Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Beneficial Insects and Their Value To Agriculture: GBPUA and T Pantnagar, USN, 263145, Uttarakhand, INDIA
Uploaded by
tariq mashalOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Beneficial Insects and Their Value To Agriculture: GBPUA and T Pantnagar, USN, 263145, Uttarakhand, INDIA
Uploaded by
tariq mashalCopyright:
Available Formats
Research Journal of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences __________________________________ ISSN 2320-6063
Vol. 3(5), 25-30, May (2015) Res. J. Agriculture and Forestry Sci.
Beneficial Insects and their Value to Agriculture
Getanjaly, Vijay Laxmi Rai, Preeti Sharma and Ranjit Kushwaha
GBPUA and T Pantnagar, USN, 263145, Uttarakhand, INDIA
Available online at: www.isca.in, www.isca.me
Received 13th February 2015, revised 19th March 2015, accepted 21th April 2015
Abstract
There are many insects found on agriculture land those are not threat to the crop production but beneficial to the farmers in
different aspects, as Natural enemies, Pollinators, productive insects, Scavengers, weed killer and Soil builders. In present
scenario the motive of the farmers is single sided, to gain only maximum profit, ignoring the impact on the beneficial insects,
environment and human health. Insecticide can be a important crop production tool to maximize yield but Heavy and
indiscriminate use of chemicals also exposes farmers to serious health risks, resulted in negative consequences for the insect
those are beneficial to the farmers. Fields shared by many beneficial insects, positively affect the crop yield so careful
decision should be taken to manage the insect pest and awareness among the farmers towards the beneficial insects.
Keywords: Beneficial insects, Crop production, Natural enemies.
Introduction flowering plants, including numerous cultivated plant species
i.e. Sunflower, Cucurbitaceous vegetables, Alfalfa, Coriander,
Beneficial insects provide regulating ecosystem services to Cardmom, Gingelly, Apple etc. Many crops depend on
agriculture such as Pollination and the natural regulation of pollination for seed production and fruit set to achieve good
plant pests. It aims to enhance insect-derived ecosystem services yield. Globally, an estimated 35% of crop production is a result
from a conservation perspective (i.e. enhancing beneficial of insect pollination.
insects in agricultural landscapes that provide ecosystem
services to crops. Human cultures and civilizations have been The Apis meliffera L. (European honey bee) is responsible for
maintained in countless ways through these beneficial insects, the pollination servicesin majority of crops. Non-Apis bees also
they regulate the pest population of many harmful pest species, are important pollinators of crops, especially for crops in which
produce natural products, and they also dispose the waste and honey bees are inefficient pollinators (e.g. alfalfa, squash). A
recycle the organic nutrients. It should be consider in Thought few non-Apis species are managed for crop pollination.
that how much we depend on them for our survival and what Examples of managed non-Apis species include bumble bees,
kind of life would be without insects. Bombus impatiens Cresson (Hymenoptera: Apidae) managed for
cranberry (Vaccinium spp.) and greenhouse tomato (Solanum
Requirements for Enhancing Beneficial Insects lycopersicum L.) pollination. Although bees are considered the
most effective insect-pollinator of most plant species, other
The generalized intensification of agriculture and the use of insects have been recognized for their contributions to
broad-spectrum pesticides decrease the diversity of natural pollination.
enemy populations and increase the likelihood of pest out
breaks. Indeed, pesticide use has been shown to be associated Flower visiting flies (Diptera) have been documented as
with a large decrease in natural pest control services. Thus, proficient pollinators of several crops including carrot (Dacus
enhancement of agro ecosystem appears to be one of the best carota L.), mustard (Brassica spp.), leek, (Allium
ways in which we can decrease the use of chemical pesticides ampeloprasum L.), and almond (Prunis dulcis).
for pest and disease control. And it will increase the
sustainability of crop production1. Weevil Elaeidobius kamerunicus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae)
plays great role in pollination of Oil palm. Fig wasps are
Role of Beneficial Insects As responsible for the pollination in both Smyra and Capri Fig
Pollinators: Insect pollinators are flower visiting Insects that Plantation2.
forage on flowering plants to obtain plant-provided food (nectar,
Natural Enemies: Insect predators and parasitoids that attack
pollen). Flower-visiting insects have the potential to transfer
and feed on other insects, particularly on insect pests of plants
male gametes (contained in pollen) to the female gametes while
are considered natural enemies. Through this type of feeding,
foraging, resulting in pollination. Insect-mediated pollination is
natural enemies contribute to a type of pest regulation referred
an essential step in reproduction for the majority of the world’s to as natural biological control. Natural enemies responsible
International Science Congress Association 25
Research Journal of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences _______________________________________________ ISSN 2320-6063
Vol. 3(5), 25-30, May (2015) Res. J. Agriculture and Forestry Sci.
nearby 33% of the natural pest control in cultivated systems. Trichogramma sp., xiii. Damselfly, xiv. Coccinella sp., xv.
