Professional Documents
Culture Documents
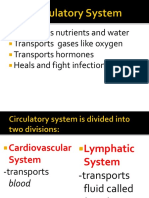
Circulatory System
Circulatory System
Uploaded by
Anonymous qOlj04LOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Circulatory System
Circulatory System
Uploaded by
Anonymous qOlj04LCopyright:
Available Formats
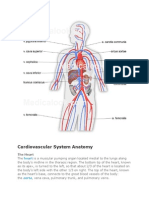
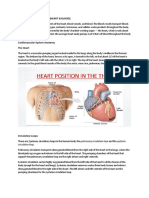
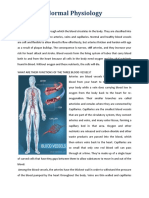
a. Heart—hollow, muscular organ that pumps blood through the body.
b. Lungs—elastic, spongy organs used in breathing, must be supplied with adequate blood.
c. Kidneys—paired organ that removes waste from the blood.
d. Arteries—Tubular vesicles that carry oxygenated blood from the heart to the rest of the body.
e. Aorta—principal artery that carries oxygenated blood to other smaller arteries in the body.
f. Capillary—tiny blood vessels that connect veins to arteries.
g. Valve—Closure on arteries and veins
h. Red blood cells—oxygen-carrying components of the blood, most numerous blood cells
i. White blood cells—make up 1% of the blood, attack foreign bodies in the blood.
j. Platelets—sticky surfaces allow them to form structures to stop blood flow; a portion of the blood
k Plasma—clear, yellowish liquid that forms the fluid portion of blood and lymph. Plasma transports red
and white blood cells and platelets
l. Ventricle—either of the two lower chambers of the heart that receives blood from the upper chambers
(atria) and pumps it into the arteries by contraction of its thick muscular walls
m. Veins—in anatomy, blood vessels that conduct the deoxygenated blood from the capillaries back
to the heart.
You might also like
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Vascular System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionFrom EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Vascular System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System ReviewDocument9 pagesCardiovascular System ReviewsenjicsNo ratings yet
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Circulatory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionFrom EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Circulatory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionNo ratings yet
- Blood CirculationDocument8 pagesBlood CirculationnorafidaishakNo ratings yet
- Function of NounDocument2 pagesFunction of NounAnonymous qOlj04L100% (2)
- Cardiovascular System AnatomyDocument16 pagesCardiovascular System AnatomyJona Addatu0% (1)
- Anatomy NstemiDocument3 pagesAnatomy NstemiSheana Tmpl100% (1)
- Scientific Inquiry QuizDocument1 pageScientific Inquiry QuizAnonymous qOlj04LNo ratings yet
- Types of Circulatory SystemsDocument8 pagesTypes of Circulatory SystemsJanis Micaela EsmasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12, BioDocument26 pagesChapter 12, BioRylee LNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: Up Your Cardiovascular System. Yourheart Works As ADocument6 pagesCardiovascular System: Up Your Cardiovascular System. Yourheart Works As AMalaquias VallejosNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument1 pageCirculatory Systemandrzej36No ratings yet
- Angelo Jhuan ScienceDocument2 pagesAngelo Jhuan ScienceGoldenaholicNo ratings yet
- Bio Psychology Notes 2Document8 pagesBio Psychology Notes 2Zubin Jammaa FulaniNo ratings yet
- A Hollow Muscular Organ That Pumps The Blood Through The Circulatory System by Rhythmic Contraction and DilationDocument1 pageA Hollow Muscular Organ That Pumps The Blood Through The Circulatory System by Rhythmic Contraction and Dilationamber_harthartNo ratings yet
- Transports Nutrients and Water Transports Gases Like Oxygen Transports Hormones Heals and Fight InfectionsDocument46 pagesTransports Nutrients and Water Transports Gases Like Oxygen Transports Hormones Heals and Fight InfectionsElla LlamasNo ratings yet
- Transportation in AnimalsDocument6 pagesTransportation in AnimalskrovrainkNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular XiDocument27 pagesCardiovascular XiKhairunnisa KhairunnisaNo ratings yet
- Heart Pump Deoxygenated BloodDocument8 pagesHeart Pump Deoxygenated BloodVeronica FrancisNo ratings yet
- Subject Enrichment Activity For Term 2Document5 pagesSubject Enrichment Activity For Term 2AADITRYA JAINNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System Anatomy: The HeartDocument5 pagesCardiovascular System Anatomy: The HeartSyafiq RozaliNo ratings yet
- Sukri Tika Yuli Safrina Sughro Puji UtamiDocument10 pagesSukri Tika Yuli Safrina Sughro Puji UtamiRudy MunandarNo ratings yet
- Transport Systems Objective 2-1Document4 pagesTransport Systems Objective 2-1darielleollivierreNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System in Finfish and ShellfishDocument27 pagesCirculatory System in Finfish and ShellfishDr. Abir IshtiaqNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesCirculatory SystemDainara ReyesNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument17 pagesCardiovascular SystemPoojaNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary - Circulatory System PDFDocument1 pageVocabulary - Circulatory System PDFShankara Lakshmi GanapathyNo ratings yet
