Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anatomy - Arteries: Study Online at
Uploaded by
ParneetOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Anatomy - Arteries: Study Online at
Uploaded by
ParneetCopyright:
Available Formats
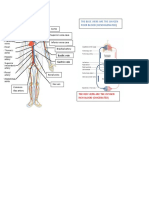
Anatomy - Arteries
Study online at quizlet.com/_12ikeb
1. At which vertebral level does L4 = bifurcation of aorta into 9. What are the 5 branches Branches of subclavian artery
the aorta bifurcate into the common iliacs of the subclavian artery? VIT C and D
common iliac arteries?
Vertebral
2. Between which two muscles Lingual artery found
Infernal thoracic
is the lingual artery usually between the hyoglossus
Thyrocervical (suprascapular +
found? and the genioglossus
transverse cervical)
3. The descending palatine Descending palatine artery
artery travels through which travels through the Costocervical
canal? pterygopalatine canal Dorsal scapular
4. The greatest drop in blood The greatest drop in blood 10. What are the 7 branches TAS-ISLA
pressure in the vessels is pressure in the vessels is of the facial artery?
seen: seen from ARTERIES to Tonsillar
ARTERIOLES Ascending palatine
Submental - Submandibular
Arterioles control the blood gland
pressure though.
5. If the hard palate is bleeding Greater palatine artery is Inferior labial
adjacent to the max 1st probably cut. Superior labial
molar, which artery is Lateral nasal
probably cut? Angular - medial of eye,
anastomose with dorsal nasal of
6. What are the 4 branches of Lingual artery
opthalmic artery.
the lingual artery? 1. Dorsal lingual (base and
body of tongue) 11. What are the branches SALFOP St. Max
2. Suprahyoid (supgrahyoid of the external carotid
muscles) artery Superior thyroid
3. Sublingual (sublingual Ascending pharyngeal
gland) Lingual
4. Deep lingual (terminal) Facial
Occipital
7. What are the 4 branches of 1. Anterior superior alveolar
Posterior auricular
the Maxillary artery that (infraorbital)
supply all the teeth? 2. Middle superior alveolar
Superficial temporal (terminal)
(infraorbital, canines, may
Maxillary (terminal)
not be present)
3. Posterior superior alveolar 12. What are the two most 1. Anterior ethmoidal artery
(premolars, molars) important arteries in (branch of opthalmic)
4. Inferior alveolar the nasal cavity? 2. Sphenopalatine (branch of
maxillary)
8. What are the 5 arteries that DATA-L
supply the palatine tonsils? 13. What arteries make up Terminal part of Internal Carotid
1. Dorsal lingual artery the Circle of Willis? Anterior cerebral
(Lingual) Middle cerebral
2. Ascending palatine artery Posterior cerebral
(Facial) Anterior communicating
3. Tonsillar branch (Facial) Posterior communicating
4. Ascending pharyngeal 14. What does the internal Internal carotid gives the
(External carotid) carotid branch into? opthalmic artery, and the
5. Lesser palatine anterior/middle cerebral arteries.
(descending palatine artery,
15. What does the maxillary Maxillary artery ends as
Maxillary)
artery end as? sphenopalatine artery,
supplies the nasal cavity.
Sphenopalatine then becomes
the nasopalatine artery.
16. What does the Opthalmic artery branches into the 28. What is the Sphenopalatine artery is from the
opthalmic artery ant/post ethmoidal arteries, which sphenopalatine maxillary artery, it supplies the nasal
branch into and what supply the nasal cavity artery a branch mucosa.
does it supply? of?
17. What does the Posterior communicating connects 29. What is The hepatic artery and the portal vein
posterior the internal carotid and posterior unusual about empty into the same sinusoids, so there is
communicating arteries. hepatic a mix of arterial and venous blood.
artery connect? circulation?
18. What innervates the Palatoglossus muscle = CN 10, 30. Whats a main Left kidney is a little higher. Both kidneys
palatoglossus NOT CN 12 difference get a ton of blood, up to 1/3 of the cardiac
muscle? between left and output.
right kidneys?
