Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Antifungal Drugs
Uploaded by
Amrinder SagguOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Antifungal Drugs
Uploaded by
Amrinder SagguCopyright:
Available Formats
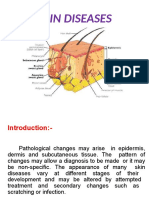
Chapter 1 Introduction
INTRODUCTION
Fungal infection of skin is also known as mycosis. Mycosis is a common fungal infection
affecting human skin and causes different dermatophyte infections. This is generally mild.
Fungi may causes serious disease in patient
with supressed and weakened immune
system. The skin is the most extensive,
readily accessible largest human body part
and it having three functional layers i.e.
epidermis, dermis, subcutaneous. The drug
delivery skin route provides many
advantages over traditional drug delivery Fig. 1.1
systems. Topical Fungal Infections of the skin are one of often faced infectious diseases in
world. The possibility of fungal infections of skin, hair and nails can increase. [1]
The productivity of the topical antifungal treatment de-pends on the entrance of medications
through the objective tissue. Subsequently, the successful medication fixation levels ought to
be accomplished in the skin. In topical organization of antifungals, the medication substances
ought to pass the stratum corneum, which is the furthest layer of the skin, to achieve bring
down layers of the skin, especially into practical epidermis. In this context, the plan may
assume a noteworthy part for penetration of medications into skin [2]. Development of option
methodologies for topical treatment of contagious contaminations of skin envelops new
transporter frameworks for endorsed and investigational compound. Delivery of antifungal
compound into skin can be upgraded with the carriers including colloidal system, vesicular
transporters, and nanoparticles.
Characterstics of fungi
1. Fungi are parasite i.e. they are dead organic matter and live off living.
2. They identify or classify by their method of reproduction, which may be sexual or
asexual.
3. Growing fungi have branched filaments called hyphae, which make the mycelium.
4. Yeasts form characterised by clusters of oval cells. In some conditions theyform a cha
in of cells called a pseudo mycelium.
SBS Polytechnic and Pharmacy College, Patti(Tarn taran) Page 1
Chapter 1 Introduction
Types of fungal infections
Mycosis is most normal contamination and an assortment of natural and physiological
condition helps in the improvement of parasitic diseases. Patients who are taking solid anti-
infection agents for long time, having high danger of contagious diseases. Since anti-
microbials executes harming microscopic organisms, as well as slaughters sound
microorganisms. The adjust of microorganisms in the digestive organs, mouth, vagina, and
different places in the human body change, and results in an excess of parasite. Components
that can bring about organism are high stickiness, invulnerable or hormone variations from
the norm [4].
1. Superficial parasitic contamination
Shallow mycosis is restricted to the furthest layers of skin and hair. Fungus disease that
predominantly influences the skin of senior individuals, particularly the trunk, back, upper
arms and legs. It doesn't influence the face. This organism delivers light spots which are
lighter than the skin or the rosy dark colored. This organism exists in two structures, one is
unmistakable spots introduce.
Dermatophytes (tinea)
Yeasts i.e. candida, malassezia, piedra
Moulds
2. Cutaneous parasitic contamination
Cutaneous mycosis broaden further into the skin epidermis, and furthermore incorporates
intrusive hair, skin and nail issues. These sicknesses are hindering the keratinized layers
introduce on hair, and nails. The shallow mycosis, impact have resistant framework reactions
might be evoked bringing about changes communicated in the different layers of the skin. [5]
Mycetoma
Chromoblastomycosis
3. Systemic parasitic diseases
This may because of taking in the spores of fungi,which normally introduce in soil or as
astute infection in invulnerable bargained people.
SBS Polytechnic and Pharmacy College, Patti(Tarn taran) Page 2
Chapter 1 Introduction
Breathed in contagious disease: it is exceptional contamination and may influence the solid
people. The creature bringing on this disease are:
Histoplasmosis
Coccidioidomycosis
Artful contamination: this is just tainting who are now debilitated or having
immunodeficiency issue. danger of disease may include:
Serious disease and debility
Cancer or leukemia
Diabetes mellitus
Transplant
Massive dosages of anti-toxins
Parenteral nourishment
Drug fixation
4. Skin parasitic infections [6]
Organisms that cause skin sicknesses are called dermatophytes."Dermatophytes" doesn't
allude to a particular gathering of parasites, however they assault the dermis. Parasitic
diseases of the skin can be regarded with topical creams and also doctor prescribed
medications.
Competitor's Foot
Competitor's foot, otherwise called tinea pedis, it is the parasitic contamination of the foot.
It causes tingling, consuming, redness, rankles and injuries.
Competitor's foot is an exceptionally normal contamination. The growth develops in the
warm, soggy condition, for example, shoes, socks, swimming pools, locker rooms, and floors
of open showers. It is most basic in the mid year and in warm, muggy atmospheres. It
happens all the more frequently in individuals who wear tight shoes and who utilize group
showers and pools.
SBS Polytechnic and Pharmacy College, Patti(Tarn taran) Page 3
Chapter 1 Introduction
Muscle head tingle:
Tineacruris, is a typical skin disease that is created by a kind of growth called tinea. The
parasite flourishes in warm, soggy ranges of the body and accordingly, contamination can
influence the private parts, internal thighs, and rear end. Contaminations happen all the more
frequently in the late spring or in warm, wet atmospheres.
