Document9 pagesBaseline Risk Assessment: Phindile Kula (Project Coordinator)EmilNo ratings yet
- Accident Investigation and ReportingDocument19 pagesAccident Investigation and Reportingvebsdgr8No ratings yet
- Portable Power Tools - Risk Assessment2Document3 pagesPortable Power Tools - Risk Assessment2Basit Nawaz100% (1)
- Fire Risk Assessment For Site Office and SiteDocument11 pagesFire Risk Assessment For Site Office and SiteSajid Shah100% (1)
- PPE Risk Assessment DocumentDocument5 pagesPPE Risk Assessment DocumentFarzanaNo ratings yet
- Think Before You Tip Induction Record: You Must Not You Must AlwaysDocument2 pagesThink Before You Tip Induction Record: You Must Not You Must Alwaysramod100% (1)
- Risk Assessment MasonryDocument1 pageRisk Assessment Masonrymohamed ghalyNo ratings yet
- Heat Stress Toolbox TopicsDocument6 pagesHeat Stress Toolbox TopicsSammie WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Hazard Identification PlanDocument11 pagesHazard Identification PlanjavithNo ratings yet
- Hse Alert-Near MissDocument1 pageHse Alert-Near MissMuhammad JamshidNo ratings yet
- Flagman/ Banksman TrainingDocument25 pagesFlagman/ Banksman TrainingAatif Patil100% (1)
- Construction Site Safety Program REV-02Document95 pagesConstruction Site Safety Program REV-0201095902062ahmedNo ratings yet
- Removal of Debris-Filling - Levelling & CompactingDocument8 pagesRemoval of Debris-Filling - Levelling & CompactingAl Mughsar CompanyNo ratings yet
- RA Excavation For ExcavationDocument13 pagesRA Excavation For ExcavationSasi KumarNo ratings yet
- AhaDocument6 pagesAhaCarlits MacallaNo ratings yet
- Personal Protective Equipment ProceduresDocument3 pagesPersonal Protective Equipment ProceduresLwandziso DlaminiNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Camp OHS Risks AssessmentDocument3 pagesEvaluation of Camp OHS Risks Assessmenthasanhse640No ratings yet
- Axyz CNC Router Manual v1Document93 pagesAxyz CNC Router Manual v1twinjaysNo ratings yet
- 1-Demolation Risk Assessment ReportDocument8 pages1-Demolation Risk Assessment ReportSyed Ali HassanNo ratings yet
- OHS PlanDocument35 pagesOHS Plansefto0% (1)
- JSA 06 (Rebar Assembly Work)Document8 pagesJSA 06 (Rebar Assembly Work)abdulthahseen007100% (1)
- Cast-In Place Concrete - Risk Assessment SheetDocument3 pagesCast-In Place Concrete - Risk Assessment SheetYash SharmaNo ratings yet
- Fall From Height Drill: Dammam Crude & Gas Development ProjectDocument17 pagesFall From Height Drill: Dammam Crude & Gas Development ProjectBala MuruganNo ratings yet
- HSE ViolationDocument1 pageHSE ViolationVIKASNo ratings yet
- BGC Project Hse Plan (Insert Project Title)Document14 pagesBGC Project Hse Plan (Insert Project Title)ahmadNo ratings yet
- Safety Everyday Safety Pep - Talk: Wrigley BangaloreDocument34 pagesSafety Everyday Safety Pep - Talk: Wrigley Bangaloreramkumardotg_5807772No ratings yet
- 14-F02 Ppe Hazard AssessmentDocument3 pages14-F02 Ppe Hazard AssessmentZaheer AhmedNo ratings yet
- Job Safety Analysis - Work SheetDocument4 pagesJob Safety Analysis - Work Sheetrickie7809No ratings yet
- Method Statement For Interfacing With The Tarping & De-Tarping Station of 021-c13 Ver.00Document6 pagesMethod Statement For Interfacing With The Tarping & De-Tarping Station of 021-c13 Ver.00bryanNo ratings yet
- Declaration Penalty Matrix PDFDocument3 pagesDeclaration Penalty Matrix PDFrohit jaiswalNo ratings yet
