Professional Documents
Culture Documents
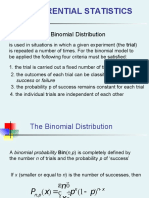
The Binomial Distribution
Uploaded by
tiara hanan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesThe binomial distribution describes the probability of successes in a fixed number of independent yes/no trials, where the probability of success is the same for each trial. It has three main characteristics: 1) there are two possible outcomes per trial, 2) there is a fixed number of trials, and 3) the probability of success remains constant from trial to trial. The binomial probability distribution function provides the formula to calculate the probability of getting x successes in n trials with probability p of success on each trial.
Original Description:
statek
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe binomial distribution describes the probability of successes in a fixed number of independent yes/no trials, where the probability of success is the same for each trial. It has three main characteristics: 1) there are two possible outcomes per trial, 2) there is a fixed number of trials, and 3) the probability of success remains constant from trial to trial. The binomial probability distribution function provides the formula to calculate the probability of getting x successes in n trials with probability p of success on each trial.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesThe Binomial Distribution
Uploaded by
tiara hananThe binomial distribution describes the probability of successes in a fixed number of independent yes/no trials, where the probability of success is the same for each trial. It has three main characteristics: 1) there are two possible outcomes per trial, 2) there is a fixed number of trials, and 3) the probability of success remains constant from trial to trial. The binomial probability distribution function provides the formula to calculate the probability of getting x successes in n trials with probability p of success on each trial.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
The binomial Distribution
a binomial random variables is definend as the number of
successes achieved in the n trials of a Bernoulli process.
A Bernoulli process consists of a series of n indepent
and identical trials of an experiment such that on each
trial:
1. there are only two possible outcomes, conventionally
labeled success = p and failure = 1-p = q
2. the probabilities of success and failure remain the
same from trial to trial
characteristics of a binomial distribution:
1. a trial has only two possible outcomes (“success or
failure”)
2. there is a fixed number, n, of identical trials
3. the trials of the experiment are independent of each
other
4. the probability of success, p, remains constats from
trial to trial
Binomial Probability Distribution function
p(x) = probability of x successes
n = sample size
p= probability of success
x= number of success in sample (x = 0,1,2,....,n)
example : toss 1 coin 5 times in a row. Note number of tails.
what’s the probability of 3 tails?
You might also like
- Schaum's Easy Outline of Probability and Statistics, Revised EditionFrom EverandSchaum's Easy Outline of Probability and Statistics, Revised EditionNo ratings yet
- Third Term SS 2 Further Maths 2022Document79 pagesThird Term SS 2 Further Maths 2022koredekayode099No ratings yet
- 4.2 Binomial DistributionsDocument13 pages4.2 Binomial DistributionssakshiNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 - Activity 2 - Binomial Distribution WorksheetDocument2 pagesUnit 5 - Activity 2 - Binomial Distribution WorksheetNidhi VyasNo ratings yet
- BINOMIAL PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTION BASICSDocument20 pagesBINOMIAL PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTION BASICSJohn LinaresNo ratings yet
- Binomial DistributionDocument12 pagesBinomial DistributionRajdeep KhushwahaNo ratings yet
- Binomial DistributionDocument7 pagesBinomial DistributionsadyehNo ratings yet