Chrysoperla carnea.
Predaceous natural enemies belong to several insect orders and
are generally characterized as free-living, mobile, larger than Some Products from Beneficial Insects
their insect prey, and are able consume several preys throughout
their life cycle. But the parasitoids mainly belong to two orders Production if Honey and Bee Wax: From thousands of year
Hymenoptera and Diptera, and their host ranges are considered Apis meliffera L. (Honey bees) are important for gaining
to be more specialized than that of predator. Free-living adult Honey and bee wax. And honey was the only sweetener, viscous
parasitoids seek out a host, and depending on the parasitoid fluid, produced by honeybees. It is collected from nectar from
species, parasitize different life stages of their host (i.e. egg, nectories at base flowers. Also collected from nectar secreted by
larva, and pupa, adult). Parasitoids can lay an egg (solitary) or plant parts other than flowers known as extra floral nectories. It
several eggs (gregarious) on or within their host and the is also collected from fruit juice, cane juice etc. In present, the
immature parasitoid(s) feed on their host to complete developing markets are available for the other two products
development, kill their host, and emerge as free-living adult. In (Bee pollen and royal jelly) from honey. The bee pollen collect
agricultural landscapes, natural enemies have the potential to by pollen trap from ingoing pollen foragers. It is rich protein
prevent crop pests from reaching economically damaging levels source. Bee pollen is a "complete" and good supplement in diet.
(table-1). It is available in health food stores. The royal jelly is secreted
by gland of nurse bees when the glands are fully active. It is
Predators and parasitoids can suppress or delay pest population very nutritious food and is fed to the young workers larvae and
growth by contributing to pest mortality that is most vulnerable queen larvae and adult. Royal jelly is milky and light pale in
to herbivores. When diverse populations of natural enemies are color. And it is also a good ingredient of some expensive skin
present, pest control became more effective due to differing care products, which helps in reducing wrinkles and works as
phenology. anti aging.
Beyond natural biological control, natural enemies can be Production of Silk: A unique natural fiber silk cloth, which
manipulated as part of integrated pest management programs usually derives from silkworm, Bombyx mori. This "domestic"
through the importation and establishment of exotic natural silk is famous for its finishing and light colors. The silk can also
enemy species (classical biological control), direct manipulation harvest from the many other species e. i. Antherea spp., that
of populations (augmentative biological control), and, more found in the India, Japan and China’s forests. The silk provided
pertinent to this research, through manipulation of their by willed spp e.i. Eri, Muga, Tussah and Yamamai are heavier
environment (conservation biological control)3. and dark in color hence they are less valued than that of Bombyx
mori. Silk can be dyed, spun, in to thread and woven in to
Weed Killers: So many insects feed upon unwanted weeds just
fabric. Cloth of Silk is warm in winters, cool in summers, light
the same manner they do with the cultivated crops. In many
in weight, and resistant to wrinkling.
cases the occurrence of these insects has contributed much
towards eradication of the weeds.
Production of shellac: laccifer lacca, is a scale insect that
Soil Builders: Insects which live in soil make tunnels, creating secret a hard encrustation over the body as a protective
channels for smaller organisms, water, air, and roots to travel covering. It is of brown color usually and these insects grow on
through. Insects improves soil aeration, and earthworm activity acacia trees in India and Burma. Scale insects present on twigs
can enhance soil nutrient cycle, the soil physical properties, are heated to extract the resins and then purify. One gram of
such as soil structure and tilth and activity of other beneficial Lac is extracted from Up to 200 insects. In present the synthetic
soil organisms. Small Dung beetles makes tunnel walls with material such as Polyurethane and vinyl has been taken place of
dung and also make dung balls that helps in maintaining the Lac, even after Lac is still in use as dyes, inks, polishes, sealing
quality of the soil. Excreta of insets also enrich the soil. waxes, and as stiffening agents in the fabrication of felt hats. It
Examples- Beetles, Ants, Cut-worms, Larvae of flies, Crickets, is animal originated and commercial resin.