19. What is a sinusoid? Sinusoid = discontinuous
The renal arteries split right after the
endothelium. Found in lymphoid
superior mesenteric artery.
tissue, spleen, bone marrow, liver,
and endocrine. 31. What supplies The lingual artery = sublingual gland.
blood to the Also supplies the tongue, suprahyoid,
20. What is Area where 5 arteries in nasal cavity
sublingual palatine tonsils, and floor of mouth.
Kiesselbacharea's anastomose, common area for
gland?
area? epistaxis.
32. Where are Berry aneurysm = Circle of Willis
21. What is the aortic The aortic body contains
Berry
body? baroreceptors and chemoreceptors.
aneurysms
It is innervated by CN 10 = aortic
found?
body
33. Where does Atherosclerosis is the emergence of plaque
22. What is the carotid Cluster of chemoreceptors in the
atherosclerosis between the basement membrane and the
body? common carotid bifurcation that
occur? endothelial cells of the tunica intima.
measures the pH, pO2, pCO2, and
temperature. 34. Where does the Aorta passes through diaphragm at T12
aorta pass
23. What is the carotid Dilation of the internal carotid
through the
sinus? artery at its origin. It has
diaphragm?
baroreceptors to measure the blood
pressure and is innervated by CN 9 35. Where does the Middle meningeal artery comes from the
= carotid sinus middle first part of the maxillary artery along with
meningeal the inferior alveolar
24. What is the function Tunica media function
artery come
of the tunica media in
from?
LARGE arteries and Large arteries = elastic fibers
SMALL arteries? Small arteries = smooth muscle 36. Where does the Vertebral artery branches off subclavian
vertebral artery and enters at C6, goes up and enters in
25. What is the most Diameter is the most important
enter the spine? foramen magnum.
important role in factor in the rate of blood flow
determining the rate (Poiseuille's Law, radius is to the
The two vertebral arteries join to create the
of blood flow through 4th power)
basilar artery.
a vessel?
26. What is the path of Hepatic artery + Portal vein => Vertebrals = Posterior inferior cerebellar
venous blood flow sinusoids artery.
going into and out of
the liver? Sinusoids -> Common central vein - Basilar = Anterior inferior cerebellar artery
> Hepatic vein -> Inferior vena cava
37. Which artery is Strokes often happen in the middle
27. What is the portal 1. Hepatic artery a stroke most cerebral artery, it's the largest one.
triad? 2. Portal vein likely in?
3. Bile duct The anterior cerebral artery is a smaller
branch that supplies oxygenated blood to
At the vertices of the hexagonal liver the most medial portions of the frontal
lobule. lobes and parietal lobes.
38. Which artery is most likely to be damaged Middle meningeal artery (branch of Maxillary artery).
in trauma to the side of the head?
Middle meningeal artery goes through the foramen spinosum to supply the dura mater
and calvaria. It's the largest one. The skull is thin near the pterion which is why it
gets hit hard.
39. Which artery runs on the superficial Superficial surface of tongue = dorsal lingual artery of lingual artery.
surface of the tongue?
40. Which artery supplies blood to the Submandibular gland = Facial artery
submandibular gland?
41. Which artery supplies the mandibular The maxillary artery, believe it or not...
incisive teeth?
Ex. carotid -> Maxillary -> Inferior alveolar -> Incisive
42. Which artery supplies the TMJ and what is TMJ artery = masseteric artery from the maxillary artery.
its origin?
Masseteric also supplies the masseter muscle
43. Which nerve is most likely to be found Inferior alveolar bundle is adjacent to the lingual nerve.
alongside the inferior alveolar nerve,
artery, and vein?
