Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Conservation of Momentum
Uploaded by
zendamariesabinay0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
76 views9 pagesmomentum
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentmomentum
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
76 views9 pagesConservation of Momentum
Uploaded by
zendamariesabinaymomentum
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 9
“The total Momentum of a
system before and after
collision does not change if
there are no external forces
acting on it”.
Types of Collision:
1. Elastic Collision
Two objects collide and return
to their original shapes with no
change in kinetic energy. After
collision, the two objects move
separately.
2. Inelastic Collision
The two objects deform during
collision, and the total kinetic
energy decreases, but the
objects move separately after
the collision.
3. Perfectly Inelastic
The two objects stick together
and move with a common
velocity after the collision.
Both objects are deformed.
’ ’
m1v1 + m2v2 = m v + m v
1 1 2 2
where:
m1= mass of the 1 object
st
m2= mass of the 2 object
nd
v1= velocity before collision of
st
the 1 object
v2= velocity before collision of
nd
the 2 object
’
v1 = velocity after collision of
st
the 1 object
’
v2 = velocity after collision of
nd
the 2 object
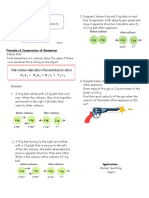
2. A 0.02 kg ball moving to the right
at 0.25m/s makes an elastic head-on
collision with the second ball of
0.04kg moving to the left at 0.15
m/s. After the collision, the smaller
ball moves to the left at 0.16m/s.
What is the velocity of the second
ball after collision?
3. A 0.25kg arrow with a velocity
of 15 m/s to the east strikes and
pierces the bull’s-eye of a
70kg target. What is the final
velocity of the combined mass?
You might also like
- Impulse and MomentumDocument2 pagesImpulse and MomentumRoriel Hernandez BenamirNo ratings yet
- RUBRIC Math Problem SolvingDocument2 pagesRUBRIC Math Problem SolvingYvonne Pearl Delos Santos100% (2)
- Law of Conservation of MomentumDocument32 pagesLaw of Conservation of MomentumZaira JallorinaNo ratings yet
- Collisions WorksheetDocument3 pagesCollisions WorksheetjessicaNo ratings yet
- CollisionDocument3 pagesCollisionbernardNo ratings yet
- Inertia and Momentu GroupDocument10 pagesInertia and Momentu GroupayydenNo ratings yet
- Module 4-Mechanics: CollisionsDocument32 pagesModule 4-Mechanics: CollisionsHead LightNo ratings yet
- Science Grade9 Q4 LP4Document8 pagesScience Grade9 Q4 LP4Marian GalosoNo ratings yet
- Class - XI - ch-6, Work Energy Power, Module 5Document14 pagesClass - XI - ch-6, Work Energy Power, Module 5Sayan MajiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5&6Document24 pagesChapter 5&6Junyi JiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 - Physics For Engineers 1Document77 pagesLesson 7 - Physics For Engineers 1Norman AcainNo ratings yet
- MomentumDocument18 pagesMomentumpalicpicantorearichNo ratings yet
- Conservation of MomentumDocument16 pagesConservation of Momentum황동현No ratings yet
- Physical Science Chapter 2Document4 pagesPhysical Science Chapter 2Nurhanifa MustafaNo ratings yet
- Presentation - Elastic CollisionDocument10 pagesPresentation - Elastic CollisionPaul Jacob InfanteNo ratings yet
- Moment VectorDocument9 pagesMoment VectorGlen GulayNo ratings yet
- Divesh Jaiswal (P) - 1Document8 pagesDivesh Jaiswal (P) - 1Youtube ki GamingNo ratings yet
- AP Phys1 Momentum Skill Based Problems 2023-10-28Document13 pagesAP Phys1 Momentum Skill Based Problems 2023-10-28whis2022No ratings yet
- Linear Momentum, Impulse, CollisionDocument19 pagesLinear Momentum, Impulse, CollisionrezaewewqewqeNo ratings yet
- 69Document5 pages69Josh Dominic TeleronNo ratings yet
- Collision of Two ObjectDocument6 pagesCollision of Two ObjectCarolina NainggolanNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Momentum and COLLISIONDocument23 pagesConservation of Momentum and COLLISIONMarisa Jane RamelNo ratings yet
- Collisions: Before During AfterDocument18 pagesCollisions: Before During AfterKrishna KishoreNo ratings yet
- Linear Momentum HonorsDocument44 pagesLinear Momentum HonorsDaniel MatarazzoNo ratings yet
- ND RDDocument25 pagesND RDsdfasdgNo ratings yet
- Elastic Collision With C++Document12 pagesElastic Collision With C++qud86No ratings yet
- Motion ReviewDocument3 pagesMotion ReviewNathan SandbergNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5 Work, EnergyDocument4 pagesAssignment 5 Work, EnergySrijan MalNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Linear Momentum 1Document19 pagesConservation of Linear Momentum 1Kella OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Momentum (Example)Document1 pageMomentum (Example)Norizan GhazaliNo ratings yet