Termites, Wasps etc
Production of Cochineal: Cochineal pigments use in
Scavengers: Insects which feed on dead and decaying matter of Painting: A scale insect Dacylopius coccus found in Mexico
plants and animals are called as scavengers. Insects (scavengers and Central America on prickly pear cacti. Cochineal pigment is
and decomposers) help in the biochemical cycling of the extracted from these scale insects. For the first time it was used
nutrients. Examples: Bark beetle, water scavenger beetle, by Aztec Indians as medicines, body paints and as textile dye.
Termites, Ants etc4 The cochineal pigment was important for the intensity and
permanency of colors. It was very costly because of its scarcity,
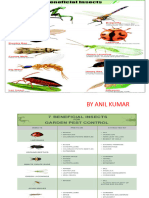
Some Beneficial Insects and Their Pictures: i. Honey bee, ii. so it was used in only the finest fabrics. Now a day’s aniline
Silk worm larvae, iii. Lac insect, iv. Assassin bug, v. Hover fly, dyes have taken place of Cochineal in textile industries which is
vi. Aphidius calamani, vii. Syrphid fly, viii. Zygogramma very economic. But the cochineal pigment is still giving the
bicolorata, ix. Termites, x. Dragon fly, xi. Praying mantis, xii. colors in foods, beverages, cosmetics (lipsticks) and art product.
International Science Congress Association 26
Research Journal of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences _______________________________________________ ISSN 2320-6063
Vol. 3(5), 25-30, May (2015) Res. J. Agriculture and Forestry Sci.
Table-1
Natural enemies and their use
Predator/
Group Beneficial insect or Invertebrate Pest attacked Impact on pest
Parasitod
Able to handle a wide range
Ladybirds (Family Coccinellidae), Red and Aphids, mites, thrips, of prey and are immediately
Beetles Blue beetles (Dicranolaius bellulus), Green mealybugs, moth eggs effective. Some species
Predators
(Coleopter) carab beetles (Calosoma schayeri), Green including Heliothis (e.g. ladybirds) both the
soldier beetles (Chauliognathus pulchellus) spp. and larvae. adult and larvae are
predatory.
Assassin bugs (Family Reduviidae),
Bigeyed bugs (Geocoris lubra), brown
Aphids, Diamondback Pierces pest using
smudge bugs (Deraeocoris signatus),
moth, eggs of and mouthparts and then sucks
Damsel bugs (Nabis kingbergii), glossy
Bugs larvae of Heliothis out interior. Depending on
Predators shield bug (Cermatulus nasalis), Pirate bug
(Hemiptera) spp., cutworms the species of predatory
(Orius spp.), Apple dimple bug
(Spodoptera litura), bug, adults, larvae or eggs
(Campylomma liebknectic), Spined
false loopers may be attacked.
predatory shield bug (Oechalia), Broken
backed bug (Taylorilygus pallidulus)
Larvae spear aphids with
Predatory jaws and suckout internal
Predators Hoverfly larvae (Family Syrphidae), Aphids
Larvae juices. Adult hoverfly are
not predacious.
Predatory mites from different Families- Blue Oat mite, Predacious on other mite
Mites
Predators e.g. Anystidae, Bdellidae, Erythraeida, Lucerne flea, Red- species and Lucerne fleas
(Acarina)
Parasitidae and Cunaxidae legged earth mite, (Sminthurus viridis)
Larvae insert jaws into soft-
bodies insects and eggs and
Aphids, moth larvae
suck out contents. Larvae of
Green (Mallada signatus) and brown and eggs, whitefly,
Predators Lacewings both Brown and green
(Micromus tasmaniae) Lacewings thrips, mites and
lacewings are predatory.
mealybugs.
Adult brown lacewings feed
on heliothis eggs and mites.
Variety of species including wolfspiders,
nightstalking spiders, orbweavers, tangle Predators or a range of
Predators Spiders Pest species are consumed.
web spiders, flower spiders, jumping insect pests.
spiders and lynx spiders.
Wasp inserts egg into aphid.
The developing larvae
Aphid Trioxys Complanatus, Aphidius ervi,
Parasitoids Aphids eventually killing the aphid
Parasitoids Lysiphlebus testaceipes, Aphidius colemani
"mummy" as the adult wasp
emerges.
Hymenoptera: Numerous parasitic wasps
including Banded caterpillar parasite Female lays eggs in host
(Ichneumon promissorius), Two-toned pupae as the parisitoid
Caterpillar Heliothis and other
Parasitoids caterpillar parasite (Heteropelma scaposum) larvae develop in the host it
Parasitoids moth larvae
(Family Ichneumonidae), Microplitis causes the death of the
demolitor, Cotesia spp. (Family pupa.