You might also like
- Anatomy and Physiology MnemonicsDocument7 pagesAnatomy and Physiology MnemonicsLalajimNo ratings yet
- True Oral CavityDocument3 pagesTrue Oral CavityHanneke Du PlessisNo ratings yet
- Board Review Blood SupplyDocument6 pagesBoard Review Blood Supplynewguy927No ratings yet
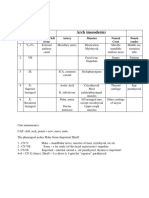
- Pharyngeal Arches: Normal DevelopmentDocument10 pagesPharyngeal Arches: Normal DevelopmentBeniya EmilNo ratings yet
- ENT - Anatomy and Physiology of The Nose 2014Document3 pagesENT - Anatomy and Physiology of The Nose 2014pbmaristelaNo ratings yet
- 01 Head and Neck JMDocument16 pages01 Head and Neck JMJowi SalNo ratings yet
- 2 Head and NeckDocument45 pages2 Head and NeckosamaeNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Anatomy and FunctionsDocument5 pagesRespiratory System Anatomy and FunctionsA-Naeem To'mah Al-sawaieNo ratings yet
- Pharyngeal Arches For ANA StudentsDocument1 pagePharyngeal Arches For ANA Studentscelltech111No ratings yet
- Pharyngeal Apparatus Development SummaryDocument5 pagesPharyngeal Apparatus Development SummaryMustapha Ibrahim suleimanNo ratings yet
- Dental Boards Review: Basic Medicine TopicsDocument106 pagesDental Boards Review: Basic Medicine TopicsDENTAL REVIEWER ONLY100% (3)
- Prof. Hamiadji - Ear, Nose, Throat PDFDocument28 pagesProf. Hamiadji - Ear, Nose, Throat PDFSANDA NABILAH FATINNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System: A Fixed Learning ModuleDocument38 pagesThe Respiratory System: A Fixed Learning ModulerezaNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Anatomy and PartsDocument5 pagesDigestive System Anatomy and PartsA-Naeem To'mah Al-sawaieNo ratings yet
- Surgical Anatomy (Dr. ElNashar)Document19 pagesSurgical Anatomy (Dr. ElNashar)shehla khanNo ratings yet
- Cranial Bones and Meninges RevisionDocument20 pagesCranial Bones and Meninges Revisionbannanastew7975No ratings yet
- CEREBELLUMDocument5 pagesCEREBELLUMAIRA BIANCA B. MANALANGNo ratings yet
- 2 - Anatomy of Salivary Glands EditedDocument18 pages2 - Anatomy of Salivary Glands EditedHenok BelyaNo ratings yet
- Regio FaceiDocument25 pagesRegio FaceiIndra MahaputraNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Study MaterialDocument16 pagesAnatomy Study MaterialAyeshik ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy: Al Esraa GroupDocument9 pagesAnatomy: Al Esraa Groupوحش الصاعقهNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 2Document2 pagesActivity No. 2Jefferson SociasNo ratings yet
- The Trigeminal NerveDocument83 pagesThe Trigeminal NerveRicha BhosaleNo ratings yet
- I. Facial MusclesDocument5 pagesI. Facial MusclesAnya RamosNo ratings yet
- BREGMA COMPILERS ANATOMY NOTES SUMMARYDocument10 pagesBREGMA COMPILERS ANATOMY NOTES SUMMARYCoy NuñezNo ratings yet
- Thorax and Abdomen Muscle NotesDocument2 pagesThorax and Abdomen Muscle NotesJean OpallaNo ratings yet
- 105 - Head and Neck Anatomy SessionDocument11 pages105 - Head and Neck Anatomy Sessionarjun.k5796No ratings yet
- Mouth, 10 Nov 2006Document2 pagesMouth, 10 Nov 2006api-19921479No ratings yet
- General AnatomyDocument95 pagesGeneral AnatomyAhmed hegazyNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply To BrainDocument3 pagesBlood Supply To BrainMuzzammil LiaqatNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY.3.1SkeletalSystem-AxialSkeleton.TransDocument13 pagesANATOMY.3.1SkeletalSystem-AxialSkeleton.TransmalvincayabyabNo ratings yet