Side effects of muscle head tingle include:
• Itching, abrading, or consuming in the crotch or thigh
• A roundabout, red, raised rash with lifted edges
• Redness in the crotch or thigh
• Flaking, peeling, or breaking skin
Ringworm
Ringworm may likewise know as tineacorporis, is not a worm, but rather a parasitic
contamination of the skin. It can show up anyplace on the body and it would appear that a
round, red, level sore. It is regularly joined by layered skin. The external piece of the sore can
be brought while the skin up in the center seems typical. Ringworm can be unattractive, yet it
is normally not a genuine condition.
Yeast Infections
Yeast contaminations of skin is cutaneous candidiasis and are brought about by yeast-like
growths called candida. They happen when yeast on the skin develops all the more
effectively and causes a red, scaling, bothersome rash on the skin. Yeast diseases are not
infectious.
Yeast contaminations may influence almost any skin surface on the body, yet are well on the
way to happen in warm, sodden, wrinkled ranges including the armpits and the crotch.
Candida contamination is particularly regular among individuals who are stout or who have
diabetes. Individuals going for broke.
FUNGAL ORGANISMS
Fungal organisms are broadly classified as follows :-
Hyphae(Moulds): Hyalohyphomycoses, Aspergillus spp., Pseudallescheriaboydii.
SBS Polytechnic and Pharmacy College, Patti(Tarn taran) Page 4
Chapter 1 Introduction
Dermatophytes:Epidermophytonfloccosum, Trichophyton spp., Microsporum spp.
Phaeohyphomycoses, Alternaria spp., Anthopsisdeltoidea, Bipolarishawaiiensis,
Cladosporium spp.,Curvulariageniculata, Exophiala spp., Fonsecaeapedrosoi, Phialophora
spp., Fusarium spp. ZygomycetesAbsidiacorymbifera, Mucorindicus, Rhizomucorpusillus
Dimorphic Fungi:Blastomyces spp., Coccidioides spp., Paracoccidioides spp., Histoplasma
spp.,Sporothrixspp
Yeasts: Candida spp., Cryptococcusneoformans
COCCIDIOIDOMYCOSIS :-
Coccidioidomycosisis caused by C. immitis, a thermal dimorphic fungus like H.
capsulatumand B. dermatitidis. In soil, it grows as a mold with Arthroconidia but converts to
a spherule containing 200 to 400 endospores each in host tissues. The number of
multiplyingcoccidioidal organisms is significantly higher than H. capsulatum or B.
dermatitidis, which may explain the higher incidence of clinical infection following exposure
to C. immitis. Primary pulmonary infection occurs in the susceptible host when airborne
Arthroconidia generated by dust storms or strong winds are inhaled. T-cell immunity is
critical for control of infection. Host immune response results in the production of
immunoglobulin M (IgM) and immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies; although they do not
confer specific protection to disease development, serologic tests measuring antibody levels
have diagnostic and prognostic value.
Diagnosis: Definitive diagnosis is made with fungal culture and stains of blood, tissue, and
fluids. However, blood cultures are frequently negative. Growth of the organism on
appropriate media typically is apparent in 3 to 5 days.
CRYPTOCOCCOSIS :-
Cryptococcus neoformans is an opportunistic fungal pathogen that causes invasive diseases
primarily in patients with underlying immunodeficiency and rarely in hosts with normal
defenses. It exists as an encapsulated yeast surrounded by a polysaccharide capsule and has a
worldwide distribution. Infection is acquired via inhalation of the spores of C. neoformans
into the lungs. In patients with intact T-cell immunity, primary infection usually is contained
within the lungs, whereas rapid dissemination to other sites, most notably the CNS, occurs in
immune compromised hosts.
SBS Polytechnic and Pharmacy College, Patti(Tarn taran) Page 5
Chapter 1 Introduction
Diagnosis: Diagnosis of cryptococcosis is made by isolating the organism from a sterile body
site, by histopathology, or by cryptococcal capsular antigen testing. Blood cultures are
positive in 70% of patients with AIDS who are infected with C. neoformans. India ink stain
outlines the polysaccharide capsule of the yeast.
ASPERGILLOSIS :-
Aspergillosis, the most common invasive mold infection worldwide, is caused by the
ubiquitous fungus Aspergillus spp. Approximately 150 species have been identified thus far.
Pathogenic species that commonly cause invasive diseases include A. fumigatus, A. flavus,
A. niger, A. terreus, and A. nidulans. A. fumigatus is the predominant species causing
invasive aspergillosis; it accounts for approximately 90% of all cases. The rate of progression
of invasive diseases may be closely related to the growth rate of the organisms. Macrophage
ingestion and killing of the spores and extracellular killing of hyphae by neutrophils are the
primary host defenses against Aspergillus in the lungs. Corticosteroids can substantially
impair the functions of macrophages and neutrophils. Tcell function is thought to be
important in the more chronic forms of invasive aspergillosis.
Signs and symptoms are more prominent and tend to extend over weeks or months; they
include chronic productive cough, mild to moderate hemoptysis, lowgrade fever, malaise, and
weight loss. In contrast, patients who are the most immunocompromised are least likely to
have symptoms and may progress within 7 to 10 days from onset of disease to death.[7]
CANDIDIASIS :-
Candida species are opportunistic pathogens that are a part
of the normal human commensals. Candidaas a cause of
oral lesions was first identified in the 1840s. Over the past
decade, the incidence of infections owing to Candida sp
has increased dramatically. Based on a case control study
well matched for age, sex, service, underlying diagnosis,
and duration of hospital stay, nosocomial candidemia was Fig.-1.2
found to result in a crude mortality of 61% compared with 12% among cases and controls
respectively, with an excess mortality of 49%. Those who survived spent an extra 11 days in
the hospital.