Braconidae)
Sorghum midge parasites (Eupelmus Wasp lays eggs in midge
Caterpillar
Parasitoids australiensis, Aprostocetus diplosidis, Sorghum midge larvae and emerges at pupal
Parasitoids
Tetrastichus spp.) stage.
Female lays eggs in host
Heliothis, looper,
pupae as the parisitoid
Caterpillar armyworm,
Parasitoids Tachinid flies larvae develop in the host it
Parasitoids grasshopper and other
causes the death of the
larvae
pupa.
International Science Congress Association 27
Research Journal of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences _______________________________________________ ISSN 2320-6063
Vol. 3(5), 25-30, May (2015) Res. J. Agriculture and Forestry Sci.
Helicoverpa Hymenoptera: Trichogramma (Family
Helicoverpa and other Tiny wasps that parasitise
Parasitoids Egg Trichogrammatidae) and Telenomus
Lepidoptera Lepidopteran
parasitoids (Family Scelionidae) egg parasitoids
Whitefly Eretmocerus spp. and Encarsia spp. Small parasitoid wasps that
Parasitoids Whitefly
Parasitoids including Encarsia Formosa attack whitefly nymphs.
Small black wasp that
parasitises GVB; doesn’t
GVB egg distinguish between eggs of
Parasitoids Trissolcus basalis Green vegetable bug
Parasitoids pests and beneficials and
will also parasitise eggs of
predatory shield bugs.
Table-2 Skin diseases5.
Weed Killers Table-3
Biotic agent / Some insects and their products as medicine
Weed Scientific name
insects Insects / insect Uses
Dactylopius products
Prickly pear Opuntia dilleni
opuntiee Maggots Wounds Healing
Congress grass Parthenium Zygogramma Honey Wounds Healing, skin disease,
or Carrot weed hysterophorus bicolorata infection
Lantana weed Lantana camara Ophiomyia lantanae Royal-jelly Post Menopausal symptoms
Choromoloena Pariuchaetes Been and Ant venom Joints pain
Siam weed
odorata pseudoinsulata Propolis Infection
Cryptobagus Canthiridine Skin Diseases
Water fern Salvinia molesta
singularis
Garden attracts many beneficial insects: The larva of many
Production of Tannic Acid: Tannic acid first produced by an beneficial insect predators e.g. Predators such as hover flies,
abnormal pant growth found on oak trees in Asia known as lacewings, lady beetle, and parasitic wasps feed on large
Allepo gall. Tiny wasps (Family Cynipidae) secrete some number of harmful insect pests. But adult of these feed on
chemical and in response of it the tree produces gall tissues. pollen and nectar. Provide adults with food and habitat in your
Tannic acid is a chemical compound used in the dying, in garden with a variety of plants will encourage the production of
leather industries, for tanning and in the manufacture of some all life stages of insect predators and will help in reducing
inks. It can also be extracted economically from Quebracho tree, undesirable insect pests naturally.
hence there is no commercial market for oak gall is present
today. Variety of plantings can be create to provide habitat and food
for different insect species and life stages- eggs, larvae, pupa
Insects as Food: Human ancestors were used to get nutrition and adults. Many small flower plants including yarrow,
from Insects. Even today, the insects are being used by people sunflower, alyssum, asters, cosmos, mints, lobelia, basil,
as food in many countries. High in protein and low in fat dried stonecrops, thyme, parsley, dill, borage and many other herbs
grasshopper are sold in village markets of Mexico. Insects are are preferable. In garden eco-system natural predator consume
mixed with flour to make tortillas and can be fried or ground their food from pests present. Pesticides kill many beneficial
into meal. Wood-boring beetle’s larvae can be boiled or roasted
insects. So Eliminating use of pesticide encourage beneficial
over a fire. And there is long list of nutritive edible insects e.g.
insects6-8.
Ants, bees, termites, water grubs, caterpillars, flies, crickets,
katydids, beetle larvae, and nymphs of dragon fly are among the
list. And in Thailand the pupa of silkworm are used as food for Additional Highly Attractive Plants: Aster family plants,
human being. Cosmos, zinnia, small sun flowers, daisy coneflower, Bok choy,
cabbage, mustard, broccoli, and radish allowed to flower, Many
herbs are allowed e.g. Lavender, Chamomile, rosemary, basil,
Insects as Medicines borage, horehound. Some Mints- pennyroyal, bergamot, wood
Since ancient times Insects derived products have been widely
betony, thyme, Carrot family plants: angelica, coriander,
used in medicines (table-3). Maggots and honey showed healing
parsley, dill, fennel, anise. Sage family plants – scarlet sage,
property in chronic and post surgical wounds. And honey is also
being used to treat burns and combining with bee wax it found Cleveland sage. Pea family plants: Vetch, clover. Buck wheat.
curative for the dermatological disorders. Another product of Fern leaf yarrow and other yarrows. Allium tanguticum,
honey is royal jelly is used to treat post menopausal symptoms. lavender globe lily. Achillea filipendulina, common yarrow.
