Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Evolution of Human Society
Uploaded by
paz0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views1 pageThe document summarizes the stages of human cultural evolution from the Paleolithic era to modern post-industrial societies. It describes the key characteristics of human societies and the transition from nomadic hunter-gatherer societies to agricultural societies and eventually industrial societies. The stages include the Old Stone Age (Paleolithic), the transitional Mesolithic period, the New Stone Age (Neolithic) marked by polished stone tools and domestication of plants/animals, and the ages of copper, bronze and iron.
Original Description:
Cultural Evolution
Original Title
Cultural Evolution
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes the stages of human cultural evolution from the Paleolithic era to modern post-industrial societies. It describes the key characteristics of human societies and the transition from nomadic hunter-gatherer societies to agricultural societies and eventually industrial societies. The stages include the Old Stone Age (Paleolithic), the transitional Mesolithic period, the New Stone Age (Neolithic) marked by polished stone tools and domestication of plants/animals, and the ages of copper, bronze and iron.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views1 pageEvolution of Human Society
Uploaded by
pazThe document summarizes the stages of human cultural evolution from the Paleolithic era to modern post-industrial societies. It describes the key characteristics of human societies and the transition from nomadic hunter-gatherer societies to agricultural societies and eventually industrial societies. The stages include the Old Stone Age (Paleolithic), the transitional Mesolithic period, the New Stone Age (Neolithic) marked by polished stone tools and domestication of plants/animals, and the ages of copper, bronze and iron.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
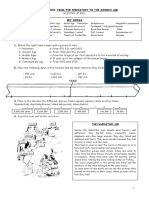
Stages of Man’s Cultural Evolution Human Society
Paleolithic (Old Stone Age) Characteristics of Human Society
1. It is a social system.
Came from the Greek words Palaios, meaning
2. A society is relatively large.
“old” and lithos means “stone”.
3. A society recruits most of its members from
About 2.5 million years ago. within.
4. A society sustains itself across generations.
Cultural Development
5. A society’s members share a culture.
Use of simple pebble tools 6. A society occupies a territory.
Unpolished Stone Tools
Types of Societies
Discovered the use of fire Hunting and Gathering Society
Hunting and gathering stage • The earliest form of human society.
• Subsisted from day to day on whatever was
Nomadic way of living available.
Mesolithic (Transitional) • They used tools made of stones, bones and
woods.
Because of the final retreat of the glaciers about 10,000
• Nomadic
BC, Europe was covered with dense forests. Some
2. Horticultural Society
animals hunted by Paleolithic became extinct and they
People learned to use human muscle power and hand
adjusted to the new environment. They developed a
held tools to cultivate fields.
new culture known as the Mesolithic or transitional
Often forced to relocate when the resources of the land
culture.
are depleted or when the water supplies decrease.
Subsistence Farming
Neolithic (New Stone Age) Involves only producing enough food to feed the group
Surplus Farming
The word Neolithic came from the Greek words Food supply is more than enough to feed the members
Neo meaning “new”, and lithos meaning of society.
“stone”. 3. Pastoral Society
This period was shorter than the Old Stone Age, It relied on herding and domestication
lasting from 8,000 BC to 4,000 BC. of animals for food and clothing to
satisfy the greater needs of the groups.
Cultural development:
Most pastoralists were nomads who
Polished Stone tools followed their herds in a never- ending
quest for pasture and water.
Domestication of plants and animals.
It was organized along male- centered
Food Producing Culture kinship groups.
Settlement in permanent places. 4. Agricultural Society
Animals are used to pull plows.
Appearance of such crafts as pottery and Plowing allows for the cultivation of larger
weaving areas of land.
Age of Metals High volumes of food production allow
people to build permanent homes in a
Copper
single location.
The first metal used in the orient particularly 5. Industrial Society
the Sumerians and Egyptians. It is a soft metal, that the a society driven by the use of technology to
tools and weapons made from it soon became dull. enable mass production, supporting a large
Bronze population with a high capacity for division
of labor.
About 3,500 BC. The oriental people learned Advance forms of technology were applied
that by mixing copper and tin, a harder metal could be and machineries were invented.
produced. Industrialization produced a number of
Iron changes in society.
6. Post-Industrial Society
About 1,500 BC began the use of a harder
Stage of society's development when the
metal. The Hittites of Asia minor were the first people
service sector generates more wealth than the
to use iron tools and it was spread by to the
neighboring Europe. manufacturing sector of the economy.