- Anatomy MnemonicsDocument4 pagesAnatomy Mnemonicskiara91% (56)
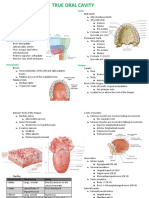
- Special Senses - Oral Cavity Etc.Document18 pagesSpecial Senses - Oral Cavity Etc.Dunkin DonutNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Midterm Reviewer1Document14 pagesAnaphy Midterm Reviewer1juddee.conejosNo ratings yet
- Anatomy NotesDocument3 pagesAnatomy NotesKaren Kaye Canlas100% (3)
- Medical Surgical Nursing ReviewerDocument8 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing ReviewerDavid Brillo0% (1)
- My Blood Vessels Lead All The Way To My Destination!: ArteriesDocument4 pagesMy Blood Vessels Lead All The Way To My Destination!: ArteriesA-Naeem To'mah Al-sawaieNo ratings yet
- 4 Infratemporal Region Slides 2019-1Document23 pages4 Infratemporal Region Slides 2019-1Ambg GhalyNo ratings yet
- Forearm and Hand AnatomyDocument58 pagesForearm and Hand AnatomyRamon Jovi Lumayag100% (1)
- Mouth - Pharynx - LarynxDocument15 pagesMouth - Pharynx - Larynxaloysius limNo ratings yet
- Basic Structure and Function Basic Structure and Function of The of The Wrist and Hand Wrist and HandDocument54 pagesBasic Structure and Function Basic Structure and Function of The of The Wrist and Hand Wrist and HandJoseNo ratings yet
- Page of 1 3 Carotid Arteries L2 Vascular Biology: Musculofascial CollarDocument3 pagesPage of 1 3 Carotid Arteries L2 Vascular Biology: Musculofascial CollarFazreena EleenaNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply of Lower Limb: Arteries and Veins</TITLEDocument29 pagesBlood Supply of Lower Limb: Arteries and Veins</TITLEAdewunmi ToluNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lab RespiratoryDocument3 pagesAnaphy Lab RespiratoryRyan Dave UmayamNo ratings yet
- l15 CerebrumDocument31 pagesl15 CerebrumDr. Pinki RaiNo ratings yet
- EL Husseiny's Essentials of Endocrinology 1247Document152 pagesEL Husseiny's Essentials of Endocrinology 1247حنين عاطفNo ratings yet
- 4c. Nasal Blood Supply NNDocument8 pages4c. Nasal Blood Supply NNCyrus ChanNo ratings yet
- Embryo of Thyroid GlandDocument3 pagesEmbryo of Thyroid GlandMeemziiNo ratings yet
- Scalp - Face - BrainDocument7 pagesScalp - Face - Brainaloysius limNo ratings yet
- 48 & 72 HR Chick PDFDocument3 pages48 & 72 HR Chick PDFpinky peachNo ratings yet
- L15 CerebrumDocument27 pagesL15 CerebrumEvilneko1No ratings yet
- Aorta Superior Vena Cava: The Blue Viens Are The Oxygen Poor Blood (De9OxigenatedDocument6 pagesAorta Superior Vena Cava: The Blue Viens Are The Oxygen Poor Blood (De9OxigenatedShaira CogollodoNo ratings yet
- Blood Vessels: Artery Capillary VeinDocument27 pagesBlood Vessels: Artery Capillary Veinapi-19641337No ratings yet
- Elbow and Humerus - Examiner RoleplayDocument2 pagesElbow and Humerus - Examiner Roleplaysanju ghimireNo ratings yet
- Angiology: (LECTURE-3)Document6 pagesAngiology: (LECTURE-3)আহানাফ তাহমিদ শব্দNo ratings yet
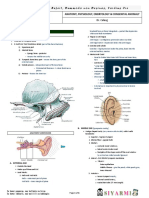
- EAR Anatomy, Physiology, Embryology & Congenital AnomalyDocument6 pagesEAR Anatomy, Physiology, Embryology & Congenital AnomalyThakoon TtsNo ratings yet
