Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson Planning-EMD-I July 2019
Uploaded by
Hrithik SharmaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson Planning-EMD-I July 2019
Uploaded by
Hrithik SharmaCopyright:
Available Formats
PANDIT DEENDAYAL PETROLEUM UNIVERSITY
SCHOOL OF TECHNOLOGY
B. TECH. (ELECTRICAL ENGG.), SEMESTER - VII, July 2019
ELECTRICAL MACHINE DESIGN-I (19EE401T)
LESSON PLANNING
Sr. Topics Hours
No.
1. BASIC CONSIDERATION IN ELECTRICAL MACHINE DESIGN (06)
1.1 • Introduction 02
• Design factors, limitations in design
• Modern trends in design of electrical machines
1.2 Conducting materials, Magnetic materials, Insulating materials and its 02
classification.
1.3 Temperature rise, Expression for temperature rise, heating and cooling time 01
constants, examples.
1.4 Types of duties and ratings, Selection of motor capacity 01
2 DESIGN OF DIRECT CURRENT MACHINES (16)
2.1 Specifications, Main Dimensions, Total Loadings 01
2.2 Specific Loadings, Output equation, Choice of Specific Magnetic and 02
Electrical Loading
2.3 Factors affecting size of machines, Seperation of Dand L, Selection of number of 02
poles, examples
2.4 Core length, armature diameter, pole proportions and profile, Number of 02
ventilacting ducts
2.5 Length of air gap, Estimation of Length of air gap, examples. 01
2.6 ARMATURE DESIGN: 03
Number of armature conductiors, size of armature conductors, choice of
armature winding, Number of armature slots, number of ventilating
ducts, Slot dimensions, Depth of armature core, resistance of armature
winding, copper losses in armature winding, examples.
2.7 Design of Yoke, Magnetic circuit 01
2.8 Design of field system, Design of shunt and series field winding, 02
examples.
2.9 Design of Interpoles, Design of Commutator and Brushes, examples. 02
3 WINDINGS OF ELECTRICAL MACHINES (10)
3.1 D.C. Armature Windings: Terms related to armature winding, single layer 02
and double layer windings, open and closed winding
3.2 Types of d.c. armature winding: Simplex lap and wave winding, winding 01
pitches
3.3 Dummy coils, equalizer connections 01
3.4 Winding table, sequence and developed diagram of simplex lap and wave 02
winding, Design Problems
3.5 A.C. armature windings: Number of phases and phase spread, 01
classification of ac winding,
3.6 Single layer windings: Concentric winding, Mush winding 01
3.7 Double layer windings: 02
1
• Integral slot winding
• Fractional slot winding
4. DESIGN OF TRANSFORMERS (20)
4.1 Types of Transformers, Specifications, Output equation 02
4.2 Relation between EMF per turn and transformer rating 01
4.3 Stacking factor, Ratio of iron loss to copper loss, Relation between core 01
area and weight of iron and copper
4.4 Choice of design parameters: flux density, current density and window 02
space factor
4.5 Design of core, window dimensions 02
4.6 Design of yoke, Overall dimensions, examples 02
4.7 Types of transformer windings, Design of high voltage and low voltage 02
winding, examples.
4.8 Estimation of operating characteristics: Primary and Secondary 02
resistance, Leakage reactance of windings, Regulation, examples.
4.9 Mechanical forces, No load current calculation 02
4.10 Temperature rise of transformer, Design of tank, examples 02
4.11 Design of Current Transformer: Introduction, construction, design 02
principles, turns compensation.
Approximate Total Hours 52
Text Books and References
1. A course in Electrical machine design by A. K. Sawhney, Dhanpat Rai & Co.
2. Design of electrical machines by V.N.Mittal & A.Mittal, Standard Publishers distributors
3. The performance and design of alternating current machines by M. G. Say, CBS
Publishers & Distributors
4. K. G. Upadhyay, “Design of electrical machines”, New age international publishers.
5. Juha Pyrhonen, Tapani Jokinen, Valeria Hrabovsova, “Design of rotating electrical
machines” Wiley publication.
6. J. G. Jamnani, “Elements of electrical design’ 6th Edition, Mahajan publishing
house.