You might also like
- Respect and Cultural Differences ReviewDocument33 pagesRespect and Cultural Differences ReviewPaolo Miguel VALENCIANo ratings yet
- PREHISTORIC AGE CHRONOLOGY AND TECHNOLOGYDocument28 pagesPREHISTORIC AGE CHRONOLOGY AND TECHNOLOGYjpriyarmanNo ratings yet
- UCSPDocument37 pagesUCSPvianvi3No ratings yet
- CH 1 Lesson 1Document8 pagesCH 1 Lesson 1Freda Buking DayogNo ratings yet
- Looking Back at Human Biocultural and Social EvolutionDocument22 pagesLooking Back at Human Biocultural and Social EvolutionJose Renato NatañoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in World History 1Document41 pagesReviewer in World History 1Jesille May Hidalgo BañezNo ratings yet
- Mid-Term Exam ReviewDocument13 pagesMid-Term Exam ReviewJose RosarioNo ratings yet
- Civilizations Chapter01-Prehistory To Civilizations PDFDocument62 pagesCivilizations Chapter01-Prehistory To Civilizations PDFMargaretNo ratings yet
- Understanding the Evolution of Culture and SocietyDocument3 pagesUnderstanding the Evolution of Culture and SocietyJay CabalgadaNo ratings yet
- Culture and Society As Anthropological and Sociological ConceptsDocument60 pagesCulture and Society As Anthropological and Sociological ConceptsMaryann Mojica Gonzales0% (1)
- How Human Society and Culture EvolvedDocument12 pagesHow Human Society and Culture EvolvedMelchoralyn Cabaron100% (1)
- Human Biocultural and Social EvolutionDocument39 pagesHuman Biocultural and Social EvolutionBeware DawNo ratings yet
- World History: The Human Experience - Chapter 1.1-1.3 OutlineDocument5 pagesWorld History: The Human Experience - Chapter 1.1-1.3 OutlineJavier De La RosaNo ratings yet
- Cultural EvolutionDocument1 pageCultural EvolutionJoeleiyane P. SoteloNo ratings yet
- Learning Modules in History of MathematicsDocument18 pagesLearning Modules in History of MathematicsEarl Vincent OmacNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Looking Back at Human Biocultural and Social EvolutionDocument23 pagesLesson 3 Looking Back at Human Biocultural and Social EvolutionJose Renato NatañoNo ratings yet
- STS Introduction: The Interconnections of Science, Technology, and SocietyDocument7 pagesSTS Introduction: The Interconnections of Science, Technology, and SocietyLuisa Mae BaniquedNo ratings yet
- Module 1.3Document3 pagesModule 1.3Kyla Maxine R. JALANDONINo ratings yet
- Chapters Two: The Development of Human Culture OutlineDocument132 pagesChapters Two: The Development of Human Culture Outlinewandimu solomonNo ratings yet
- Chapters Two: The Development of Human Culture OutlineDocument101 pagesChapters Two: The Development of Human Culture Outlinewandimu solomonNo ratings yet
- Foundations: C. 8000 B.C.E.-600 C.E. Major DevelopmentsDocument33 pagesFoundations: C. 8000 B.C.E.-600 C.E. Major Developmentsanon-178069No ratings yet
- "The Upright Man": Human Capacity For CultureDocument5 pages"The Upright Man": Human Capacity For Culturefernando tamayoNo ratings yet
- STS ReviewerDocument15 pagesSTS ReviewerKS AceNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 Social Science 1Document13 pagesLesson 7 Social Science 1Dennis RaymundoNo ratings yet
- Acellus 6th Grade Social Studies Textbook GuideDocument179 pagesAcellus 6th Grade Social Studies Textbook GuideRaluca PopNo ratings yet
- Stone AgeDocument11 pagesStone Agejlopez092292No ratings yet
- UCS&P: Paleolithic Vs NeolithicDocument70 pagesUCS&P: Paleolithic Vs NeolithicJustin CariagaNo ratings yet
- Sts Module 1Document6 pagesSts Module 1nixiansvtNo ratings yet
- STS Module 2Document68 pagesSTS Module 2Desiree GalletoNo ratings yet
- 4th Powerpoint Human OriginsDocument29 pages4th Powerpoint Human OriginsJohn Lorenze ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- UCSP WEEK 4 Analyze The Significance of Cultural Social Pol and Econ Symbols and PracticesDocument9 pagesUCSP WEEK 4 Analyze The Significance of Cultural Social Pol and Econ Symbols and PracticesPaula DT PelitoNo ratings yet