A derivative of blister beetle Cantharidin being used in treating Aster sp., asters (sun, low growing)
International Science Congress Association 28
Research Journal of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences _______________________________________________ ISSN 2320-6063
Vol. 3(5), 25-30, May (2015) Res. J. Agriculture and Forestry Sci.
1 2. 3
4 5. 6
7 8. 9
10 11 12
13 14 15
Figure-1
Some Beneficial Insects
Conclusion
International Science Congress Association 29
Research Journal of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences _______________________________________________ ISSN 2320-6063
Vol. 3(5), 25-30, May (2015) Res. J. Agriculture and Forestry Sci.
Above description shows the economic importance and use of 3. Pickett C.H. and Bugg R.L., Enhancing biological
beneficial insects. Lack of awareness among the farmers about control: habitat management to promote natural enemies
these insects and their benefits they use different management of agricultural pests, Berkeley, CA: University of
practices to kill them along with the insect-pests. We should California Press, 421 (1998)
have broad principles for supporting the beneficial insects and
4. Ross H. H., Ross C.A. and Ross J. R., A Textbook of
more specific management practices. Training and program
Entomology, John Wiley and Sons, New York, NY,
should be run for the awareness among the farmers about the
figure-3, 611, figure-7, 609, figure-11, 618 (1982)
beneficial insects and activities likely to harm them, limited use
of broad spectrum insecticides, habitat conservation in the form 5. Eraldo Medeiros and Costa. Neto., Entomotherapy, or the
of larger patches of remnant vegetation for their survival. Better Medicinal Use of Insects, J. of Ethnobiol., 25(1), 93-114
understanding of the benefits can make conservation more (2005)
effective and more harmonious land use with effective crop 6. Cicero K., Making a home for beneficial insects, The
production. New Farm, February, 28-33 (1993)
7. Colley M.R. and Luna J.M., Relative attractiveness of
References
potential beneficial insectary plants to aphidophagous
1. Metcalf C.L. and Flint W.P., Destructive and Useful hoverflies, Environ. Entomol., (29), 1054-1059 (2000)
Insects. McGraw-Hill Co., New York., (9), 67 (1962) 8. Jones G.A. and Gillett J.L., Intercropping with
2. Hilton Pond Center, The importance of pollinators, sunflowers to attract beneficial insects in organic
http://www.hiltonpond.org/ This Week 031008.html agriculture, Florida Entomologist., (88), 91-96 (2005)
(2003)
International Science Congress Association 30
You might also like
- PEST AND DISEASES MANAGEMENT (Autosaved)Document44 pagesPEST AND DISEASES MANAGEMENT (Autosaved)Yeoj Secnarev100% (1)
- Biological PestsDocument13 pagesBiological PestsShubham SinghNo ratings yet
- Helpful Insects, Spiders and PathogensDocument138 pagesHelpful Insects, Spiders and PathogensAnonymous HXLczq3100% (1)
- Beneficial Organims For The Garden BCDocument11 pagesBeneficial Organims For The Garden BCapi-612420481No ratings yet
- Fangamas Con PajeDocument235 pagesFangamas Con PajeTuhaf LotaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Crop Protection Hand-OutsDocument21 pagesAdvanced Crop Protection Hand-OutsDaphne Cuaresma100% (1)
- Organic COncoctions ManualDocument25 pagesOrganic COncoctions ManualRanya Esmail SandiganNo ratings yet
- Research Report - Zero Budget Natural Farming (Draft)Document43 pagesResearch Report - Zero Budget Natural Farming (Draft)Thashkent PaikadaNo ratings yet
- Manual Amazone D8-30Document132 pagesManual Amazone D8-30Hernán Arandilla Álvarez67% (3)
- Mc1 ReviewerDocument29 pagesMc1 ReviewerHarvy HermosoNo ratings yet
- Importance of InsectsDocument7 pagesImportance of InsectsMol maharjanNo ratings yet
- RT Vol. 11, No. 1 Grain of TruthDocument1 pageRT Vol. 11, No. 1 Grain of TruthRice TodayNo ratings yet