- Ap Phys1 - Momentum Skill Based Problems - 2022 02 20Document14 pagesAp Phys1 - Momentum Skill Based Problems - 2022 02 20黃吏維No ratings yet
- Momentum and Impulse NotesDocument33 pagesMomentum and Impulse NotesEarlJaysonAlvaranNo ratings yet
- 2-D Collisions - Day 2Document2 pages2-D Collisions - Day 2Makenzie EakinsNo ratings yet
- Momentum and CollisionsDocument1 pageMomentum and CollisionsAidan Gabriele DrewNo ratings yet
- Law of Conservation MomentumDocument1 pageLaw of Conservation Momentumtrinitykaren999No ratings yet
- KCM Nchaga Secondary Trust School-As Physics Notes-2020: Definition of Linear Momentum MomentumDocument7 pagesKCM Nchaga Secondary Trust School-As Physics Notes-2020: Definition of Linear Momentum MomentumCartwright Ntahandi Nduwa ChipoyaNo ratings yet
- MomentumDocument23 pagesMomentumRonnel Ladac UseroNo ratings yet
- Weekly Exam 5Document102 pagesWeekly Exam 5JoeNo ratings yet
- 1.1.2 Speed and Velocity: Youtube VideoDocument39 pages1.1.2 Speed and Velocity: Youtube Videoام دانيالNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Impulse & MomentumDocument7 pagesModule 4 - Impulse & MomentumG02 - BALACANAO JHERICE A.No ratings yet
- 2.5 MomentumDocument1 page2.5 MomentumWAN NOOR AZILAH BT WAN UMAR MoeNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Conservation of MomentumDocument2 pagesWeek 4 Conservation of MomentumMeralyn Puaque BustamanteNo ratings yet
- Momentum and CollisionsDocument13 pagesMomentum and CollisionsImran TabakovićNo ratings yet
- Precalc 3Document28 pagesPrecalc 3ApichayaNo ratings yet
- Mass and InertiaDocument7 pagesMass and InertiaShafiqah AzuddinNo ratings yet
- Momentum 2.0Document29 pagesMomentum 2.0Esther SparksNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument6 pagesPhysicsmahamushtaha0No ratings yet
- COLLISIONSDocument16 pagesCOLLISIONSfiqih saadahNo ratings yet
- Mini PhyDocument22 pagesMini PhyMichael LeungNo ratings yet
- MomentumDocument40 pagesMomentumAdri versouisseNo ratings yet
- CHP 27Document19 pagesCHP 27Abhiram Reddy0% (1)
- Conservation of MomentumDocument19 pagesConservation of MomentumwscienceNo ratings yet
- MomentumDocument8 pagesMomentumapi-3806615No ratings yet
- Elastic Collision FormulaDocument5 pagesElastic Collision FormulaSheena AntonioNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4Document15 pagesLesson 4Ryan KoNo ratings yet
- Acceleration Due To Gravity ForcesDocument28 pagesAcceleration Due To Gravity Forcesfelipee20No ratings yet
- WEP Ws 002Document4 pagesWEP Ws 002JASBIR SINGHNo ratings yet
- PP ShmsDocument8 pagesPP ShmsFad HunterNo ratings yet
- CollisionDocument15 pagesCollisionFelipe Jr. AdolfoNo ratings yet
- Individual Learning Monitoring Plan TemplateDocument1 pageIndividual Learning Monitoring Plan TemplatezendamariesabinayNo ratings yet
- LDM2 Module 2 TrueDocument5 pagesLDM2 Module 2 TruezendamariesabinayNo ratings yet
- SIP JudgeDocument15 pagesSIP JudgezendamariesabinayNo ratings yet
- Edd Report PhiloDocument8 pagesEdd Report PhilozendamariesabinayNo ratings yet
- CoffeeDocument25 pagesCoffeevijay2623100% (20)
- RQA SportsDocument4 pagesRQA SportszendamariesabinayNo ratings yet
- Rqa - Sy2019 2020.Shs - AcademicDocument14 pagesRqa - Sy2019 2020.Shs - AcademiczendamariesabinayNo ratings yet
- Principles of Behavior Modification (PSY 333) : Gary L. Cates, PH.D., NCSPDocument86 pagesPrinciples of Behavior Modification (PSY 333) : Gary L. Cates, PH.D., NCSPsonypall3339No ratings yet
- Behavior Modification: January 1984Document17 pagesBehavior Modification: January 1984zendamariesabinayNo ratings yet
- WS03 - Behavior ModificationDocument17 pagesWS03 - Behavior ModificationAnonymous 7EpVWt1No ratings yet
- Using The Behavioral ApproachDocument16 pagesUsing The Behavioral ApproachpraatiNo ratings yet
- RecapDocument21 pagesRecapzendamariesabinayNo ratings yet
- RasmolDocument54 pagesRasmolzendamariesabinay100% (1)
- 1 DepED SHS Voucher ProgramDocument18 pages1 DepED SHS Voucher ProgramZenda Marie Facinal Sabinay100% (1)
- Edd Report P6 PE & ME Hand OutsDocument5 pagesEdd Report P6 PE & ME Hand OutszendamariesabinayNo ratings yet
- Taxonomic Nomenclature2Document18 pagesTaxonomic Nomenclature2zendamariesabinayNo ratings yet
- 1 DepED SHS Voucher ProgramDocument14 pages1 DepED SHS Voucher ProgramZenda Marie Facinal SabinayNo ratings yet
- Emcee - 1st Moving Up Ceremony 2016... THISDocument4 pagesEmcee - 1st Moving Up Ceremony 2016... THISzendamariesabinayNo ratings yet