- 04 UPD ChE Laboratory Safety Manual PDFDocument24 pages04 UPD ChE Laboratory Safety Manual PDFGill Leyson100% (1)
- ErtyyuioluiolDocument16 pagesErtyyuioluiolVinoth Sudalai100% (1)
- RA For Plumbing and HeatingDocument8 pagesRA For Plumbing and HeatingAngela DaveyNo ratings yet
- Living in Camp Accommodation RA-R9-01-010-01Document1 pageLiving in Camp Accommodation RA-R9-01-010-01cmrig74No ratings yet
- Risk Assessment (Night Shift) BND3Document11 pagesRisk Assessment (Night Shift) BND3Shazayn KhanNo ratings yet
- Hazard Identification and Risk Control-TemplateDocument2 pagesHazard Identification and Risk Control-TemplateShristika Pradhan100% (1)
- Risk Assessment No. 08 BUNKERING IN GENERAL Rev. 02 20.03.09Document2 pagesRisk Assessment No. 08 BUNKERING IN GENERAL Rev. 02 20.03.09Devi Ratna Pratiwi91% (11)
- Fencing, Installation and Repair.: Activity DescriptionDocument6 pagesFencing, Installation and Repair.: Activity DescriptionVictorNo ratings yet
- Guide To Common Fungi HCR PDFDocument158 pagesGuide To Common Fungi HCR PDFShekel Denino100% (1)
- Life Saving Rules Engagement Final Pack June - 2022Document40 pagesLife Saving Rules Engagement Final Pack June - 2022vinil radhakrishna100% (1)
- Induction Training For Visitors - MaonaDocument31 pagesInduction Training For Visitors - MaonaMaona power plant Plant100% (1)
- Risk Assessment - House and Office CleaningDocument6 pagesRisk Assessment - House and Office CleaningVimal Thomas100% (1)
- Camp Safety Orientation Checklist FormDocument1 pageCamp Safety Orientation Checklist FormTharanyaanandNo ratings yet
- Painting WorksDocument2 pagesPainting WorksAhoyAoaNo ratings yet
- FSM DC 2138 B FinDocument15 pagesFSM DC 2138 B FinvrajakisoriDasiNo ratings yet
- Updated - COSHH Risk Assessment 1 - Sherwin Willams PrimerDocument2 pagesUpdated - COSHH Risk Assessment 1 - Sherwin Willams PrimerPaul McGahanNo ratings yet
- How Fast Is A Twisted Photon?: A L, T R, N W, S V, C M, J L, M J. P, D FDocument5 pagesHow Fast Is A Twisted Photon?: A L, T R, N W, S V, C M, J L, M J. P, D FShekel DeninoNo ratings yet
- Earth & Space: Grade 6Document35 pagesEarth & Space: Grade 6Shekel DeninoNo ratings yet
- Mass Transfer by Migration & Diffusion (Ch. 4)Document16 pagesMass Transfer by Migration & Diffusion (Ch. 4)Shekel DeninoNo ratings yet
- Chimpanzee Health Improvement, Maintenance, and Protection ActDocument10 pagesChimpanzee Health Improvement, Maintenance, and Protection ActShekel DeninoNo ratings yet
- FW SALZENSTEIN Weaponization of SpaceDocument6 pagesFW SALZENSTEIN Weaponization of SpaceShekel DeninoNo ratings yet
- Animal Life Spans: CFE 3209VDocument10 pagesAnimal Life Spans: CFE 3209VShekel DeninoNo ratings yet
- Astronomy Unit Resources SchoolpointeDocument17 pagesAstronomy Unit Resources SchoolpointeShekel DeninoNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet (SDS) : 01. Product and Company IdentificationDocument6 pagesSafety Data Sheet (SDS) : 01. Product and Company IdentificationShekel DeninoNo ratings yet
- Animal Naming FormDocument8 pagesAnimal Naming FormShekel DeninoNo ratings yet
- Endangered, Threatened, and Candidate Species of LouisianaDocument9 pagesEndangered, Threatened, and Candidate Species of LouisianaShekel DeninoNo ratings yet
- Singer PDFDocument12 pagesSinger PDFShekel DeninoNo ratings yet