SBS Polytechnic and Pharmacy College, Patti(Tarn taran) Page 6
Chapter 1 Introduction
Candida organisms are yeasts that exist microscopically as small (4–6 µm), thin-walled,
ovoid cells that reproduce by budding. Other morphologic forms, such as pseudohyphae and
hyphae, also can be seen in clinical specimens for most Candida sp except C. glabrata. More
than 150 Candida sp have been identified previously; however, approximately 10 are
considered important human
pathogens. The pathogenic
species include C. albicans, C.
tropicalis,C.parapsilosis,
C.glabrata (formerly classified as
Torulopsisglabrata), C. krusei, C.
guilliermondii, C. lusitaniae, C.
kefyr(C. pseudotropicalis), C.
rugosa, C. dubliniensis, and C.
stellatoidea (now considered C.
albicans). Speciation of the
pathogens is important owing to
the varied pathogenic potential
and susceptibility to antifungal
agents. A rapid presumptive
identification of Candida albicans
usually can be made by
performing the specific germ tube Fig.-1.3
test. Breakdown of the normal host defense mechanisms is necessary for Candida organisms
to become pathogens. An intact integument is required for protection against cutaneous
invasion. When invasion occurs, functioning neutrophils, macrophages, and lymphocytes are
important host defenses against the development of systemic disease.[8]
VULVOVAGINITIS:-
Vulvovaginalcandidiasis is estimated to occur at least once during reproductive years in 75%
of women with no recognizable predisposing factors. However, identifiable risk factors
include broad-spectrum antibiotics, high estrogen-containing oral contraceptives, poorly
controlled diabetes, and pregnancy. Among patients infected with HIV, one large cross-
sectional study found similar incidence (9%) of vaginal candidiasis compared with patients
SBS Polytechnic and Pharmacy College, Patti(Tarn taran) Page 7
Chapter 1 Introduction
who do not have HIV. Clinical signs and symptoms include whitish cheesy discharge,
vulvovaginal pruritus, irritation, soreness, dyspareunia, and burning on micturition[9].
ANTIFUNGAL DRUGS AND THEIR MECHANISM OF ACTION
The fungal cell wall is composed of multiple layers where mannoproteins and glucan make
up more than 80% of the cell wall composition, while chitin represents less than 2% [10].
Mannoproteins are predominantly expressed at the external surface. The plasma membranes
of fungi are primarily composed of ergosterol [11].
Antifungals are grouped on the basis of their structure and mechanism of action: The azoles
and triazoles interfere with the ergosterol biosynthesis pathway by inhibiting cytochrome
P450-dependent 14--demethylase and blocking the oxidative removal of 14--methyl from
lanosterol resulting into the structural changes in the lipid membrane. They are directed
against lanosterol 14-alpha-demethylase, a cytochrome P-450 enzyme containing a heme
moiety in its active site, in the ergosterol pathway. Azoles have also been reported to inhibit
membrane-surface enzymes and lipid biosynthesis. Azoles, include imidazoles (ketoconazole
and miconazole) and triazoles(fluconazole, itraconazole, and voriconazole). The topical
azoles include clotrimazole, miconazole, oxiconazole, sulconazole, econazole, ketoconazole,
sertaconazole. Sertaconazole is fungicidal and has anti-inflammatory and anti-itch properties
[12]. Luliconazole is another FDA approved topical imidazole for treatment of
interdigitaltineapedis, tineacruris, and tineacorporis [13].Recently, US Food and Drug
Administration (FDA) approved First Topical Triazole, efinaconazole 10% topical solution,
for the treatment of onychomycosis [14]. Polyenes include amphotericin B and nystatin. They
increase the permeability of the plasma membrane. They bind to fungal membrane sterol,
resulting in the formation of aqueous pores through which essential cytoplasmic materials
leak out and thereby destroying the proton gradient within the membrane [15]. Allylamines
(naftifine, terbinafine and the related benzylaminebutenafine) and thiocarbamates (tolnaftate
and tolciclate) inhibit the conversion of squalene to 2,3-oxidosqualene by the enzyme
squaleneepoxidase [16-18]. This enzyme blocks ergosterol biosynthesis, leading to
intracellular accumulation of squalene which is toxic to fungal cells and leads to cell death
[19].Allylaminesarelipophilic, bind effectively to the stratum corneum and also penetrate
deeply into hair follicles [20]. Ciclopiroxolamine is a topical fungicidal agent. It causes
membrane instability by accumulating inside fungal cells and interfering with amino acid
SBS Polytechnic and Pharmacy College, Patti(Tarn taran) Page 8
Chapter 1 Introduction
transport across the fungal cell membrane [21]. Candins function by inhibiting the synthesis
of β 1,3-glucan which is the major structural polymer of the cell wall [22].
MANAGEMENT- ALLOPATHIC
CLOTRIMAZOLE :-Clotrimazole, sold under the brand name Canestenamong others, is
an antifungal medication. It is used to
treat vaginal yeast infections, oral
thrush, diaper rash, pityriasisversicolor, and
types of ringworm including athlete's
foot and jock itch. It can be taken by mouth
or applied as a cream to the skin or in
the vagina. Fig.-1.4
It is commonly available without a prescription in various dosage forms, such as a
Cream, vaginal tablet, or as a prescription troche or throat lozenge (prescription only).