- 2018 Ag 8576 (Tahir Musharraf)Document4 pages2018 Ag 8576 (Tahir Musharraf)Abdullah UzairNo ratings yet
- Economiczoology 170604183247Document142 pagesEconomiczoology 170604183247aimaNo ratings yet
- Economiczoology 170604183247Document142 pagesEconomiczoology 170604183247yeateshwarriorNo ratings yet
- Theory Notes - Management of Beneficial InsectsDocument79 pagesTheory Notes - Management of Beneficial InsectsVIVEK SUTARNo ratings yet
- Beneficial Insects Play A Crucial Role in AgricultureDocument5 pagesBeneficial Insects Play A Crucial Role in AgricultureA.K ZOOLOGY CLASSESNo ratings yet
- BIOTIC Factors of AgricultureDocument46 pagesBIOTIC Factors of AgricultureMashrup HasanNo ratings yet
- Hans 2021Document10 pagesHans 2021MAambiental ambientalNo ratings yet
- Integrated Pest and Disease Management MethodsDocument6 pagesIntegrated Pest and Disease Management MethodsDeepankumar PNo ratings yet
- Agricultural entomology Note Unit 3Document20 pagesAgricultural entomology Note Unit 3AmitChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Pests & Control Methods in AgricultureDocument6 pagesPests & Control Methods in AgricultureAmal LalNo ratings yet
- Ento 365 NotesDocument79 pagesEnto 365 NotesSubbu ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Biological Control To Maintain Natural Densities of Insects and Mites by Field Releases of Lady Beetles (Coleoptera - Coccinellidae)Document7 pagesBiological Control To Maintain Natural Densities of Insects and Mites by Field Releases of Lady Beetles (Coleoptera - Coccinellidae)Juan Vera SanchezNo ratings yet
- Beneficial InsectsDocument16 pagesBeneficial InsectsA.K ZOOLOGY CLASSESNo ratings yet
- Entomology ENTO-365-PRINTED-NOTESDocument81 pagesEntomology ENTO-365-PRINTED-NOTESSakshi SargarNo ratings yet
- CB 1. Fonseca Et Al.Document6 pagesCB 1. Fonseca Et Al.Maria NaudeauNo ratings yet
- Pest Management MethodsDocument7 pagesPest Management MethodsRenalyn OrioNo ratings yet
- How to manage weeds for benefits in farmingDocument25 pagesHow to manage weeds for benefits in farmingMallinath HemadiNo ratings yet
- Bio-Efficacy of Biopesticides and Botanicals On Rugose Spiralling WhiteflyDocument3 pagesBio-Efficacy of Biopesticides and Botanicals On Rugose Spiralling Whiteflykaviya sNo ratings yet
- Organic Approved PesticidesDocument20 pagesOrganic Approved PesticidesIbrahim IbbuNo ratings yet
- SER-UW Beneficial Insectary Design Potoshnik 2018Document13 pagesSER-UW Beneficial Insectary Design Potoshnik 2018Paradayil KiranNo ratings yet
- Beneficial Insects Impacted by PesticidesDocument24 pagesBeneficial Insects Impacted by PesticidesWajahat MalikNo ratings yet
- Credit Seminar1Document45 pagesCredit Seminar1Janardan SaikiaNo ratings yet
- AphidsDocument3 pagesAphidsIza FaboresNo ratings yet
- Agro-Chemical ExamDocument14 pagesAgro-Chemical ExamFS MBNo ratings yet
- Aromatic PlantsDocument8 pagesAromatic PlantspankkichanNo ratings yet
- The Trigona Species, (Stingless Bees) .Document4 pagesThe Trigona Species, (Stingless Bees) .They Hock KimNo ratings yet
- The HoneybeeDocument2 pagesThe HoneybeeDejan MilinovićNo ratings yet
- Importance of Fungi in Agriculture, Food, MedicineDocument2 pagesImportance of Fungi in Agriculture, Food, MedicineAbdur Rehman FazalNo ratings yet
- Entomopathogenic Nematodes Against Insect Pests of RiceDocument8 pagesEntomopathogenic Nematodes Against Insect Pests of RiceIJEAB JournalNo ratings yet
- Chapter II PDFDocument14 pagesChapter II PDFjudyline ariolaNo ratings yet
- Biological Control AgentsDocument24 pagesBiological Control AgentsJerson RoblesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Alien Insect Pests On Agriculture Associated With Indian Region and ManagementDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Alien Insect Pests On Agriculture Associated With Indian Region and ManagementDWARKA PRASAD ATHYANo ratings yet