- Private Files UCSP MODULE-3Document8 pagesPrivate Files UCSP MODULE-3Marvin PameNo ratings yet
- STSMODULE2Document37 pagesSTSMODULE2RAGUDO, ELEAZAR O.No ratings yet
- Lesson 3: Biological and Cultural Evolution Concept MappingDocument35 pagesLesson 3: Biological and Cultural Evolution Concept MappingJanafaye KrishaNo ratings yet
- Ucsp Week-6-7 Part 1Document22 pagesUcsp Week-6-7 Part 1Angelica LuceNo ratings yet
- Ealry Human History and AgricultureDocument33 pagesEalry Human History and AgricultureRandiel James AsisNo ratings yet
- STS - Science, Technology and Society Through the Stone AgesDocument46 pagesSTS - Science, Technology and Society Through the Stone AgesBhie BhieNo ratings yet
- Amsco Book - Period Overview Notes Template CH 1-2Document9 pagesAmsco Book - Period Overview Notes Template CH 1-2AmberlynNo ratings yet
- Standard - Bronze Age - World History Human Legacy TextbookDocument11 pagesStandard - Bronze Age - World History Human Legacy TextbookChris ChiangNo ratings yet
- World History SLRC Lecture NotesDocument8 pagesWorld History SLRC Lecture NotesMarie Faith DumpaNo ratings yet
- Chapter IDocument44 pagesChapter IEllen Mae PormanesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Peopling The EarthDocument28 pagesChapter 1 - Peopling The EarthJose RosarioNo ratings yet
- REVISION ACTIVITIES GeografiaDocument11 pagesREVISION ACTIVITIES GeografiaAnonymous tYRXs9No ratings yet
- UNIT 2: The Role of Science and Technology in Shaping SocietiesDocument5 pagesUNIT 2: The Role of Science and Technology in Shaping SocietiesNOEL STEPHEN BUENAVENTENo ratings yet
- Man's Cultural EvolutionDocument34 pagesMan's Cultural Evolutionedwin o surwelaNo ratings yet
- Act 1.2 Evolution of ManDocument3 pagesAct 1.2 Evolution of ManRay FaustinoNo ratings yet
- Prehistory: Palaeolithic - Mesolithic - Neolithic - Metal AgesDocument20 pagesPrehistory: Palaeolithic - Mesolithic - Neolithic - Metal Agesapi-443568616No ratings yet
- Five prehistoric innovations that shaped humanityDocument1 pageFive prehistoric innovations that shaped humanityCaereel LopezNo ratings yet
- Pre-Historic ArchitectureDocument42 pagesPre-Historic ArchitectureLindseyNo ratings yet
- "Old Stone Age". "Middle Stone Age" "New Stone Age"Document2 pages"Old Stone Age". "Middle Stone Age" "New Stone Age"Grace LeeNo ratings yet
- Human Origins and The Capacity For CultureDocument3 pagesHuman Origins and The Capacity For Culturesofia tolentinoNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 The Development of Human PopulationDocument7 pagesMODULE 1 The Development of Human PopulationGeorgia Alexandria SerraNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Anthropology: Lecture # 6 The Stone AgeDocument30 pagesFundamentals of Anthropology: Lecture # 6 The Stone AgeAnam Saghir BSPSY-MNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Human BeingsDocument6 pagesEvolution of Human BeingsJoseph Ndung'uNo ratings yet
- Man and Prehistory NotesDocument33 pagesMan and Prehistory NotesiggyNo ratings yet
- Timeline of The Human SocietyDocument3 pagesTimeline of The Human SocietyAtencio Barandino JhonilNo ratings yet
- The Stone AgeDocument8 pagesThe Stone AgeMARIA AMIN KHANNo ratings yet
- Great Civilizations and Great Perils: What Can Ancient Civilizations Teach Us?From EverandGreat Civilizations and Great Perils: What Can Ancient Civilizations Teach Us?No ratings yet
- The Story of Civilization: A Child's Primer of EconomicsFrom EverandThe Story of Civilization: A Child's Primer of EconomicsNo ratings yet
- Forty Percent Discnt ASI Publ-2014 PDFDocument26 pagesForty Percent Discnt ASI Publ-2014 PDFmoni_john_1No ratings yet
- Discovery & Extent of Indus Valley Civilization - General Knowledge TodayDocument2 pagesDiscovery & Extent of Indus Valley Civilization - General Knowledge TodayBaloram DeyNo ratings yet