Topically, clotrimazole is used for vulvovaginal candidiasis (yeast infection) or yeast
infections of the skin. For vulvovaginal candidiasis (yeast infection), clotrimazole tablets and
creams are inserted into the vagina. Troche or throat lozenge preparations are used
for oropharyngeal candidiasis (oral thrush) or prophylaxis against oral thrush
in neutropenic patients[22].
Clotrimazole is usually used 5 times daily for 14 days for oral thrush, twice daily for 2 to 8
weeks for skin infections, and once daily for 3 or 7 days for vaginal infections[23].
MICONAZOLE :-Miconazole is an antifungal medicationused to treat ring worm,
pityriasisversicolor, and yeast infections of the
skin or vagina. It is applied to the skin or
vagina as a cream or ointment.Common side
effects include itchiness or irritation of the area
in which it was applied. Use in pregnancy is
believed to be safe for the baby. Miconazole is
in the imidazole family of medications. It
works by decreasing the ability of fungi to
make ergosterol, an important part of its Fig.-1.5
SBS Polytechnic and Pharmacy College, Patti(Tarn taran) Page 9
Chapter 1 Introduction
cell membrane. Miconazole is mainly used externally for the treatment of athlete's
foot, ringworm, and jock itch. Internal application is used for oral or vaginal thrush (yeast
infection). The oral gel may also be used for the lip disorder angular cheilitis [24].
KETACONAZOLE :-Ketoconazole is a synthetic imidazole antifungal drug used primarily
to treat fungal infections. Ketoconazole is sold commercially as a tablet
for oral administration, and in a variety of formulations for topical
administration, such as creams (used to treat tinea; cutaneous
candidiasis, including candidal paronychia; and pityriasisversicolor) and
shampoos (used primarily to treat dandruff—seborrhoeic dermatitis of
the scalp).
Topical antifungal Fig.-1.6
Topically administered ketoconazole is usually prescribed for fungal infections of the skin
and mucous membranes, such as athlete's foot, ringworm, candidiasis (yeast infection or
thrush), jock itch, and tineaversicolor. Topical ketoconazole is also used as a treatment
for dandruff (seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp) and for seborrheic dermatitis on other areas
of the body, perhaps acting in these conditions by suppressing levels of the
fungus Malassezia furfur on the skin.
Systemic antifungal
Ketoconazole has activity against many kinds of fungi that may cause human disease, such
as Candida, Histoplasma, Coccidioides, and Blastomyces (although it is not active
against Aspergillus). First synthesized in 1977, ketoconazole was the first orally-
active azole antifungal medication. However, ketoconazole has largely been replaced as a
first-line systemic antifungal medication by other azole antifungal agents, such
as itraconazole, because of ketoconazole's greater toxicity, poorer absorption, and more
limited spectrum of activity [25].
ECONAZOLE:-Econazole (commonly used as
the nitrate salt) is an antifungal medication of
the imidazole class. It is sold under the brand
names Spectrazole (United States) and Ecostatin
(Canada), among others. It is a component of
Pevisone and Ecoderm-
TA(econazole/triamcinolone). Fig.-1.7
SBS Polytechnic and Pharmacy College, Patti(Tarn taran) Page 10
Chapter 1 Introduction
Econazole is used as a cream to treat skin infections such as athlete's
foot, tinea, pityriasisversicolor, ringworm, and jock itch. It is also sold in Canada under the
brand name Ecostatinas vaginal ovules to treat vaginalthrush.
BENZOIC ACID AND SALICYLIC ACID :-Benzoic acid C7H6O2 (or C6H5COOH), is a
colorless crystalline solid and a simple aromatic carboxylic acid. The name is derived
from gum benzoin, which was for a long time its only known source. Benzoic acid occurs
naturally in many plants and it serves as an intermediate in the biosynthesis of
many secondary metabolites. Salts of benzoic acid are used as food preservatives and benzoic
acid is an important precursor for the industrial synthesis of many other organic substances.
The salts and esters of benzoic acid are known as benzoates
Benzoic acid is a constituent of Whitfield's ointment which is used for the treatment of fungal
skin diseases such as tinea, ringworm, and athlete's foot. As the principal component of gum
benzoin, benzoic acid is also a major ingredient in both tincture of benzoin and Friar's
balsam. Such products have a long history of use as topical antiseptics and
inhalant decongestants.
Salicylic acid as a medication is used to help remove the outer layer of the skin. As such it is
used to treat warts, calluses, psoriasis, dandruff, acne, ringworm, and ichthyosis. For
conditions other than warts, it is often used together with other medications. It is applied to
the area affected [25].
ITRACONAZOLE :-Itraconazole, is a triazole antifungal agent for fungal infections. The
drug may be given by mouth or intravenously.Itraconazole has a broader spectrum of activity
than fluconazole (but not as broad
as voriconazole or posaconazole). In particular, it
is active against Aspergillus, which fluconazole is
not. It is also licensed for use
in blastomycosis, sporotrichosis, histoplasmosis,
and onychomycosis. Itraconazole is over 99%
protein-bound and has virtually no penetration
into cerebrospinal fluid. Therefore, it should
never be used to treat meningitis or other central Fig.-1.8
nervous system infections. According to the Johns Hopkins Abx Guide, it has "negligible
SBS Polytechnic and Pharmacy College, Patti(Tarn taran) Page 11
Chapter 1 Introduction
CSF penetration, however treatment has been successful for cryptococcal and coccidioidal
meningitis".It is also prescribed for systemic infections, such as aspergillosis, candidiasis,
and cryptococcosis, where other antifungal drugs are inappropriate or ineffective [25].