- Evaluation of A Few Botanical Insecticides Against The Insect Pest Henosepilachna Vigintioctopunctata (Fab.) On Solanum Melongena PlantDocument5 pagesEvaluation of A Few Botanical Insecticides Against The Insect Pest Henosepilachna Vigintioctopunctata (Fab.) On Solanum Melongena PlantIOSRjournalNo ratings yet
- Mushrooms Plants Photosynthesis Carbon Dioxide Carbohydrates Cellulose Sunlight EnergyDocument29 pagesMushrooms Plants Photosynthesis Carbon Dioxide Carbohydrates Cellulose Sunlight EnergyAbisinuola OlapadeNo ratings yet
- DR. JSK, Invasive Alien SpeciesDocument7 pagesDR. JSK, Invasive Alien SpeciesTerrance DodsonNo ratings yet
- RRL Revised Ver 1 3Document3 pagesRRL Revised Ver 1 3mae tNo ratings yet
- Crop Protection ManagementDocument17 pagesCrop Protection ManagementArpita SonawaneNo ratings yet
- The-Efficacy-of-Mixed-Oregano...Document45 pagesThe-Efficacy-of-Mixed-Oregano...RICHARD SANOPAONo ratings yet
- TermitesDocument8 pagesTermitesNorelyn TanaNo ratings yet
- Good Bugs, Bad Bugs: The Insects That Impact The Food We EatDocument4 pagesGood Bugs, Bad Bugs: The Insects That Impact The Food We EatMarkNo ratings yet
- Honeybees' Crucial Role in Ecosystems and Biodiversity (39 charactersDocument1 pageHoneybees' Crucial Role in Ecosystems and Biodiversity (39 characterssimpleidNo ratings yet
- Soil Borne Diseases of Major Pulses and Their Biological ManagementDocument11 pagesSoil Borne Diseases of Major Pulses and Their Biological ManagementSp SarathyNo ratings yet
- Cp-Entomology Part 2Document165 pagesCp-Entomology Part 2RAFTITTI IncNo ratings yet
- Notes. Principles of Crop ProtectionDocument3 pagesNotes. Principles of Crop ProtectionAliah Alleyne Canals - BSA - 1ANo ratings yet
- Uc 2 Hand Out 2Document15 pagesUc 2 Hand Out 2Mercy BonggoNo ratings yet
- Biological control sustainable pest controlDocument8 pagesBiological control sustainable pest controlElvis Aaron Torres CarhuaninaNo ratings yet
- Comparative Studies On Effects of Garlic (Allium Sativum) and Ginger (Zingiber Officinale) Extracts On Cowpea Insects Pest AttackDocument8 pagesComparative Studies On Effects of Garlic (Allium Sativum) and Ginger (Zingiber Officinale) Extracts On Cowpea Insects Pest AttackChristian jade QuijanoNo ratings yet
- Salvo & Valladares 2007 Leafminer Parasitoids and Pest ManagementDocument18 pagesSalvo & Valladares 2007 Leafminer Parasitoids and Pest Managementluzlunar100% (1)
- Biology ProjectDocument13 pagesBiology ProjectDaffodil PriliaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Content MasterDocument14 pagesLesson Content MasterDada PeerNo ratings yet
- JPDS2.35mushroompaperVol. 7 5edit139 43Document6 pagesJPDS2.35mushroompaperVol. 7 5edit139 43PRAJIT BHADURINo ratings yet
- Insect Pests of Millets: Systematics, Bionomics, and ManagementFrom EverandInsect Pests of Millets: Systematics, Bionomics, and ManagementNo ratings yet
- National Visa Embassy RequirementsDocument4 pagesNational Visa Embassy Requirementstariq mashalNo ratings yet
- Federal Public Service CommissionDocument2 pagesFederal Public Service Commissiontariq mashalNo ratings yet
- DSitDocument5 pagesDSittariq mashalNo ratings yet
- Tariq Mashal CVDocument4 pagesTariq Mashal CVtariq mashalNo ratings yet
- ProductionstatusofmajorvegetablesinPakistantheirproblemsandsuggestions docFINALDocument13 pagesProductionstatusofmajorvegetablesinPakistantheirproblemsandsuggestions docFINALtariq mashalNo ratings yet
- Tariq Mashal CVDocument2 pagesTariq Mashal CVtariq mashalNo ratings yet
- Forest-Rangeland Ecotones in The Highlands of Balochistan, PakistanDocument7 pagesForest-Rangeland Ecotones in The Highlands of Balochistan, Pakistantariq mashalNo ratings yet
- Tariq Mashal CVDocument2 pagesTariq Mashal CVtariq mashalNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 506Document4 pagesAssignment - 506tariq mashalNo ratings yet