- Binomial Distribution Explained: Formula, Examples & MoreDocument5 pagesBinomial Distribution Explained: Formula, Examples & MoreUttam RastogiNo ratings yet
- Binomial DistributionDocument14 pagesBinomial DistributionRNKNo ratings yet
- WIN SEM (2022-23) MAT1011 ETH AP2022236000112 Reference Material I 21-Feb-2023 Lecture16Document15 pagesWIN SEM (2022-23) MAT1011 ETH AP2022236000112 Reference Material I 21-Feb-2023 Lecture16Sai krishna kowshik VelagaNo ratings yet
- Learn Binomial Probability DistributionsDocument17 pagesLearn Binomial Probability Distributionssanjay reddyNo ratings yet
- Binomial Distribution NotesDocument2 pagesBinomial Distribution NotesRANJITHANo ratings yet
- 5-3 Binomial Probability DistributionsDocument14 pages5-3 Binomial Probability DistributionsHasun MalingaNo ratings yet
- Binomial DistributionDocument17 pagesBinomial DistributionAnjali PandeNo ratings yet
- Binomial Distribution in 38Document29 pagesBinomial Distribution in 38MarkNo ratings yet
- Probability & Statistics: DefinationDocument3 pagesProbability & Statistics: DefinationSufi TechNo ratings yet
- Statistics - The Binomial Probability DistributionDocument15 pagesStatistics - The Binomial Probability DistributionALLAPARTHI SHANMUKHA PRIYA RAMA ABHILASH 15MIS0077No ratings yet
- Lecture No.8Document6 pagesLecture No.8Awais RaoNo ratings yet
- W?usp SharingDocument7 pagesW?usp SharingANNo ratings yet
- Chapter5specialprobabilitydistribution v1 28week5 29Document35 pagesChapter5specialprobabilitydistribution v1 28week5 29Alvin HawkinsNo ratings yet
- Binomial Probability Distribution ExplainedDocument7 pagesBinomial Probability Distribution ExplainedVinayak PatilNo ratings yet
- BS Chapter4 2021 Discrete Probability Distribution Binomial Hyper Poisen 22Document40 pagesBS Chapter4 2021 Discrete Probability Distribution Binomial Hyper Poisen 22ShayanNo ratings yet
- Basic Statistics (3685) PPT - Lecture On 21-01-2019Document19 pagesBasic Statistics (3685) PPT - Lecture On 21-01-2019M Hammad ManzoorNo ratings yet
- Binomial Distribution-8Document4 pagesBinomial Distribution-8Shobha Kumari ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- 2 - INF STAT Bin DistrDocument6 pages2 - INF STAT Bin DistrharsmanNo ratings yet
- Binomial DistributionDocument9 pagesBinomial DistributionMa.Mikee Camille CamoraNo ratings yet
- Probability DistributionsDocument3 pagesProbability DistributionsHarpoon BKNo ratings yet
- Binomialdistribution 190124111432 PDFDocument26 pagesBinomialdistribution 190124111432 PDFPremjit SenguptaNo ratings yet
- BPT-Probability-binomia Distribution, Poisson Distribution, Normal Distribution and Chi Square TestDocument41 pagesBPT-Probability-binomia Distribution, Poisson Distribution, Normal Distribution and Chi Square TestAjju NagarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Probability DistributionDocument26 pagesChapter 1 Probability DistributionmfyNo ratings yet
- Advanced Statistics Hypothesis TestingDocument42 pagesAdvanced Statistics Hypothesis TestingShermaine CachoNo ratings yet
- BinomialnotesDocument3 pagesBinomialnotesapi-228450074No ratings yet
- Binomial DistributionDocument35 pagesBinomial DistributionBaber H. ElahiNo ratings yet
- Evidence 2.1 2.3Document10 pagesEvidence 2.1 2.3alan ErivesNo ratings yet
- Ist 214-Statictics Ii: Week 4: Binomial Distribution and Poison Distribution, Expected Values and VarianceDocument18 pagesIst 214-Statictics Ii: Week 4: Binomial Distribution and Poison Distribution, Expected Values and Variancemelekkbass10No ratings yet
- Binomial Distribution Mean & VarianceDocument11 pagesBinomial Distribution Mean & Variancemusaab_zeeshanNo ratings yet
- Types of ProbabilityDistributionsDocument4 pagesTypes of ProbabilityDistributionsMeenakshi RajputNo ratings yet
- Probability Distribution: Meaning Uses Types Assumptions Properties ApplicationsDocument19 pagesProbability Distribution: Meaning Uses Types Assumptions Properties Applicationschunmun__sNo ratings yet