TERBINAFINE:-Terbinafine, sold under the brand name Lamisil among others, is
an antifungal medication used to
treat ringworm, pityriasisversicolor
,and fungal nail infections. It is
either taken by mouth or applied to
the skin as a cream or
ointment. The cream and ointment
are not effective for nail infections.
Terbinafine is mainly effective on
the dermatophyte group of fungi.
As a cream or powder, it is used topically for superficial skin infections such as jock
itch (tineacruris), athlete's foot (tineapedis), and other types of ringworm (tineacorporis).
Terbinafine cream works in about half the time required by other antifungals.Tablets by
mouth are often prescribed for the treatment of onychomycosis, a fungal nail infection,
typically by a dermatophyte or Candida species. Fungal nail infections are located deep under
the nail in the cuticle to which topically applied treatments are unable to penetrate in
sufficient amounts.
FLUCONAZOLE:-Fluconazole is an antifungal medication used for a number of fungal
infections. This includes candidiasis,
blastomycosis, coccidiodomycosis, c
ryptococcosis, histoplasmosis, dermat
ophytosis, and pityriasisversicolor. It
is also used to prevent candidiasis in
those who are at high risk such as
following organ transplantation, low
birth weight babies, andthose with
low blood neutrophil counts. It is
given either by mouth or by injection into a vein. Fig.-1.9
SBS Polytechnic and Pharmacy College, Patti(Tarn taran) Page 12
Chapter 1 Introduction
Fluconazole is a first-generation triazole antifungal medication. It differs from earlier azole
antifungals (such as ketoconazole) in that its structure contains a triazole ring instead of
an imidazole ring. While the imidazole antifungals are mainly used topically, fluconazole and
certain other triazole antifungals are preferred when systemic treatment is required because of
their improved safety and predictable absorption when administered orally.
Fluconazole's spectrum of activity includes most Candida species (but not Candida
krusei or Candida glabrata), Cryptococcus neoformans, some dimorphic fungi, and
dermatophytes, among others. Common uses include:
The treatment of non-systemicCandida infections of the vagina ("yeast infections"),
throat, and mouth.
Certain systemicCandida infections in people with healthy immune systems, including
infections of the bloodstream, kidney, or joints. Other antifungals are usually preferred
when the infection is in the heart or central nervous system, and for the treatment of
active infections in people with weak immune systems.
The prevention of Candida infections in people with weak immune systems, such as
those neutropenic due to cancer chemotherapy, those with advanced HIV infections,
transplant patients, and premature infants.
As a second-line agent for the treatment of cryptococcalmeningoencephalitis, a fungal
infection of the central nervous system [26].
AMPHOTERACIN :-Amphotericin B is an antifungal medication used for serious fungal
infections and leishmaniasis.The fungal infections it is used to treat
include aspergillosis, blastomycosis, candidiasis, coccidioidomycosis,
and cryptococcosis. For certain infections it is given
with flucytosine.[3] It is typically given by injection
into a vein.One of the main uses of amphotericin B
is treating a wide range of systemic fungal
infections. Due to its extensive side effects, it is
often reserved for severe infections in critically ill,
or immuno compromised patients. It is considered
first line therapy for invasive mucormycosis Fig.-1.10
infections, cryptococcal meningitis, and certain aspergillus and candidal infections. It has
been a highly effective drug for over fifty years in large part because it has a low incidence of
SBS Polytechnic and Pharmacy College, Patti(Tarn taran) Page 13
Chapter 1 Introduction
drug resistance in the pathogens it treats. This is because amphotericin B resistance requires
sacrifices on the part of the pathogen that make it susceptible to the host environment, and
too weak to cause infection.Lipid formulations of amphotericin B should not be used to treat
urinary tract infections because they do not penetrate into the kidney or achieve adequate
concentrations in the urine.
VORICONAZOLE:-Voriconazole is
a triazole antifungal medicationused to treat and
prevent invasive fungal infectionsincluding
aspergillosis and candidiasis and fungal
infections caused by Scedosporium and
Fusarium species.Voriconazole is used to treat
invasive aspergillosis and candidiasis and
fungal infections caused by Scedosporium and
Fusariumspecies, which may occur in immune Fig.1.11
compromised patients, including people undergoing allogeneic bone marrow
transplant(BMT), who have hematologic cancersor who undergo organ transplants [27].
HERBAL MANAGEMENT
BETEL(Piper Betel):-- The betel (Piper betle) is the
leaf of a vine belonging to the Piperaceae - family,
which includes pepper and kava. Betel leaf is mostly
consumed in Asia, and elsewhere in the world by
some Asian emigrants, as betel quid or in paan,
with Areca nut and/or tobacco.
In Sri Lanka and in many parts of India a sheaf of Fig.-1.12
Betel leaves is traditionally offered as a mark of respect and auspicious beginnings.
Occasions include, greeting elders at wedding ceremonies, New Year, offering payment
to Ayurvedic physicians and astrologers where usually money and/or areca nut are kept on
top of the sheaf of leaves and offered to the elders for their blessings.
The betel plant is an evergreen perennial, with glossy heart-shaped leaves and white catkin.
The betel plant originated in South and South East Asia [28].