- Anterior Triangle of The Neck Dr. BanezDocument6 pagesAnterior Triangle of The Neck Dr. BanezMelissa SalayogNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Voice: How to Enhance and Project Your Best VoiceFrom EverandAnatomy of Voice: How to Enhance and Project Your Best VoiceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- 1 4988197119476105255 PDFDocument171 pages1 4988197119476105255 PDFParneetNo ratings yet
- Questions and Answers in Community DentistryDocument335 pagesQuestions and Answers in Community Dentistryleeminhoangrybird88% (8)
- 2 5228900173509297666Document7 pages2 5228900173509297666ParneetNo ratings yet
- Anterior Teeth Ndbe McqsDocument5 pagesAnterior Teeth Ndbe McqsParneetNo ratings yet
- Newfoundland and Labrador Dentistry AssociationDocument21 pagesNewfoundland and Labrador Dentistry AssociationParneetNo ratings yet
- Oral AnatomyDocument2 pagesOral AnatomyParneetNo ratings yet
- Optragate: Nova Easy ClipDocument4 pagesOptragate: Nova Easy ClipParneetNo ratings yet
- French For Beginners - The Best Handbook For Learning To Speak French PDFDocument101 pagesFrench For Beginners - The Best Handbook For Learning To Speak French PDFsudhakara.rr359100% (7)
- NBDE 1: Exam 7 (Micro) : Study Online atDocument4 pagesNBDE 1: Exam 7 (Micro) : Study Online atParneetNo ratings yet
- Ndebreleasedquestions 2019 1 PDFDocument383 pagesNdebreleasedquestions 2019 1 PDFManish JunejaNo ratings yet
- Must Have Notes For NBDE and Other Dentistry ExamsDocument175 pagesMust Have Notes For NBDE and Other Dentistry ExamsParneet100% (2)
- BateriaDocument1 pageBateriaParneetNo ratings yet
- Pass Nbde - RqsDocument3 pagesPass Nbde - RqsnayeemmajedNo ratings yet
- Master RQsDocument81 pagesMaster RQsBahaa Ibrahim Helmi100% (2)
- NBDE Biochem Study GuideDocument3 pagesNBDE Biochem Study GuideParneetNo ratings yet
- TMJ PDFDocument3 pagesTMJ PDFParneetNo ratings yet
- Nbde 2006quizletDocument7 pagesNbde 2006quizletParneetNo ratings yet
- Ndeb ShortcutsDocument5 pagesNdeb ShortcutsParneetNo ratings yet
- NBDE 1: Exam 7 (Micro) : Study Online atDocument4 pagesNBDE 1: Exam 7 (Micro) : Study Online atParneetNo ratings yet
- NBDE Microbiology - Antimicrobial Control: Study Online atDocument2 pagesNBDE Microbiology - Antimicrobial Control: Study Online atParneetNo ratings yet
- RQ of Nbde Part 2 Dec 2017Document7 pagesRQ of Nbde Part 2 Dec 2017ParneetNo ratings yet
- Facts To Remember AnatomyDocument2 pagesFacts To Remember AnatomyParneetNo ratings yet
- Pass Nbde - RqsDocument3 pagesPass Nbde - RqsnayeemmajedNo ratings yet
- (The European Society of Cardiology Series) Marco Tubaro (Editor), Pascal Vranckx (Editor), Susanna Price (Editor), Christiaan Vrints (Editor), Eric Bonnefoy (Editor) - The ESC Textbook of Intensive ADocument1,088 pages(The European Society of Cardiology Series) Marco Tubaro (Editor), Pascal Vranckx (Editor), Susanna Price (Editor), Christiaan Vrints (Editor), Eric Bonnefoy (Editor) - The ESC Textbook of Intensive AEdu MartinsNo ratings yet
- ArrhythmiaDocument2 pagesArrhythmiaZoe AcostaNo ratings yet
- LO Dan WO Cardio Week 4 (Jumat)Document38 pagesLO Dan WO Cardio Week 4 (Jumat)Alan Dwi SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyTrixia ArcegonoNo ratings yet
- Gilroy JDocument5 pagesGilroy JrothagatsuNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Tamponad E: Pathophysiology and ManagementDocument105 pagesCardiac Tamponad E: Pathophysiology and ManagementBimaNo ratings yet
- Impact of High Sensitivity Troponins For 6nov Cardiac ForumDocument39 pagesImpact of High Sensitivity Troponins For 6nov Cardiac Forummouna6685No ratings yet
- Mitral StenosisDocument43 pagesMitral StenosisEricka SantosNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: The Heart: Chapter 19 - Lecture NotesDocument73 pagesCardiovascular System: The Heart: Chapter 19 - Lecture Noteshersheys72002No ratings yet
- TESDA Basic Life Support ReviewerDocument5 pagesTESDA Basic Life Support ReviewerAnna Sto DomingoNo ratings yet
- Visualise Renal ArteriesDocument15 pagesVisualise Renal Arteriess0800841739No ratings yet
- Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation: Dr. Abdul Rashad Senior Lecturer United College of Physical TherapyDocument27 pagesCardiopulmonary Resuscitation: Dr. Abdul Rashad Senior Lecturer United College of Physical TherapypashaNo ratings yet
- Blood Is Thicker Than WaterDocument4 pagesBlood Is Thicker Than WateraontreochNo ratings yet
- HemoDynamics and CardiologyDocument452 pagesHemoDynamics and CardiologyYuliawati Haruna100% (1)
- Mammalian Circulation Driven by Coordinated Heart Contraction CyclesDocument5 pagesMammalian Circulation Driven by Coordinated Heart Contraction CyclesMayar HasanNo ratings yet
- Pulse Pressure - A Review of Mechanisms and Clinical RelevanceDocument10 pagesPulse Pressure - A Review of Mechanisms and Clinical RelevanceHoliNo ratings yet
- Cardio DrillDocument22 pagesCardio DrillDemuel Dee L. BertoNo ratings yet
- ALTERATION/ ABNORMAL FINDINGS IN PULSEDocument7 pagesALTERATION/ ABNORMAL FINDINGS IN PULSEShalabh JoharyNo ratings yet
- How to Spot a Stroke F.A.S.TDocument31 pagesHow to Spot a Stroke F.A.S.TAlexisRoyENo ratings yet
- Caldwell Esselstyn PDFDocument53 pagesCaldwell Esselstyn PDFMuhammad Azhar Saleem100% (6)
- Electrocardiography: The ECG: A.D. John, MD, Lee A. Fleisher, MDDocument19 pagesElectrocardiography: The ECG: A.D. John, MD, Lee A. Fleisher, MDCésar Vásquez AguilarNo ratings yet
- Left Sided Heart FailureDocument25 pagesLeft Sided Heart FailurePaulNo ratings yet
- ArteriDocument1 pageArterifakira tanzilNo ratings yet
- Ncm09: Pedia: Erjen Alexandria M. Sia Bsn2BDocument12 pagesNcm09: Pedia: Erjen Alexandria M. Sia Bsn2BErjen Alexandria SiaNo ratings yet
- Sci9 - q1 - Mod1 - Respiratory and Circulatory Systems Working With Other Organ Systems - v2Document28 pagesSci9 - q1 - Mod1 - Respiratory and Circulatory Systems Working With Other Organ Systems - v2Jelly Flores100% (11)
- Heart Failure Clinical Presentation - History, Physical Examination, Predominant Right-Sided Heart Failure PDFDocument11 pagesHeart Failure Clinical Presentation - History, Physical Examination, Predominant Right-Sided Heart Failure PDFislamiah 89No ratings yet
- Intrapartum Fetal Monitoring EditedDocument51 pagesIntrapartum Fetal Monitoring EditedObgyn DischargesNo ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGYDocument2 pagesPATHOPHYSIOLOGYangeliccat_sweet157992No ratings yet
- Electrolyte ImbalanceDocument4 pagesElectrolyte ImbalanceBharathbushan V MandiriNo ratings yet
- PericarditisDocument11 pagesPericarditisrbarcellonaNo ratings yet