- Transportation 1 PDFDocument9 pagesTransportation 1 PDFNakshatra PaliwalNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System AnatomyDocument13 pagesCardiovascular System AnatomyDwi Junita SariNo ratings yet
- 6th Lecture Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument8 pages6th Lecture Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDwnya S HasanNo ratings yet
- Ron Seraph Anjello Javier - Q1 Sci. 9 FA No.1Document4 pagesRon Seraph Anjello Javier - Q1 Sci. 9 FA No.1Mute GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SysDocument10 pagesCirculatory SysnaviNo ratings yet
- Transport in Animals o Level2018Document12 pagesTransport in Animals o Level2018MuneebNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument7 pagesCirculatory SystemWisdom DzombeNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument50 pagesThe Circulatory SystemIshan Jacob PiadocheNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument50 pagesThe Circulatory SystemGay For anime girlzNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument50 pagesThe Circulatory Systemfan dingNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Cardio XIIDocument15 pagesAnaphy Cardio XIIRue Cheng MaNo ratings yet
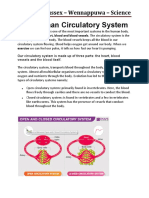
- The Human Circulatory System: Grade 9 - Sussex - Wennappuwa - ScienceDocument23 pagesThe Human Circulatory System: Grade 9 - Sussex - Wennappuwa - ScienceSwarnapaliliyanageNo ratings yet
- BookDocument8 pagesBookmohamed aweys abuukarNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System in HumansDocument4 pagesCirculatory System in Humanspetra.t.ayalNo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular SystemDocument8 pagesThe Cardiovascular Systemsri samrithikaNo ratings yet
- Cardio Vascular System of Prawn.Document3 pagesCardio Vascular System of Prawn.Roy AronNo ratings yet
- Mang, Normal PhysiologyDocument5 pagesMang, Normal PhysiologyThartea RokhumNo ratings yet
- English 1 Final ExamDocument5 pagesEnglish 1 Final ExamMariam AbesadzeNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument25 pagesCirculatory SystemNaiomiNo ratings yet
- Flowering PlantsDocument6 pagesFlowering Plantsshela ambasNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory Systems HandoutsDocument1 pageThe Circulatory Systems HandoutsTeacher MelNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular and Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesCardiovascular and Respiratory SystemGodsend OparaNo ratings yet
- Review and Comprehension (Blood Vessel)Document4 pagesReview and Comprehension (Blood Vessel)9pjh6pzxmsNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument10 pagesThe Circulatory Systemhaniyasherif40No ratings yet
- Blood Circulation and TransportDocument23 pagesBlood Circulation and TransportcikzafirahNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Science Summary - The Circulatory SystemDocument10 pagesGrade 7 Science Summary - The Circulatory SystemNadine Salah El-DinNo ratings yet
- HeartDocument3 pagesHeartKeith Jason CortesNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System: Composed With Epsilon Notes in AndroidDocument8 pagesCirculatory System: Composed With Epsilon Notes in AndroidTanaka muzuwaNo ratings yet
- Notes in Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesNotes in Circulatory SystemVianney CamachoNo ratings yet
- Science Form 3: Chapter 2 Blood Circulation and TransportDocument39 pagesScience Form 3: Chapter 2 Blood Circulation and TransportNadzirah RedzuanNo ratings yet
- Blood VesselsDocument3 pagesBlood VesselsRabia KhalilNo ratings yet
- Jaja PagawaDocument1 pageJaja PagawaDan ZkyNo ratings yet
- Vocab 16Document3 pagesVocab 16api-287178936No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: Parts and FunctionDocument14 pagesCardiovascular System: Parts and FunctionkeykeepNo ratings yet
- Bermoy, Rachelle Fate M. 708-Bro - Obed Product Design Principles of Design Color Theory Appropriate Age Design Costumer Preference Body PhysiqueDocument3 pagesBermoy, Rachelle Fate M. 708-Bro - Obed Product Design Principles of Design Color Theory Appropriate Age Design Costumer Preference Body PhysiqueAnonymous qOlj04LNo ratings yet
- Home and Industrial Sewing Machine: Vance M. Villanueva Bro. Obed-708 TLEDocument1 pageHome and Industrial Sewing Machine: Vance M. Villanueva Bro. Obed-708 TLEAnonymous qOlj04LNo ratings yet
- Quest For The Most Consequential Device of The Bio-IndustryDocument1 pageQuest For The Most Consequential Device of The Bio-IndustryAnonymous qOlj04LNo ratings yet
- Mila Leonor M. Bermoy Mapeh 706-Bro. ObedDocument1 pageMila Leonor M. Bermoy Mapeh 706-Bro. ObedAnonymous qOlj04LNo ratings yet
- The Fitt Principle and The Components of FitnessDocument18 pagesThe Fitt Principle and The Components of FitnessAnonymous qOlj04LNo ratings yet
- What Are The Misconceptions of Dance?Document2 pagesWhat Are The Misconceptions of Dance?Anonymous qOlj04LNo ratings yet
- The Fitt Principle and The Components of FitnessDocument18 pagesThe Fitt Principle and The Components of FitnessAnonymous qOlj04LNo ratings yet