SBS Polytechnic and Pharmacy College, Patti(Tarn taran) Page 14
Chapter 1 Introduction
VINCA ROSEA (Catharanthus Roseus):-
Catharanthusroseus, commonly known as the
Madagascar periwinkle, Rose periwinkle, rosy
periwinkle is a species of flower ing plant in the
dogbane family Apocynaceae. It is native
and endemic to Madagascar, but grown
elsewhere as an ornamental and medicinal plant,
a source of the drugs vincristine and vinblastine, Fig.-1.13
used to treat cancer.The species has long been cultivated for herbal medicine and as
an ornamental plant. In Ayurveda (Indian traditional medicine) the extracts of its roots and
shoots, though poisonous, are used against several diseases. In traditional Chinese medicine,
extracts from it have been used against numerous diseases, including diabetes, malaria,
and Hodgkin's lymphoma. Many of the vincaalkaloids were first isolated from
Catharanthusroseus, including vinblastine and vincristine used in the treatment
of leukemiaand Hodgkin's lymphoma [29].
CLOVE:--Cloves are the aromatic flower buds
of a tree in the family Myrtaceae,
Syzygiumaromaticum. They arenativeto
the Maluku Islandsin Indonesia, and are
commonly used as a spice. Cloves are
commercially harvested primarily in Bangladesh,
Indonesia, India, Madagascar, Zanzibar, Pakistan, Fig.-1.14
Sri Lanka, and Tanzania. Cloves are available through out the year.
SPEARMINT(binomial Menthaspicata,
synonym Menthaviridis), also known
as garden mint, common mint, lamb
mintand mackerel mint, is a species
of mint native to much of Europe and
Asia (Middle East, Himalayas, China etc.),
and naturalized in parts of northern and western Fig.-1.15
Africa, North America, and South America, as well as various oceanic islands.
SBS Polytechnic and Pharmacy College, Patti(Tarn taran) Page 15
Chapter 1 Introduction
Spearmint is used for its aromatic oil, referred to as oil of spearmint. The most abundant
compound in spearmint oil is R-(–)-carvone, which gives spearmint its distinctive smell.
Spearmint oil also contains significant amounts of limonene, dihydrocarvone, and 1,8-
cineol.Unlike oil of peppermint, oil of spearmint contains minimal amounts
of menthol and menthone. It is used as a flavoring for toothpaste and confectionery, and is
sometimes added to shampoos and soaps[30].
Used as a fumigant, spearmint essential oil is an effective insecticide against adult moths.
AJWAIN:- Ajowanis an annual herb in the family Apiaceae. It originated in India. Both the
leaves and the fruit of the plant are consumed by humans. The plant is also called bishop's
weed, but this is a common name it shares with some other different plants. The "seed" (i.e.,
the fruit) is often confused with lovage "seed”.
Ajwain is used in traditional Ayurvedic
medicine primarily for stomach
disorders such as indigestion and
flatulence.In Tamil it is called oomam
and in Telugu it is known as vaamu
in Siddha medicine, it is used as a
cleanser, detox, and antacid. In general,
the crushed fruits are applied externally as a poultice [31]. Fig.-1.16
Essential oil
Hydrodistillation of ajwain fruits yields an essential oil consisting primarily
of thymol, gamma-terpinene and p-cymene as well as more than 20 trace compounds
(predominately terpenoids) [32].
SBS Polytechnic and Pharmacy College, Patti(Tarn taran) Page 16
You might also like
- Doctor's Book of Survival Home RemediesDocument8 pagesDoctor's Book of Survival Home RemediesLouay Dan0% (2)
- A Simple Guide to Skin Fungal Infections, (Updated 2023) Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Skin Fungal Infections, (Updated 2023) Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Fungi of Medical ImportanceDocument11 pagesFungi of Medical ImportanceRi FitrianaNo ratings yet
- The Musculoskeletal System...Document24 pagesThe Musculoskeletal System...Charity Grace Magno67% (3)
- Fungal InfectionsDocument9 pagesFungal InfectionsCoral Srinivasa RamaluNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic CommunicationDocument4 pagesTherapeutic CommunicationLloyd Rafael Estabillo100% (1)
- AutismDocument30 pagesAutismKasra Chehrazy100% (1)
- ESPEN Guideline Clinical Nutrition in SurgeryDocument28 pagesESPEN Guideline Clinical Nutrition in SurgeryekalospratamaNo ratings yet
- Chapter22 LectureDocument45 pagesChapter22 Lecturecee_prasetyo100% (1)
- MRCS Part B OSCEDocument117 pagesMRCS Part B OSCEMuhammadKhawar100% (1)
- Human Body Amazing FactsDocument9 pagesHuman Body Amazing Factsapi-268927130100% (1)
- L. Gifford The Mature Organism ModelDocument12 pagesL. Gifford The Mature Organism ModelRoar SyltebøNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapy of Fungal DiseasesDocument51 pagesChemotherapy of Fungal DiseasesSalmaan KhanNo ratings yet