Faculty/Course Coordinator: Dr. Jitendra G. Jamnani
Teaching and Examination Scheme:
19EE401T Electrical Machine Design-I
Teaching Scheme Examination Scheme
Theory Practical
Hrs/ Total
L T P C LE/
Week MS ES IA LW Marks
Viva
4 - - 4 4 25 50 25 - - 100
You might also like
- Electrical Interview Question PDFDocument22 pagesElectrical Interview Question PDFGopi Srikanth VegiNo ratings yet
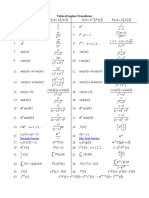
- Laplace Table PDFDocument2 pagesLaplace Table PDFHrithik SharmaNo ratings yet
- Exercise No. 7 Code For Studying Different Characterstics of Shunt DC MotorDocument2 pagesExercise No. 7 Code For Studying Different Characterstics of Shunt DC MotorHrithik SharmaNo ratings yet
- New Doc 2019-09-04 23.09.34Document2 pagesNew Doc 2019-09-04 23.09.34Hrithik SharmaNo ratings yet
- Motion Control For Advanced MechatronicsDocument12 pagesMotion Control For Advanced MechatronicsHrithik SharmaNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Planning For Procurement of Construction ContractsDocument41 pagesPlanning For Procurement of Construction ContractsJoel AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- TTO-ST-0-SPC-05100 - Structural Steel SpecificationDocument18 pagesTTO-ST-0-SPC-05100 - Structural Steel Specificationsara saravananNo ratings yet
- Metrolla Steels Industrial Visit ReportDocument39 pagesMetrolla Steels Industrial Visit ReportSanjay R Nair100% (1)
- Valve PagesDocument5 pagesValve PagesJoyal ThomasNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1: Drive Fundamentals: (4 Marks)Document1 pageAssignment 1: Drive Fundamentals: (4 Marks)kd35No ratings yet
- Pic Attack1Document13 pagesPic Attack1celiaescaNo ratings yet
- DP Misc Wnt5 x86-32 ChangelogDocument5 pagesDP Misc Wnt5 x86-32 ChangelogBrandal KalocyNo ratings yet
- Fuel Consumption Hyster Rev3Document7 pagesFuel Consumption Hyster Rev3crash2804No ratings yet
- 24 - Article - $mbps Vs $MHZ Why Is This ImportantDocument2 pages24 - Article - $mbps Vs $MHZ Why Is This ImportantShiraz SiddiqNo ratings yet
- Shell Spirax S6 Txme: Performance, Features & BenefitsDocument2 pagesShell Spirax S6 Txme: Performance, Features & BenefitsAbdelhadi HoussinNo ratings yet
- B200S-LF Low Freq Sounder Base Install 56-4151-003R-06-10Document4 pagesB200S-LF Low Freq Sounder Base Install 56-4151-003R-06-10George P ReynoldsNo ratings yet
- Excel ExercisesDocument37 pagesExcel ExercisesBERNIELLE DAVE FALDASNo ratings yet
- 90203-1104DEC E Cont Operations PDFDocument414 pages90203-1104DEC E Cont Operations PDFelmacuarro5No ratings yet
- Creeping Flow Near A Rotating Sphere PDFDocument10 pagesCreeping Flow Near A Rotating Sphere PDFne gerek var anonimNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Control of Side Face Beam Cracking - FroschDocument10 pagesModeling and Control of Side Face Beam Cracking - FroschphamminhquangNo ratings yet
- Epanet Vs Watergems (083011)Document9 pagesEpanet Vs Watergems (083011)MABA02100% (1)
- 1.ar-315 BC&BL Lighting & IlluminationDocument28 pages1.ar-315 BC&BL Lighting & IlluminationUsha Sri GNo ratings yet
- Hot Work ProcedureDocument10 pagesHot Work ProcedureOws AnishNo ratings yet
- OurLocalExpert Exeter 2013-14Document15 pagesOurLocalExpert Exeter 2013-14Nick HallNo ratings yet
- Westfalia Cycle CarrierDocument20 pagesWestfalia Cycle CarrierBarry John FitzGeradNo ratings yet
- New Premium ListDocument10 pagesNew Premium ListAshwani SainiNo ratings yet
- DATA SHEET Industrial Enamel BlancoDocument4 pagesDATA SHEET Industrial Enamel BlancoAlfredo OrellanaNo ratings yet
- Drive Test AnalysisDocument47 pagesDrive Test Analysis3a9aNo ratings yet
- Yale PD2, C85, D85Document28 pagesYale PD2, C85, D85LGWILDCAT73No ratings yet
- Case Adhesives BrochureDocument6 pagesCase Adhesives BrochureChanakyaNo ratings yet
- Call To Order: Pledge of AllegianceDocument269 pagesCall To Order: Pledge of AllegianceBrookhaven PostNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet For Toys TestDocument2 pagesData Sheet For Toys TestAnonymous TYGiADNo ratings yet
- Operating Systems: Credits: 4 Credits Course Coordinator: V.V.SubrahmanyamDocument4 pagesOperating Systems: Credits: 4 Credits Course Coordinator: V.V.SubrahmanyamHarendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Scaffolding Price ListDocument7 pagesScaffolding Price ListAl Patrick Dela CalzadaNo ratings yet
- How To Use Volatility - v2Document65 pagesHow To Use Volatility - v2John SedoskiNo ratings yet