- Balkan TribesDocument3 pagesBalkan TribesCANELO_PIANONo ratings yet
- 133 156 Budden Hoskins Malovoz Wu 1Document24 pages133 156 Budden Hoskins Malovoz Wu 1Boris FržovićNo ratings yet
- Gyulai Archaeobotany in HungaryDocument480 pagesGyulai Archaeobotany in HungaryOrsi Gyurka100% (1)
- Brukenthalia 6Document184 pagesBrukenthalia 6Voicu TudorNo ratings yet
- DAVIS, Thomas W. (2004) - Shifting Sands, The Rise and Fall of Biblical Archaeology PDFDocument200 pagesDAVIS, Thomas W. (2004) - Shifting Sands, The Rise and Fall of Biblical Archaeology PDFJinete del BarrilNo ratings yet
- TABARANGAO, Janiňa T. - RPH - Activity 2 - Manunggul JarDocument1 pageTABARANGAO, Janiňa T. - RPH - Activity 2 - Manunggul JarJaniña TabarangaoNo ratings yet
- Archaeology in BulgariaDocument5 pagesArchaeology in BulgariaElizz AlexNo ratings yet
- Ancient World Civilizations Document for Class IXDocument6 pagesAncient World Civilizations Document for Class IXHemant bwivediNo ratings yet
- Tom D. Dillehay, Alan L. Kolata (2004) Pre-Industrial Human and Environment Interactions in Northern Peru During The Late HoloceneDocument11 pagesTom D. Dillehay, Alan L. Kolata (2004) Pre-Industrial Human and Environment Interactions in Northern Peru During The Late HoloceneMaria FarfanNo ratings yet
- Buckwell Farm, Usk, Monmouthshire. Desk Based AssessmentDocument20 pagesBuckwell Farm, Usk, Monmouthshire. Desk Based AssessmentAPAC LtdNo ratings yet
- Ophel StudiiDocument8 pagesOphel StudiiCristian PetrescuNo ratings yet
- Wallace-Hadrill 2011-Herculaneum Past FutureDocument169 pagesWallace-Hadrill 2011-Herculaneum Past FutureDardenay100% (3)
- First FarmersDocument25 pagesFirst FarmersmarypopescuNo ratings yet
- PYQ Ancient HistoryDocument101 pagesPYQ Ancient Historyakhand kishoreNo ratings yet
- Thesprotia Dodoni 5 (1976), P. 273 F. PREND!, CAH 2 III 1, P. 220 P. MOUNTJOY, Mycenaean Decorated Poltery: A Guide To IdentificationDocument13 pagesThesprotia Dodoni 5 (1976), P. 273 F. PREND!, CAH 2 III 1, P. 220 P. MOUNTJOY, Mycenaean Decorated Poltery: A Guide To Identificationtesting124100% (1)
- Collier's Way, Tonypandy, Rhondda Cynon Taff. Watching BriefDocument15 pagesCollier's Way, Tonypandy, Rhondda Cynon Taff. Watching BriefAPAC LtdNo ratings yet
- Shorncliffe Redoubt, Shorncliffe, FolkestoneDocument49 pagesShorncliffe Redoubt, Shorncliffe, FolkestoneWessex Archaeology100% (2)
- Transformation of Chinese ArchaeologyDocument36 pagesTransformation of Chinese ArchaeologyGilbert QuNo ratings yet
- Arrangement of Vinca Culture Figurines A Study of Social Structure and IonDocument17 pagesArrangement of Vinca Culture Figurines A Study of Social Structure and Ionancrnobrnja4297No ratings yet
- Religion EcologyDocument21 pagesReligion EcologyAmir Ardalan EmamiNo ratings yet
- 2012-45 Boughton Malherbe Hoard Excavation ReportDocument13 pages2012-45 Boughton Malherbe Hoard Excavation ReportCroxford100% (1)
- The Sociology of Pottery in Ancient IsraelDocument153 pagesThe Sociology of Pottery in Ancient IsraelXavier100% (1)
- Folklore and Paganism Podcast TranscriptDocument2 pagesFolklore and Paganism Podcast TranscriptwolfofarcadiaNo ratings yet
- What This Awl Means: Feminist Critiques of ArchaeologyDocument14 pagesWhat This Awl Means: Feminist Critiques of ArchaeologyAung Htun LinnNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Postcolonial ArchaeologyDocument527 pagesHandbook of Postcolonial Archaeologyelfifd100% (1)
- Dwarka and The Mahabharata Every IndianDocument5 pagesDwarka and The Mahabharata Every IndianRajasekhar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Middle Paleolithic ToolsDocument11 pagesMiddle Paleolithic ToolsNAGESH A P me15b045No ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Architectural Heritage 1Document82 pagesChapter 16 Architectural Heritage 1Farah ChedidNo ratings yet