- What Are CutaneDocument6 pagesWhat Are CutaneTayech TilahunNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Microbiology and Parasitology (PHMP211)Document59 pagesPharmaceutical Microbiology and Parasitology (PHMP211)Crisamor Rose Pareja ClarisaNo ratings yet
- Lec 4Document6 pagesLec 4Ahmed JamalNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis and Clinical Groupings of Fungal Diseases (MycosesDocument8 pagesPathogenesis and Clinical Groupings of Fungal Diseases (MycosesElena ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Subcutaneous MycosesDocument3 pagesSubcutaneous MycosesiwennieNo ratings yet
- Easjms 41 19-23Document5 pagesEasjms 41 19-23sangeetha guhanNo ratings yet
- Best Dermatologist in KolkataDocument2 pagesBest Dermatologist in Kolkatasudhirmishra650No ratings yet
- MYCOSESDocument41 pagesMYCOSESDayana PrasanthNo ratings yet
- Cutaneous Mycoses MikologiDocument10 pagesCutaneous Mycoses MikologisherinaNo ratings yet
- Super Ficial Fungal Infections: Key PointsDocument4 pagesSuper Ficial Fungal Infections: Key PointsBagus Putra KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Fungal Skin Infections ملزمةDocument6 pagesFungal Skin Infections ملزمةعبدالرحمن طارق عبدالله صالحNo ratings yet
- Common Skin Disorders: Dermatitis, Bacterial Infections, and MoreDocument9 pagesCommon Skin Disorders: Dermatitis, Bacterial Infections, and Moretwahyuningsih_16No ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Superficial and Subcutaneous Mycoses IgnacioDocument2 pagesAssignment 2 Superficial and Subcutaneous Mycoses IgnacioManuel LimchuNo ratings yet
- Medical Microbiology Mycoses ClassificationDocument7 pagesMedical Microbiology Mycoses ClassificationAisha Nur Ashri WidyaNo ratings yet
- MycosisDocument3 pagesMycosisMartin Ponce de León100% (1)
- Plants Used To Treat Skin Diseases - ReviewDocument9 pagesPlants Used To Treat Skin Diseases - ReviewPsicólogo Clinico clinicoNo ratings yet
- KAYE ROJAS Skin Infection BSN 1 Y2 3Document10 pagesKAYE ROJAS Skin Infection BSN 1 Y2 3HERLIN HOBAYANNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Disease of The SkinDocument54 pagesBacterial Disease of The SkinsalmaNo ratings yet
- Fungal InfectionsDocument29 pagesFungal InfectionsKaran MassNo ratings yet
- Day 9 Mycology & Applied January 2021Document338 pagesDay 9 Mycology & Applied January 2021ShriefElghazalyNo ratings yet
- Pathogens that Invade SkinDocument6 pagesPathogens that Invade SkinKarla Karina Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Skin Infections GuideDocument37 pagesBacterial Skin Infections GuideAngelie PedregosaNo ratings yet
- Clase IiiDocument4 pagesClase IiiVictoria FloresNo ratings yet
- Cutaneous and Subcataneous MycosesmDocument15 pagesCutaneous and Subcataneous MycosesmMaxamed Faarax XaashiNo ratings yet
- RingwormDocument7 pagesRingwormSAMSON, MAXZENE ANICKANo ratings yet
- Bacterial and Viral Skin Diseases: Classification and Causative AgentsDocument14 pagesBacterial and Viral Skin Diseases: Classification and Causative Agentsleticia floresNo ratings yet
- Integumentary DisorderDocument6 pagesIntegumentary Disorderhxqf25mbvvNo ratings yet
- Microbial Diseases of The SkinDocument6 pagesMicrobial Diseases of The SkinIza FaboresNo ratings yet
- Fungal Infections: Authored by Dr. Coleman RotsteinDocument3 pagesFungal Infections: Authored by Dr. Coleman RotsteinDavid Restu Prasetia ManikNo ratings yet
- Infectious Dermatosis (Bacterial Skin Infections)Document31 pagesInfectious Dermatosis (Bacterial Skin Infections)Melch PintacNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Fungal Infections: Gary GarberDocument2 pagesAn Overview of Fungal Infections: Gary GarberSUBHADIPNo ratings yet
- 15 Pathogenic FungiDocument8 pages15 Pathogenic FungiSathish KumarNo ratings yet
- Mycotic InfectionDocument22 pagesMycotic InfectionDevanshi Kulkarni100% (1)
- Skin and Eye InfectionsDocument2 pagesSkin and Eye InfectionsEriQuitaraNo ratings yet
- Plants Used to Treat Skin DiseasesDocument14 pagesPlants Used to Treat Skin DiseasesI PNo ratings yet
- Superficial MycosisDocument17 pagesSuperficial Mycosisapi-19969058100% (1)
- MycosesDocument28 pagesMycosesAiman TymerNo ratings yet
- Tinea Corporis, Tinea Cruris, Tinea Nigra, and Piedra: Dermatologic Clinics August 2003Document7 pagesTinea Corporis, Tinea Cruris, Tinea Nigra, and Piedra: Dermatologic Clinics August 2003Dicky KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Fungi & Systemic MycosesDocument42 pagesFungi & Systemic MycosesariffdrNo ratings yet
- M13 - Dermatology - Chapter 5Document11 pagesM13 - Dermatology - Chapter 5Idham BaharudinNo ratings yet
- 03 Cutaneous MycosesDocument30 pages03 Cutaneous MycosesFelix AyornuNo ratings yet
- L2 14 Feb 2012 Mycoses Generalities and ClassificationDocument18 pagesL2 14 Feb 2012 Mycoses Generalities and ClassificationSafe GuardNo ratings yet