- Check List of Spider (Araneae) Fauna of Pakistan: A Review: Journal of Entomology and Zoology Studies January 2016Document13 pagesCheck List of Spider (Araneae) Fauna of Pakistan: A Review: Journal of Entomology and Zoology Studies January 2016tariq mashalNo ratings yet
- National Visa Embassy RequirementsDocument4 pagesNational Visa Embassy Requirementstariq mashalNo ratings yet
- National Visa Embassy RequirementsDocument4 pagesNational Visa Embassy Requirementstariq mashalNo ratings yet
- TLE 8 Remedial Class Agricultural Crop Production Guide JulyDocument8 pagesTLE 8 Remedial Class Agricultural Crop Production Guide JulyLeah Pinili BlancoNo ratings yet
- AMERICAN FARM SHEPHERDS ILLUSTRATED 2021 June Volume 1, Issue 2Document8 pagesAMERICAN FARM SHEPHERDS ILLUSTRATED 2021 June Volume 1, Issue 2Old-fashioned Black and Tan English Shepherd AssocNo ratings yet
- Individual AssignmentDocument4 pagesIndividual AssignmentGetachew GetachewNo ratings yet
- 0 2003 Chance Haciendas Ranchos Indians-Towns Late Colonial PueDocument31 pages0 2003 Chance Haciendas Ranchos Indians-Towns Late Colonial PueajuriaNo ratings yet
- 2021 Nas Study GuideDocument20 pages2021 Nas Study GuideZvandaziva NelisherNo ratings yet
- Impact of Weed Management Strategies On Performance of Lentil (Lens Culinaris L.)Document4 pagesImpact of Weed Management Strategies On Performance of Lentil (Lens Culinaris L.)mansi nautiyalNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 Interpret Farm Plans and LayoutsDocument49 pagesLesson 7 Interpret Farm Plans and LayoutsLeo Nino DulceNo ratings yet
- Cassava GroupDocument17 pagesCassava GroupTOLA ABENo ratings yet
- Arthapedia - In-Agricultural Produce Market Committee APMCDocument6 pagesArthapedia - In-Agricultural Produce Market Committee APMCIrinaDipsNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes of Improvement in Food Resources Class 9Document11 pagesRevision Notes of Improvement in Food Resources Class 9Mayank ShiniNo ratings yet
- Green Revolution NotesDocument17 pagesGreen Revolution NotesHabib UllahNo ratings yet
- Haryana Crop Production District-wise 1997-2006Document252 pagesHaryana Crop Production District-wise 1997-2006mohitNo ratings yet
- Circus Problem Solved Using Polya's 4 StepsDocument3 pagesCircus Problem Solved Using Polya's 4 StepsNor-ayn PalakasiNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of Adjustable Multiseasonal Harvesting MachineDocument8 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Adjustable Multiseasonal Harvesting Machinebilash mehediNo ratings yet
- Recent Advances in Sugarcane Production TechnologiesDocument71 pagesRecent Advances in Sugarcane Production Technologieschaithra M0% (1)
- Racelona EdnaDocument30 pagesRacelona EdnaCharles NeilNo ratings yet
- Tablelands Agricultural ProfileDocument3 pagesTablelands Agricultural ProfileJayNo ratings yet
- Organic Agriculture and BiodiversityDocument4 pagesOrganic Agriculture and BiodiversityFransisca Meyla AryawatiNo ratings yet
- Agricultural Tourism For Sustainable Rural DevelopmentDocument7 pagesAgricultural Tourism For Sustainable Rural DevelopmentSilene VenessaNo ratings yet
- Ad Sna NarrativeDocument13 pagesAd Sna NarrativeTeresa A. SomorostroNo ratings yet
- Computers and Electronics in AgricultureDocument15 pagesComputers and Electronics in AgricultureJoe BotelloNo ratings yet
- JulyDocument242 pagesJulyBhrt RmnniNo ratings yet
- Syndicate Report: Water Resource Development in Rural Area of Tehsil Isakhel, District MianwaliDocument3 pagesSyndicate Report: Water Resource Development in Rural Area of Tehsil Isakhel, District MianwaliFahad ZulfiqarNo ratings yet
- Pastures Improved Promoted by SNV CIATDocument3 pagesPastures Improved Promoted by SNV CIATcrispusmugabiNo ratings yet
- AE Agriculture Engineer in HorticultureDocument5 pagesAE Agriculture Engineer in HorticulturejohnNo ratings yet
- Telangana History Topic WiseDocument3 pagesTelangana History Topic WiseMarupakaNo ratings yet