- Animal Pattern-Learning Experiments: Some Mathematical BackgroundDocument12 pagesAnimal Pattern-Learning Experiments: Some Mathematical BackgroundShekel DeninoNo ratings yet
- Influenza F PDFDocument1 pageInfluenza F PDFShekel DeninoNo ratings yet
- Children Travelling Alone FormDocument2 pagesChildren Travelling Alone FormShekel DeninoNo ratings yet
- 32 Sweeneyetal2010 PDFDocument14 pages32 Sweeneyetal2010 PDFShekel DeninoNo ratings yet
- Bandera PaperDocument9 pagesBandera PaperShekel DeninoNo ratings yet
- 1) Flower Model: Petal, Sepal, Receptacle, Ovary, Style, Stigma, Filament, AntherDocument8 pages1) Flower Model: Petal, Sepal, Receptacle, Ovary, Style, Stigma, Filament, AntherShekel DeninoNo ratings yet
- Instructions Operation - Maintenance: Secondary Distribution SwitchgearDocument30 pagesInstructions Operation - Maintenance: Secondary Distribution SwitchgearMurtadha Kadhim100% (1)
- 3.2.methode Stament - Wiring Device InstallationDocument8 pages3.2.methode Stament - Wiring Device InstallationSubhan Nur RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Decyl Glucoside MSDS-2Document7 pagesDecyl Glucoside MSDS-2Iulia StoicaNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware Servicing NC II 1Document69 pagesComputer Hardware Servicing NC II 1Jhon Rhem Escandor Hije100% (1)
- Chipping REV1Document2 pagesChipping REV1anon_781855461No ratings yet
- Firefighter Best Practices: Model ProgramDocument46 pagesFirefighter Best Practices: Model ProgramRoberto ZabalaNo ratings yet
- Job Hazard Analysis Awareness TrainingDocument56 pagesJob Hazard Analysis Awareness TrainingchimaraiykeNo ratings yet
- Safety - Job Site Safety 101Document6 pagesSafety - Job Site Safety 101fawnNo ratings yet
- Clear ShotDocument5 pagesClear ShotPrabhjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- SDS Tixolex 17 (English)Document10 pagesSDS Tixolex 17 (English)simbua72No ratings yet
- MS For Cabinets InstallationDocument10 pagesMS For Cabinets InstallationNijo JoseNo ratings yet
- EN 13586 Cranes AccessDocument36 pagesEN 13586 Cranes Accessmateusz mateuszNo ratings yet
- RIANact BIOCHEMDocument2 pagesRIANact BIOCHEMRianna JalmaaniNo ratings yet
- Quiz Midterm Exam Ni Poging JayDocument6 pagesQuiz Midterm Exam Ni Poging JayMYKE MIGGYL MORALESNo ratings yet
- Flow Chart: Health and Safety FormsDocument2 pagesFlow Chart: Health and Safety FormsBenouna FertNo ratings yet
- Xylene MsdsDocument11 pagesXylene Msdssheqarayzan0% (1)
- Safety Data Sheet: Product Name: MOBILGREASE XHP 222Document10 pagesSafety Data Sheet: Product Name: MOBILGREASE XHP 222DenisNo ratings yet
- R1 - Proposed Commercial and Residential Project Radhe InfinityDocument35 pagesR1 - Proposed Commercial and Residential Project Radhe InfinityJalpesh PatelNo ratings yet
- MSDS - GcaDocument3 pagesMSDS - Gcapassword2013No ratings yet
- EOS Horticultural Production L-III PDFDocument175 pagesEOS Horticultural Production L-III PDFHasan100% (1)
- Consoveyo MICS CCEP Pallet Conveyor Load Out RAMS Rev 2Document21 pagesConsoveyo MICS CCEP Pallet Conveyor Load Out RAMS Rev 2Peter BrownNo ratings yet
- Alpacondescalantiii GB Vers2Document10 pagesAlpacondescalantiii GB Vers2ECO Green and BlueNo ratings yet
- Flygt 3153: Installation, Operation, and Maintenance ManualDocument72 pagesFlygt 3153: Installation, Operation, and Maintenance ManualvyshakhNo ratings yet