- Master Plan Onn Skin DisordersDocument5 pagesMaster Plan Onn Skin DisordersSakthi DeviNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Superficial Cutaneous Mycosis HandoutsDocument8 pagesLesson 2 Superficial Cutaneous Mycosis HandoutsKhay Mae DonascoNo ratings yet
- What Is Subcutaneous MycosesDocument4 pagesWhat Is Subcutaneous MycosesArslan SaeedNo ratings yet
- Skin and Soft Tissue InfectionsDocument8 pagesSkin and Soft Tissue InfectionsMARTIN REY EDRICK SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Fungal MicrobiologyDocument10 pagesFungal MicrobiologyGrace joy DoocNo ratings yet
- Distribution of Fungi Diseases in Hot Climate ConditionsDocument4 pagesDistribution of Fungi Diseases in Hot Climate ConditionsCentral Asian StudiesNo ratings yet
- What is a skin infection? Types, causes, symptoms and treatmentsDocument42 pagesWhat is a skin infection? Types, causes, symptoms and treatmentsKathleen Daban RagudoNo ratings yet
- AdrianDocument3 pagesAdrianJohn David ZabalaNo ratings yet
- Review On Mucormycosis Black FungusDocument3 pagesReview On Mucormycosis Black FungusInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- IKD2-K11 - Mikosis Superfisialis, Mikosis Sistemik Dan Mikosis OportunistikDocument64 pagesIKD2-K11 - Mikosis Superfisialis, Mikosis Sistemik Dan Mikosis OportunistikHalseyNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Disorders of The Integumentary SystemDocument70 pagesPediatric Disorders of The Integumentary SystemJezreel OrquinaNo ratings yet
- Topical Treatment of Common Superficial Tinea InfectionsDocument8 pagesTopical Treatment of Common Superficial Tinea InfectionsColate LocoNo ratings yet
- Fungal InfectionsDocument5 pagesFungal InfectionsSpurgeNo ratings yet
- CryoglobulinsDocument39 pagesCryoglobulinsanamariavNo ratings yet
- 150 Science Essay Topic IdeasDocument9 pages150 Science Essay Topic IdeasJan MarcNo ratings yet
- IBWDocument5 pagesIBWDedik KurniawanNo ratings yet
- A Laboratory based study on the Larvicidal effects of Aquatain, a Monomolecular Film and Mousticide™ [Trypsin Modulating Oostatic Factor [TMOF-Bti] formulation for the control of Aedes albopictus (Skuse) and Culex quinquefasciatus Say in PakistanDocument6 pagesA Laboratory based study on the Larvicidal effects of Aquatain, a Monomolecular Film and Mousticide™ [Trypsin Modulating Oostatic Factor [TMOF-Bti] formulation for the control of Aedes albopictus (Skuse) and Culex quinquefasciatus Say in PakistanRizwan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Tooth Morphology and Access Cavity PreparationDocument232 pagesTooth Morphology and Access Cavity Preparationusmanhameed8467% (3)
- Radiologic Technologist Licensure Examination Results March 9 2022Document2 pagesRadiologic Technologist Licensure Examination Results March 9 2022RapplerNo ratings yet
- Arctium LappaDocument2 pagesArctium LappaIkkasama NaguenneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document34 pagesChapter 7Hima AlqahtaniNo ratings yet
- JAIPUR Artificial LIMBS-Social EntrepreneurshipDocument8 pagesJAIPUR Artificial LIMBS-Social Entrepreneurshipeapen123No ratings yet
- Soal Uas B.ing Kelas XiDocument5 pagesSoal Uas B.ing Kelas XiDepi UmarNo ratings yet
- Learning To Manage Health Information: A Theme For Clinical EducationDocument48 pagesLearning To Manage Health Information: A Theme For Clinical EducationPatients Know Best100% (2)
- MMDST AdministrationDocument2 pagesMMDST Administrationvera_pamil08No ratings yet
- Medical Practitioners 23-FEB-2012Document12 pagesMedical Practitioners 23-FEB-2012Next PersonNo ratings yet
- Good Compounding PracticeDocument5 pagesGood Compounding PracticeRasselle BalangiNo ratings yet
- Obat KosongDocument5 pagesObat KosongMarselina FetraNo ratings yet
- PMAD PresentationDocument17 pagesPMAD PresentationBrittany100% (1)
- Review Article Review Article Review Article: Article Info Article Info Article InfoDocument8 pagesReview Article Review Article Review Article: Article Info Article Info Article InfoAtef AlbooqNo ratings yet
- AIRWAY ManagementDocument5 pagesAIRWAY ManagementVijay MgNo ratings yet
- 10 G Elevators Awls and Bone Hooks PDFDocument24 pages10 G Elevators Awls and Bone Hooks PDFEduardo BernardinoNo ratings yet
- Acute CervicitisDocument9 pagesAcute CervicitisVicobeingoNo ratings yet
- Alergi Penisilin PDFDocument6 pagesAlergi Penisilin PDFShaffa Aprilia Amanda PutriNo ratings yet
- Echo-Screen Reference GuideDocument92 pagesEcho-Screen Reference Guideanasrl2006100% (3)






































































![A Laboratory based study on the Larvicidal effects of Aquatain, a Monomolecular Film and Mousticide™ [Trypsin Modulating Oostatic Factor [TMOF-Bti] formulation for the control of Aedes albopictus (Skuse) and Culex quinquefasciatus Say in Pakistan](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/362668767/149x198/6b2579b410/1509011381?v=1)

