- Probability Distribution OverviewDocument37 pagesProbability Distribution OverviewEngdaw Asmare GeramiNo ratings yet
- TF3001 Sm2 09-10 Course Notes 7Document5 pagesTF3001 Sm2 09-10 Course Notes 7Jonathan KurniaNo ratings yet
- Probabilitas Dan Statistika: Some Discrete Probability DistributionsDocument30 pagesProbabilitas Dan Statistika: Some Discrete Probability DistributionsFirman WisnuNo ratings yet
- Binomial Distribution Ku SP 22Document3 pagesBinomial Distribution Ku SP 22youmnaqazi0103No ratings yet
- Class 1 - BinomialDocument25 pagesClass 1 - Binomialkabbilaash kumarNo ratings yet
- Binomial DistributionDocument3 pagesBinomial DistributionTeena ThaparNo ratings yet
- MATH220 Probability and Statistics: Asst. Prof. Merve BULUT YILGÖRDocument26 pagesMATH220 Probability and Statistics: Asst. Prof. Merve BULUT YILGÖRCan AtarNo ratings yet
- Continuous Probability DistributionDocument6 pagesContinuous Probability DistributionDipika PandaNo ratings yet
- Summary of Chapter "Random Variable"Document10 pagesSummary of Chapter "Random Variable"Adil Khan LodhiNo ratings yet
- Binomial DistributionDocument22 pagesBinomial DistributionGlenn AvelinoNo ratings yet
- 3 Stat ProbabilityDocument52 pages3 Stat ProbabilityKathiravan GopalanNo ratings yet
- Binomial DistributionDocument15 pagesBinomial DistributionAnonymous eDV7aJoD100% (1)
- Discrete Probability Distributions: Binomial Distribution Poisson DistributionDocument17 pagesDiscrete Probability Distributions: Binomial Distribution Poisson DistributionDipak Kumar PatelNo ratings yet
- 23 4 14 Prob DistributionDocument132 pages23 4 14 Prob DistributionAlvin Adrian100% (1)
- Binomial DistributionDocument15 pagesBinomial DistributionNelsonMoseMNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Probability DistributionDocument46 pagesTopic 1 - Probability DistributionnajmiNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2023-24_BMAT202L_TH_VL2023240502271_2024-02-26_Reference-Material-IDocument28 pagesWINSEM2023-24_BMAT202L_TH_VL2023240502271_2024-02-26_Reference-Material-Impkvarun69No ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document38 pagesChapter 5Prasath Pillai Raja VikramanNo ratings yet
- 05 Discrete Probability DistributionDocument16 pages05 Discrete Probability DistributionNirmal TariqNo ratings yet
- Binomial Distribution Formula and TableDocument10 pagesBinomial Distribution Formula and TableVivian Brooklyn ChenNo ratings yet
- 3 DistributionsDocument42 pages3 DistributionsAngga Ade PutraNo ratings yet
- Math NewwwwwDocument13 pagesMath Newwwwwanupbarman.coochbeharNo ratings yet
- A Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormFrom EverandA Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Calculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeFrom EverandCalculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Mathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingFrom EverandMathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Mental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorFrom EverandMental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsFrom EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Making and Tinkering With STEM: Solving Design Challenges With Young ChildrenFrom EverandMaking and Tinkering With STEM: Solving Design Challenges With Young ChildrenNo ratings yet
- Basic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeFrom EverandBasic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Assessment Prep for Common Core Mathematics, Grade 6From EverandAssessment Prep for Common Core Mathematics, Grade 6Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Build a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.From EverandBuild a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Fluent in 3 Months: How Anyone at Any Age Can Learn to Speak Any Language from Anywhere in the WorldFrom EverandFluent in 3 Months: How Anyone at Any Age Can Learn to Speak Any Language from Anywhere in the WorldRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (79)